吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 647-657.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240308
D-柠檬烯对胶质母细胞瘤细胞增殖的抑制作用及其机制
- 1.大理大学药学院,云南 大理 671000
2.广州医科大学附属清远医院 广东省清远市人民医院,广东 清远 511500
Inhibitory effect of D-limonene on proliferation of glioblastoma cells and its mechanism
Tengfei WANG1,2,Feng CHEN1,2,Ling QI2,Ting LEI1( ),Meihui SONG2(
),Meihui SONG2( )
)
- 1.School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Dali University,Dali 671000,China
2.Institute of Digestive Disease,People’s Hospital,Qingyuan City,Guangdong Province,Qingyuan 511500,China
摘要:
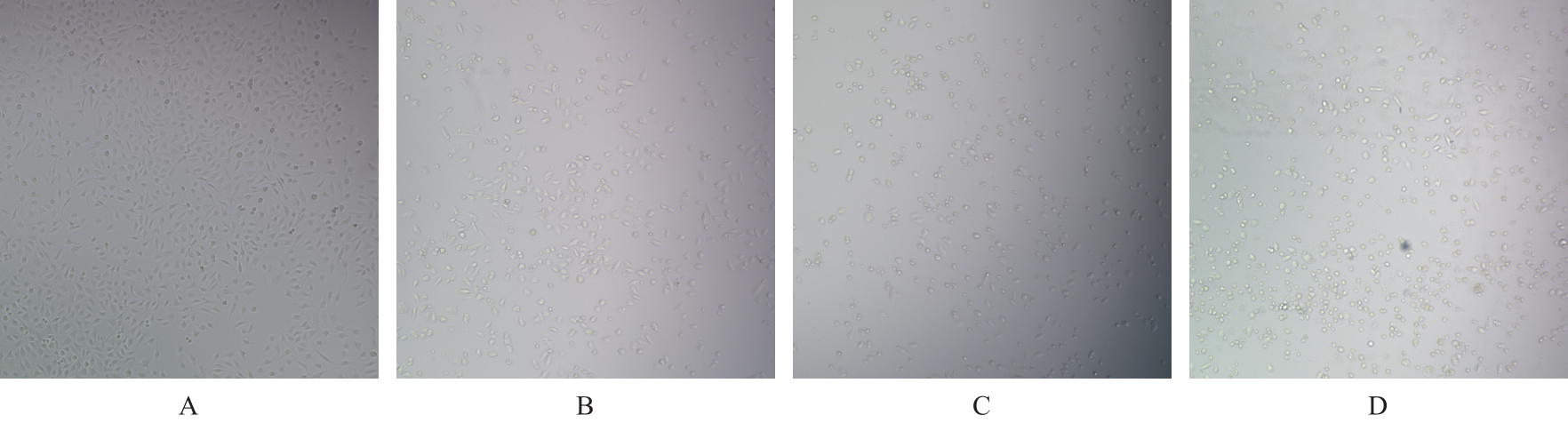
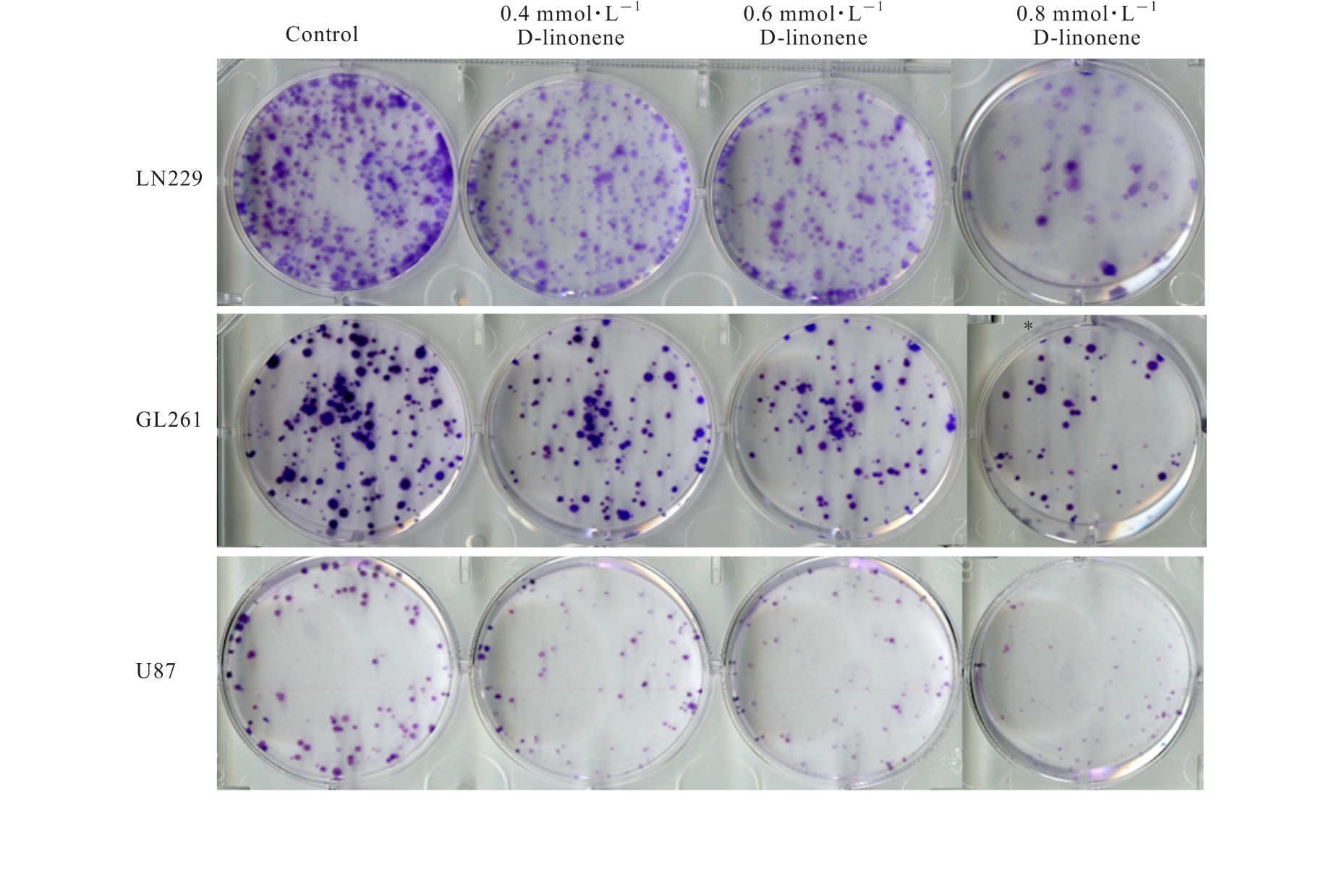
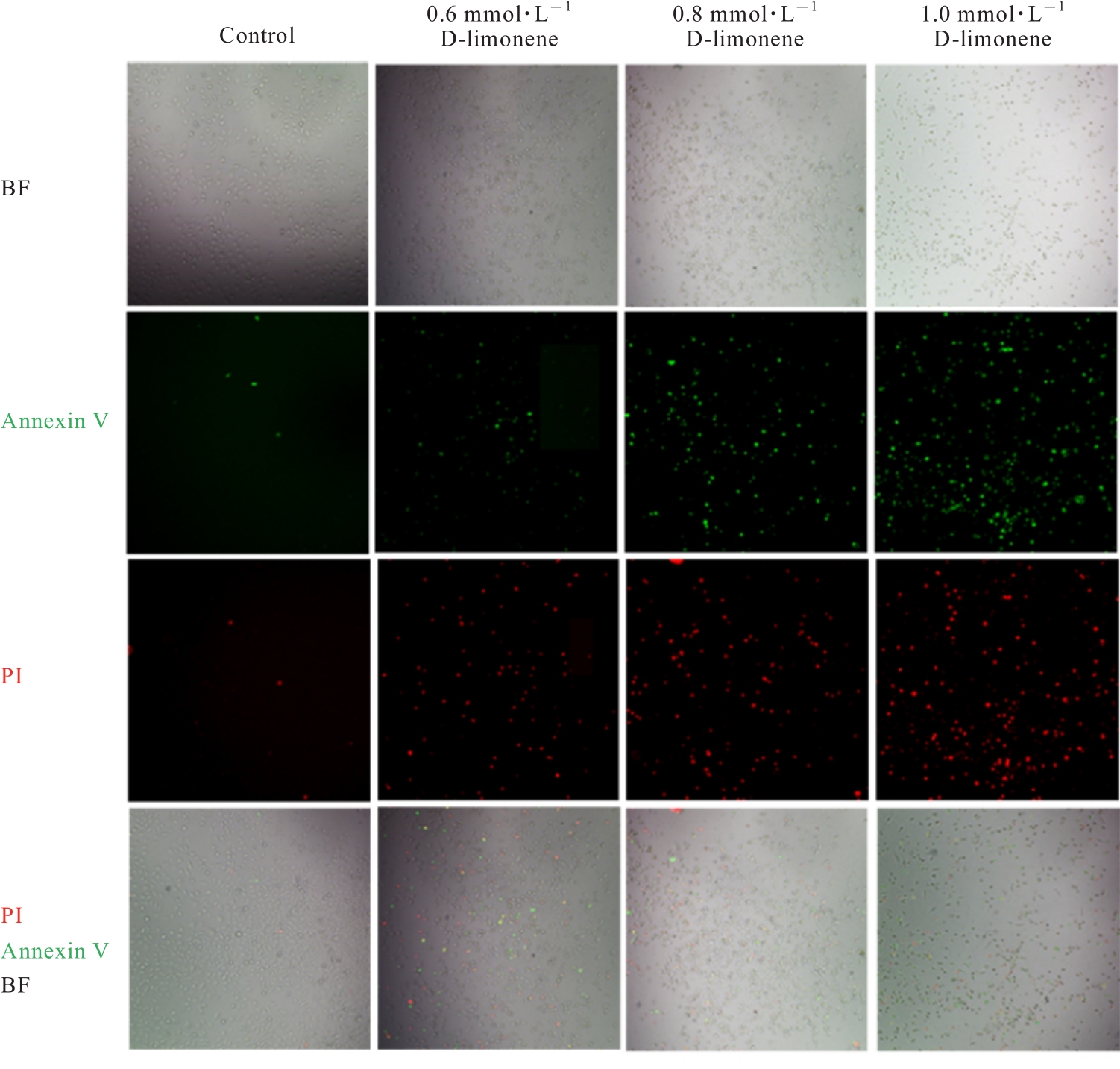
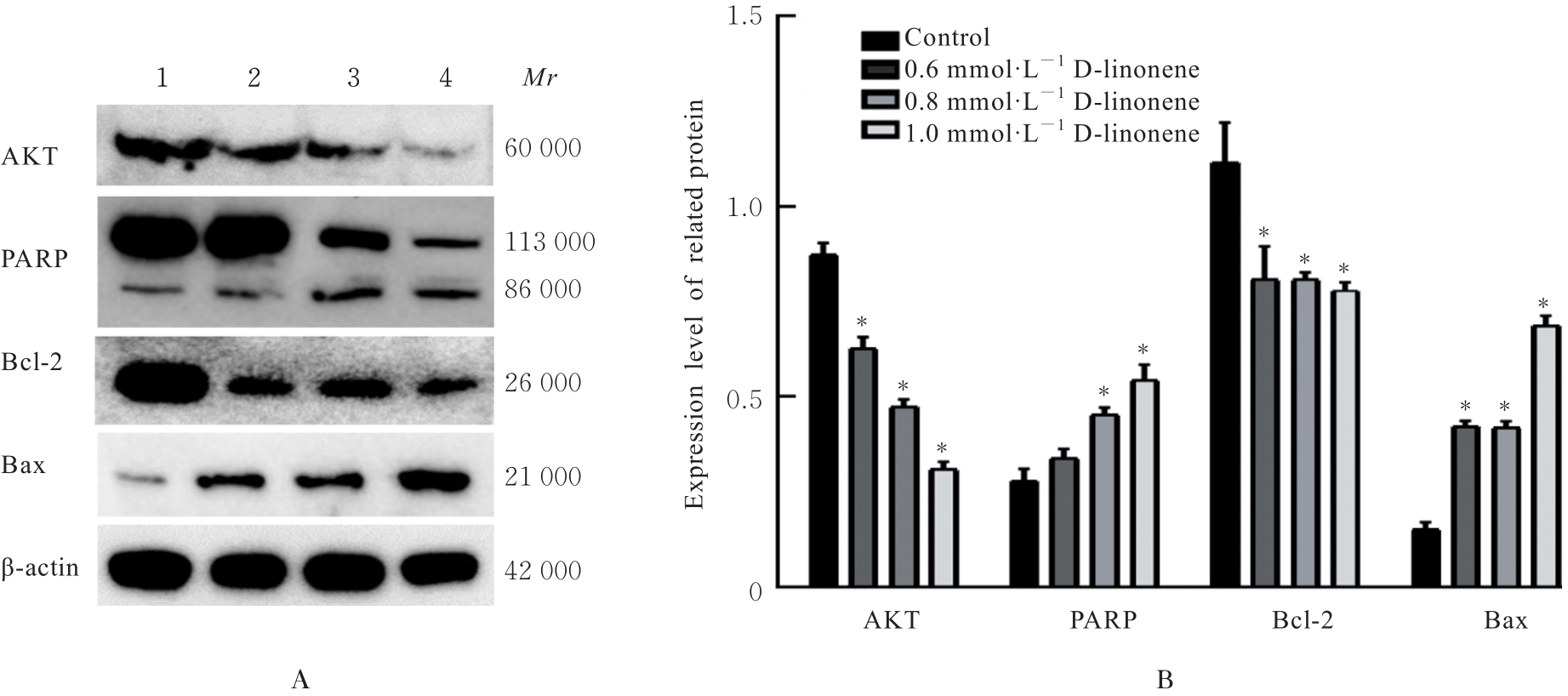
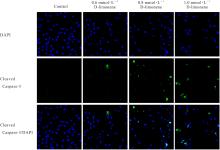
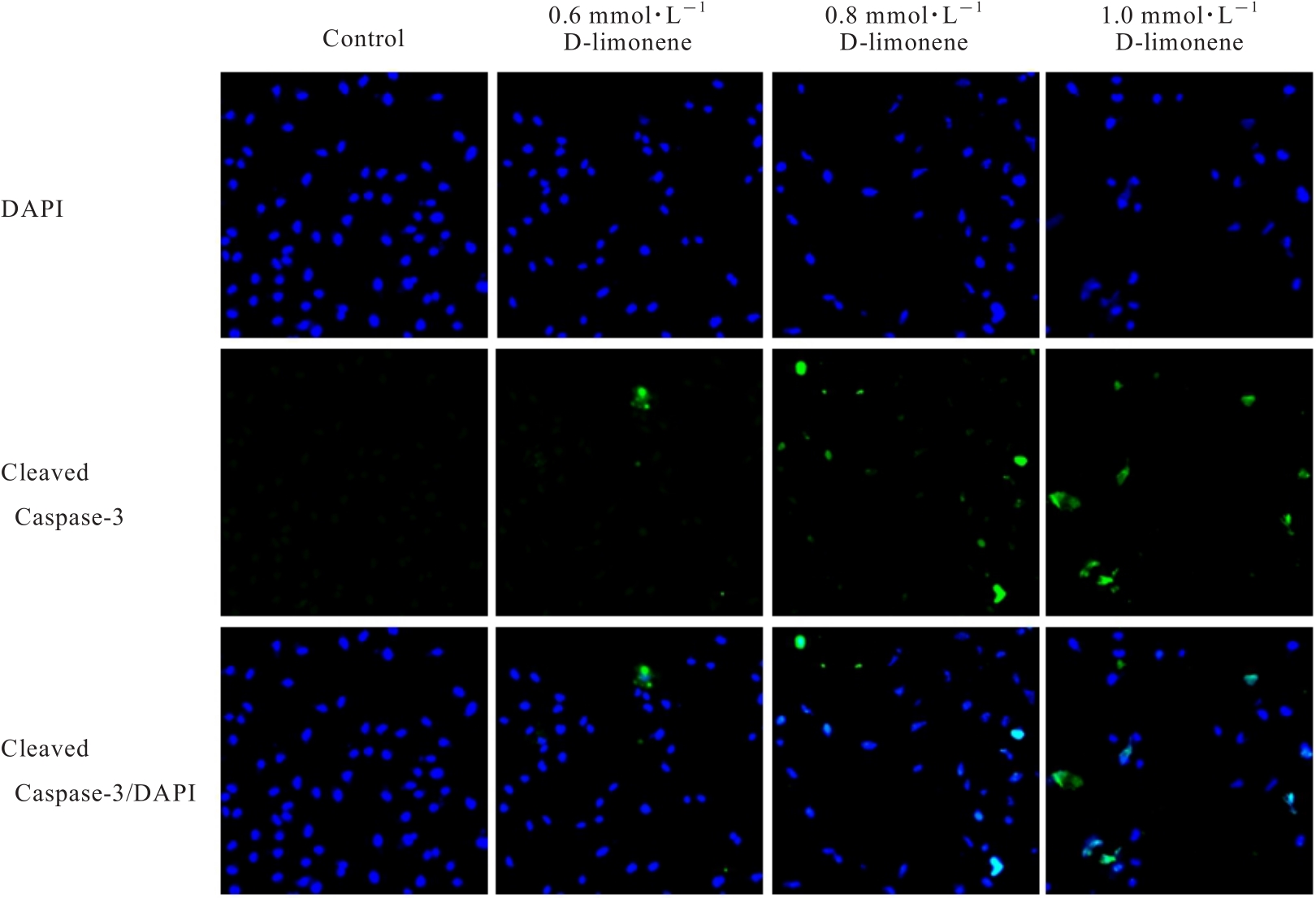
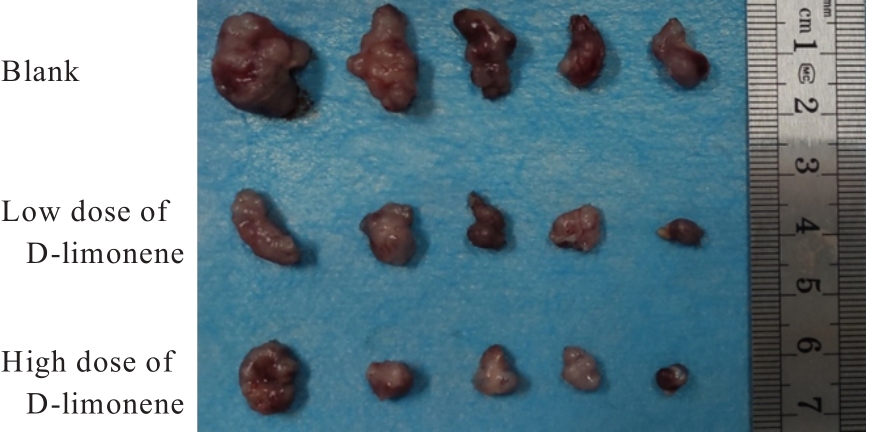
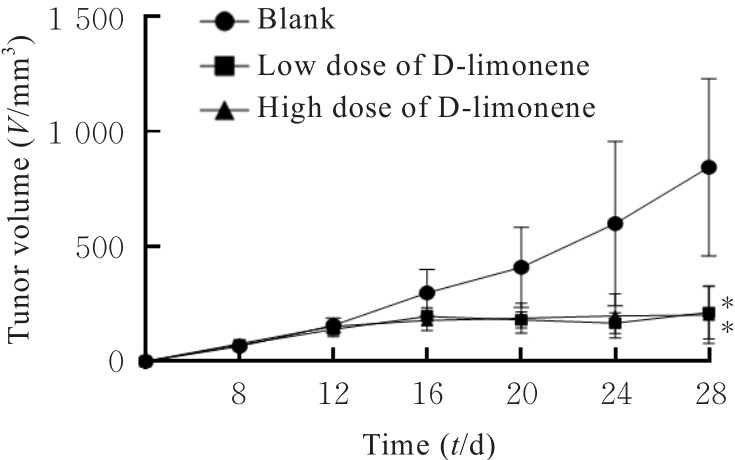
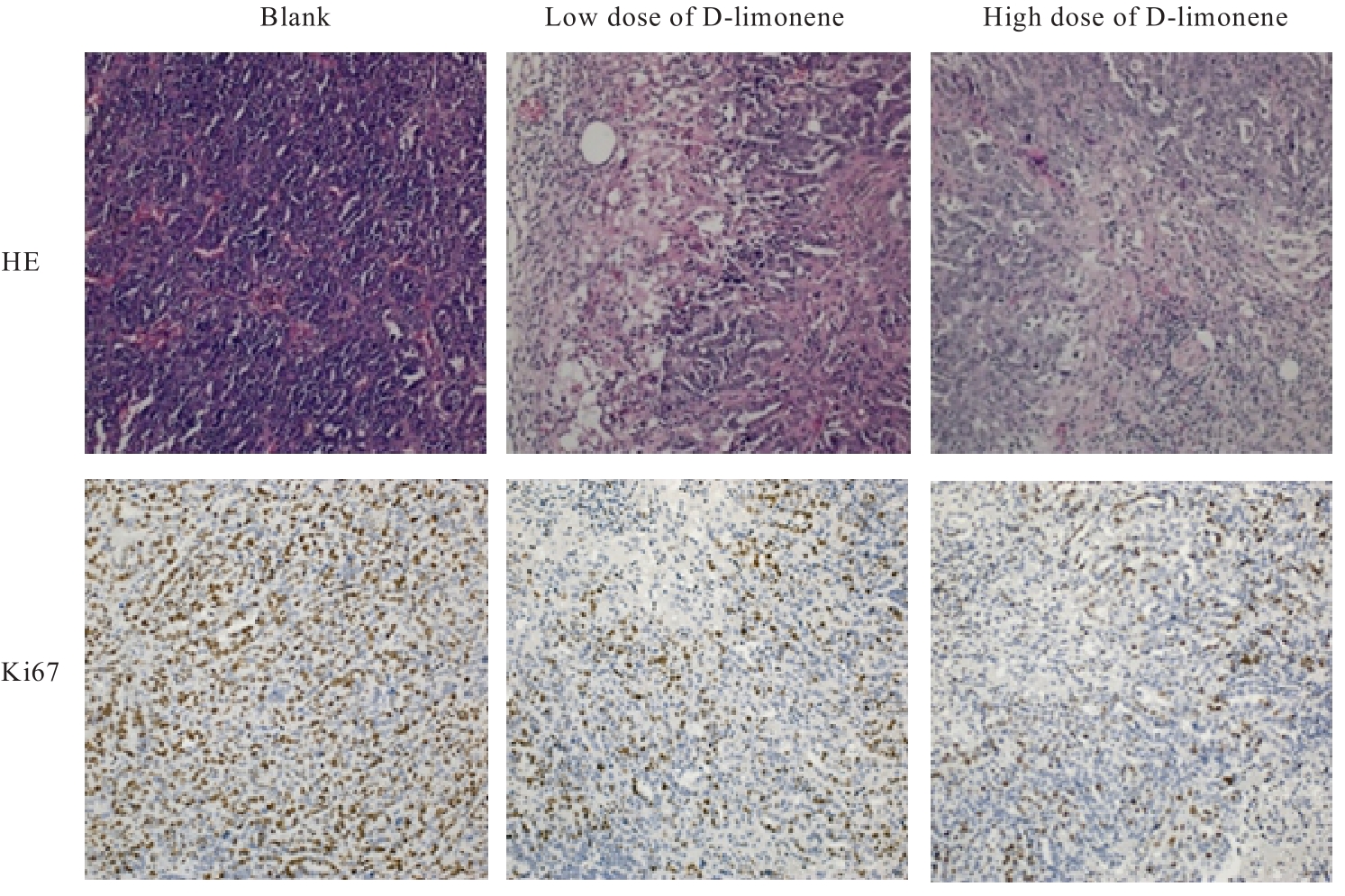
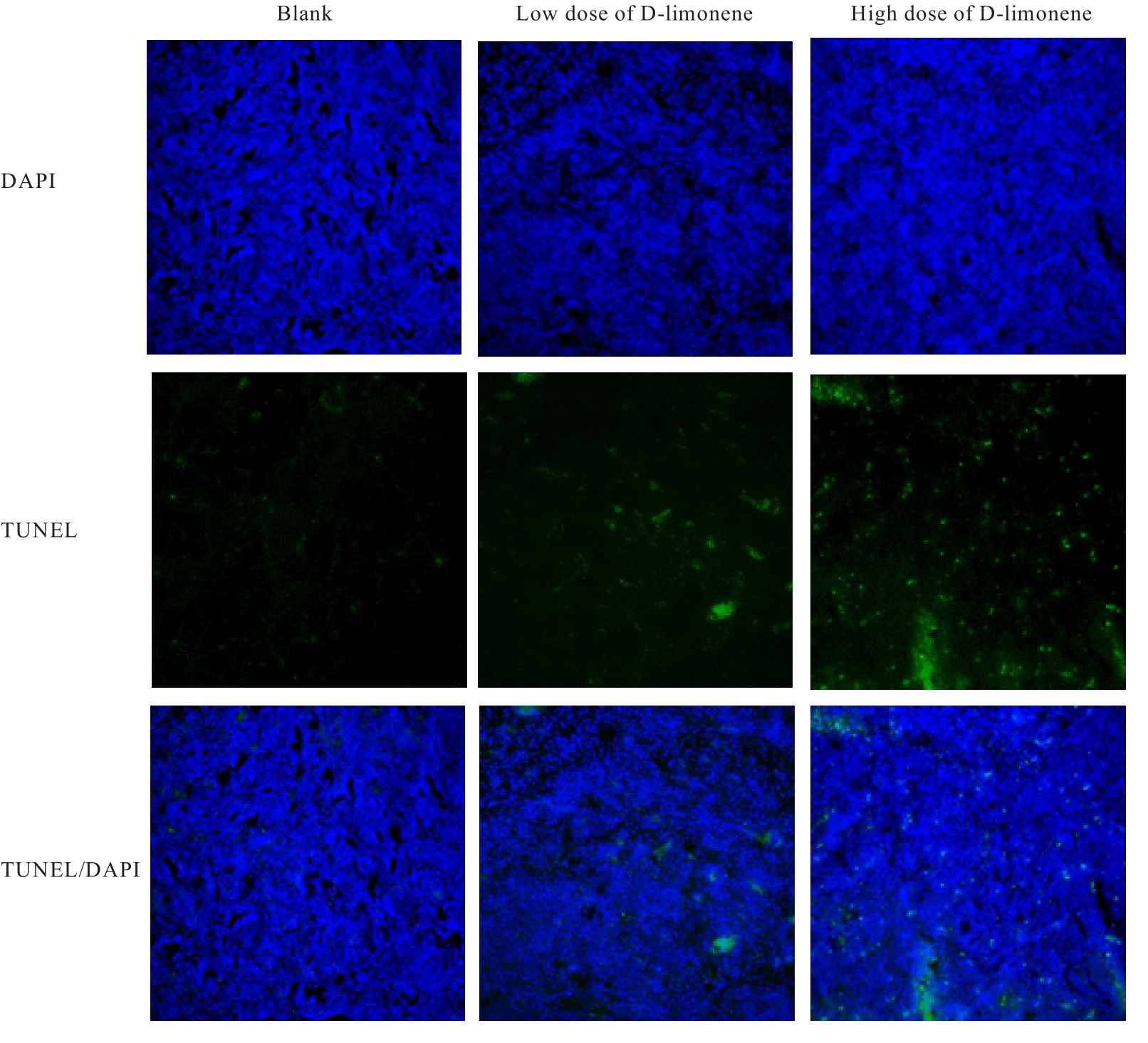
目的 探讨D-柠檬烯对胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)细胞增殖和凋亡的影响,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 将GBM细胞分为对照组(0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯)和0.2、 0.4、 0.6、 0.8及1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组。采用CCK-8法检测各组细胞增殖抑制率,克隆形成法检测各组细胞克隆形成率,Annexin Ⅴ-FITC/PI法检测各组细胞凋亡率,Western blotting法检测各组细胞中蛋白激酶B(AKT)、B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)、Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)和多聚二磷酸腺苷(ADP)核糖聚合酶(PARP)蛋白表达水平,免疫荧光法检测各组细胞中裂解的半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶(cleaved Caspase)-3 蛋白表达水平。15 只建立皮下移植瘤模型小鼠随机分为空白组(0 mg·kg-1·d-1 D-柠檬烯)、低剂量D-柠檬烯组(200 mg·kg-1·d-1 D-柠檬烯)和高剂量D-柠檬烯组(400 mg·kg-1·d-1 D-柠檬烯),每组5只。计算各组小鼠体内肿瘤抑制率,HE染色和免疫组织化学染色观察各组小鼠皮下肿瘤组织形态表现,并绘制肿瘤生长曲线,免疫组织化学法检测各组小鼠皮下瘤组织中Ki67蛋白阳性表达率,TUNEL染色法检测各组小鼠肿瘤细胞凋亡情况。 结果 对照组细胞呈长梭形,状态良好,紧密且贴壁生长,细胞器和细胞质正常;给药48 h后,0.6 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组细胞体积减小,细胞膜虽完整但通透性增强,细胞质皱缩,细胞内部产生空泡结构,部分呈碎片状漂浮在溶液表面;0.8 和1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组细胞中有明显凋亡小体生成,呈现凋亡状态。CCK-8法,与对照组比较,0.6、0.8和1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组U87、LN229及GL261细胞增殖抑制率均明显升高(P<0.01),0.4 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组U87和GL261细胞增殖抑制率均明显升高(P<0.01)。克隆形成法,与对照组比较,0.4、0.6和0.8 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组U87、LN229及GL261细胞克隆形成率均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。Annexin Ⅴ-FITC/PI法,与对照组比较,D-柠檬烯处理48 h后,0.6、0.8和1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组LN229细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.01)。Western blotting法,与对照组比较,0.6、0.8和1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组LN229细胞中Bax蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01),AKT和Bcl-2蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01);0.8和1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组LN229细胞中PARP蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。免疫荧光法,与对照组比较,0.6、0.8和1.0 mmol·L-1 D-柠檬烯组LN229细胞中cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。与空白组比较,低和高剂量D-柠檬烯组小鼠肿瘤体积均明显减小(P<0.01)。与空白组比较,低和高剂量D-柠檬烯组小鼠肿瘤质量均明显降低(P<0.05),肿瘤抑制率均明显升高(P<0.05)。空白组小鼠肿瘤细胞弥漫分布,细胞核染色加深,核浆比增大;低和高剂量D-柠檬烯组小鼠肿瘤组织出现大量肿瘤细胞变性坏死。与空白组比较,低和高剂量D-柠檬烯组小鼠肿瘤组织中Ki67蛋白阳性表达率均明显降低(P<0.01)。与空白组比较,低和高剂量D-柠檬烯组小鼠肿瘤细胞凋亡率均明显升高(P<0.01)。 结论 D-柠檬烯具有抑制GBM细胞增殖的作用,其作用机制可能与调控AKT蛋白的表达并激活Caspase-3通路诱导凋亡有关。
中图分类号:
- R739.4