吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 989-999.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240413
Myod1通过调节lncRNA SNHG15和miR-24-3p对氧糖剥夺SH-SY5Y细胞增殖及凋亡的影响
- 齐齐哈尔医学院附属第三医院神经内科,黑龙江 齐齐哈尔 161000
Effect of Myod1 on proliferation and apoptosis of oxygen-glucose-deprived SHSY5Y cells by regulating lncRNA SNHG15 and miR-24-3p
Fangchao JI,Chenxin ZHANG,Zhanjun REN,Yunzhi PAN,Qi LU,Xingyuan SUN( )
)
- Department of Neurology,Third Affiliated Hospital,Qiqihar Medical University,Qiqihar 161000,China
摘要:
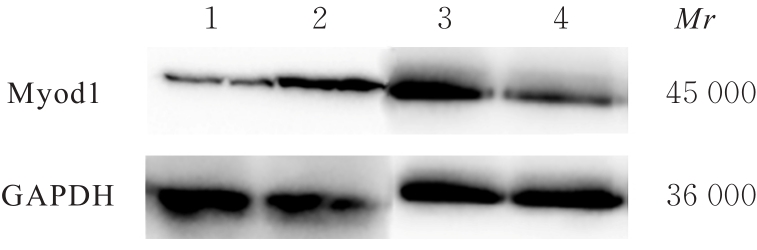
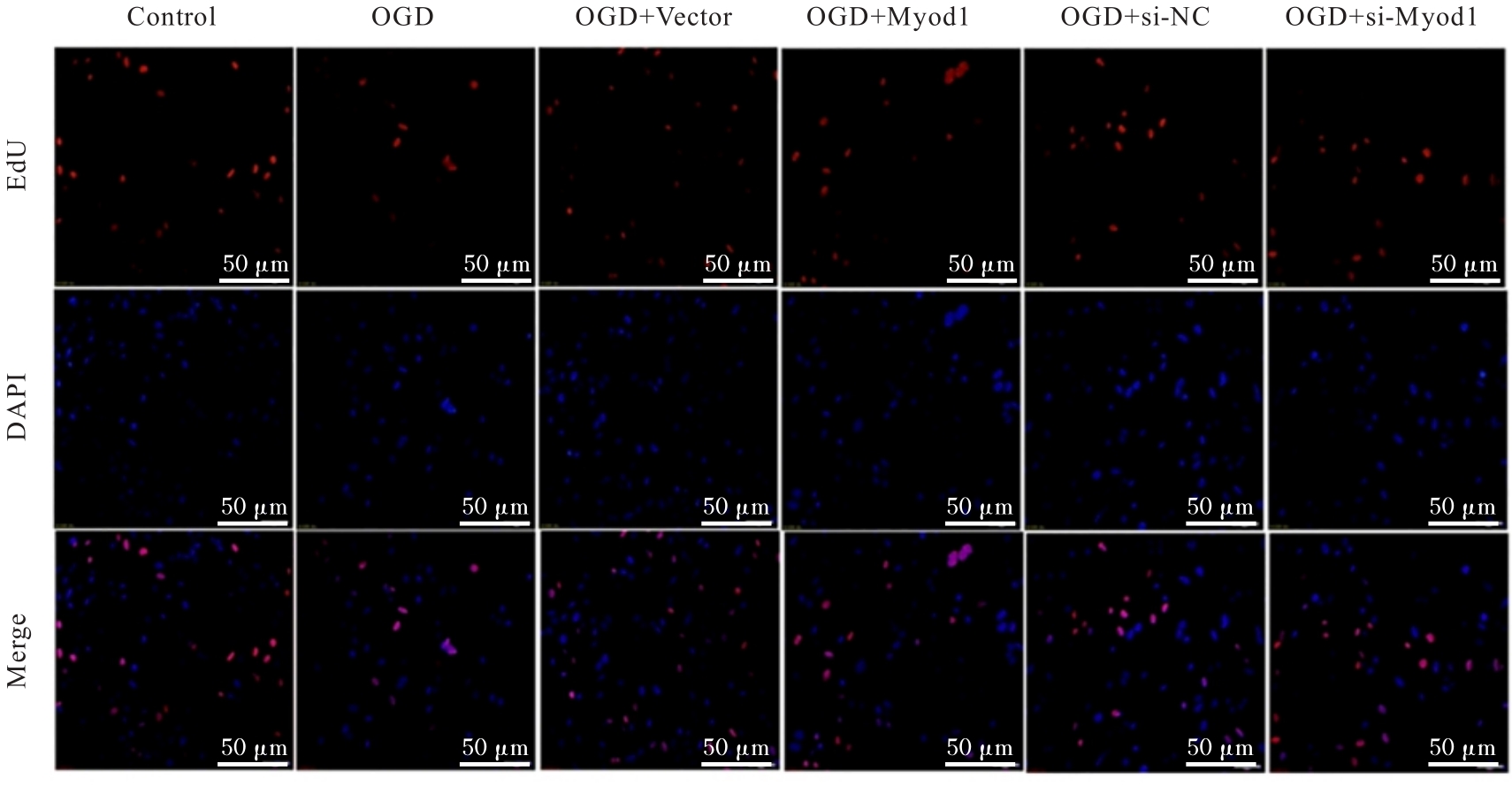
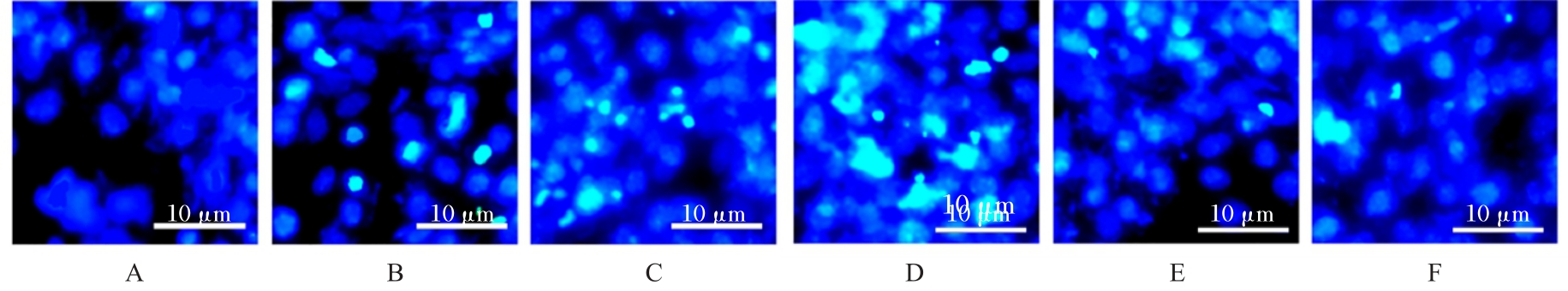
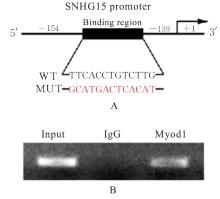
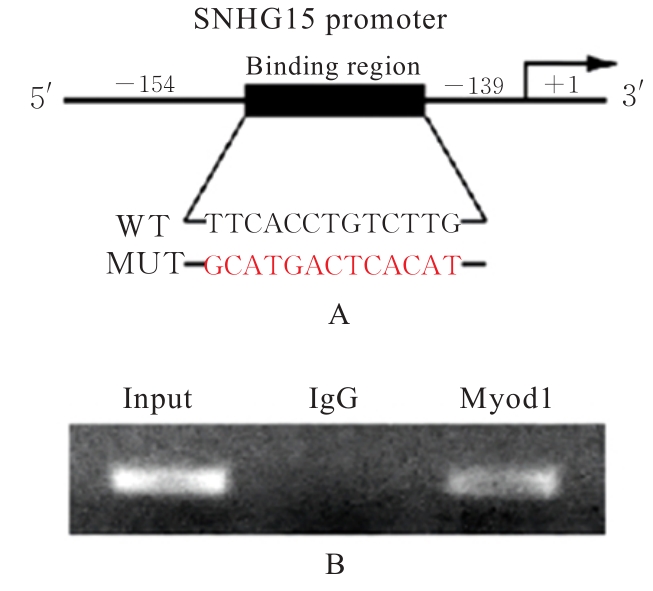
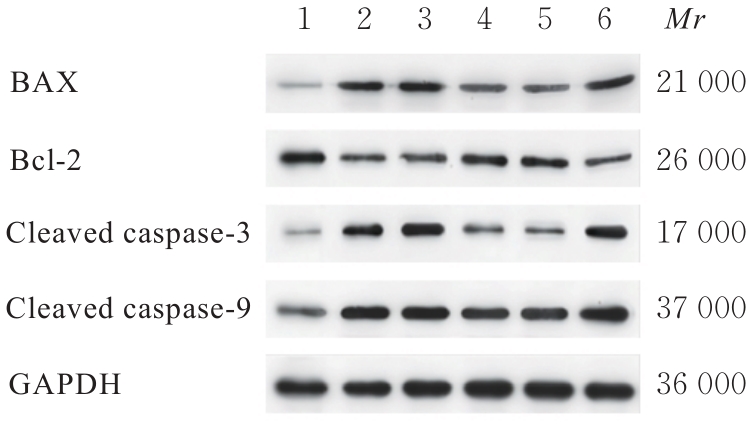
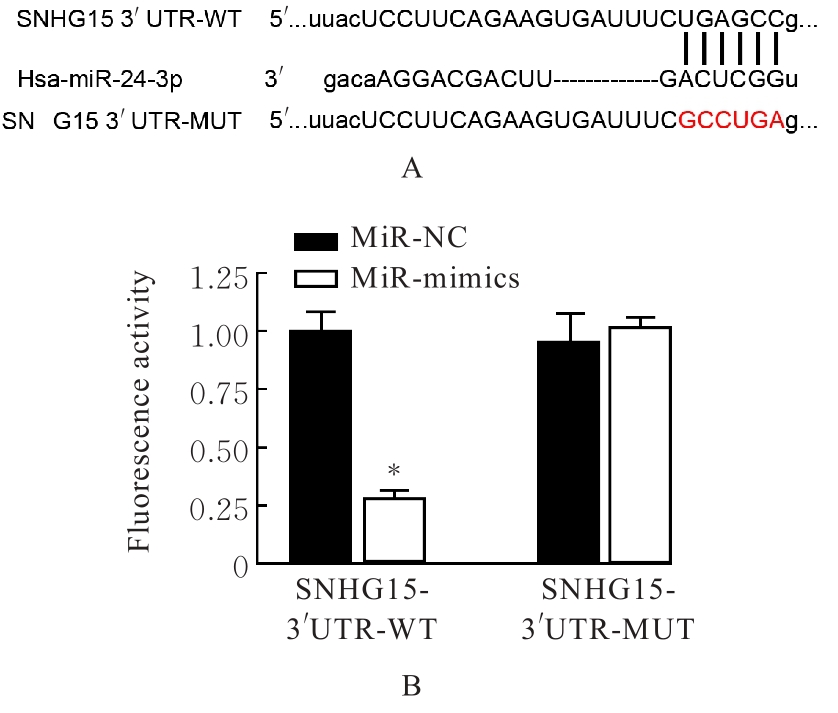
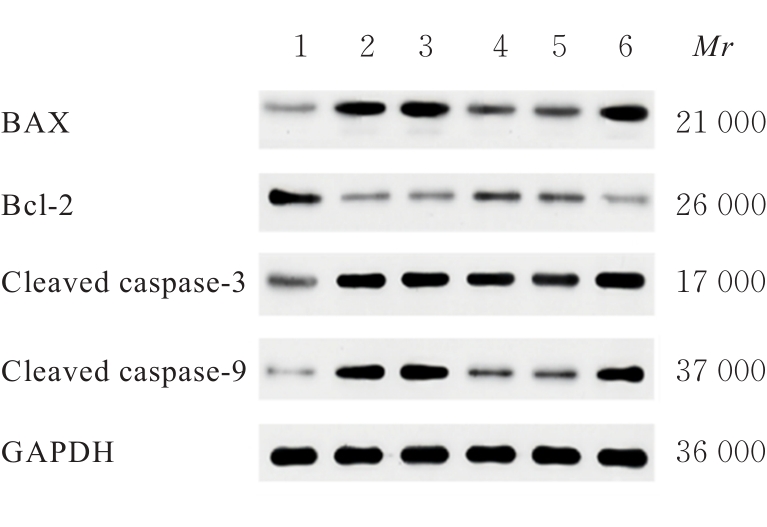
目的 探讨肌源性分化蛋白1(Myod1)对氧糖剥夺(OGD)诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞增殖抑制和凋亡的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测正常对照组研究对象和缺血性脑梗死组患者外周血及正常培养的SH-SY5Y细胞(对照组)和OGD细胞模型(OGD组)细胞中Myod1和长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)小核仁RNA宿主基因15(SNHG15)mRNA表达水平。分别采用si-Myod1、pcDNA3.0-Myod1、si-SNHG15、pcDNA3.0-SNHG15、si-NC、空载质粒(Vector)、miR-NC和miR-24-3p模拟物(miR-mimics)质粒转染SH-SY5Y细胞后,进行OGD处理,将SH-SY5Y细胞分为对照组、OGD组、OGD+Vector组、OGD+Myod1组、OGD+si-NC组、OGD+si-Myod1组、OGD+si-SNHG15组、OGD+si-SNHG15+Vector组、OGD+si-SNHG15+Myod1组、OGD+miR-NC组、OGD+miR-mimics组、OGD+miR-mimics+Vector组和OGD+miR-mimics+SNHG15组。采用CCK-8法检测各组细胞活性,采用5-乙炔基-2'-脱氧尿苷(EdU)染色法检测各组EdU阳性细胞率,采用原位末端转移酶标记(TUNEL)法检测各组TUNEL阳性细胞率,采用Western blotting法检测各组细胞中裂解的含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶3(cleaved caspase-3)、裂解的含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶9(cleaved caspase-9)、B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)蛋白表达水平。染色质免疫共沉淀(CHIP)法评估Myod1和SNHG15之间的关联。双荧光素酶报告基因实验评估Myod1与SNHG15及SNHG15与miR-24-3p的靶向关系。 结果 与正常对照组比较,缺血性脑梗死组患者外周血中Myod1和SNHG15 mRNA表达水平均升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,OGD组细胞中Myod1和SNHG15 mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。与OGD组比较,48和72 h时OGD+Myod1组细胞活性和EdU阳性细胞率均降低(P<0.01),TUNEL阳性细胞率升高(P<0.01);OGD+si-Myod1组细胞活性和EdU阳性细胞率均升高(P<0.01),TUNEL阳性细胞率降低(P<0.01)。Myod1可与SNHG15的启动子序列结合。SNHG15可吸附miR-24-3p,Myod1与SNHG15及SNHG15与miR-24-3p存在靶关系。敲低SNHG15后,与OGD组比较,48和72 h时OGD+si-SNHG15组细胞活性和EdU阳性细胞率均升高(P<0.01),TUNEL阳性细胞率降低(P<0.01),细胞中Bax、cleaved caspase-3和cleaved caspase-9蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01);与OGD+si-SNHG15组比较,48和72 h时OGD+si-SNHG15+Myod1组细胞活性和EdU阳性细胞率降低(P<0.05),TUNEL阳性细胞率升高(P<0.05),细胞中Bax、cleaved caspase-3和cleaved caspase-9蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。过表达miR-24-3p和SNHG15后,与OGD组比较,48和72 h时OGD+miR-mimics组细胞活性和EdU阳性细胞率升高(P<0.01),TUNEL阳性细胞率降低(P<0.01),细胞中Bax、cleaved caspase-3和cleaved caspase-9蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01);与OGD+miR-mimics组比较,48和72 h时OGD+miR-mimics+SNHG15组细胞活性和EdU阳性细胞率降低(P<0.05),TUNEL阳性细胞率升高(P<0.05),细胞中Bax、cleaved caspase-3 和 cleaved caspase-9 蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 Myod1可通过与SNHG15启动子区结合进而吸附miRNA-24,促进OGD诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞的增殖抑制和细胞凋亡。
中图分类号:
- R743