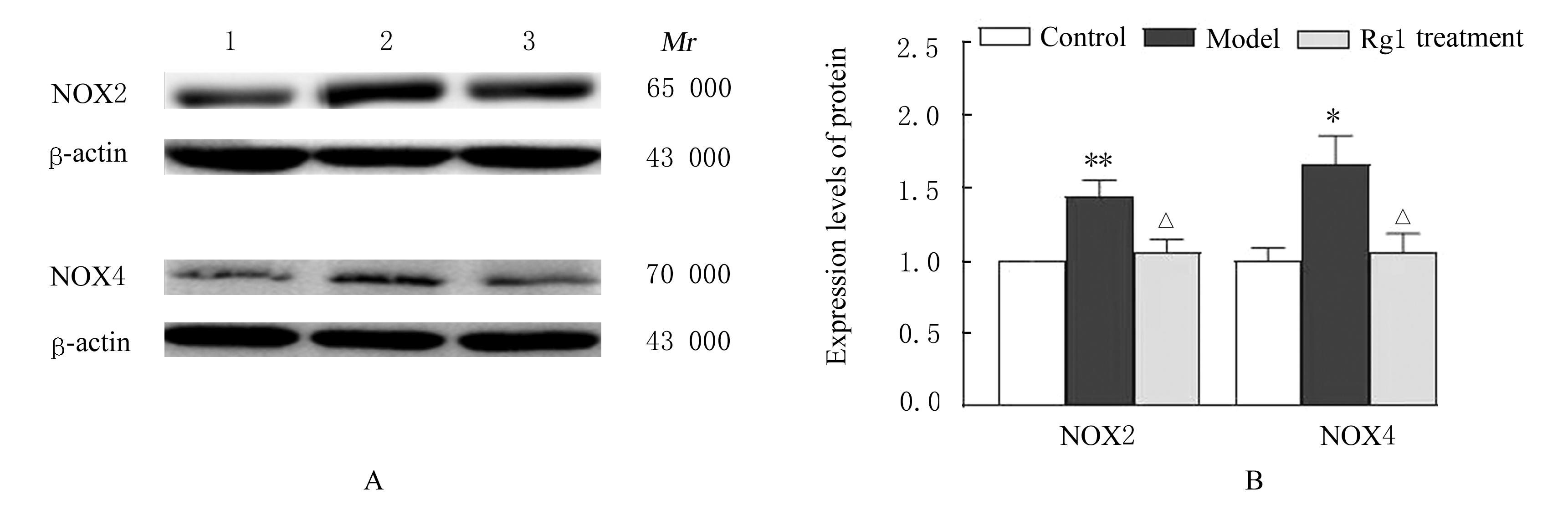
| 1 |
PORTELLI M, JONES C D. Severe acute pancreatitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and surgical management[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2017, 16(2): 155-159.
|
| 2 |
SERGEEVA S S, KUZNETSOVA T Y, KOCHERINA V V, et al. Rivaroxaban for secondary prophylaxis of atherothrombosis complications in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome[J]. Kardiologiia, 2017, 57(10): 89-97.
|
| 3 |
MEDEROS M A, REBER H A, GIRGIS M D. Acute pancreatitis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(4): 382-390.
|
| 4 |
YEGNESWARAN B, KOSTIS J B, PITCHUMONI C S.Cardiovascular manifestations of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Crit Care, 2011, 26(2): 225.e11-225.e18.
|
| 5 |
ZHANG Y X, MURUGESAN P, HUANG K, et al. NADPH oxidases and oxidase crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases: novel therapeutic targets[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2020, 17(3): 170-194.
|
| 6 |
ZHANG M, PERINO A, GHIGO A, et al. NADPH oxidases in heart failure: poachers or gamekeepers?[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2013, 18(9): 1024-1041.
|
| 7 |
BEDARD K, KRAUSE K H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology[J]. Physiol Rev,2007,87(1): 245-313.
|
| 8 |
MOE K T, KHAIRUNNISA K, YIN N O, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human cardiomyocytes is mediated by NADPH oxidase[J]. J Physiol Biochem, 2014, 70(3): 769-779.
|
| 9 |
ZENG Q H, ZHOU Q W, YAO F R, et al.Endothelin-1 regulates cardiac L-type calcium channels via NAD(P)H oxidase-derived superoxide[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2008, 326(3): 732-738.
|
| 10 |
SIRKER A, ZHANG M, SHAH A M. NADPH oxidases in cardiovascular disease: insights from in vivo models and clinical studies[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2011, 106(5): 735-747.
|
| 11 |
QIN F Z, SHITE J Y, LIANG C S. Antioxidants attenuate myocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function in CHF: association with changes in MAPK pathways[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2003, 285(2): H822-H832.
|
| 12 |
WEN Y, LIU R H, LIN N, et al. NADPH oxidase hyperactivity contributes to cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis in rats with severe experimental pancreatitis through ROS-mediated MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 4578175.
|
| 13 |
QI L W, WANG C Z, YUAN C S. Isolation and analysis of ginseng: advances and challenges[J]. Nat Prod Rep, 2011, 28(3): 467-495.
|
| 14 |
ZHU D, WU L, LI C R, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects rat cardiomyocyte from hypoxia/reoxygenation oxidative injury via antioxidant and intracellular calcium homeostasis[J]. J Cell Biochem,2009,108(1): 117-124.
|
| 15 |
卫 衡,施 展,张若冰,等.人参皂苷Rg1对顺铂致H9c2心肌细胞损伤的保护作用与机制[J/OL].吉林农业大学学报,2021.DOI:10.13327/j.jjlau.2021.1021 .
doi: 10.13327/j.jjlau.2021.1021
|
| 16 |
CHEN G Y, DAI R W, LUO H, et al. Effect of percutaneous catheter drainage on pancreatic injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis induced by sodium taurocholate[J]. Pancreatology, 2015, 15(1): 71-77.
|
| 17 |
白 槟, 徐 斌, 刘朝旭, 等. 逆行胰胆管注射牛磺胆酸钠诱导重症急性胰腺炎模型多器官损害观察[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(15): 4141-4147.
|
| 18 |
WANG Y J, LIU J Z, MA A R, et al. Cardioprotective effect of berberine against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(8): 14513-14519.
|
| 19 |
RO T K, LANG R M, WARD R P. Acute pancreatitis mimicking myocardial infarction: evaluation with myocardial contrast echocardiography[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2004, 17(4): 387-390.
|
| 20 |
CAVE A C, BREWER A C, NARAYANAPANICKER A, et al. NADPH oxidases in cardiovascular health and disease[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2006, 8(5/6): 691-728.
|
| 21 |
SELVARAJU V, JOSHI M, SURESH S, et al. Diabetes, oxidative stress, molecular mechanism, and cardiovascular disease: an overview[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2012, 22(5): 330-335.
|
| 22 |
崔明哲,王 恒,翟水亭,等.抑制磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/心肌素信号通路对血管平滑肌瘤细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2021,56(5):690-693.
|
| 23 |
张 琦,刘 静.SGLT2抑制剂的心脏保护作用[J].中国实用内科杂志,2020,40(8):630-633.
|
| 24 |
吕 瑾, 杨胜祥, 华晓芳, 等. 黑芥子苷通过p38/JNK MAPK信号通路对阿霉素心脏毒性的保护作用[J]. 国际心血管病杂志, 2020, 47(1): 48-51.
|
| 25 |
赵金红, 张新金, 李建美. p38MAPK信号通路与心脏重构关系的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2013, 19(13): 2312-2314.
|
| 26 |
贾蕾蕾, 王爱玲. 棉子酚通过干扰氧化应激反应、抑制JNK/p38 MAPK信号通路的激活减轻大鼠离体心脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2017, 52(10): 1424-1429.
|
| 27 |
YU H T, ZHEN J, PANG B,et al.Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates oxidative stress and myocardial apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J].Zhejiang Univ Sci B,2015,16(5): 344-354.
|
| 28 |
高文静, 马 宏, 项美香. 心肌能量底物代谢重构与心力衰竭关系的研究进展[J].解放军医学杂志,2021,46(8):822-826.
|
| 29 |
黄小平, 王 蓓, 邱咏园, 等. 黄芪甲苷、人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1和三七皂苷R1抗小鼠脑缺血再灌注氧化应激损伤和促进能量代谢的配伍研究[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2014, 34(7): 5-11.
|
| 30 |
陈海霞, 黄广丽, 周红瀛, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1减轻大鼠离体心脏缺血再灌注损伤的作用研究[J]. 河北医药, 2016, 38(4): 485-488.
|
 )
)