吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 865-873.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210407
基于cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路独参汤对衰老模型大鼠认知功能障碍的影响
王继凤1,刘晓冉1,隋欣1,阚默1,李辉2,郭文军1,杨擎1,张壮1,明思彤1,李娜1( ),曲晓波1(
),曲晓波1( )
)
- 1.长春中医药大学分子药理实验室,吉林 长春 130117
2.吉林省前卫医院普外科,吉林 长春 130012
Effect of Dushen Tang on cognitive dysfunction of aging model rats based on cAMP/PKA/CREB signal pathway
Jifeng WANG1,Xiaoran LIU1,Xin SUI1,Mo KAN1,Hui LI2,Wenjun GUO1,Qing YANG1,Zhuang ZHANG1,Sitong MING1,Na LI1( ),Xiaobo QU1(
),Xiaobo QU1( )
)
- 1.Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Department of General Surgery,Qianwei Hospital of Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
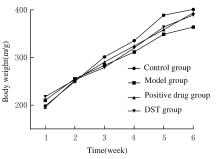
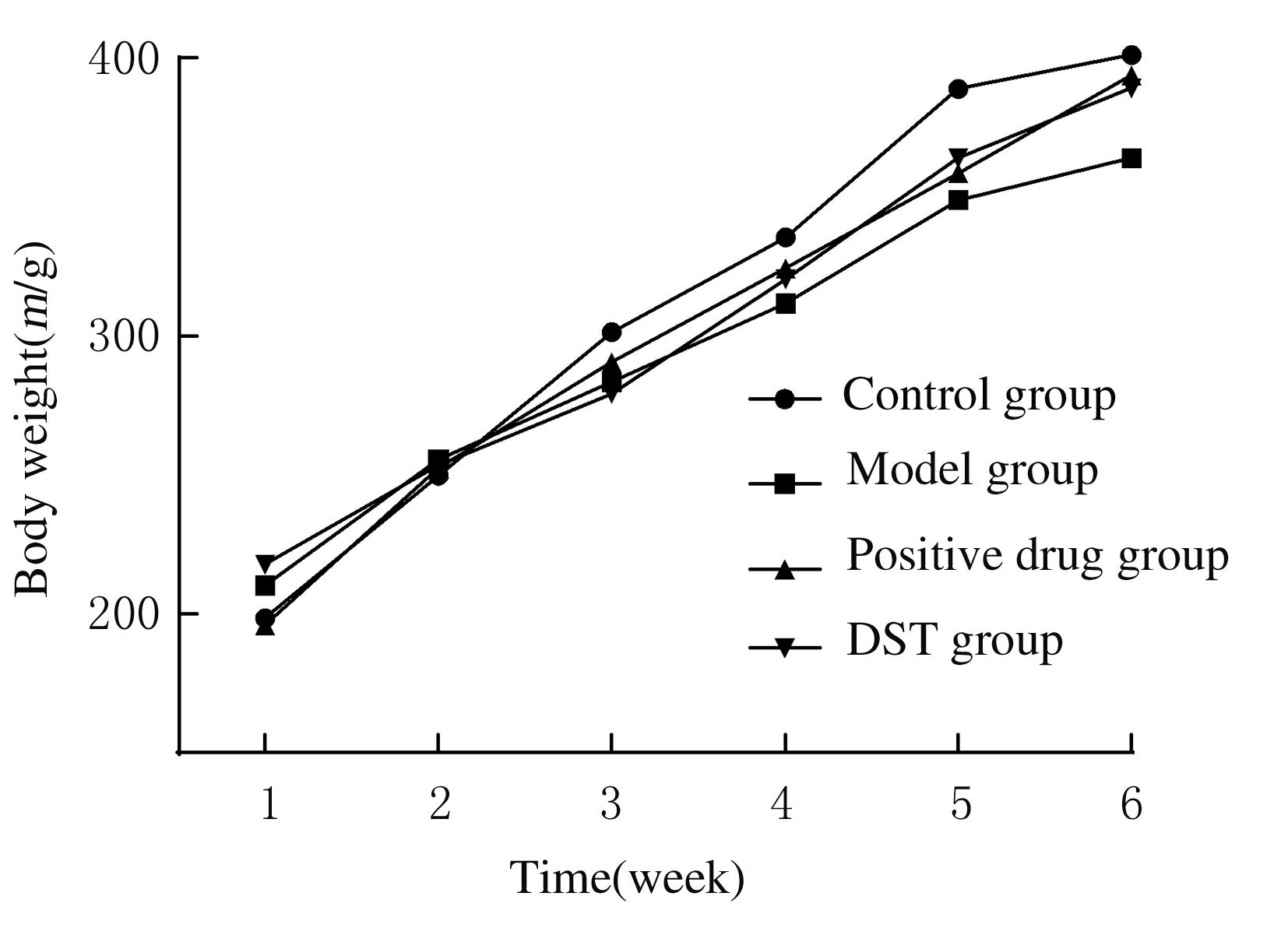
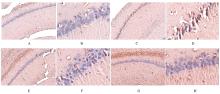
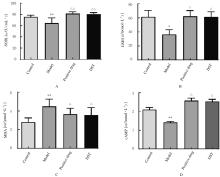
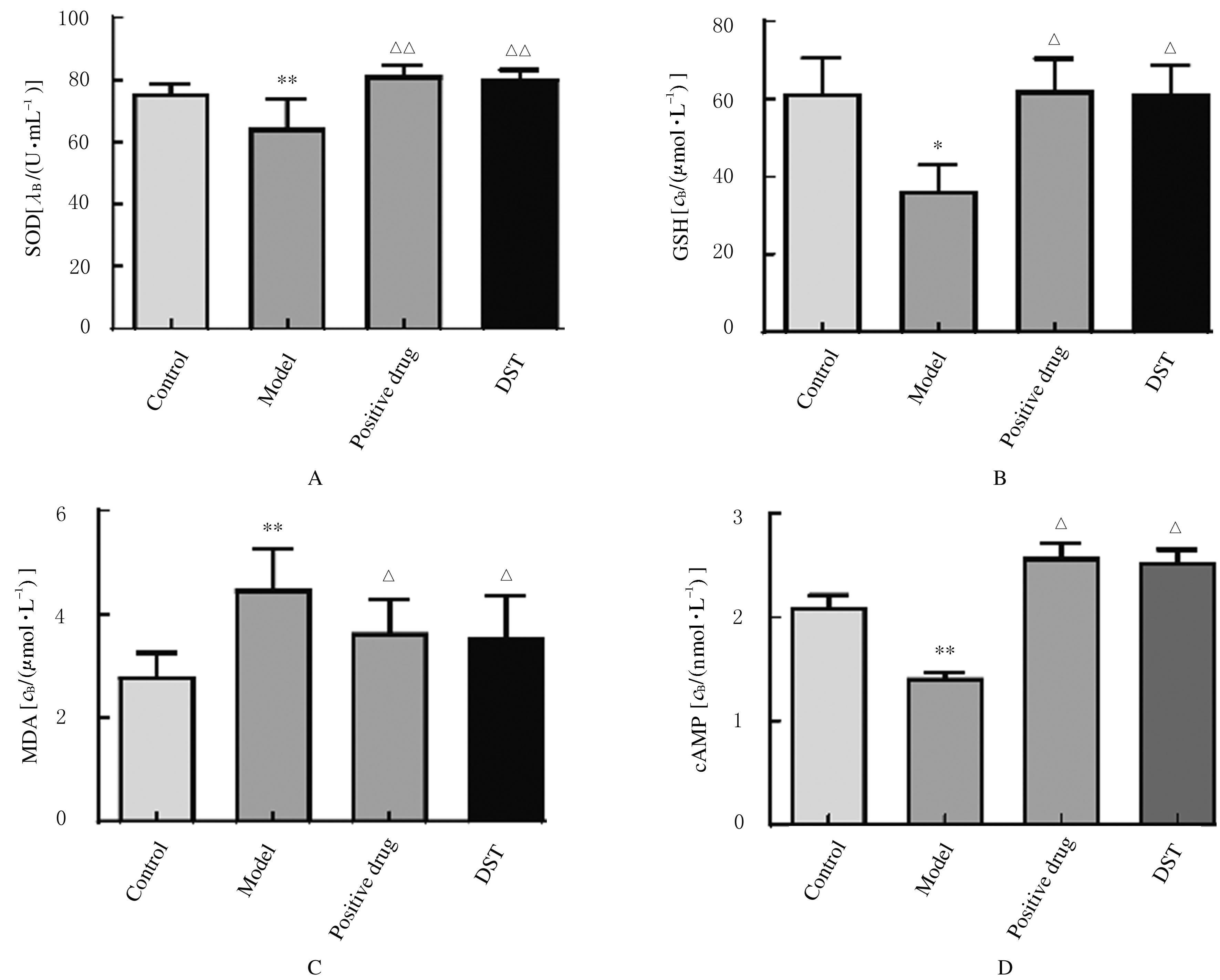
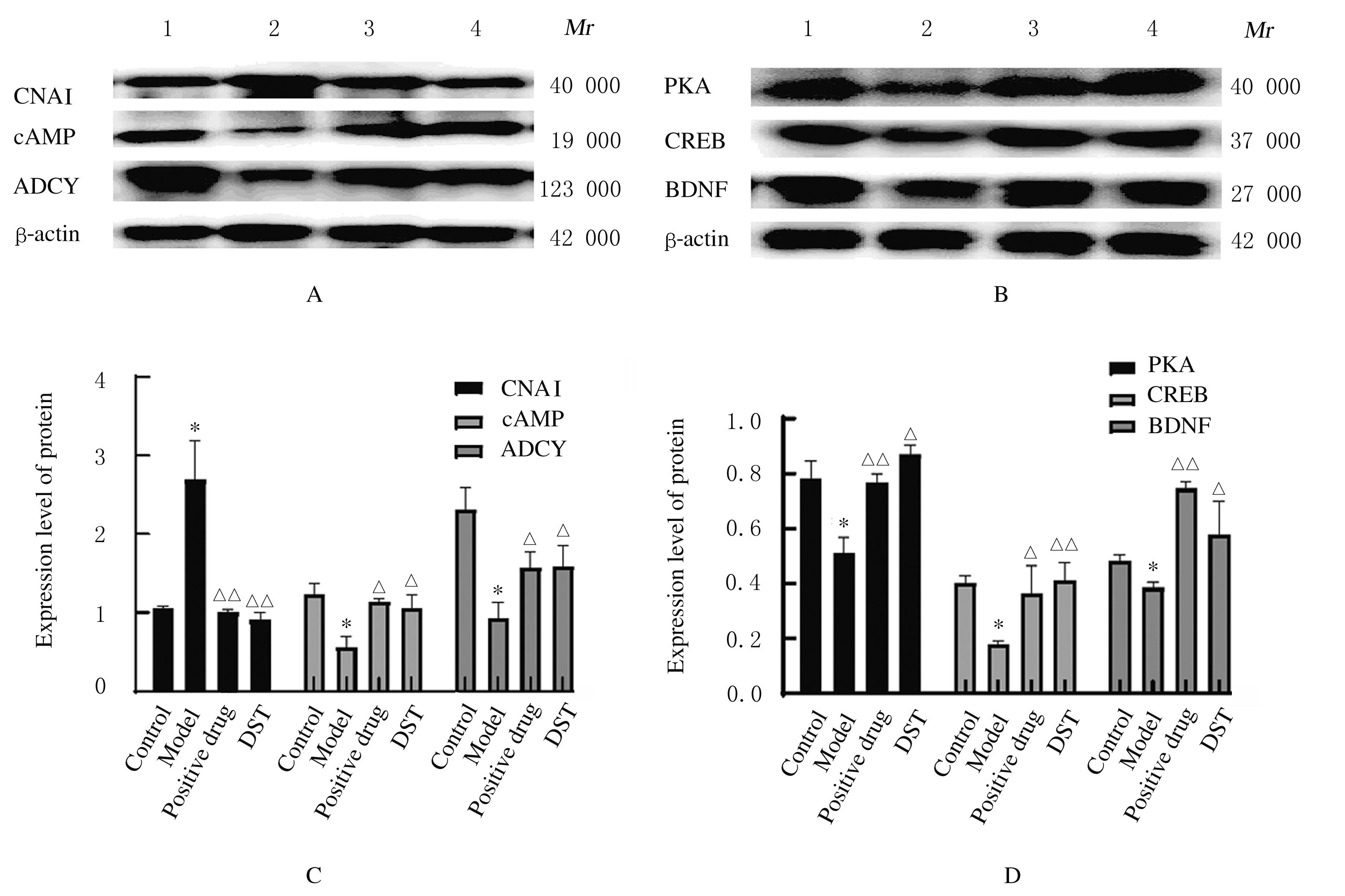
摘要: 探讨独参汤(DST)对D-半乳糖(D-gal)诱导的衰老模型大鼠神经元损伤、脑组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和谷胱甘肽(GSH)的活性、丙二醛(MDA)和环磷酸腺苷(cAMP)水平的影响以及对cAMP/蛋白激酶A(PKA)/cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(CREB)信号通路的激活,阐明DST对D-gal诱导衰老模型大鼠认知功能障碍的改善作用。 40只SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、阳性药组和DST组,每组10只。除对照组外,其余各组大鼠均按500 mg·kg-1·d-1剂量腹腔注射D-gal 40 d建立大鼠衰老模型,建模第5天,阳性药组大鼠给予维生素E 0.027 g·kg-1,DST组大鼠给予独参汤5 mL(相当于生药量0.3 g·kg-1·d-1),共36 d。观察大鼠状态并绘制生长曲线,水迷宫实验检测大鼠学习记忆能力,采用生物化学和酶联免疫吸附测定法(ELISA)试剂盒分别检测大鼠脑组织中SOD、GSH活性及MDA和cAMP水平,透射电镜观察大鼠海马区神经元超微结构表现,刚果红染色观察大鼠海马组织老年斑形成情况,Western blotting法检测大鼠海马组织中cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路相关蛋白表达水平。 与模型组比较,阳性药组和DST组大鼠体质量增加,水迷宫实验中逃避潜伏期和运动总距离明显缩短(P<0.05),穿越平台有效区域次数明显增加(P<0.05),大鼠脑组织中SOD、GSH活性和cAMP水平明显升高(P<0.05),MDA水平明显降低(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,阳性药组和DST组大鼠神经元超微结构病理性改变明显改善,大鼠海马组织中橘红色沉积物及老年斑面积明显减少(P<0.01),大鼠脑组织中PKA、cAMP、腺苷酸环化酶(ADCY)、CREB和脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),鸟嘌呤核苷酸结合蛋白α抑制剂(GNAI)表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。 DST可明显提高D-gal诱导的衰老模型大鼠的认知能力,其机制可能与清除自由基和激活cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路进而改善神经细胞损伤有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5