| 1 |
SKAPEK S, FERRARI A, GUPTA A, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma [J].Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2019, 5(1): 2.
|
| 2 |
SORENSEN P H, LYNCH J C, QUALMAN S J,et al. PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR gene fusions are prognostic indicators in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the children's oncology group[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2002, 20(11): 2672-2679.
|
| 3 |
MISSIAGLIA E, SHEPHERD C J, ALADOWICZ E, et al. MicroRNA and gene co-expression networks characterize biological and clinical behavior of rhabdomyosarcomas[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 385: 251-260.
|
| 4 |
ZHANG L, PANG Y W, CUI X B, et al. MicroRNA-410-3p upregulation suppresses proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(1): 936-943.
|
| 5 |
SHANG H, LIU Y, LI Z Z, et al. MicroRNA-874 functions as a tumor suppressor in rhabdomyosarcoma by directly targeting GEFT[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(4): 668-681.
|
| 6 |
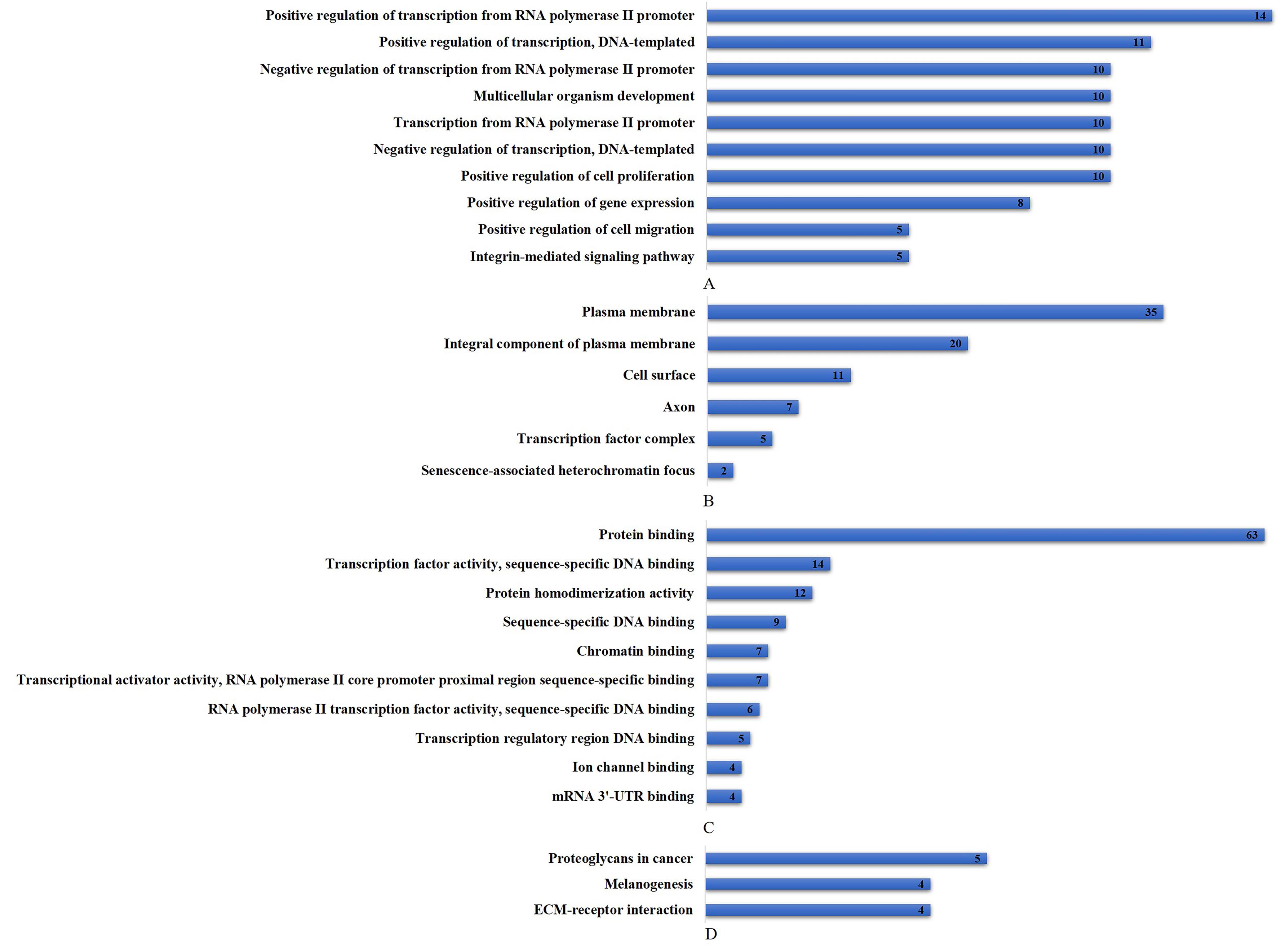
ESPINOZA-SÁNCHEZ N A, GÖTTE M. Role of cell surface proteoglycans in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2020, 62: 48-67.
|
| 7 |
MACHACKOVA T, VYCHYTILOVA-FALTEJSKOVA P, SOUCKOVA K, et al. MiR-215-5p reduces liver metastasis in an experimental model of colorectal cancer through regulation of ECM-receptor interactions and focal adhesion[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(12): E3518.
|
| 8 |
THEOCHARIS A D, KARAMANOS N K. Proteoglycans remodeling in cancer: Underlying molecular mechanisms[J]. Matrix Biol, 2019, 75/76: 220-259.
|
| 9 |
ZHAO X, WANG Q Y, LIN F F, et al. RNA sequencing of osteosarcoma gene expression profile revealed that miR-214-3p facilitates osteosarcoma cell proliferation via targeting ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein 1 (UQCRC1)[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 4982-4991.
|
| 10 |
PHATAK P, BYRNES K A, MANSOUR D, et al. Overexpression of miR-214-3p in esophageal squamous cancer cells enhances sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting survivin directly and indirectly through CUG-BP1 [J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(16): 2087-2097.
|
| 11 |
HUANG H J, LIU J, HUA H, et al. MiR-214 and N-ras regulatory loop suppresses rhabdomyosarcoma cell growth and xenograft tumorigenesis[J]. Oncotarget, 2014, 5(8): 2161-2175.
|
| 12 |
VEERIAH S, BRENNAN C, MENG S S, et al. The tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD is a tumor suppressor that is frequently inactivated and mutated in glioblastoma and other human cancers[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(23): 9435-9440.
|
| 13 |
MEEHAN M, PARTHASARATHI L, MORAN N, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor delta acts as a neuroblastoma tumor suppressor by destabilizing the aurora kinase A oncogene[J]. Mol Cancer, 2012, 11: 6.
|
| 14 |
SOLOMON D A, KIM J S, CRONIN J C, et al. Mutational inactivation of PTPRD in glioblastoma multiforme and malignant melanoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(24): 10300-10306.
|
| 15 |
FUNATO K, YAMAZUMI Y, ODA T, et al. Tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD suppresses colon cancer cell migration in coordination with CD44[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2011, 2(3): 457-463.
|
| 16 |
WANG M, ZHAO Y, YU Z Y, et al. Glioma exosomal microRNA-148a-3p promotes tumor angiogenesis through activating the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway via inhibiting ERRFI1 [J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2020, 20: 518.
|
| 17 |
YU Y, CHEN Q Y, ZHANG X L, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes the malignant progression of cholangiocarcinoma by epigenetically repressing ERRFI1 expression[J]. Cancer Sci, 2020, 111(7): 2297-2309.
|
| 18 |
YAN J W, LIN J S, HE X X. The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 135(5): 1011-1018.
|
| 19 |
YIN L H, ZHENG X Q, LI H Y, et al. Epigenetic deregulated miR-375 contributes to the constitutive activation of JAK2/STAT signaling in myeloproliferative neoplasm[J].Leuk Res, 2015,39(4):471-478.
|
| 20 |
HE X X, CHANG Y, MENG F Y, et al. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo [J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(28): 3357-3369.
|
| 21 |
HE J, CAO Y N, SU T W, et al. Downregulation of miR-375 in aldosterone-producing adenomas promotes tumour cell growth via MTDH[J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2015, 83(4): 581-589.
|
| 22 |
MAO Q Q, QUAN T, LUO B, et al. MiR-375 targets KLF4 and impacts the proliferation of colorectal carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(1): 463-471.
|
| 23 |
LIU W, ZHAO X T, ZHANG Y J, et al. MicroRNA-375 as a potential serum biomarker for the diagnosis, prognosis, and chemosensitivity prediction of osteosarcoma[J]. J Int Med Res, 2018,46(3): 975-983.
|
| 24 |
XU X D, LIU Y, LI Y, et al. Selective exosome exclusion of miR-375 by glioma cells promotes glioma progression by activating the CTGF-EGFR pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 16.
|
| 25 |
SZCZYRBA J, NOLTE E, WACH S, et al. Downregulation of Sec23A protein by miRNA-375 in prostate carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2011, 9(6): 791-800.
|
| 26 |
ZHAO W S, YAN W P, CHEN D B, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR activation screening identifies a role of ELAVL2-CDKN1A axis in paclitaxel resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(6): 1183-1200.
|
| 27 |
LI L, MOU Y P, WANG Y Y, et al. MiR-199a-3p targets ETNK1 to promote invasion and migration in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019, 215(9): 152511.
|
| 28 |
WANG X M, ZOU J L, CHEN H J, et al. Long noncoding RNA NORAD regulates cancer cell proliferation and migration in human osteosarcoma by endogenously competing with miR-199a-3p[J]. IUBMB Life, 2019, 71(10): 1482-1491.
|
| 29 |
LIU F, ZHUANG L, WU R X, et al. MiR-365 inhibits cell invasion and migration of triple negative breast cancer through ADAM10[J]. J BUON, 2019, 24(5): 1905-1912.
|
| 30 |
WANG Y J, ZHOU N, LI P, et al. EphA8 Acts as an oncogene and contributes to poor prognosis in gastric cancer via regulation of ADAM10[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(11): 20408-20419.
|
| 31 |
ZHAO R, NI D J, TIAN Y, et al. Aberrant ADAM10 expression correlates with osteosarcoma progression[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2014, 19: 9.
|
 )
)