吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1211-1220.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250507
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
血必净注射液对抗NMDAR脑炎小鼠血脑屏障损伤的改善作用及其对Th17/Treg失衡的调控作用
曾超胜( ),陈琳,闫丽敏,邢槐杰,李莉,黄少珠,陈敏,常勇,匡冰,黎晓艳
),陈琳,闫丽敏,邢槐杰,李莉,黄少珠,陈敏,常勇,匡冰,黎晓艳
- 海南医科大学第二附属医院神经内科,海南 海口 570311
Improvement effect of Xuebijing injection on blood-brain barrier damage in mice with anti-NMDAR encephalitis and its regulatory effect on Th17/Treg imbalance
Chaosheng ZENG( ),Lin CHEN,Limin YAN,Huaijie XING,Li LI,Shaozhu HUANG,Min CHEN,Yong CHANG,Bing KUANG,Xiaoyan LI
),Lin CHEN,Limin YAN,Huaijie XING,Li LI,Shaozhu HUANG,Min CHEN,Yong CHANG,Bing KUANG,Xiaoyan LI
- Department of Neurology,Second Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical University,Haikou 570311,China
摘要:
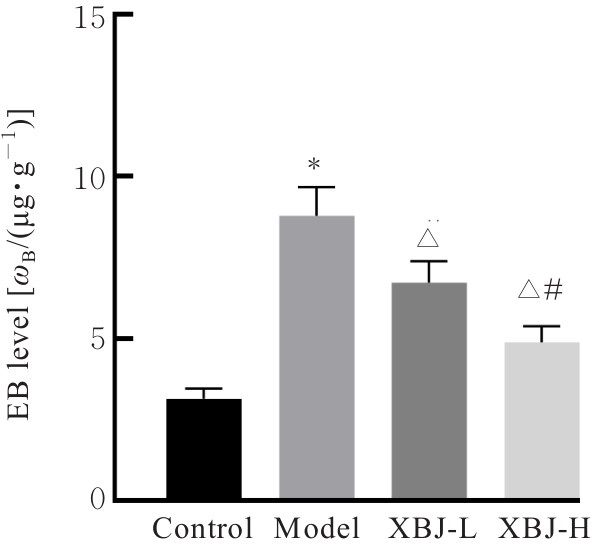
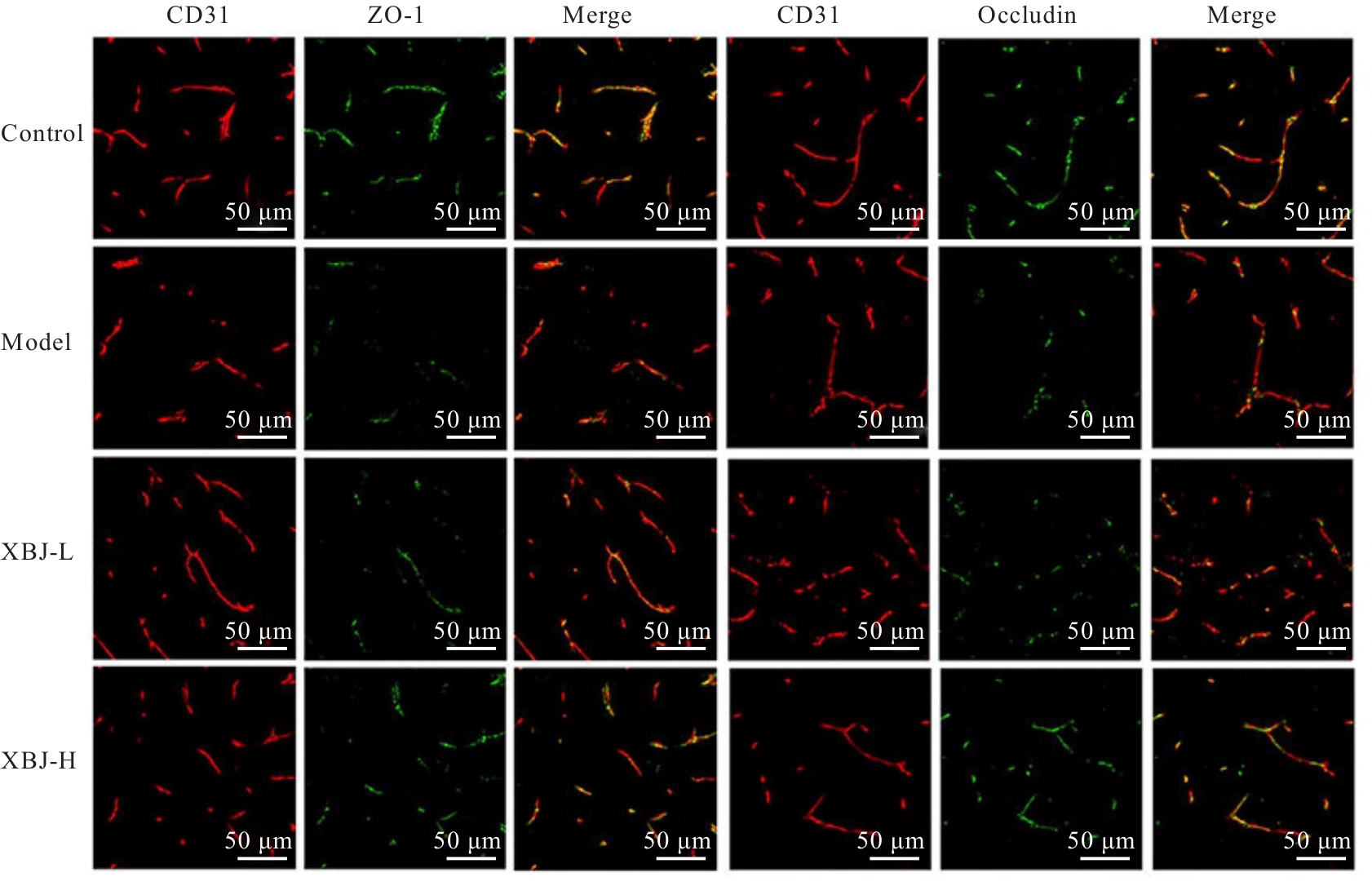
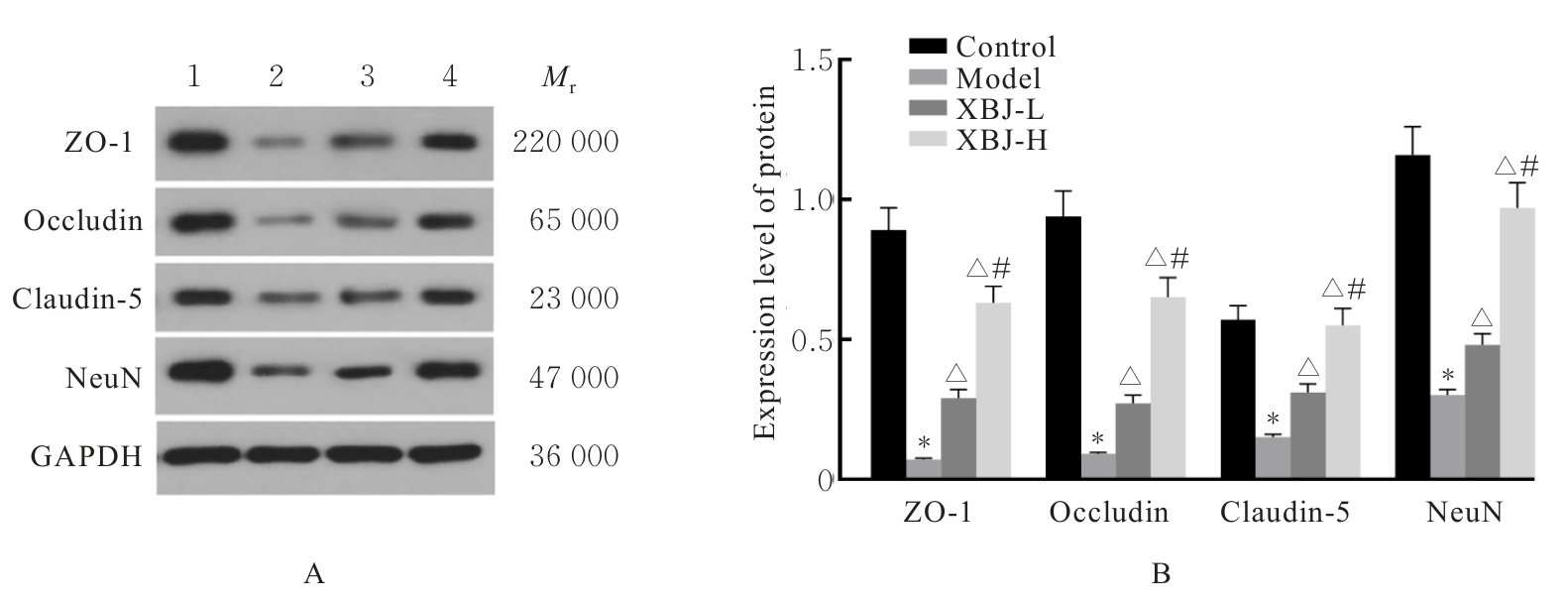
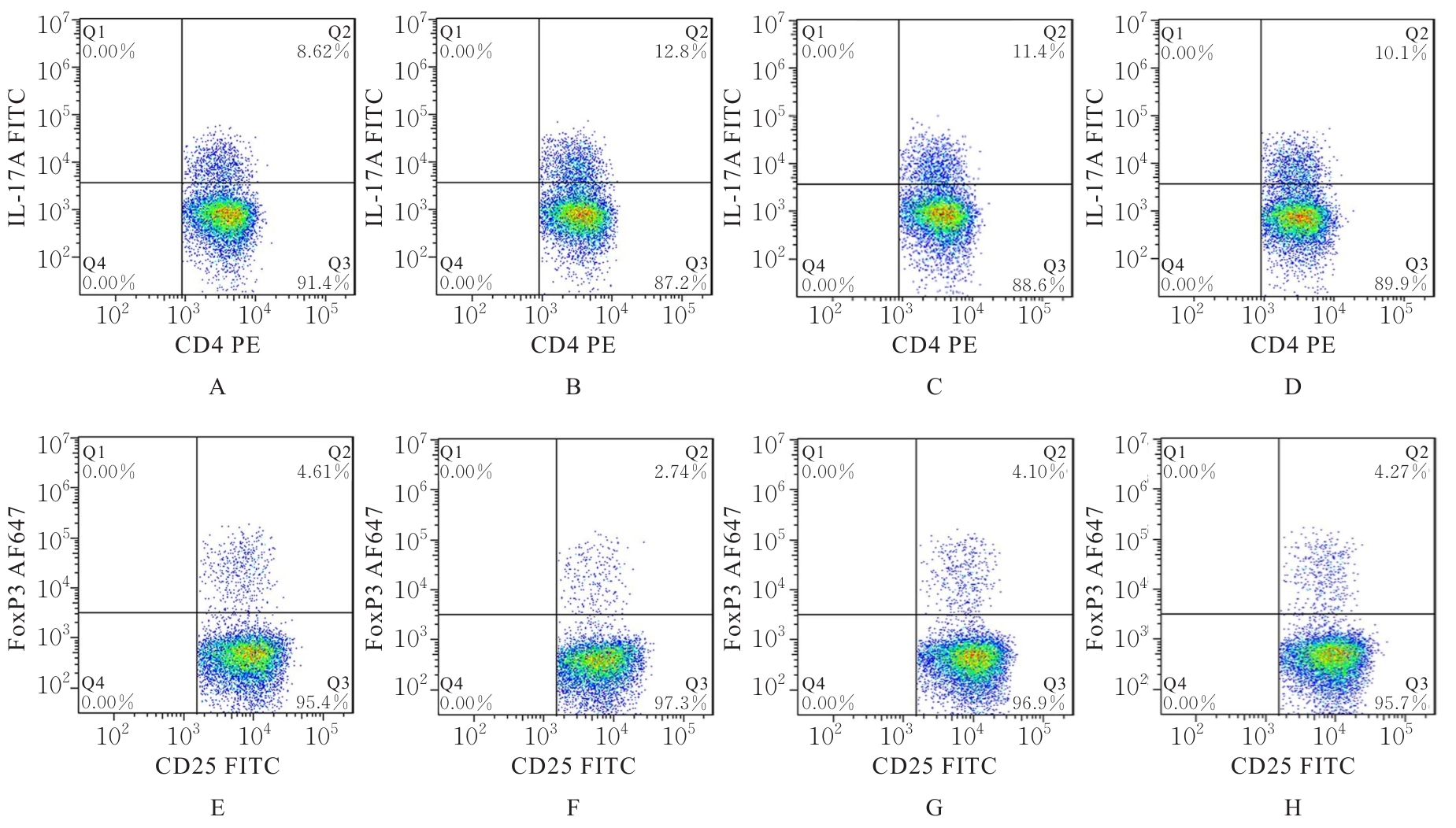
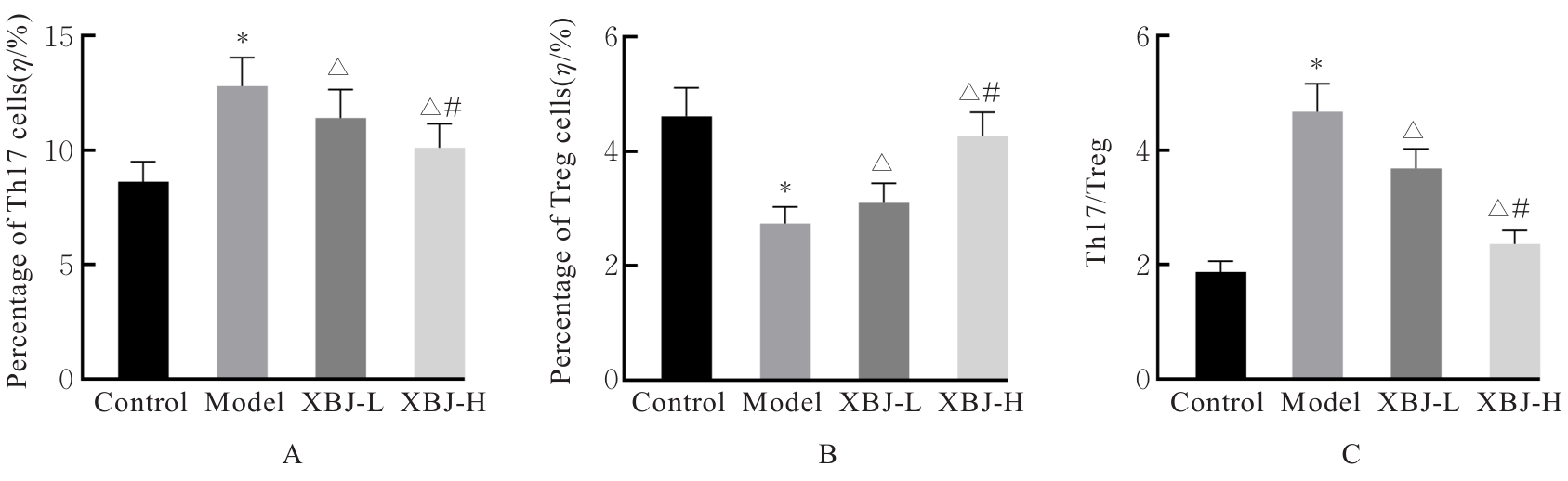
目的 探讨血必净注射液对抗N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体(NMDAR)脑炎小鼠血脑屏障(BBB)损伤的作用,并阐明其对辅助性T细胞17(Th17)/调节性T细胞(Treg)失衡的调控作用。 方法 采用谷氨酸受体N1亚基(GluN1)356-385抗原肽诱导建立主动免疫抗NMDAR脑炎小鼠模型,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测小鼠血清中抗NMDAR免疫球蛋白G(IgG)抗体水平。选取健康未建模小鼠为对照组,建模成功小鼠随机分为模型组、低剂量血必净注射液(XBJ-L)组和高剂量血必净注射液(XBJ-H)组,每组10只,XBJ-L组和XBJ-H组小鼠于建模后分别腹腔注射5和10 mL·kg-1血必净注射液。采用Longa评分法评估各组小鼠神经功能损伤情况,伊文思蓝(EB)染色检测各组小鼠BBB通透性,免疫荧光染色法检测各组小鼠大脑皮质中闭锁小带蛋白1(ZO-1)和闭合蛋白(Occludin)表达情况,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠大脑皮质中ZO-1、Occludin、紧密连接蛋白5(Claudin-5)和神经特异核蛋白(NeuN)蛋白表达水平,ELISA法检测各组小鼠血清中Th17和Treg相关细胞因子白细胞介素(IL)-17、IL-22和IL-10水平,流式细胞术检测各组小鼠外周血中Th17和Treg细胞百分率并计算Th17/Treg比值。 结果 经GluN1 356-385抗原肽诱导的小鼠血清中NMDAR IgG抗体呈阳性,说明造模成功。与对照组比较,模型组小鼠神经功能损伤评分明显升高(P<0.05);脑组织中EB水平明显升高(P<0.05),大脑皮质中ZO-1和Occludin荧光染色强度降低,大脑皮质中ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-5和NeuN蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),血清中IL-17和IL-22水平明显升高(P<0.05),IL-10水平明显降低(P<0.05),外周血中Th17细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05),Treg细胞百分率明显降低(P<0.05),Th17/Treg比值明显增加(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,XBJ-L组和XBJ-H组小鼠神经功能损伤评分明显降低(P<0.05);脑组织中EB水平明显降低(P<0.05);大脑皮质中ZO-1和Occludin荧光染色强度升高,ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-5和NeuN蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);血清中IL-17和IL-22水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-10水平明显升高(P<0.05);外周血中Th17细胞百分率明显降低(P<0.05),Treg细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05),Th17/Treg比值明显减小(P<0.05)。与XBJ-L组比较,XBJ-H组小鼠神经功能损伤评分明显降低(P<0.05);脑组织中EB水平明显降低(P<0.05);大脑皮质中ZO-1和Occludin荧光染色强度升高(P<0.05),ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-5和NeuN蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);血清中IL-17和IL-22水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-10水平明显升高(P<0.05);外周血Th17细胞百分率明显降低(P<0.05),Treg细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05),Th17/Treg比值明显减小(P<0.05)。 结论 血必净注射液能够改善抗NMDAR脑炎小鼠BBB损伤,调节Th17/Treg趋于平衡,从而减轻抗NMDAR脑炎神经功能损伤。
中图分类号:
- R742