吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 595-607.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210308
异钩藤碱上调miR-192-5p对TNF-α诱导的人支气管上皮细胞凋亡和炎症因子释放的作用及其机制
- 河南省中医院肺病科,河南 郑州 450002
Effect of isorhynchophylline on apoptosis and release of inflammatory factors in human bronchial epithelial cells induced by TNF-α via up-regulating miR-192-5p and its mechanism
Congling HOU( ),Xiaofan LU,Xiaoting LEI,Bin LI,Runyang ZHAO
),Xiaofan LU,Xiaoting LEI,Bin LI,Runyang ZHAO
- Department of Pulmonary Diseases,Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450002,China
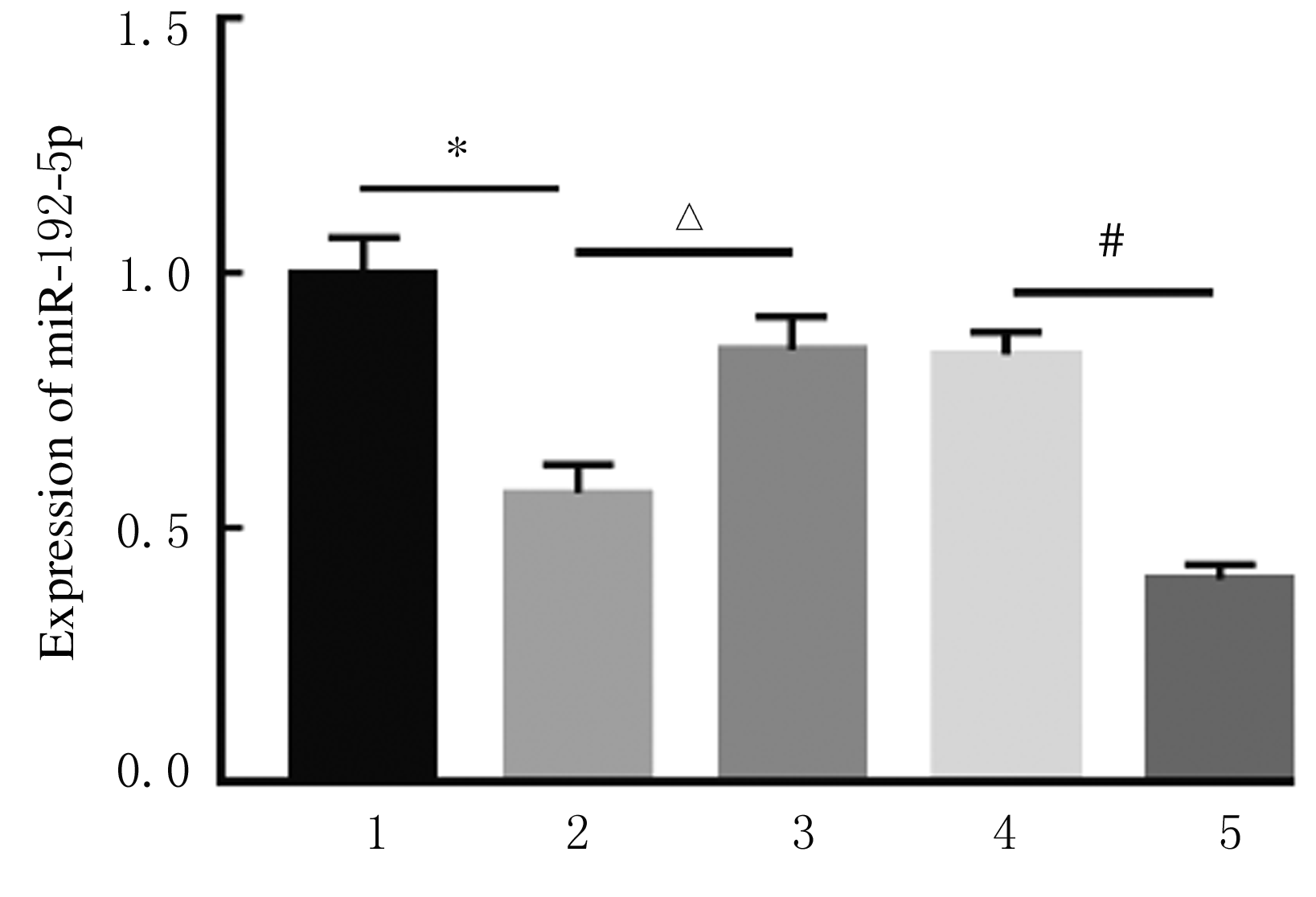
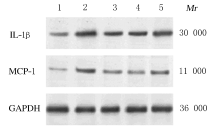
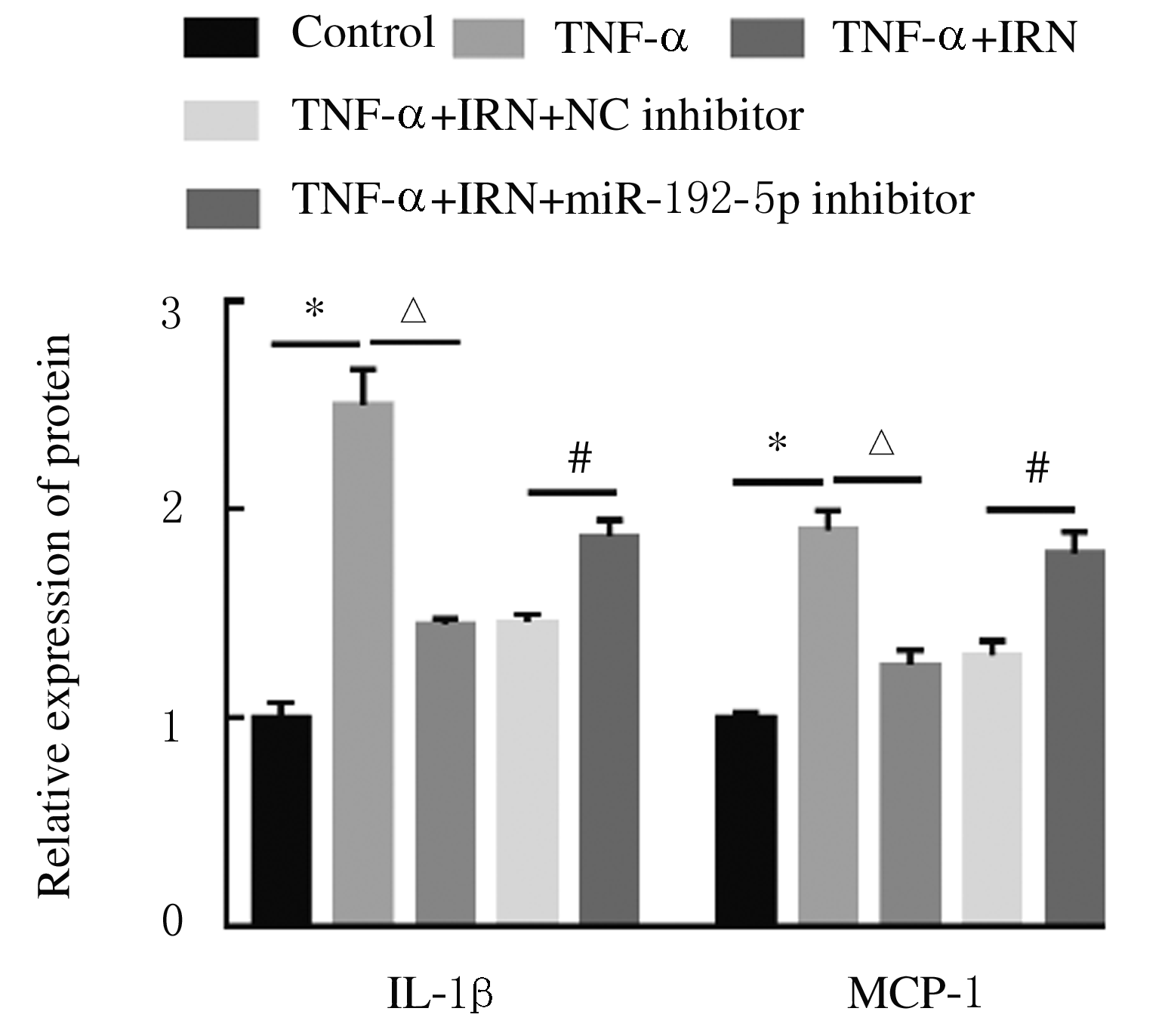
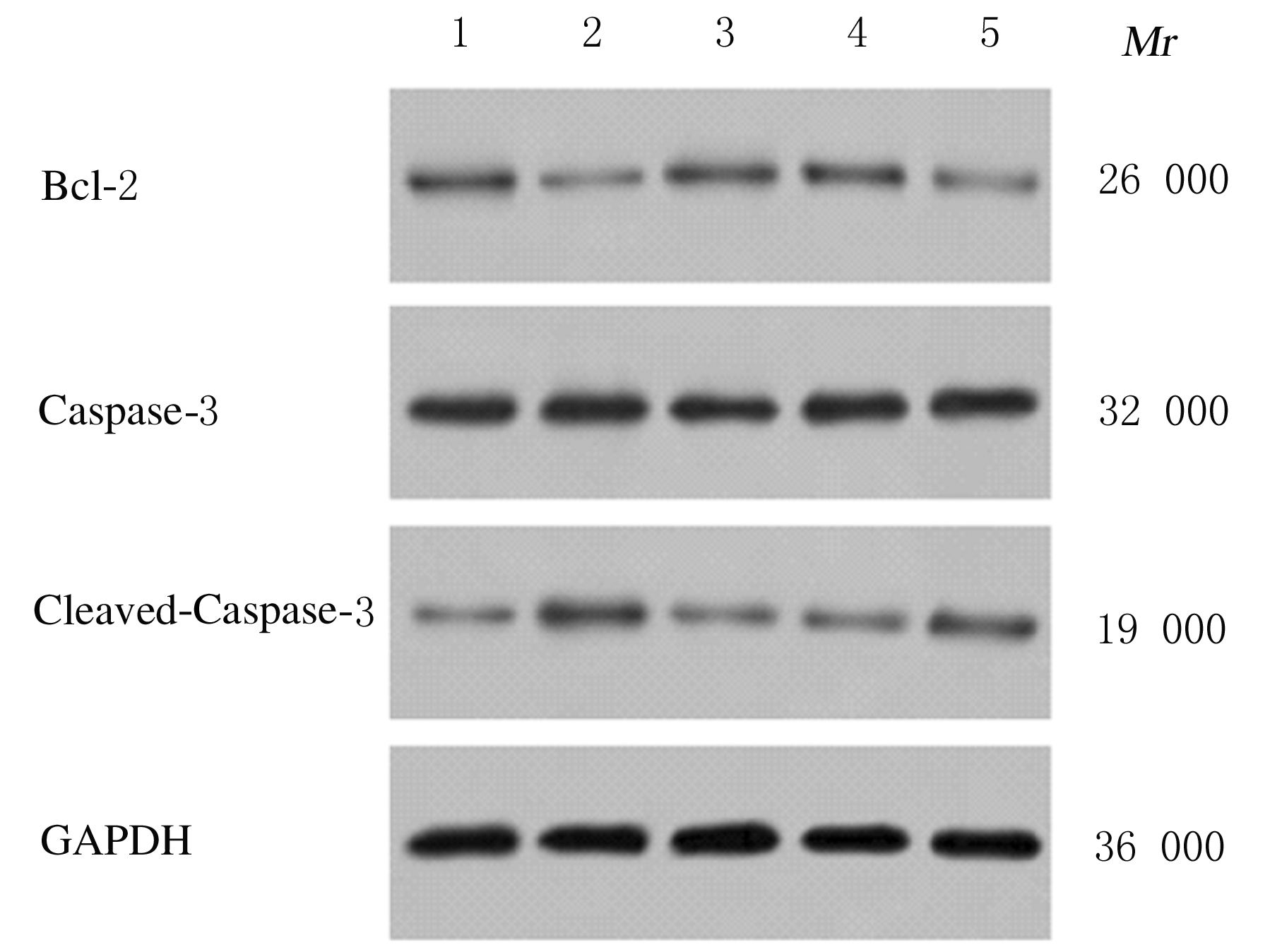
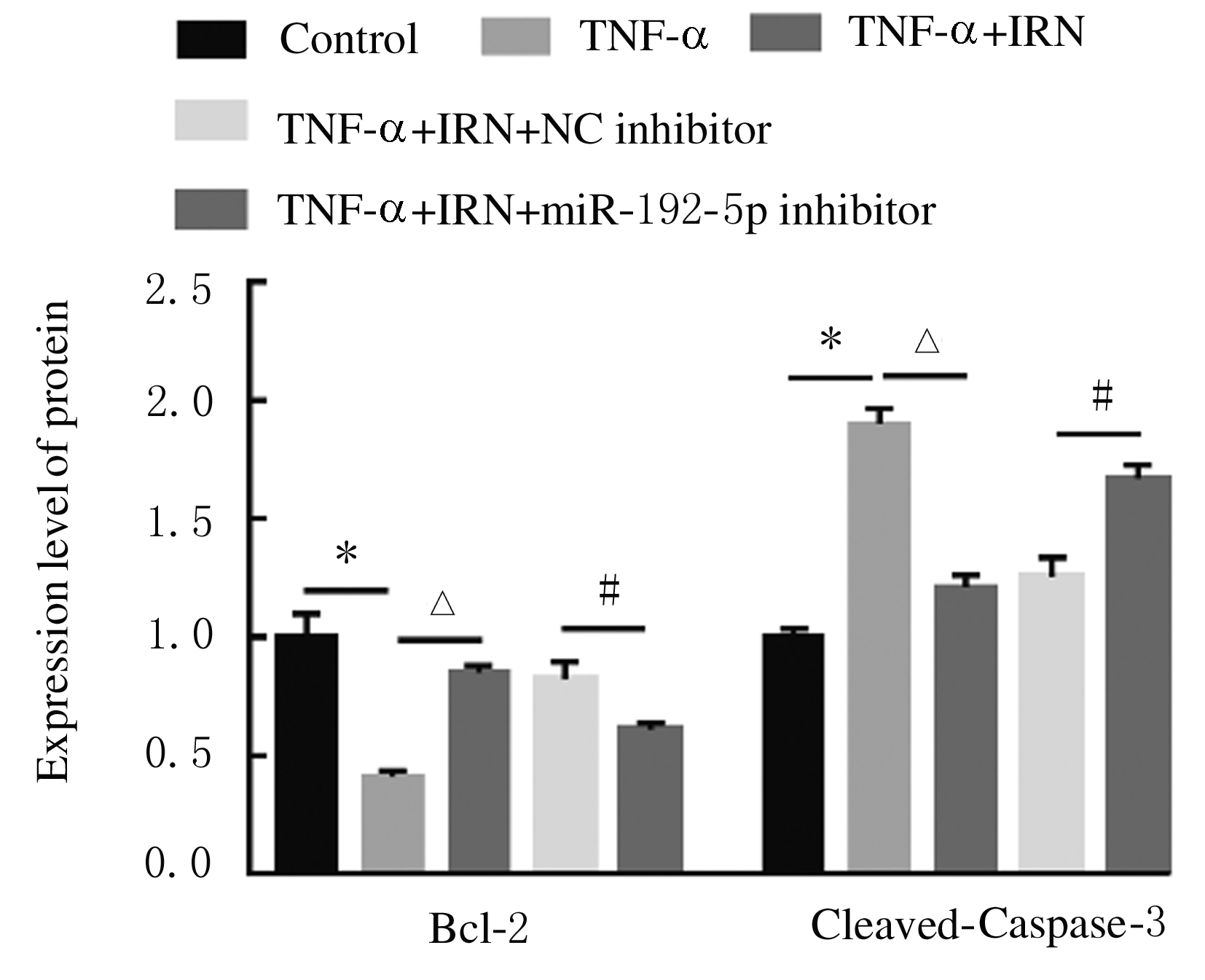
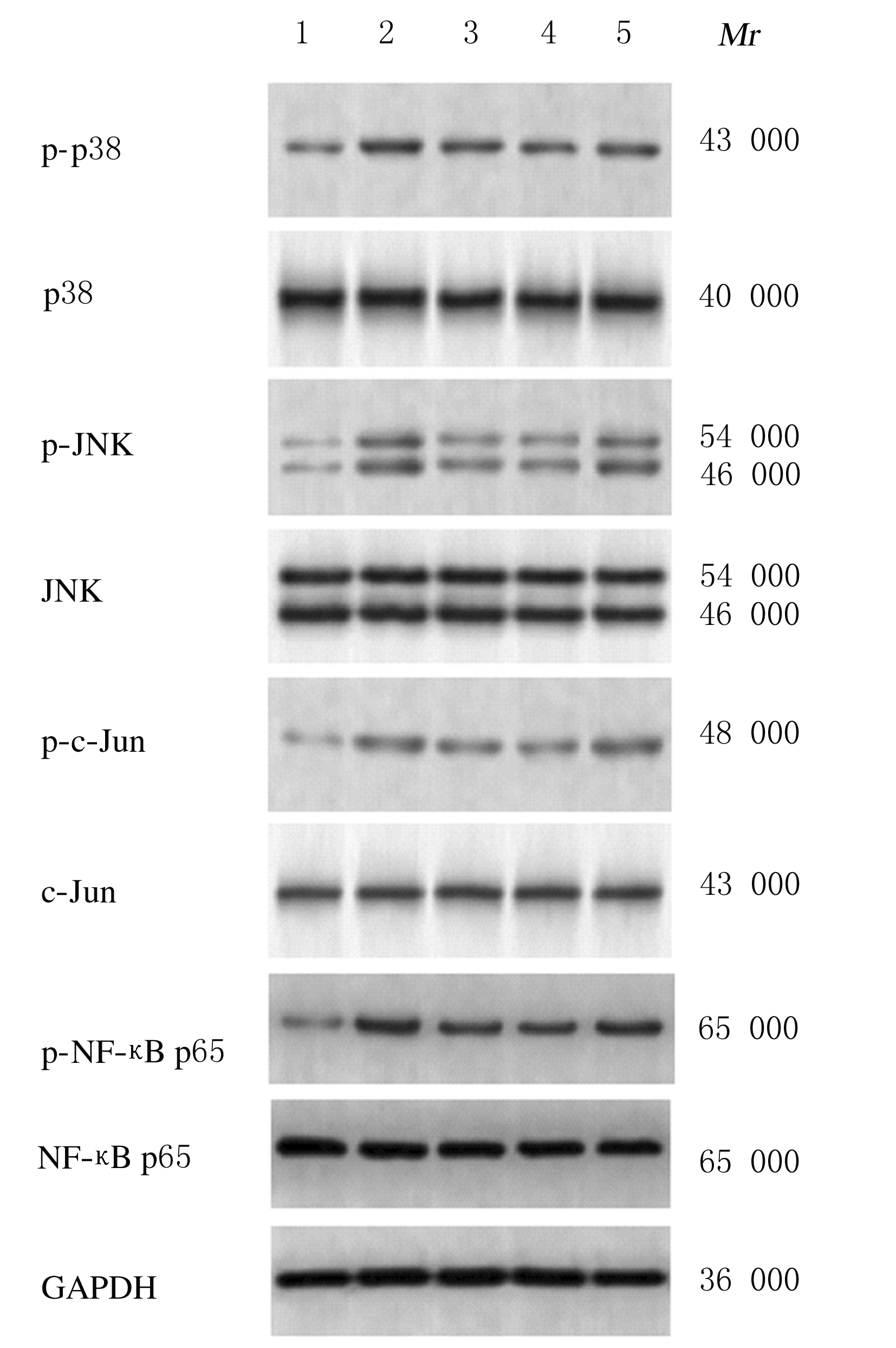
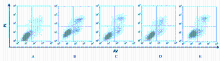
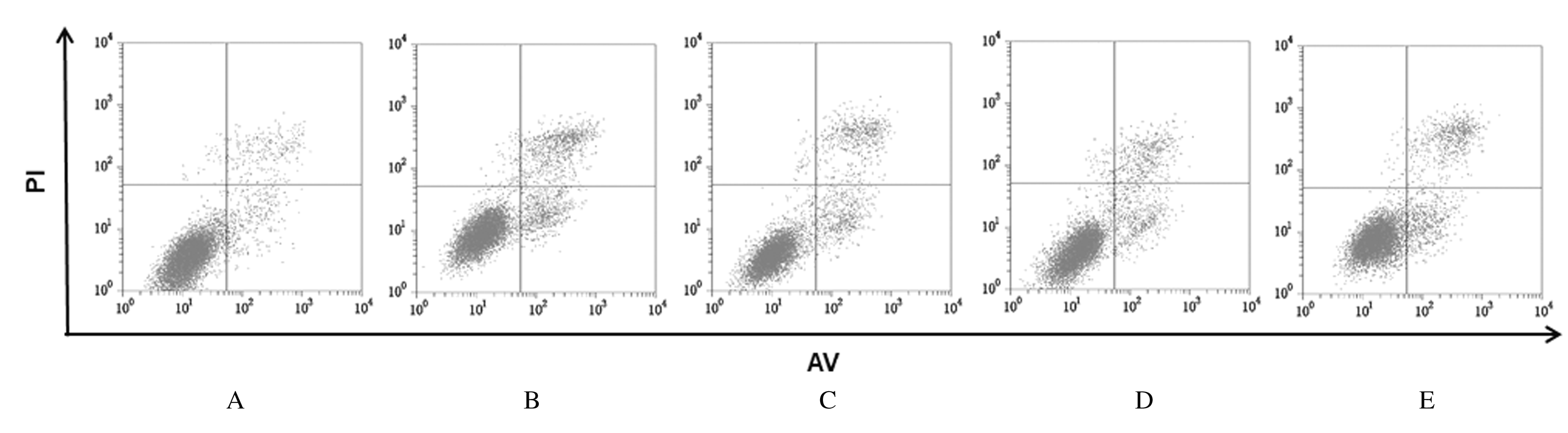
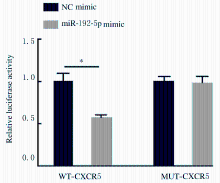
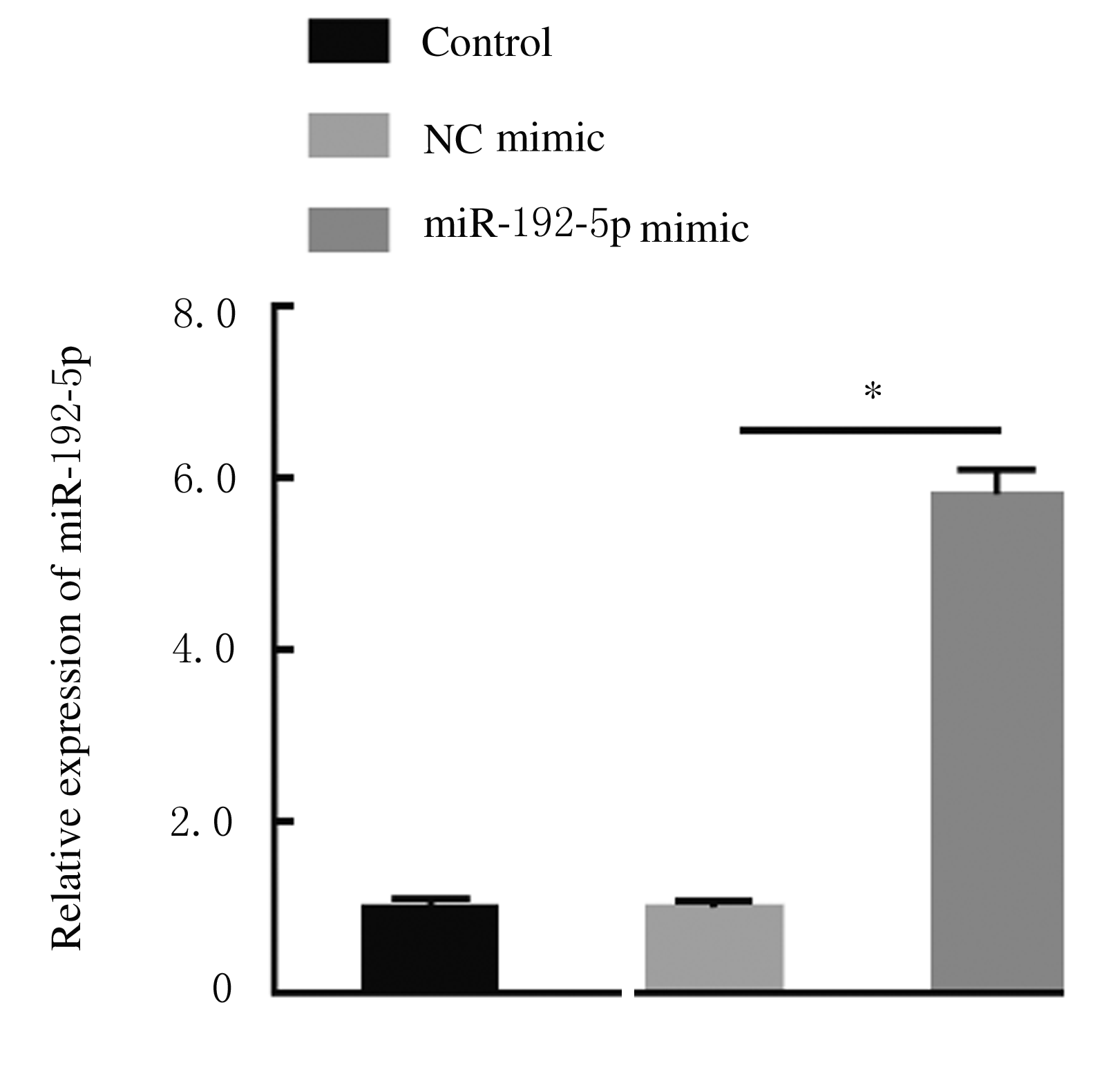
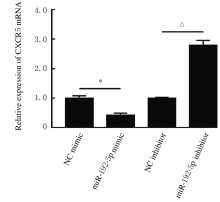
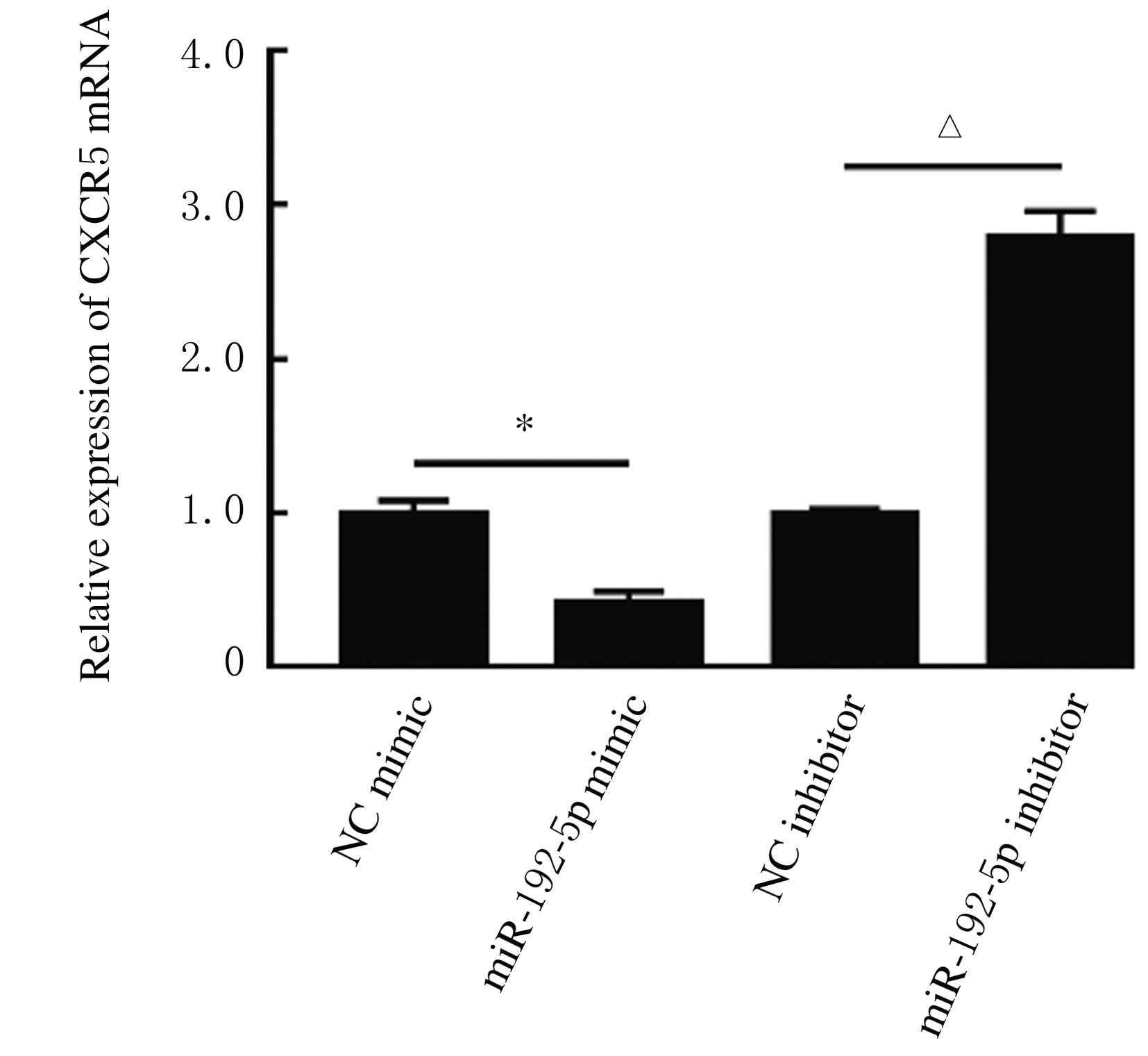
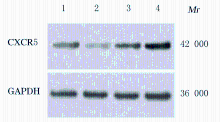
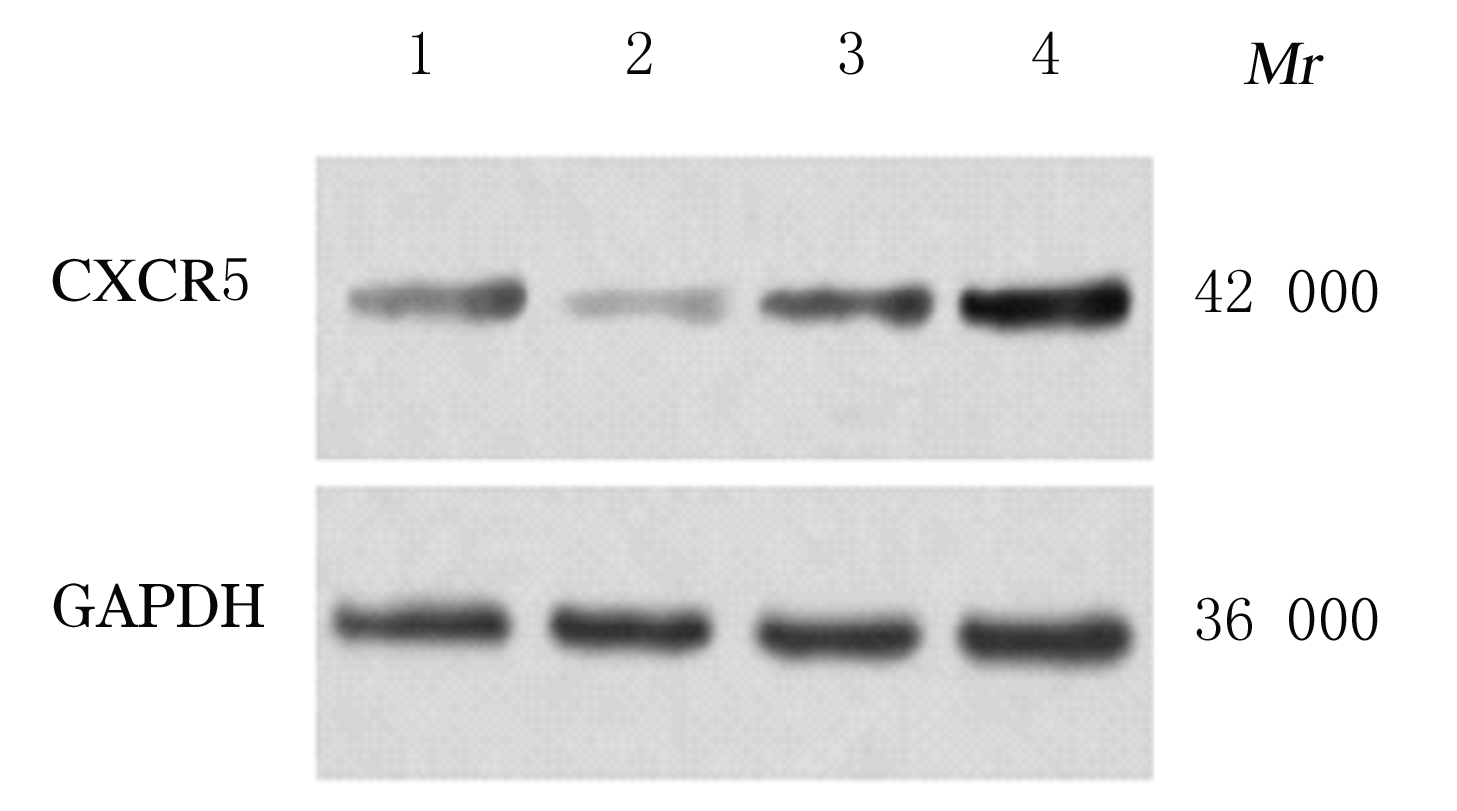
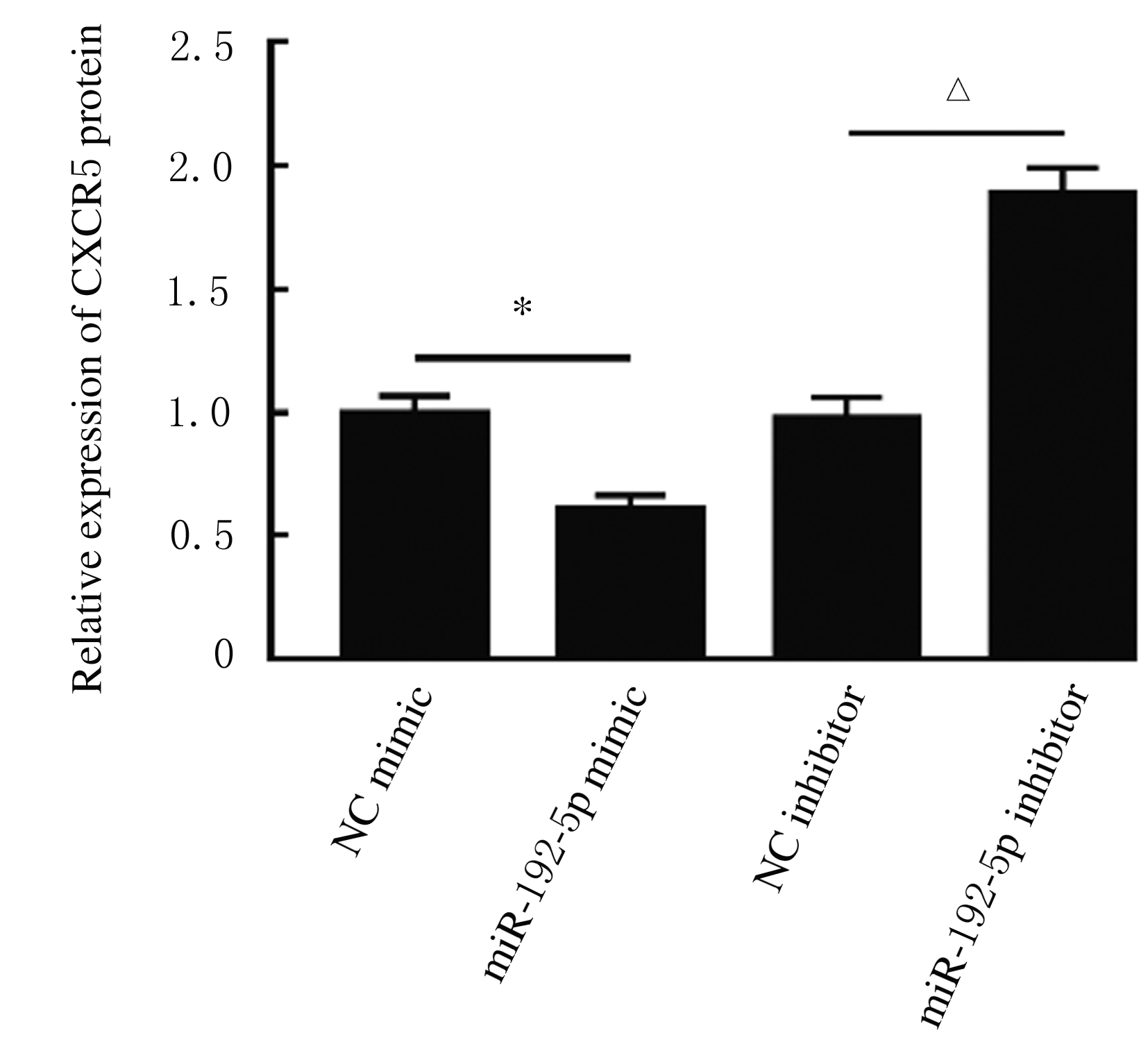
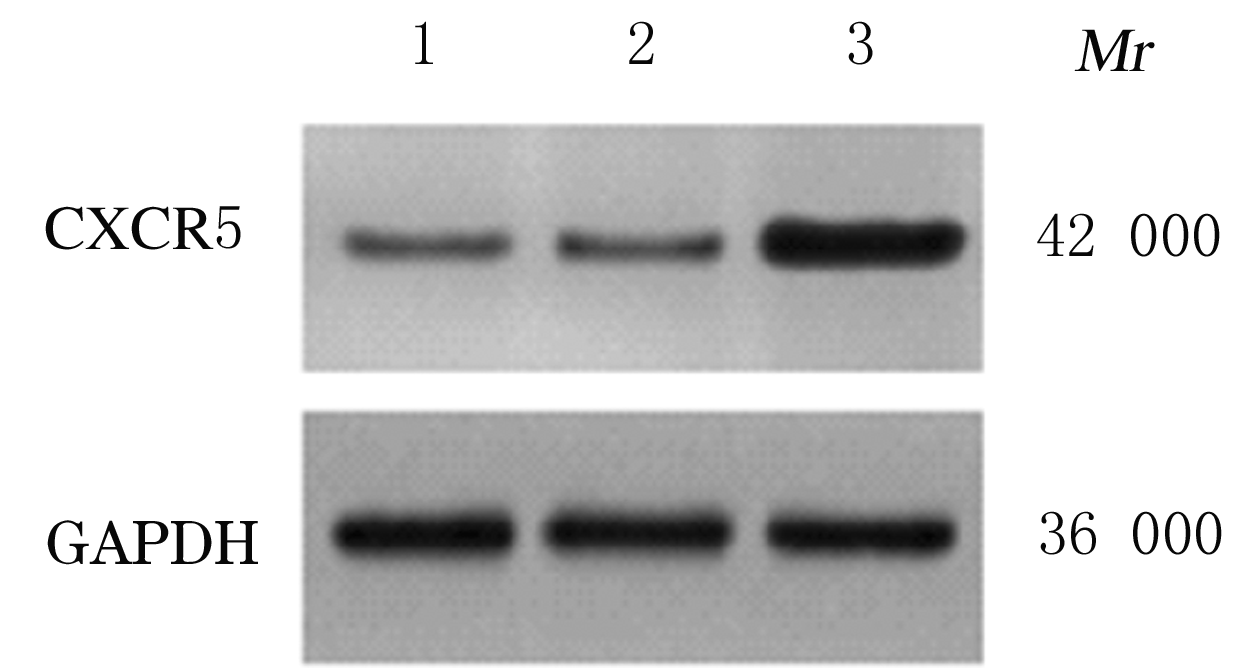
摘要: 探讨异钩藤碱(IRN)对肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)诱导的人支气管上皮细胞(16HBE)凋亡和炎症因子释放的影响,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 采用不同浓度[(0(对照组)、2.5、5.0、10.0、20.0、30.0和40.0 μmol·L-1]IRN处理16HBE细胞24 h后,采用20 mg·L-1 TNF-α处理细胞18 h。将16HBE细胞分为对照组、TNF-α组(20 mg·L-1)、IRN组(20 μmol·L-1)、TNF-α+IRN组(20 mg·L-1 TNF-α和20 μmol·L-1 IRN)、TNF-α+IRN+miR-192-5p inhibitor组(20 mg·L-1 TNF-α、20 μmol·L-1 IRN和50 nmol·L-1 miR-192-5p inhibitor)以及TNF-α+IRN+pcDNA3.1 CXCR5组[20 mg·L-1 TNF-α、20 μmol·L-1 IRN和2 μmol·L-1 pcDNA3.1-C-X-C趋化因子受体5(CXCR5)]。采用CCK-8法检测各组16HBE细胞活性,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组16HBE细胞中miR-192-5p和CXCR5 mRNA表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组16HBE细胞中白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)、单核细胞趋化蛋白 1(MCP-1)、Bcl-2、Cleaved-Caspase3、CXCR5以及磷酸化的p38、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)、c-Jun和核因子-κB(NF-κB)p65蛋白表达水平,ELISA法检测各组16HBE细胞上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平,流式细胞术检测各组16HBE细胞凋亡率,TargetScan7.1网站预测靶基因并通过双荧光素酶报告基因实验验证miR-192-5p与CXCR5之间的靶向结合关系。 与对照组比较,不同浓度TNF-α组细胞活性明显降低(P<0.05);与对照组组比较,5.0、10.0、20.0和30.0 μmol·L-1 IRN组细胞活性升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,TNF-α组16HBE细胞中miR-192-5p和Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-1β、MCP-1、Cleaved-Caspase-3、p-p38、p-JNK、p-c-Jun和p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达水平,细胞凋亡率以及上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平明显升高(P<0.05);与TNF-α组比较,TNF-α+IRN组16HBE细胞中miR-192-5p和Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),IL-1β、MCP-1、Cleaved-Caspase-3、p-p38、p-JNK、p-c-Jun和p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达水平,细胞凋亡率以及上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平明显降低(P<0.05);与TNF-α+IRN+NC inhibitor组比较,TNF-α+IRN+miR-192-5p inhibitor组16HBE细胞中miR-192-5p和Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-1β、MCP-1、Cleaved-Caspase-3、p-p38、p-JNK、p-c-Jun和p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达水平,细胞凋亡率以及上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平明显升高(P<0.05)。与NC mimic和NC inhibitor组比较,miR-192-5p mimic组16HBE细胞中CXCR5 mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),miR-192-5p inhibitor组16HBE细胞中CXCR5 mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,TNF-α组16HBE细胞中CXCR5蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),细胞活性明显降低(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.05),上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平明显升高(P<0.05);与TNF-α组比较,TNF-α+IRN组16HBE细胞中CXCR5蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),细胞活性明显升高(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率明显降低(P<0.05),上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平明显降低(P<0.05);与TNF-α+IRN+ pcDNA3.1组比较,TNF-α+IRN+ pcDNA3.1 CXCR5组16HBE细胞中CXCR5蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),细胞活性明显降低(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.05),上清液中IL-1β和MCP-1水平明显升高(P<0.05)。 IRN能减轻TNF-α诱导的人支气管上皮细胞凋亡和炎症因子释放,其作用机制可能与miR-192-5p/MAPKs/ NF-κB信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- Q71