吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 136-142.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240117
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
姜黄素联合粪菌移植对DSS诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎的改善作用
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院肛肠外科,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830054
Improvement effect of curcumin combined with fecal bacteria transplantation on mice with ulcerative colities induced by DSS
Yang LIU,Ming LU( ),Wen HONG,Kelin HUANG
),Wen HONG,Kelin HUANG
- Department of Anorectal Surgery,First Affiliated Hospital,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830054,China
摘要:
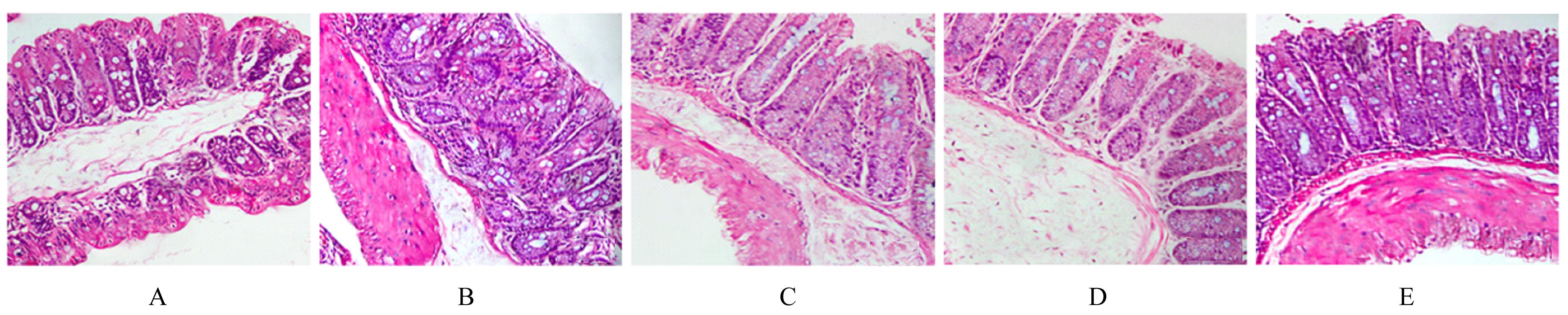
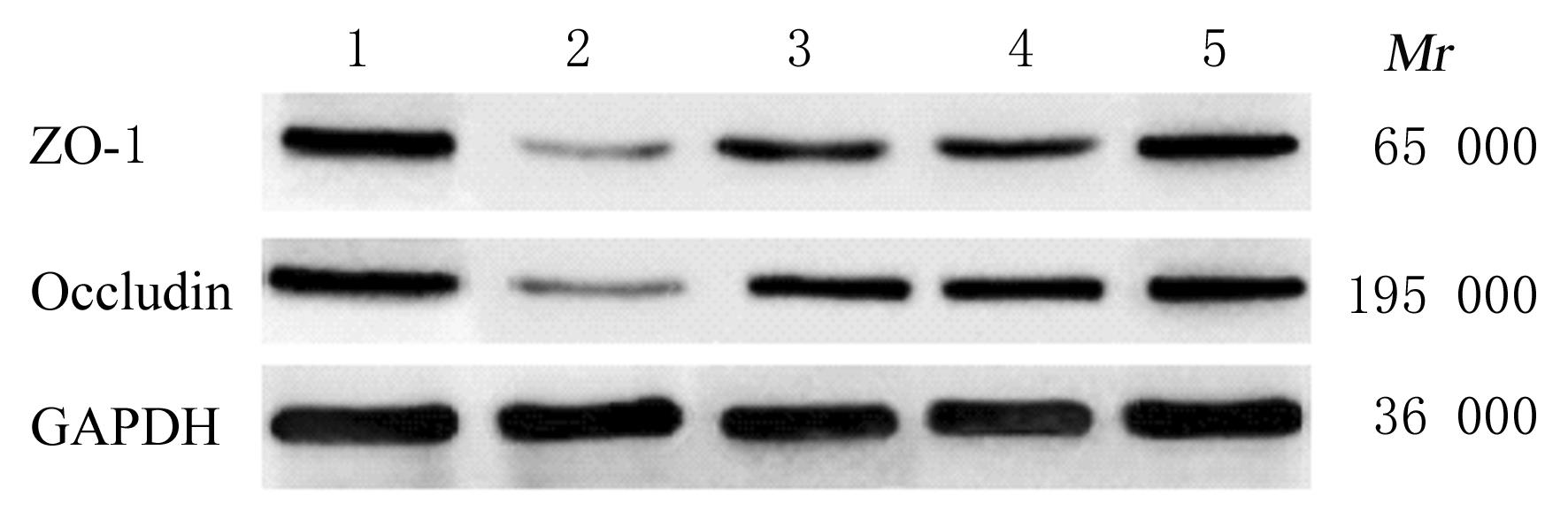
目的 探讨姜黄素联合粪菌移植对葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎(UC)的改善作用,并阐明其相关作用机制。 方法 50只小鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、姜黄素组、粪菌移植组和联合组,除对照组小鼠自由饮用纯净水外,其余各组小鼠自由饮用含2% DSS的蒸馏水建立UC模型。姜黄素组小鼠灌胃给予60 mg·kg-1姜黄素溶液0.4 mL,每日1次,连续10 d;粪菌移植组小鼠灌肠粪菌液0.2 mL,每日1次,持续10 d;联合组小鼠给予0.2 mL粪菌液灌肠后,给予60 mg·kg-1姜黄素溶液0.4 mL灌胃。实验结束后,计算各组小鼠疾病活动指数(DAI)和结肠大体形态损伤指数(CDMI),HE染色观察各组小鼠结肠组织病理形态表现,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组小鼠结肠组织中白细胞介素(IL)-1β、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、IL-4和IL-10水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法和Western blotting法检测各组小鼠结肠组织中闭合蛋白(occludin)和闭锁小带蛋白1(ZO-1)mRNA及蛋白表达水平。 结果 对照组小鼠结肠黏膜上皮结构完整且连续,腺体排列规则,无炎性细胞浸润和溃疡;模型组小鼠结肠黏膜上皮脱失,腺体排列紊乱,杯状细胞减少,黏膜和黏膜下层充血水肿,大量炎性细胞浸润,弥漫分布小溃疡;姜黄素组、粪菌移植组和联合组小鼠结肠黏膜上皮结构相对完整,炎性细胞浸润减少,黏膜和黏膜下层充血水肿减轻。与对照组比较,模型组小鼠DAI和CDMI升高(P<0.05),结肠组织中IL-1β和TNF-α水平升高(P<0.05),IL-4和IL-10水平降低(P<0.05),occludin和ZO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,姜黄素组、粪菌移植组和联合组小鼠DAI和CDMI降低(P<0.05),结肠组织中IL-1β和TNF-α水平降低(P<0.05),IL-4和IL-10水平升高(P<0.05),occludin和ZO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与姜黄素组和粪菌移植组比较,联合组小鼠DAI和CDMI降低(P<0.05),结肠组织中IL-1β和TNF-α水平降低(P<0.05),IL-4和IL-10水平升高(P<0.05),occludin和ZO-1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05)。 结论 姜黄素联合粪菌移植可改善UC小鼠结肠组织病理损伤,抑制炎症因子分泌,促进肠黏膜修复。
中图分类号:
- R285.5