吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1623-1628.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220631
实时荧光定量PCR法对ICU患者痰液标本中鲍曼不动杆菌耐药基因的检测及其评价
- 1.天津市第三中心医院检验科 天津市重症疾病体外生命支持重点实验室 天津市人工细胞工程技术研究中心 天津市肝胆研究所,天津 300170
2.天津市第三中心医院重症医学科,天津 300170
Detection of drug resistance genes of Acinetobacter baumannii in sputum samples of ICU patients by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR method and its evaluation
Yanan MA1,Bing TAN1,Lei XU2,Jiandong ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Laboratory Medicine,Tianjin Third Central Hospital,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Extracorporeal Life Support for Critical Diseases,Tianjin Artificial Cell Engineering Technology Research Center,Tianjin Institute of Hepatobiliary Disease,Tianjin 300170,China
2.Department of Critical Care Medicine,Tianjin Third Central Hospital,Tianjin 300170,China
摘要:
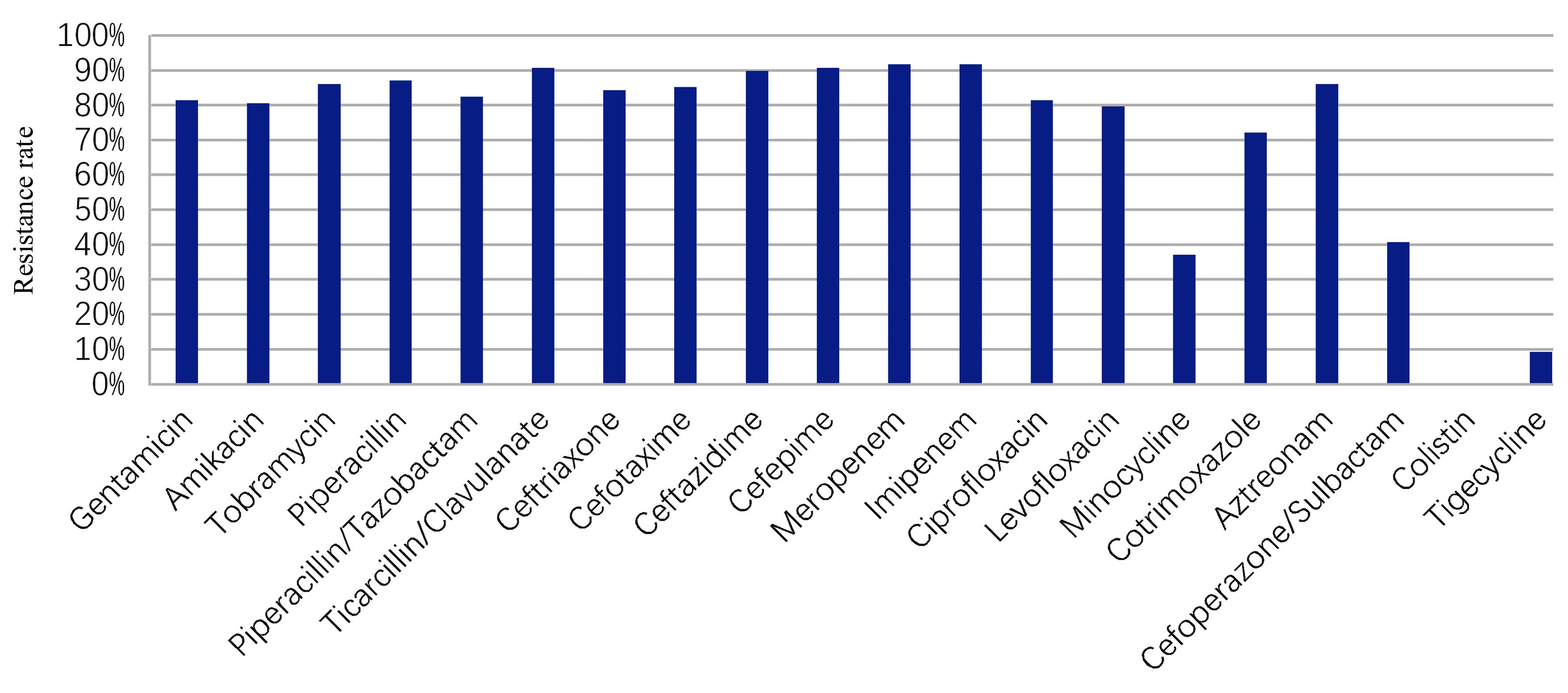
目的 探讨重症监护病房(ICU)患者感染鲍曼不动杆菌(AB)的碳青霉烯类药物耐药情况,阐明实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法进行耐药基因检测的临床应用价值。 方法 收集ICU患者的痰液标本285份,分别进行传统培养鉴定药敏和RT-qPCR耐药基因检测。统计分析耐碳青霉烯类鲍曼不动杆菌(CRAB)检出率、耐药基因检测的符合率和其他抗菌药物的耐药情况。 结果 共检出AB 151株,检出率为52.98%。AB对碳青霉烯类药物耐药率为72.20%。采用RT-qPCR法检测OXA-51基因检出AB的符合率与传统培养方法比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。OXA-23基因检出CRAB的符合率与传统培养方法比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。108株AB感染OXA-23阳性标本对米诺环素、头孢哌酮/舒巴坦、黏菌素和替加环素的耐药率较低。 结论 ICU患者痰液标本培养鉴定出AB的耐碳青霉烯类药物的检出率高。与传统培养方法比较,RT-qPCR法更简便、快速,且检测符合率更高。CRAB对米诺环素、头孢哌酮/舒巴坦、黏菌素和替加环素的耐药率低。
中图分类号:
- R446.5