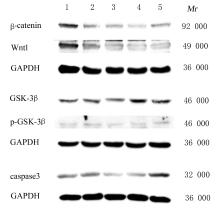
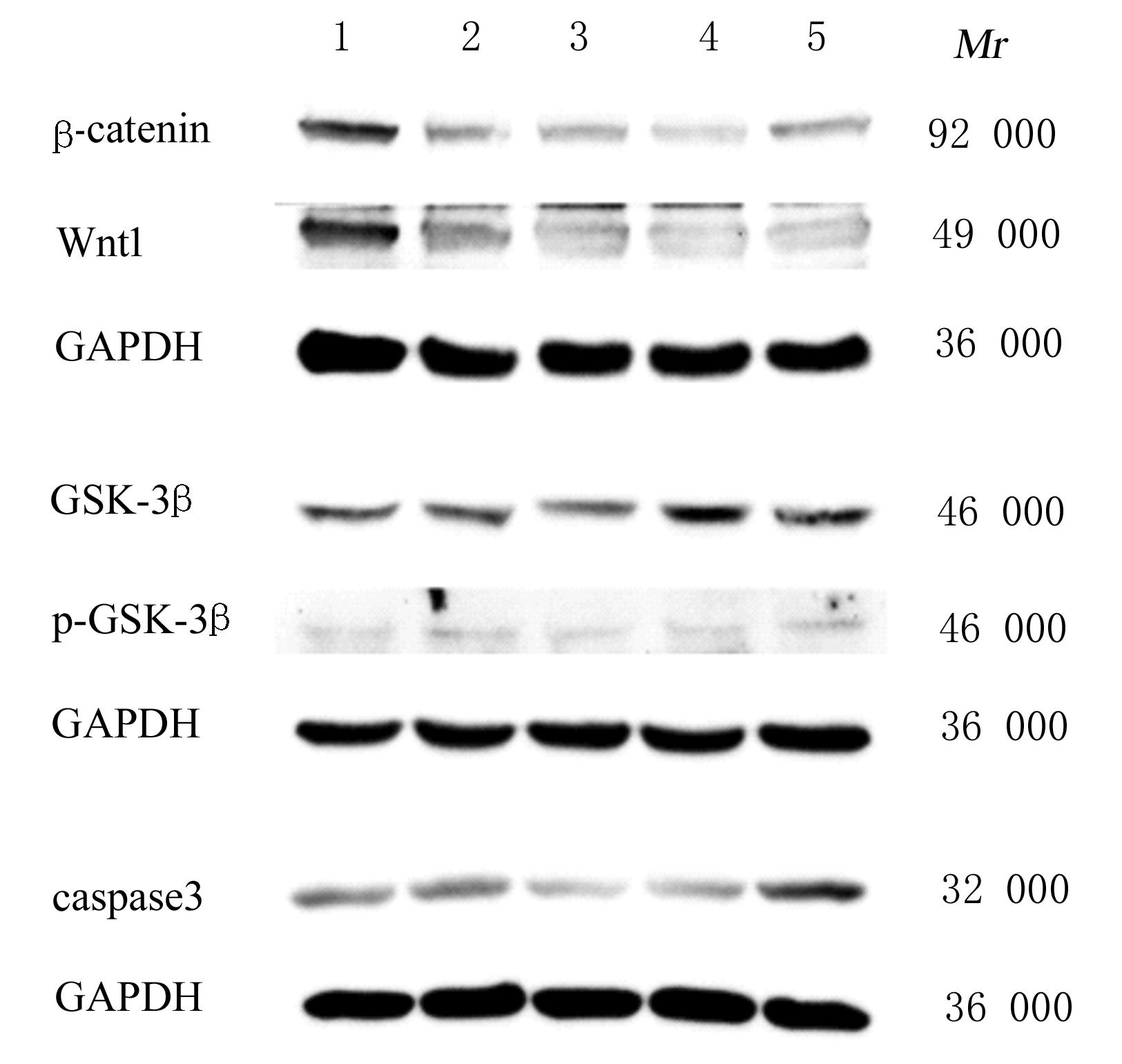
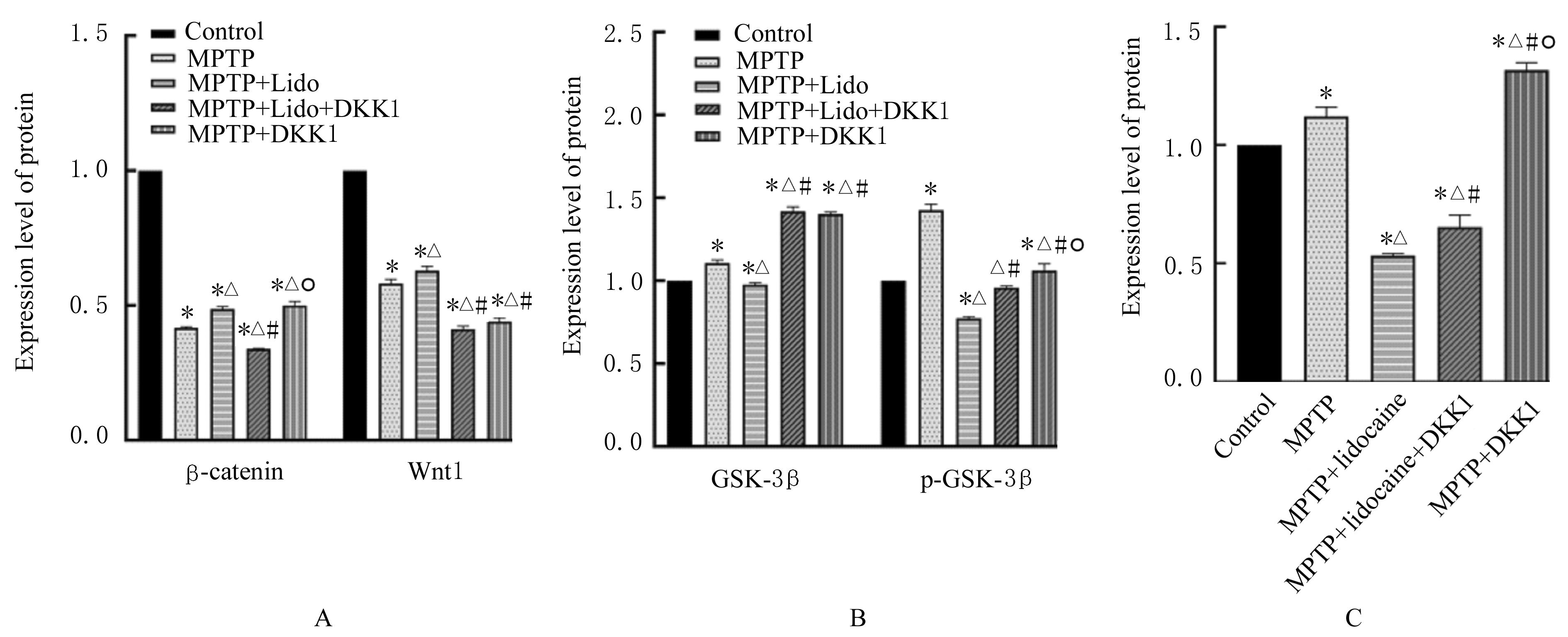
| 1 |
BEITZ J M. Parkinson’s disease: a review[J]. Front Biosci (Schol Ed), 2014, 6(1): 65-74.
|
| 2 |
REN R T, SUN Y, ZHAO X, et al. Recent advances in biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease focusing on biochemicals, omics and neuroimaging[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2015, 53(10): 1495-1506.
|
| 3 |
DORSEY E R, CONSTANTINESCU R, THOMPSON J P, et al. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030[J].Neurology,2007,68(5): 384-386.
|
| 4 |
KALIA L V, LANG A E. Parkinson’s disease[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(9996): 896-912.
|
| 5 |
BASSANI T B, VITAL M A B F, RAUH L K. Neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease and therapeutic evidence of anti-inflammatory drugs[J]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr, 2015, 73(7): 616-623.
|
| 6 |
CIERI D, BRINI M, CALÌ T. Emerging (and converging) pathways in Parkinson’s disease: keeping mitochondrial wellness[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 483(4): 1020-1030.
|
| 7 |
SHEN L, JI H F. Low uric acid levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease: evidence from meta-analysis[J]. BMJ Open, 2013, 3(11): e003620.
|
| 8 |
BLAIR H A, DHILLON S. Safinamide: a review in Parkinson’s disease[J].CNS Drugs,2017,31(2): 169-176.
|
| 9 |
ASCHERIO A, SCHWARZSCHILD M A. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: risk factors and prevention[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2016,15(12):1257-1272.
|
| 10 |
KEMPERMANN G. Adult neurogenesis: an evolutionary perspective[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2015, 8(2): a018986.
|
| 11 |
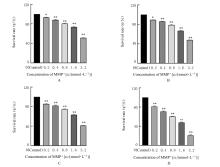
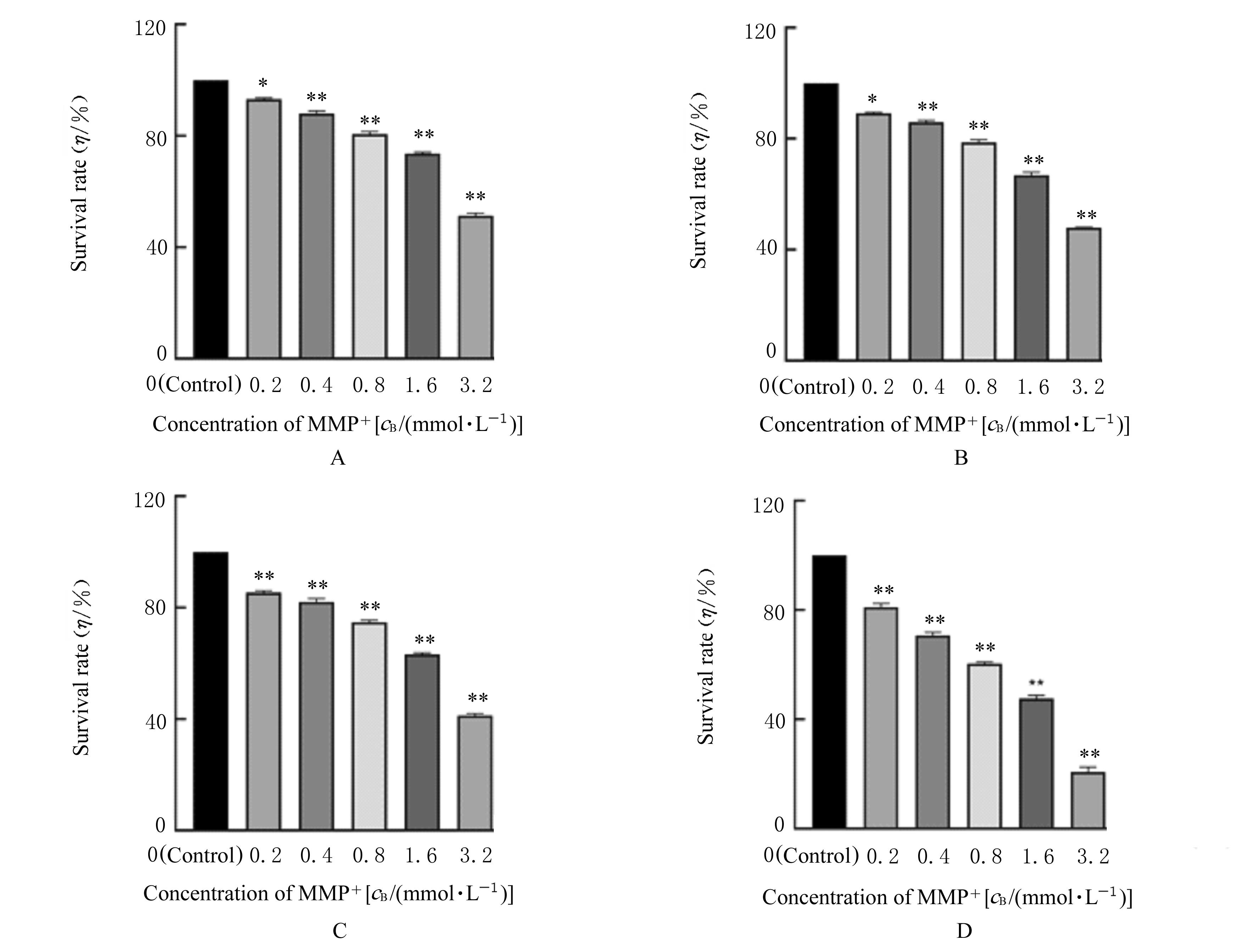
FONCK C, BAUDRY M. Toxic effects of MPP(+) and MPTP in PC12 cells independent of reactive oxygen species formation[J]. Brain Res, 2001, 905: 199-206.
|
| 12 |
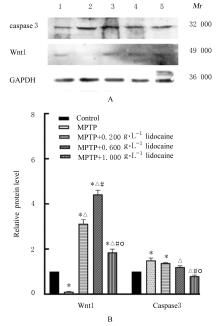
MIN C C, CHO D I, KWON K J, et al. Novel regulatory mechanism of canonical Wnt signaling by dopamine D2 receptor through direct interaction with beta-catenin[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2011, 80(1): 68-78.
|
| 13 |
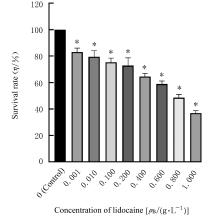
陈博文, 苏 飞, 冉继朋, 等. 利多卡因对大鼠SAH后神经细胞凋亡和迟发性脑血管痉挛的保护作用[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 2019, 35(6): 641-645.
|
| 14 |
CHEN Z C, LI G L, LIU J. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: implications for pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2020, 134: 104700.
|
| 15 |
PRESSE F, CARDONA B, BORSU L, et al. Lithium increases melanin-concentrating hormone mRNA stability and inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in PC12 cells[J]. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 1997, 52(2): 270-283.
|
| 16 |
BAYIR H, KAPRALOV A A, JIANG J, et al. Peroxidase mechanism of lipid-dependent cross-linking of synuclein with cytochrome C: protection against apoptosis versus delayed oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(23): 15951-15969.
|
| 17 |
KUMAR H, KOPPULA S, KIM I S, et al. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling in Parkinson’s disease: a promising multi therapeutic target against oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and cell death[J]. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 2012, 11(8): 1015-1029.
|
| 18 |
BEAL M F. Experimental models of Parkinson’s disease[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2001, 2(5): 325-334.
|
| 19 |
LANGSTON J W, IRWIN I. MPTP: current concepts and controversies[J]. Clin Neuropharmacol, 1986, 9(6): 485-507.
|
| 20 |
ZUO L, MOTHERWELL M S. The impact of reactive oxygen species and genetic mitochondrial mutations in Parkinson’s disease[J]. Gene, 2013, 532(1): 18-23.
|
| 21 |
JANG J, JUNG Y, KIM Y, et al. LPS-induced inflammatory response is suppressed by Wnt inhibitors, Dickkopf-1 and LGK974[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 41612.
|
| 22 |
JIN H B, YU J. Lidocaine protects H9c2 cells from hypoxia-induced injury through regulation of the MAPK/ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 18(5): 4125-4131.
|
| 23 |
WANG Z X, ZHAO Y, YU Y, et al. Effects of lncRNA SNHG20 on proliferation and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(1): 230-237.
|
| 24 |
LIN S W, JIN P P, SHAO C, et al. Lidocaine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and protects against endotoxemia in mice by suppressing HIF1α-induced glycolysis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 80: 106150.
|
| 25 |
KARNINA R, ARIF S K, HATTA M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of lidocaine[J]. Ann Med Surg (Lond), 2021, 69: 102733.
|
| 26 |
GORDON M D, NUSSE R. Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(32): 22429-22433.
|
| 27 |
SAIKI S. The association of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis with inflammation[J]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku, 2014, 54(12): 1125-1127.
|
| 28 |
谭小平,丛盛日,向春晨,等.关注遗传性帕金森病[J].中国实用内科杂志,2022,42(4):283-289.
|
| 29 |
MARCHETTI B, TIROLO C, L'EPISCOPO F,et al. Parkinson’s disease, aging and adult neurogenesis: Wnt/β-catenin signalling as the key to unlock the mystery of endogenous brain repair[J]. Aging Cell, 2020, 19(3): e13101.
|
 ),Kai LI2,3(
),Kai LI2,3( )
)