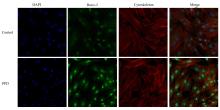
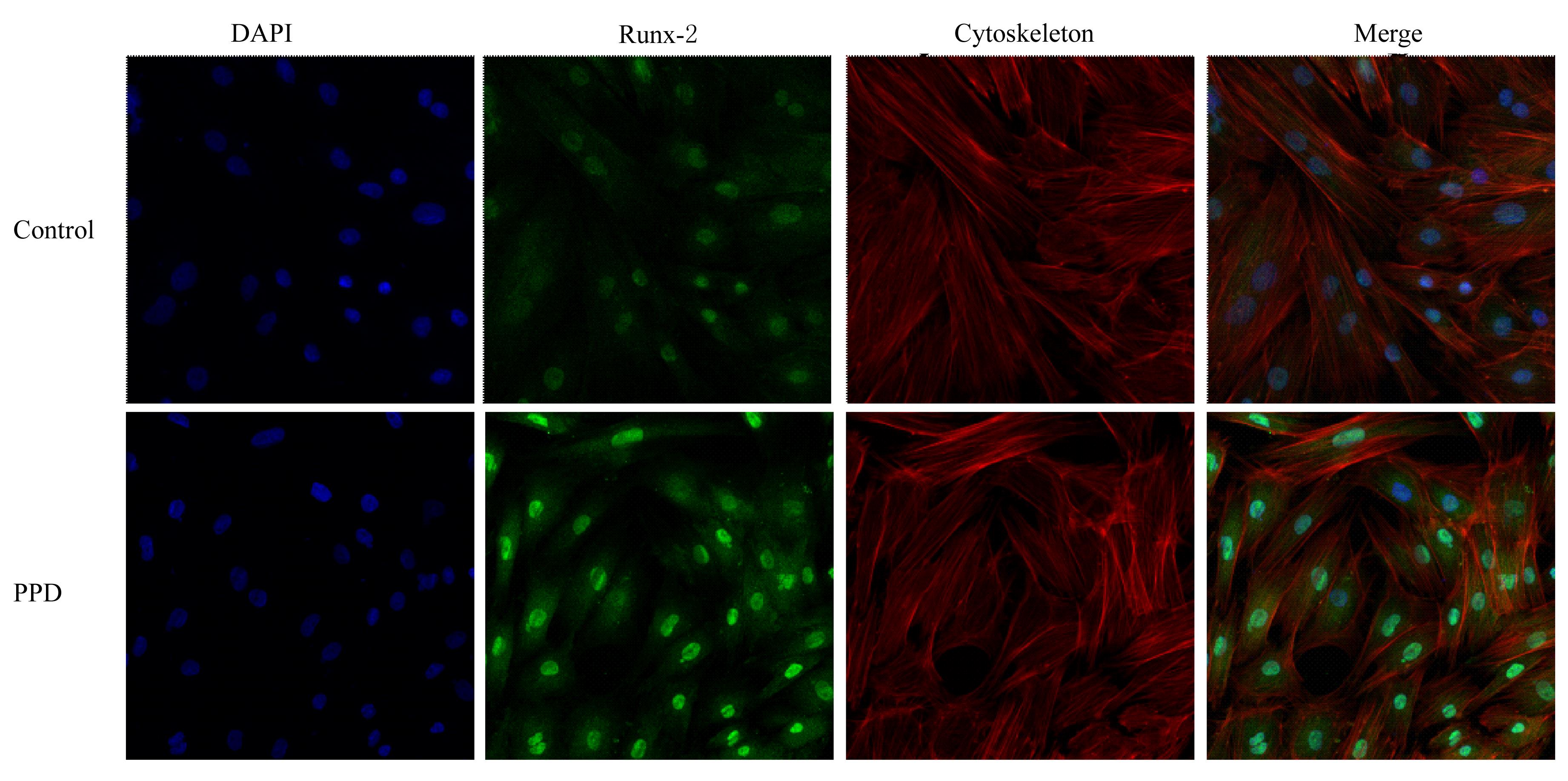
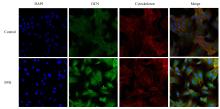
| 1 |
XING X, HAN S, CHENG G, et al. Proteomic analysis of exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a novel therapeutic strategy for tissue injury[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 6094562.
|
| 2 |
LIU C, SUN J. Impact of marine-based biomaterials on the immunoregulatory properties of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: potential use of fish collagen in bone tissue engineering[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(43): 28360-28368.
|
| 3 |
YANG N, ZHANG X, LI L F, et al. Ginsenoside rc promotes bone formation in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in vivo and osteogenic differentiation in vitro [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11): 6187.
|
| 4 |
DING L L, GU S, ZHOU B Y, et al. Ginsenoside compound K enhances fracture healing via promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 855393.
|
| 5 |
ZHANG J Q, ZHANG Q, XU Y R, et al. Synthesis and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of C20 epimeric ocotillol-type triterpenes and protopanaxadiol[J]. Planta Med, 2019, 85(4): 292-301.
|
| 6 |
GUO W N, LI Z Y, YUAN M, et al. Molecular insight into stereoselective ADME characteristics of C20-24 epimeric epoxides of protopanaxadiol by docking analysis[J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(1): 112.
|
| 7 |
PENG B, HE R, XU Q H, et al. Ginsenoside 20(S)- protopanaxadiol inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 142: 1-13.
|
| 8 |
卢泽原, 睢大筼, 于晓风, 等. 20(S)-原人参二醇抑制结直肠癌SW620细胞迁移和侵袭[J]. 人参研究, 2021, 33(6): 2-4.
|
| 9 |
阎茹玉, 吴宿慧, 方亚影, 等. 原人参二醇延缓衰老及抗氧化应激作用的机制研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2022, 38(1): 56-62.
|
| 10 |
王丽娜, 姜 珊, 王溪竹, 等. 人参茎叶中原二醇型、原三醇型人参皂苷抗疲劳作用试验[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2019, 55(8): 81-84.
|
| 11 |
LEE S H, SEO G S, KO G, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol: enhanced heme oxygenase 1 expression in RAW 264.7 cells[J]. Planta Med, 2005, 71(12): 1167-1170.
|
| 12 |
JIANG N, JINGWEI L, WANG H X,et al. Ginsenoside 20(S)-protopanaxadiol attenuates depressive-like behaviour and neuroinflammation in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive rats[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2020, 393: 112710.
|
| 13 |
冯 琳, 刘洪臣. “成血管化”对组织工程骨成骨的影响[J]. 中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2013, 11(1): 34-38.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG E Y, GAO B, SHI H L, et al. 20(S)- protopanaxadiol enhances angiogenesis via HIF-1α- mediated VEGF secretion by activating p70S6 kinase and benefits wound healing in genetically diabetic mice[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2017, 49(10): e387.
|
| 15 |
TAN Q, WU J Y, LIU Y X, et al. The neurofibromatosis type Ⅰ gene promotes autophagy via mTORC1 signalling pathway to enhance new bone formation after fracture[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(19): 11524-11534.
|
| 16 |
WANG W C, HUANG D L, REN J H, et al. Optogenetic control of mesenchymal cell fate towards precise bone regeneration[J].Theranostics,2019,9(26): 8196-8205.
|
| 17 |
PAN C H, SHAN H J, WU T Y, et al. 20(S)- protopanaxadiol inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis and RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 1538.
|
| 18 |
WU Y Q, DU J H, WU Q J, et al. The osteogenesis of Ginsenoside Rb1 incorporated silk/micro-nano hydroxyapatite/sodium alginate composite scaffolds for calvarial defect[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2022, 14(1): 10.
|
| 19 |
HONG F F, WU S L, ZHANG C, et al. TRPM7 upregulate the activity of SMAD1 through PLC signaling way to promote osteogenesis of hBMSCs[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 9458983.
|
| 20 |
ZHU H, BLAHNOVÁ V H, PERALE G, et al. Xeno-hybrid bone graft releasing biomimetic proteins promotes osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 619111.
|
| 21 |
AN J, YANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: the effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation[J]. Life Sci, 2016, 147: 46-58.
|
| 22 |
LI Y F, QIAO Z F, YU F L, et al. Transforming growth factor-β3/chitosan sponge (TGF-β3/CS) facilitates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(20): 4982.
|
| 23 |
SCHOTT N G, FRIEND N E, STEGEMANN J P. Coupling osteogenesis and vasculogenesis in engineered orthopedic tissues[J]. Tissue Eng Part B Rev, 2021, 27(3): 199-214.
|
| 24 |
NOH S H, JO H S, CHOI S, et al. Lactoferrin-anchored tannylated mesoporous silica nanomaterials for enhanced osteo-differentiation ability[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2020, 13(1): 30.
|
| 25 |
WU L, WEI Q Z, LV Y J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin pathway is involved in cadmium-induced inhibition of osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(6): 1519.
|
| 26 |
DIOMEDE F, MARCONI G D, FONTICOLI L,et al. Functional relationship between osteogenesis and angiogenesis in tissue regeneration[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(9): 3242.
|
| 27 |
YANG Y Q, CHIN A, ZHANG L K, et al. The role of traditional Chinese medicines in osteogenesis and angiogenesis[J]. Phytother Res, 2014, 28(1): 1-8.
|
| 28 |
YANG Y Q, TAN Y Y, WONG R, et al. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in ossification[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2012, 4(2): 64-68.
|
 )
)
 )
)