吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 18-24.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240103
PD-L1对人口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响
- 1.石河子大学第一附属医院口腔科,新疆 石河子 832000
2.石河子大学第一附属医院病理科,新疆 石河子 832000
3.新疆维吾尔自治区儿童医院检验科,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830000
Effect of PD-L1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human oral squamous carcinoma cells
Jie ZENG1,Xueyan YU2,Ting LUO3,Jiang XU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Stomatology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
2.Department of Pathology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
3.Department of Laboratory,Children’s Hospital,Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,Urumqi 830000,China
摘要:
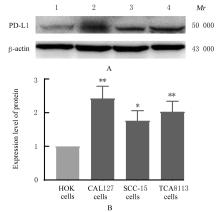
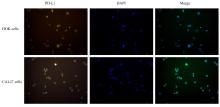
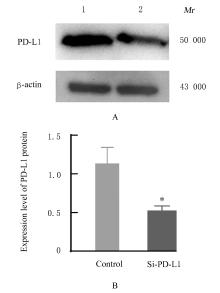
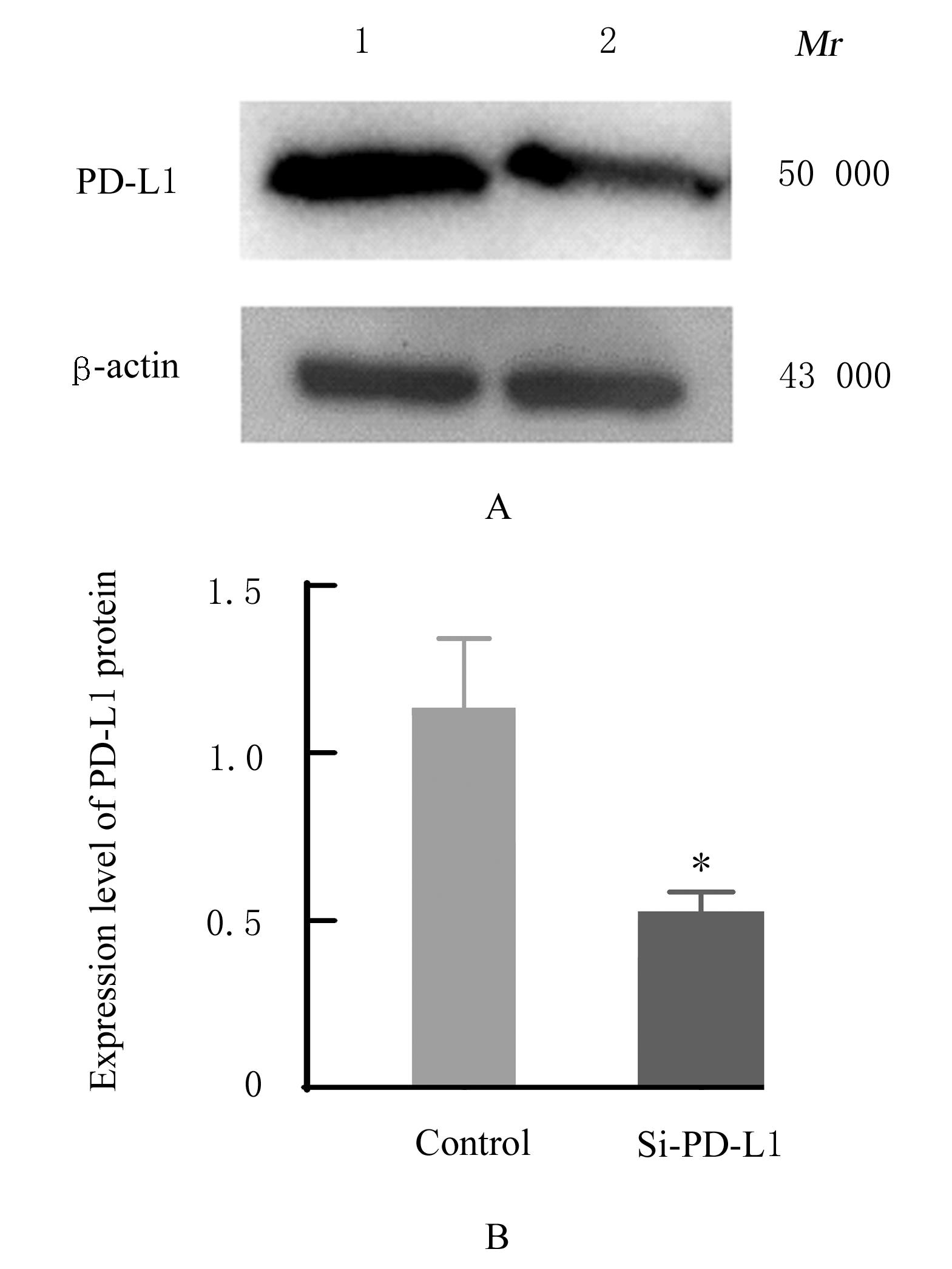
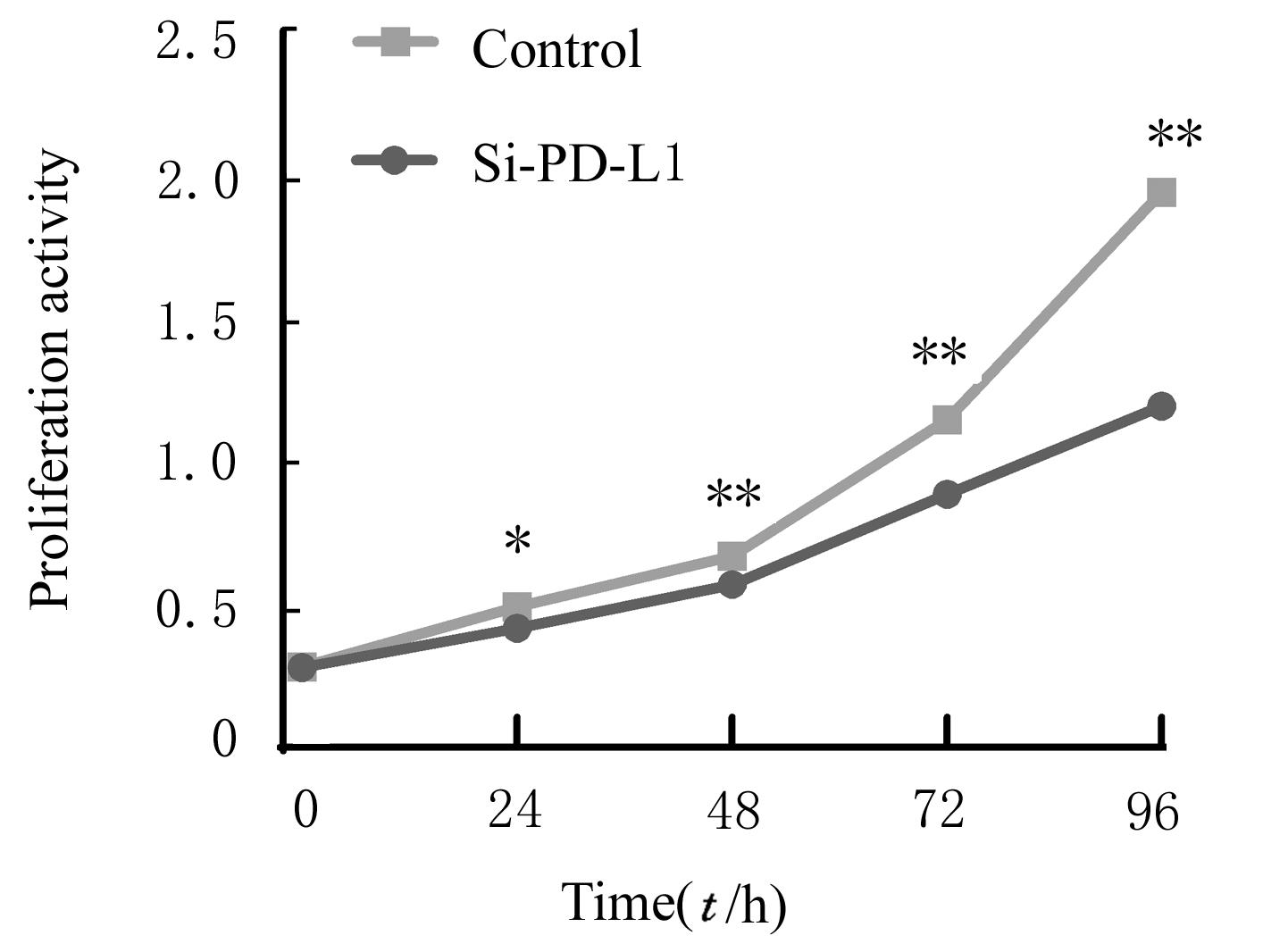
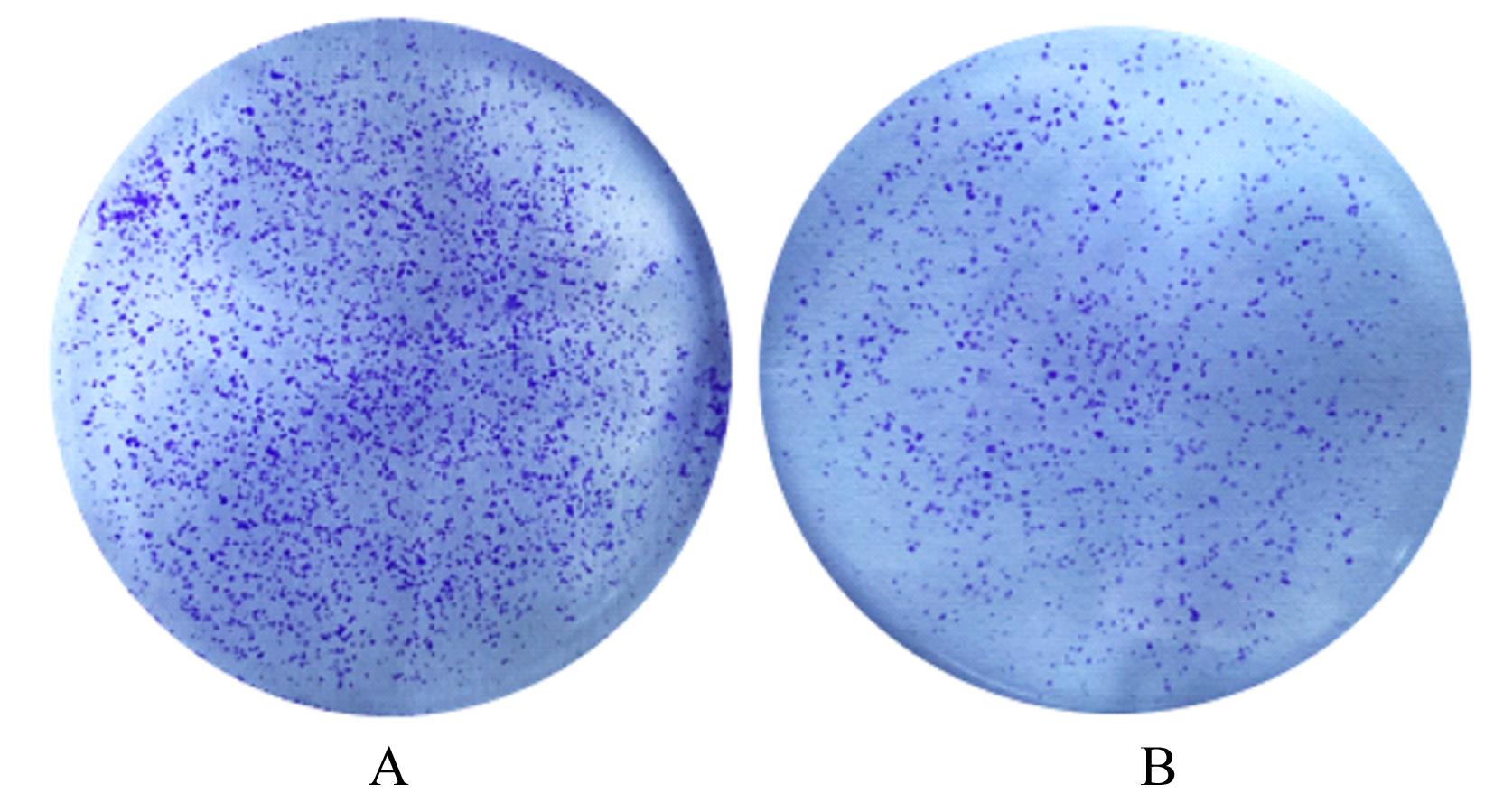
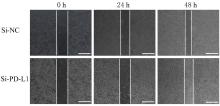
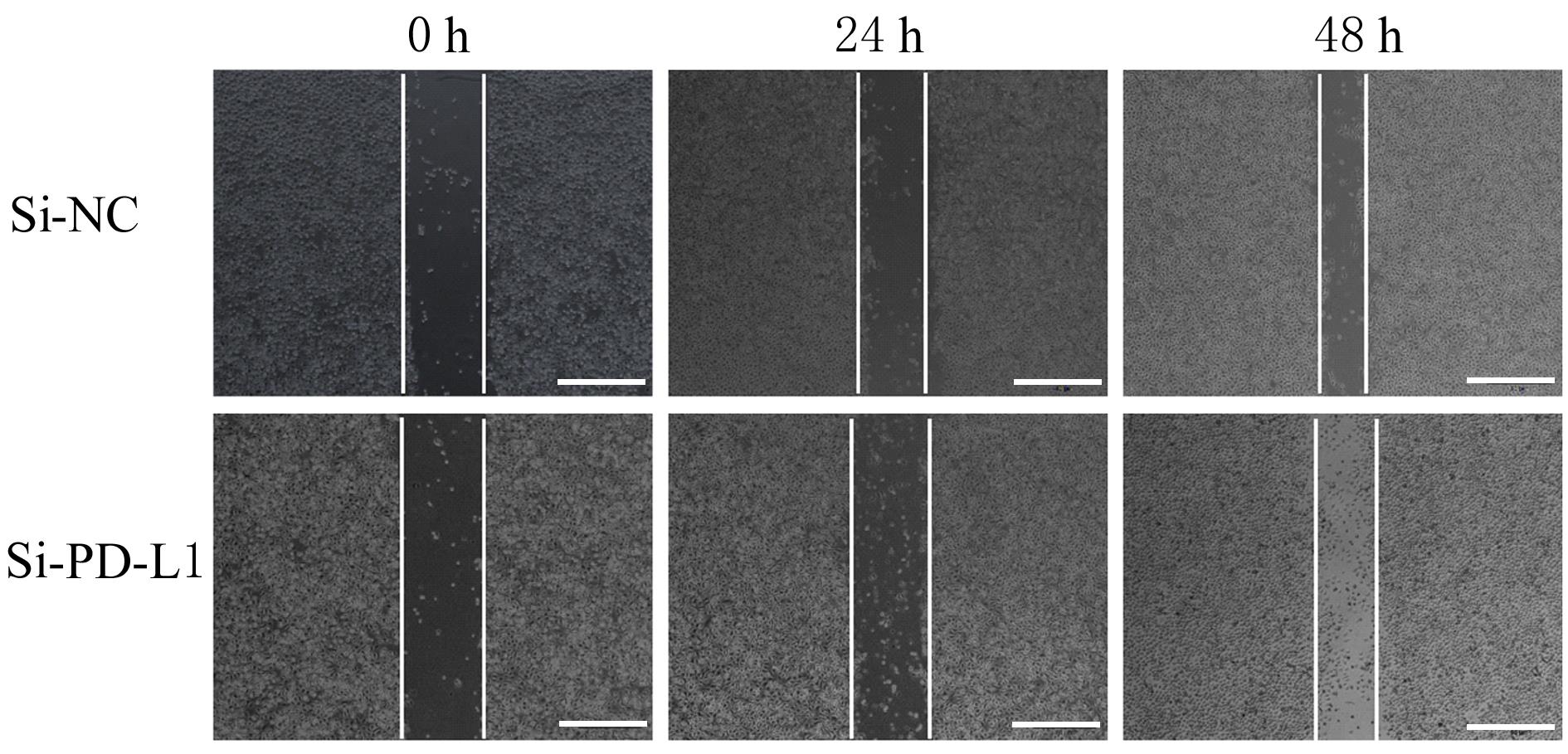
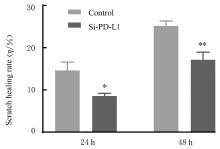
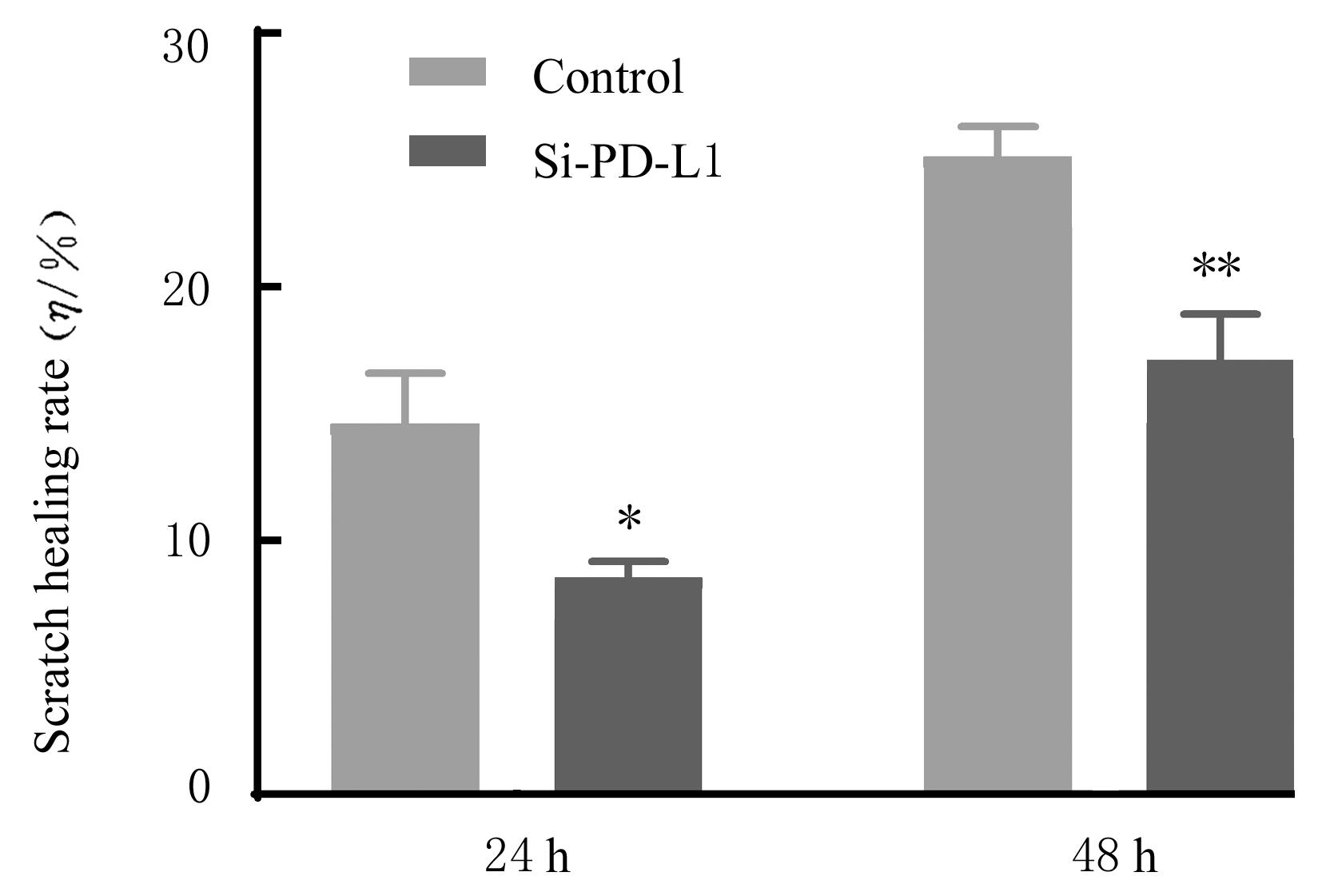
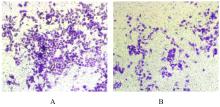
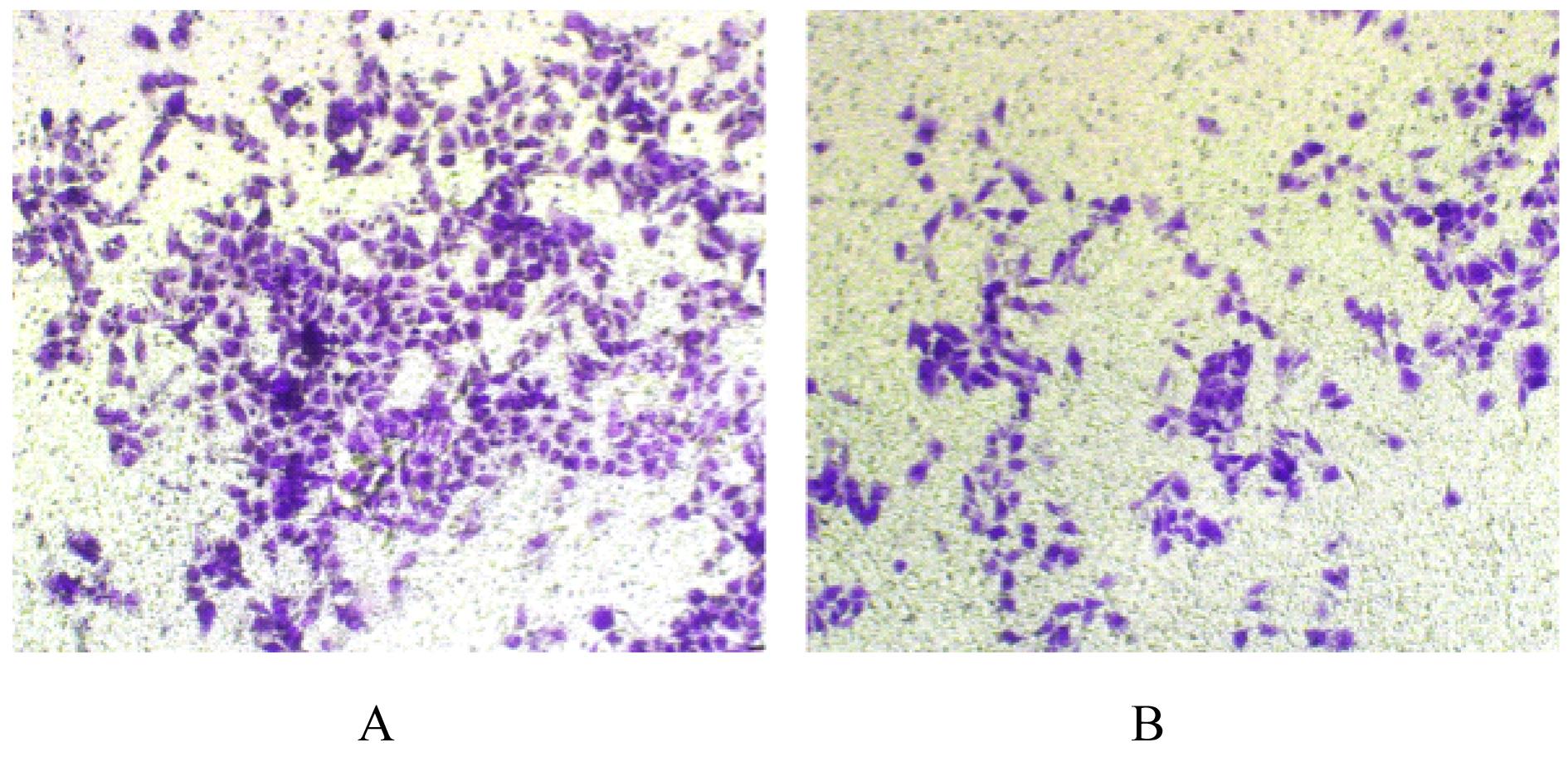
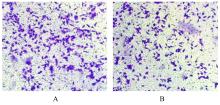
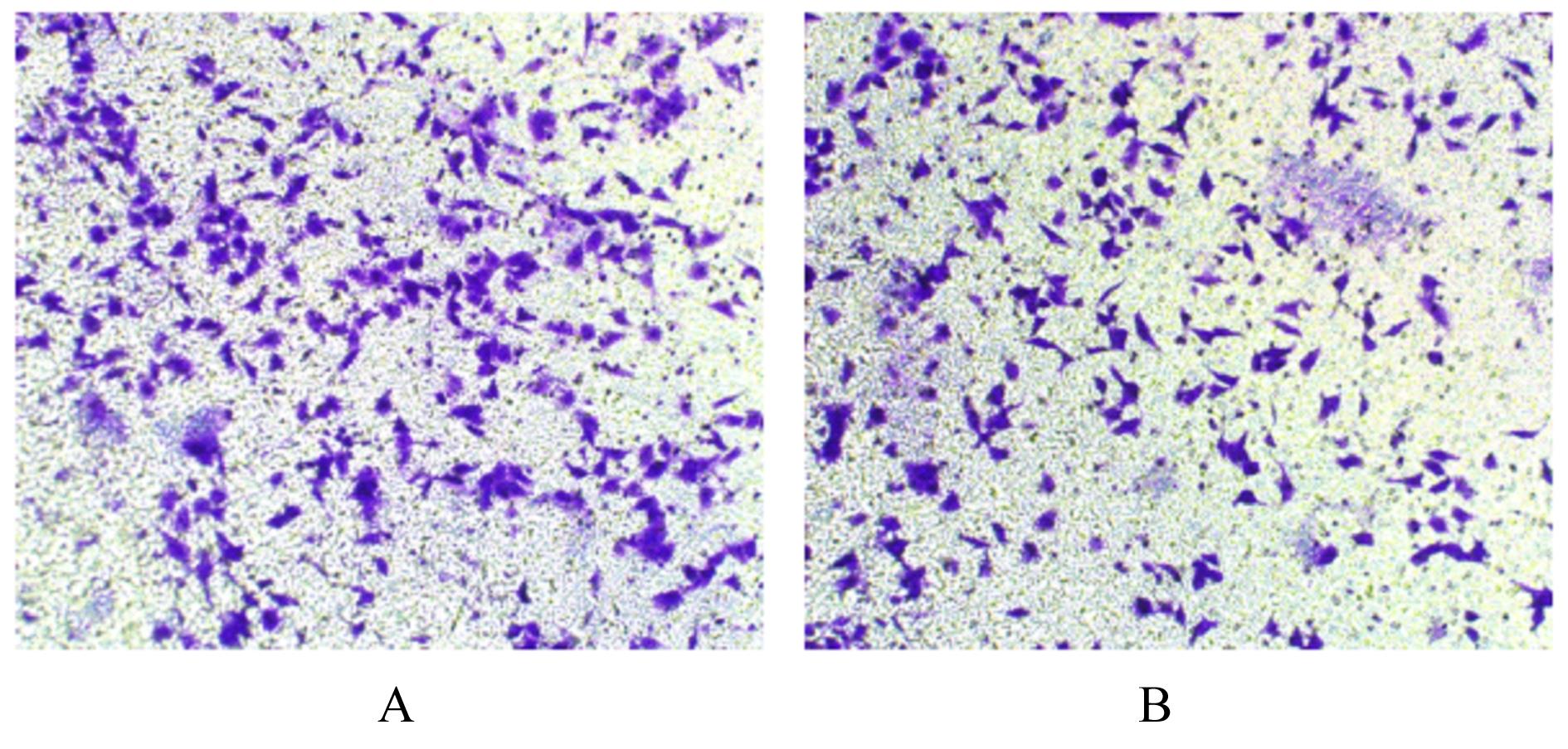
目的 探讨程序性细胞死亡配体1(PD-L1)在口腔鳞状细胞癌(OSCC)细胞中的表达及其对OSCC CAL27细胞生物学行为的影响,阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 采用Western blotting法检测口腔上皮HOK细胞和OSCC CAL27、TCA8113和SCC15细胞中PD-L1蛋白表达水平。免疫荧光染色法检测CAL27细胞中PD-L1蛋白表达和定位情况。将CAL27细胞分为对照组(转染si-NC)和si-PD-L1组(转染si-PD-L1),Western blotting法检测2组细胞干扰效率,CCK-8法检测不同时间点2组细胞增殖活性,平板克隆实验检测2组细胞克隆形成数,细胞划痕愈合实验检测2组细胞划痕愈合率,Transwell小室实验检测2组细胞中迁移和侵袭细胞数。 结果 OSCC细胞中PD-L1蛋白表达水平均高于HOK细胞(P<0.05或P<0.01),PD-L1在CAL27细胞的细胞质和细胞核中均有表达。CCK-8法和平板克隆实验,与对照组比较,不同时间点si-PD-L1组CAL27细胞增殖活性明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),克隆形成数明显减少(P<0.01)。细胞划痕愈合实验,与对照组比较,si-PD-L1组CAL27细胞划痕愈合率明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。Transwell小室实验,与对照组比较,si-PD-L1组CAL27细胞中迁移和侵袭细胞明显减少(P<0.01)。 结论 PD-L1在OSCC细胞中的表达高于口腔正常上皮细胞,敲低PD-L1表达可抑制OSCC细胞增殖、克隆形成及迁移和侵袭能力。
中图分类号:
- R739.8