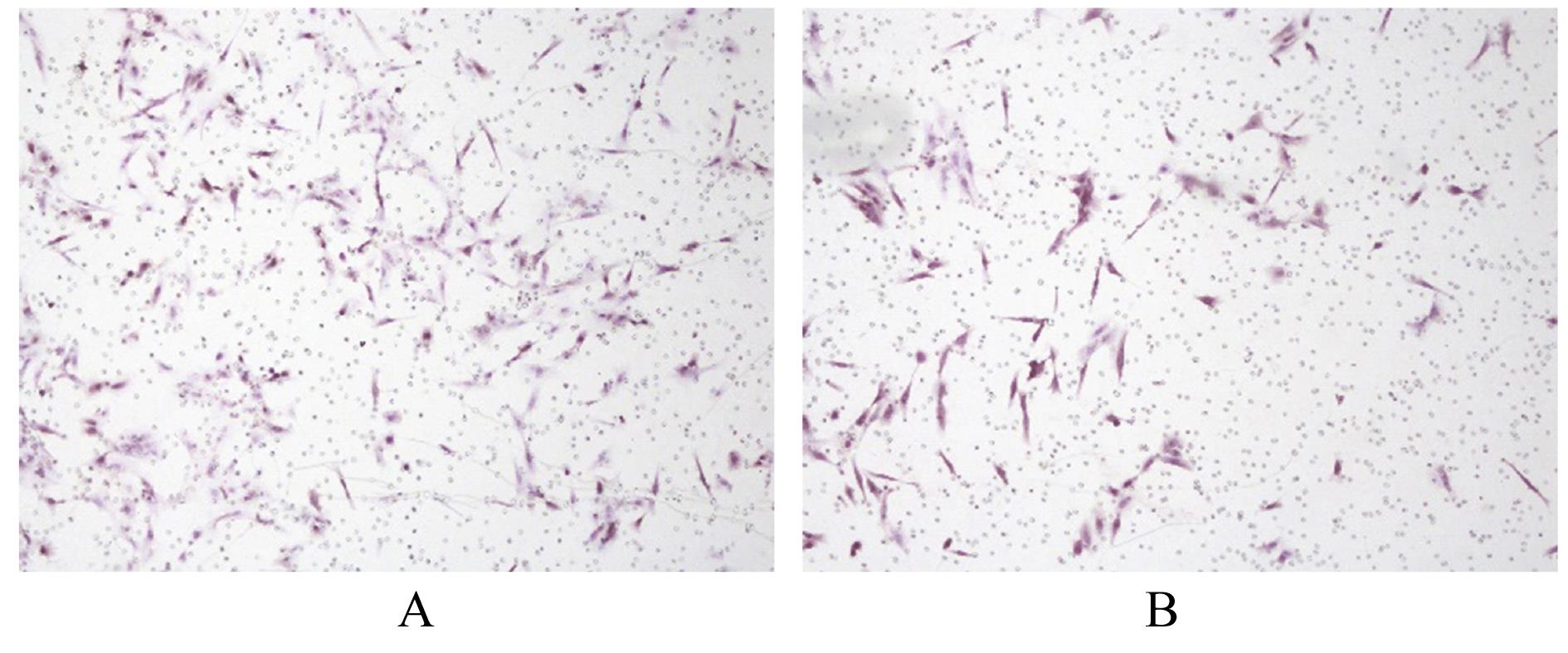
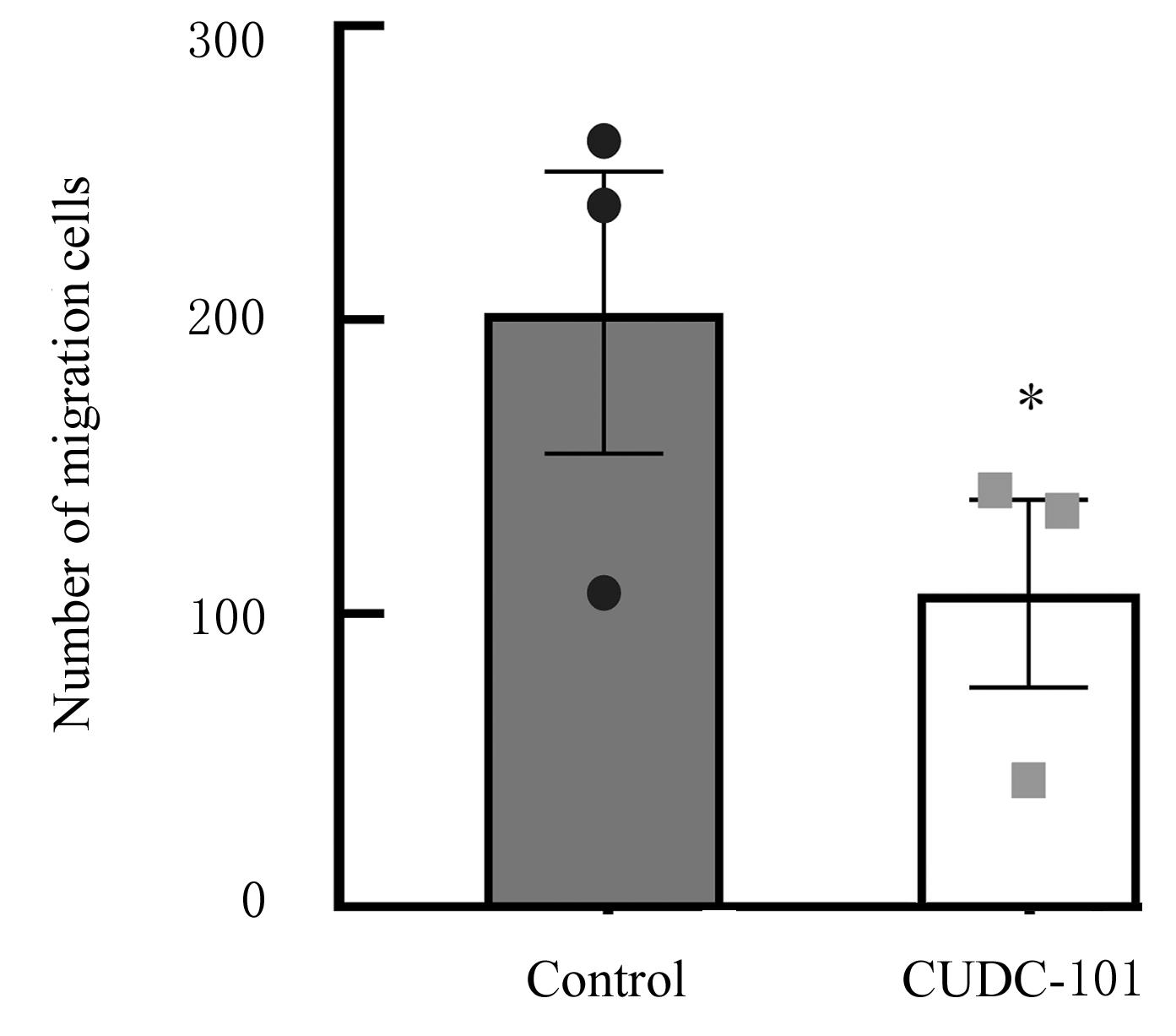
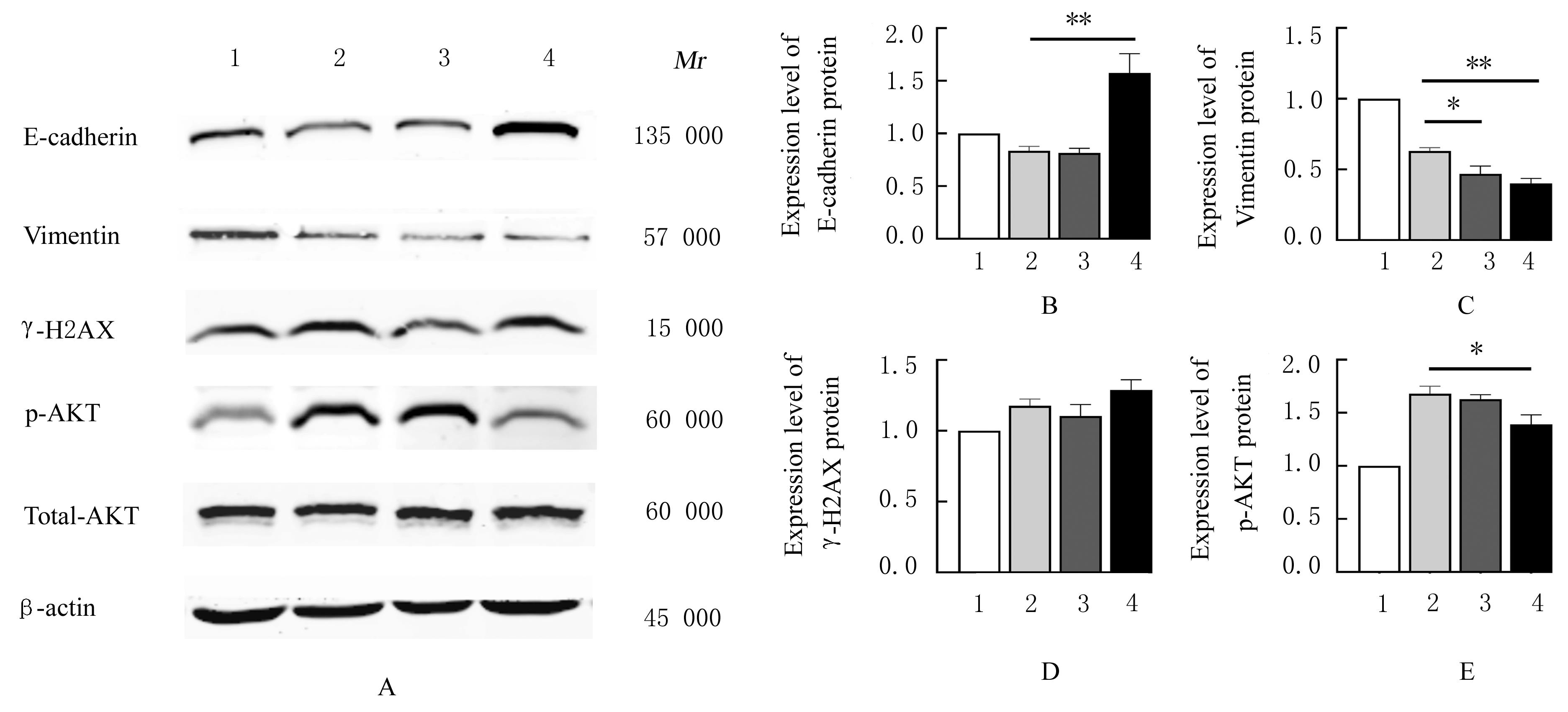
| 1 |
XIA C F, DONG X S, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022,135(5):584-590.
|
| 2 |
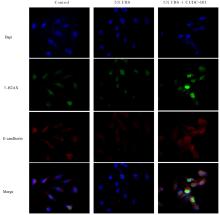
HUANG Y H, HONG W Q, WEI X W. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022,15(1):129.
|
| 3 |
BROWN T C, SANKPAL N V, GILLANDERS W E. Functional implications of the dynamic regulation of EpCAM during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition [J]. Biomolecules, 2021,11(7):956.
|
| 4 |
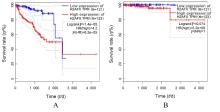
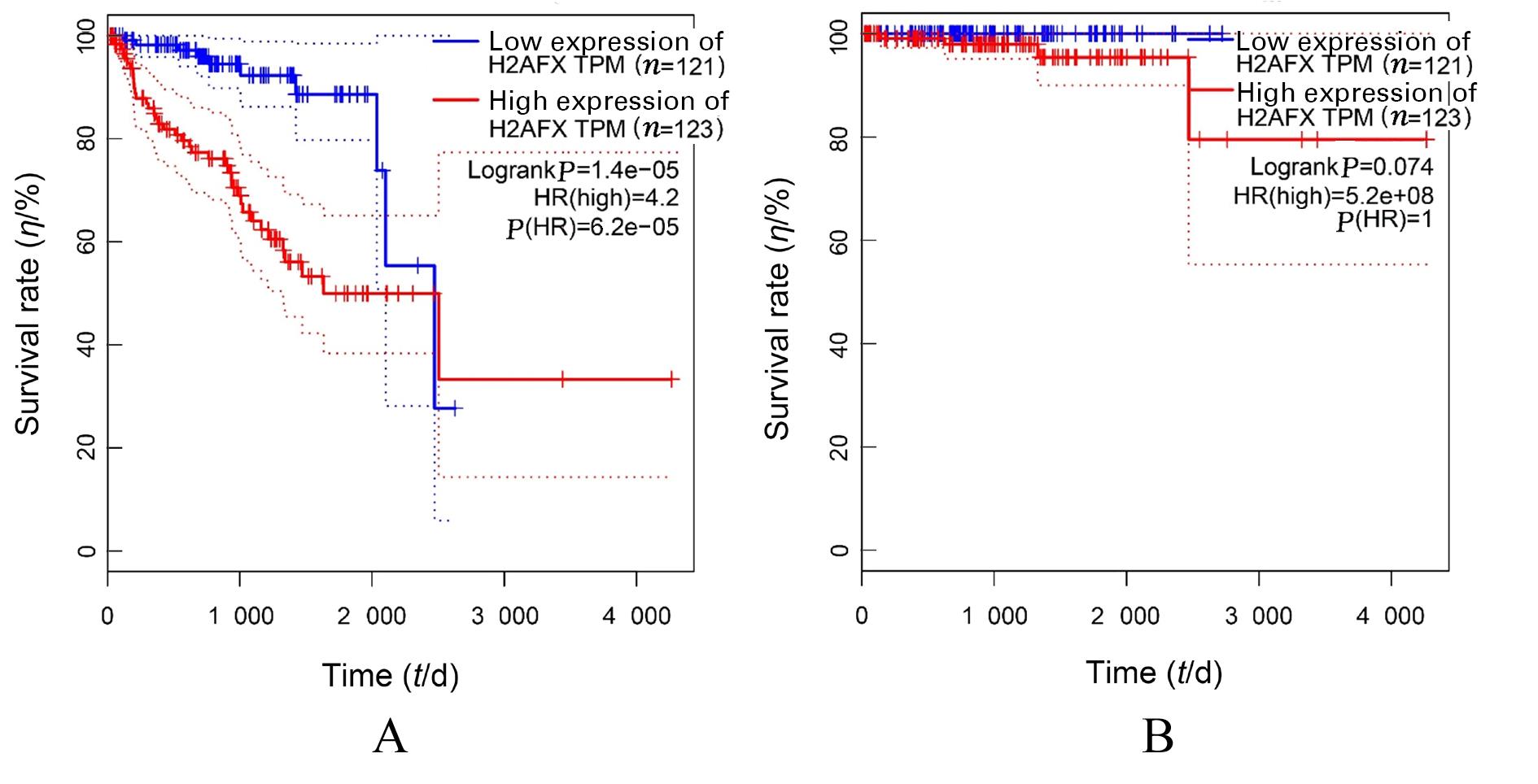
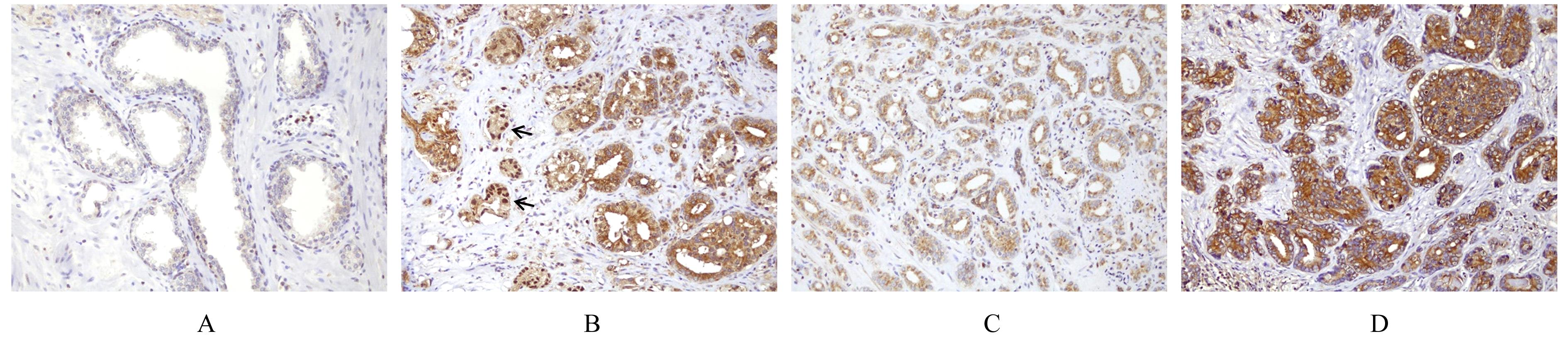
KATSUTA E, SAWANT DESSAI A, EBOS J M,et al.H2AX mRNA expression reflects DNA repair, cell proliferation, metastasis, and worse survival in breast cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2022,12(2):793-804.
|
| 5 |
乔婷婷, 葛淑静, 罗 渊, 等. H2AX磷酸化抑制肺癌细胞发生上皮-间质转化的作用机制[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2021,31(4): 277-284.
|
| 6 |
LAI C J, BAO R D, TAO X U, et al. CUDC-101, a multitargeted inhibitor of histone deacetylase, epidermal growth factor receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, exerts potent anticancer activity[J]. Cancer Res, 2010,70(9):3647-3656.
|
| 7 |
YUAN B, ZHAO X F, WANG X, et al. Patient-derived organoids for personalized gallbladder cancer modelling and drug screening[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2022,12(1):e678.
|
| 8 |
BARROSO S I, AGUILERA A. Detection of DNA double-strand breaks by γ-H2AX Immunodetection[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021,2153:1-8.
|
| 9 |
WIDJAJA L, WERNER R A, KRISCHKE E, et al. Individual radiosensitivity reflected by γ-H2AX and 53BP1 foci predicts outcome in PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2023,50(2):602-612.
|
| 10 |
YAO K, JIANG X Z, HE L Y, et al. Anacardic acid sensitizes prostate cancer cells to radiation therapy by regulating H2AX expression[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015,8(12): 15926-15932.
|
| 11 |
FAN L L, XU S H, ZHANG F B, et al. Histone demethylase JMJD1A promotes expression of DNA repair factors and radio-resistance of prostate cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020,11(4):214.
|
| 12 |
ZHAO W L, LI G H, ZHANG Q B, et al. Cardiac glycoside neriifolin exerts anti-cancer activity in prostate cancer cells by attenuating DNA damage repair through endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2023,209:115453.
|
| 13 |
DALVA-AYDEMIR S, AKYERLI C B, YÜKSEL Ş K,et al. Toward in vitro epigenetic drug design for thyroid cancer: the promise of PF-03814735, an aurora kinase inhibitor[J]. OMICS, 2019,23(10):486-495.
|
| 14 |
JI M Y, LI Z L, LIN Z H, et al. Antitumor activity of the novel HDAC inhibitor CUDC-101 combined with gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2018,8(12): 2402-2418.
|
| 15 |
GENG X Q, MA A, HE J Z, et al. Ganoderic acid hinders renal fibrosis via suppressing the TGF-β/Smad and MAPK signaling pathways[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2020,41(5):670-677.
|
| 16 |
ODERO-MARAH V, HAWSAWI O, HENDERSON V,et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and prostate cancer[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018,1095:101-110.
|
| 17 |
DU H Y, GU J Y, PENG Q, et al. Berberine suppresses EMT in liver and gastric carcinoma cells through combination with TGFβR regulating TGF-β/smad pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021,2021:2337818.
|
| 18 |
WANG Y, GUO Y B, HU Y M, et al. Endosulfan triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PTP4A3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2020,731:139234.
|
| 19 |
RATNAYAKE W S, APOSTOLATOS C A, BREEDY S, et al. Atypical PKCs activate vimentin to facilitate prostate cancer cell motility and invasion[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2021,15(1):37-57.
|
| 20 |
QUAN Y J, ZHANG X D, BUTLER W, et al. The role of N-cadherin/c-Jun/NDRG1 axis in the progression of prostate cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021,17(13):3288-3304.
|
| 21 |
MALM S W, AMOUZOUGAN E A, KLIMECKI W T.Fetal bovine serum induces sustained, but reversible, epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the BEAS-2B cell line[J]. Toxicol In Vitro, 2018,50:383-390.
|
| 22 |
TIAN H B, XU J Y, TIAN Y, et al. A cell culture condition that induces the mesenchymal-epithelial transition of dedifferentiated porcine retinal pigment epithelial cells[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2018,177:160-172.
|
| 23 |
田园芳, 陈 伟. 外显子跳跃模式中组蛋白修饰的组合模式分析[J].电子科技大学学报,2022,51(5):668-674.
|
 ),李珍玲1(
),李珍玲1( )
)
 ),Zhenling LI1(
),Zhenling LI1( )
)