吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 104-110.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220113
miRNA-27a对实验性肺结核大鼠免疫功能的调控作用及其机制
韩娜1,刘凡平1,田彦卿1,郑志清1,郎伟明1,王倩1,刘亚涛1,朱建光2( )
)
- 1.河北大学附属医院结核科,河北 保定 071000
2.中国人民解放军陆军第八十二集团军医院 耳鼻喉科,河北 保定 071000
Regulatory effect of miRNA-27a on immune function in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis rats and its mechanism
Na HAN1,Fanping LIU1,Yanqing TIAN1,Zhiqing ZHENG1,Weiming LANG1,Qian WANG1,Yatao LIU1,Jianguang ZHU2( )
)
- 1.Department of Tuberculosis,Affiliated Hospital,Hebei University,Baoding 071000,China
2.Department of Otolaryngology,No. 82 Military Hospital of PLA,Baoding 071000,China
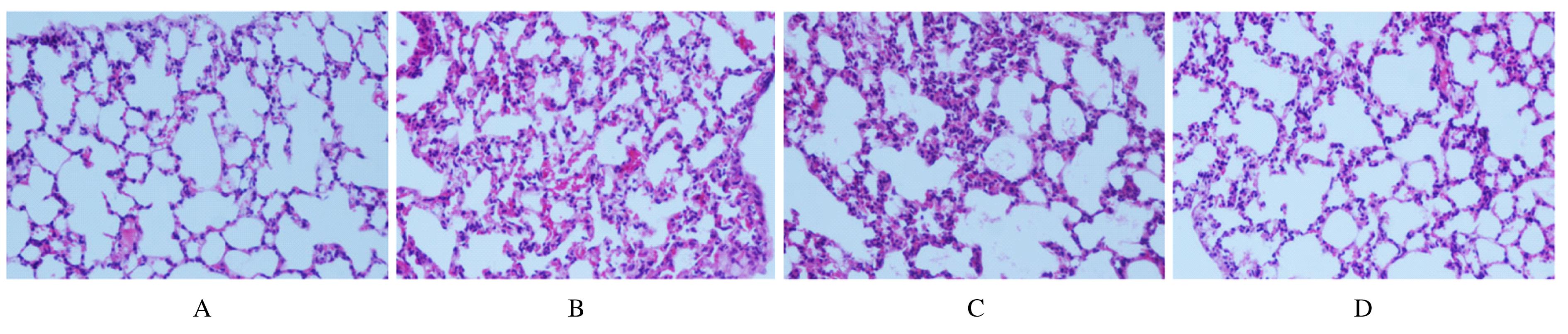
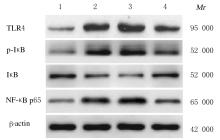
摘要: 探讨miRNA-27a对实验性肺结核模型大鼠免疫功能的调控作用,阐明其可能的作用机制。 经尾静脉注射结核杆菌悬液建立肺结核大鼠模型,将造模成功的大鼠随机分为模型组、miR-27a激动剂对照(agomir-NC)组和miR-27a激动剂(agomir)组,另取正常大鼠设为对照组,每组12只。agomir-NC组和agomir组大鼠经尾静脉注射agomir-NC或miR-27a agomir干预,每天1次,连续5 d。3周后,计算各组大鼠脾脏和胸腺指数,HE染色观察各组大鼠肺组织病理形态表现,流式细胞术检测各组大鼠外周血T淋巴细胞亚群百分率,酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠肺组织中白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组大鼠肺组织中miR-27a表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠肺组织中Toll样受体4(TLR4)、核因子κB (NF-κB)抑制蛋白α(IκBα)、磷酸化IκB(p-IκB)和NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肺组织损伤严重,脾脏及胸腺指数、外周血中CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率和肺组织中miR-27a表达水平及IκB蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),外周血中CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率及肺组织中IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平和TLR4、p-IκB及NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,agomir组大鼠肺组织病理形态表现明显改善,脾脏和胸腺指数、外周血中CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率、肺组织中miR-27a表达水平及IκB蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),外周血中CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率及肺组织中IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平和TLR4、p-IκB、NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),agomir-NC组大鼠上述各指标差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 过表达miR-27a可能通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路活化,减少炎症因子释放,调节机体免疫反应,从而改善肺结核大鼠肺损伤。
中图分类号:
- R-332