吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1241-1246.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200621
威灵仙总皂苷对类风湿关节炎大鼠外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的影响
- 河北医科大学附属唐山工人医院风湿免疫科,河北 唐山 063000
Effect of total saponins of clematis on T lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood of rats with rheumatoid arthritis
Lijun YAN,Shengquan TONG( ),Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Ping WU,Xi WANG
),Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Ping WU,Xi WANG
- Department of Rheumatology,Affiliated Tangshan Workers’ Hospital,Hebei Medical University,Tangshan 063000,China
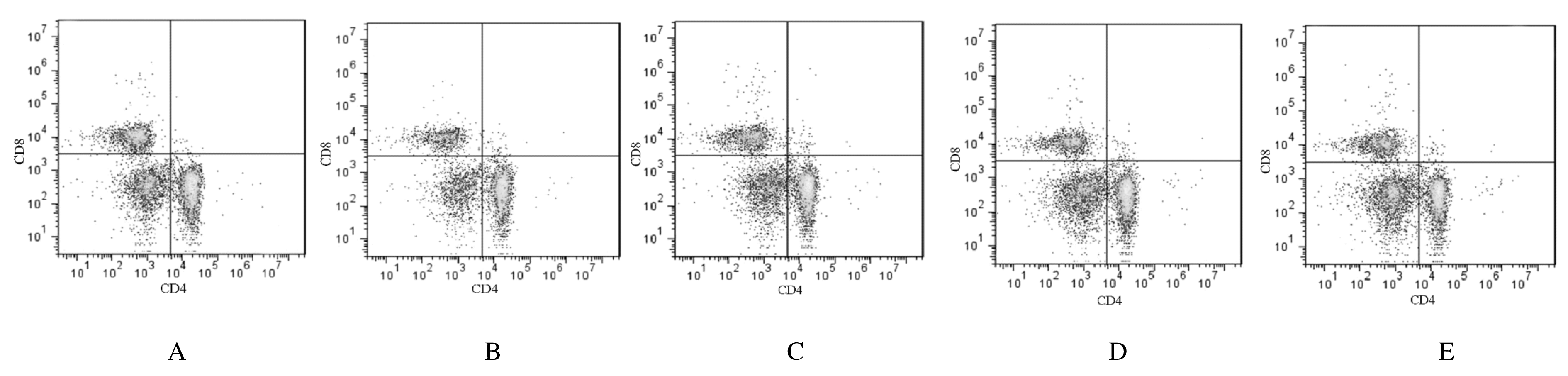
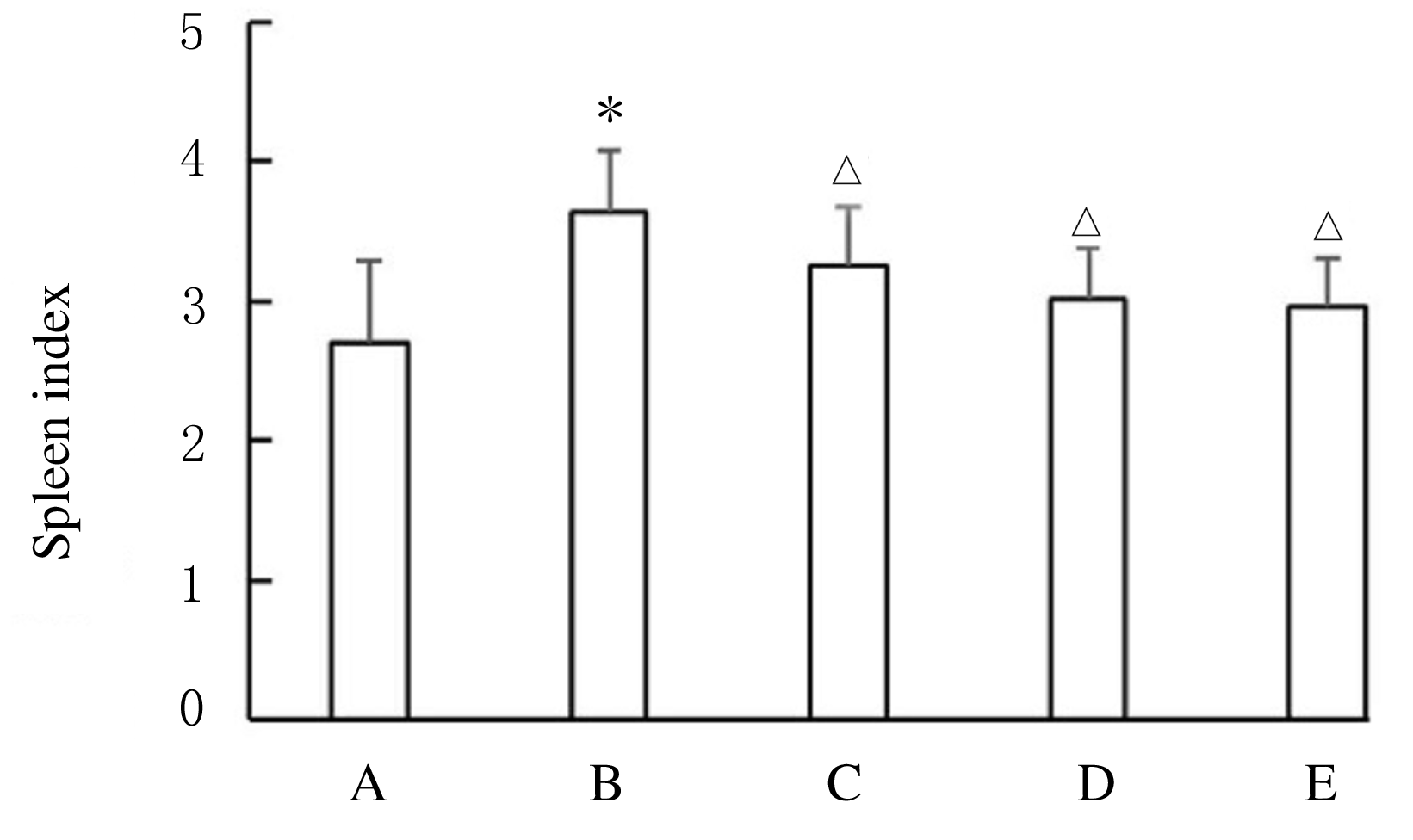
摘要: 观察威灵仙总皂苷(TSC)对类风湿关节炎(RA)大鼠外周血T淋巴细胞亚群和血清炎性因子水平的影响,并阐明其对RA的抑制作用机制。 将50只SD大鼠随机分为对照组(给予生理盐水),模型组(给予生理盐水),低、中和高剂量TSC组(给予50、100、200 mg·kg-1 TSC);每组10只。除对照组外,其余各组建立RA大鼠模型。连续给药6周后,测定大鼠踝关节肿胀度并计算大鼠关节炎指数,流式细胞术检测各组大鼠外周血CD4+T淋巴细胞和CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率及CD4+/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值,ELISA法检测各组大鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)和白细胞介素6(IL-6)水平,称量各组大鼠脾脏质量并计算脾脏指数。 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠关节炎指数明显升高(P<0.05),CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率和CD4+/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值明显升高(P<0.05),CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率明显降低(P<0.05),血清TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6水平和脾脏指数明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量TSC组大鼠关节炎指数明显降低(P<0.05),CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率和CD4+/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值明显降低(P<0.05),CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05),血清TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6水平及脾脏指数明显降低(P<0.05);与低剂量TSC组比较,中和高剂量TSC组大鼠关节炎指数明显降低(P<0.05),CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率和CD4+/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值明显降低(P<0.05),CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05),血清TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6水平及脾脏指数明显降低(P<0.05);与中剂量TSC组比较,高剂量TSC组大鼠关节炎指数明显降低(P<0.05),CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率和CD4+/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值明显降低(P<0.05),CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率明显升高(P<0.05),血清TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6水平及脾脏指数明显降低(P<0.05)。 TSC可通过调节CD4+和CD8+T淋巴细胞亚群百分率,抑制炎性细胞因子分泌,对RA起到抑制作用,且呈剂量依赖性。
中图分类号:
- R593.22