| 1 |
中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科盆底学组. 盆腔器官脱垂的中国诊治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2020, 55(5): 300-306.
|
| 2 |
陈远群, 任慕兰. 盆腔器官脱垂发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2008, 19(5): 507-509.
|
| 3 |
DUARTE THIBAULT M, CHEN L Y, HUEBNER M,et al. A comparison of MRI-based pelvic floor support measures between young and old women with prolapse[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2023,34(9):2081-2088.
|
| 4 |
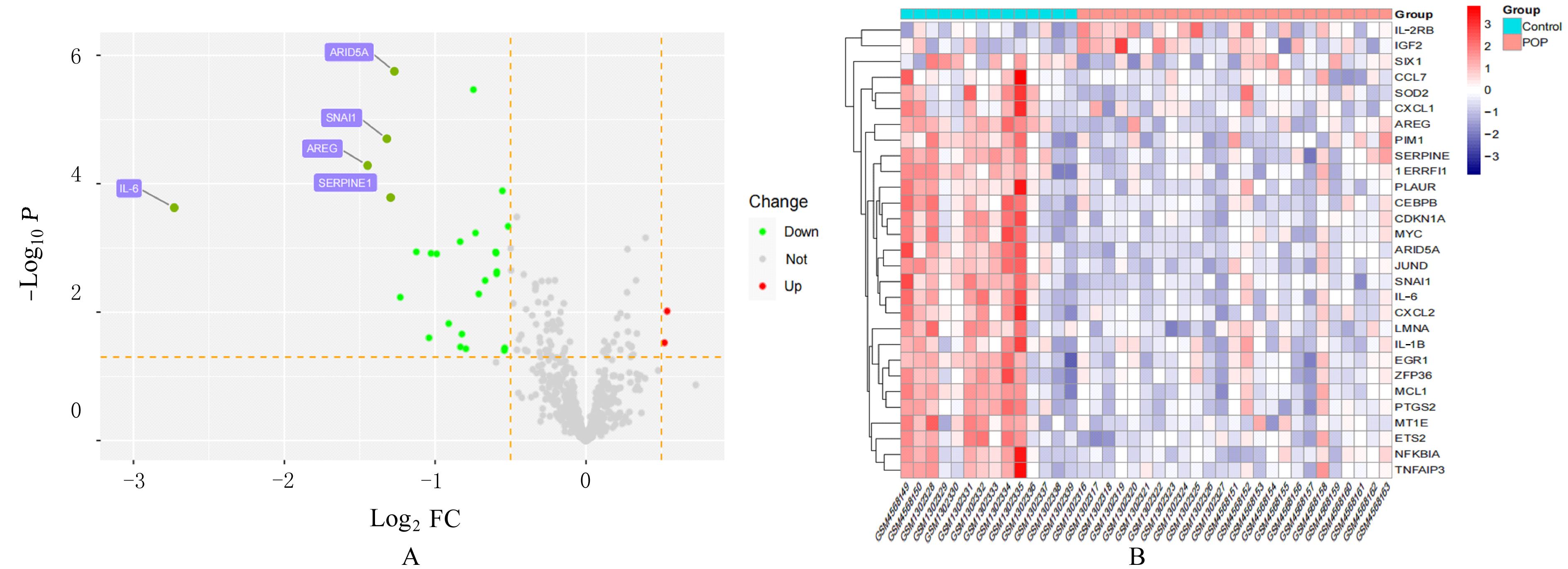
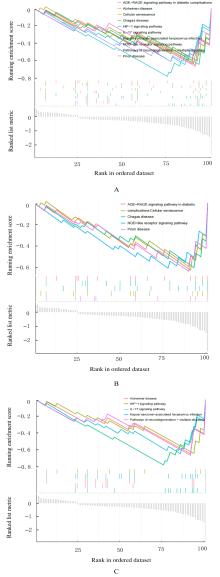
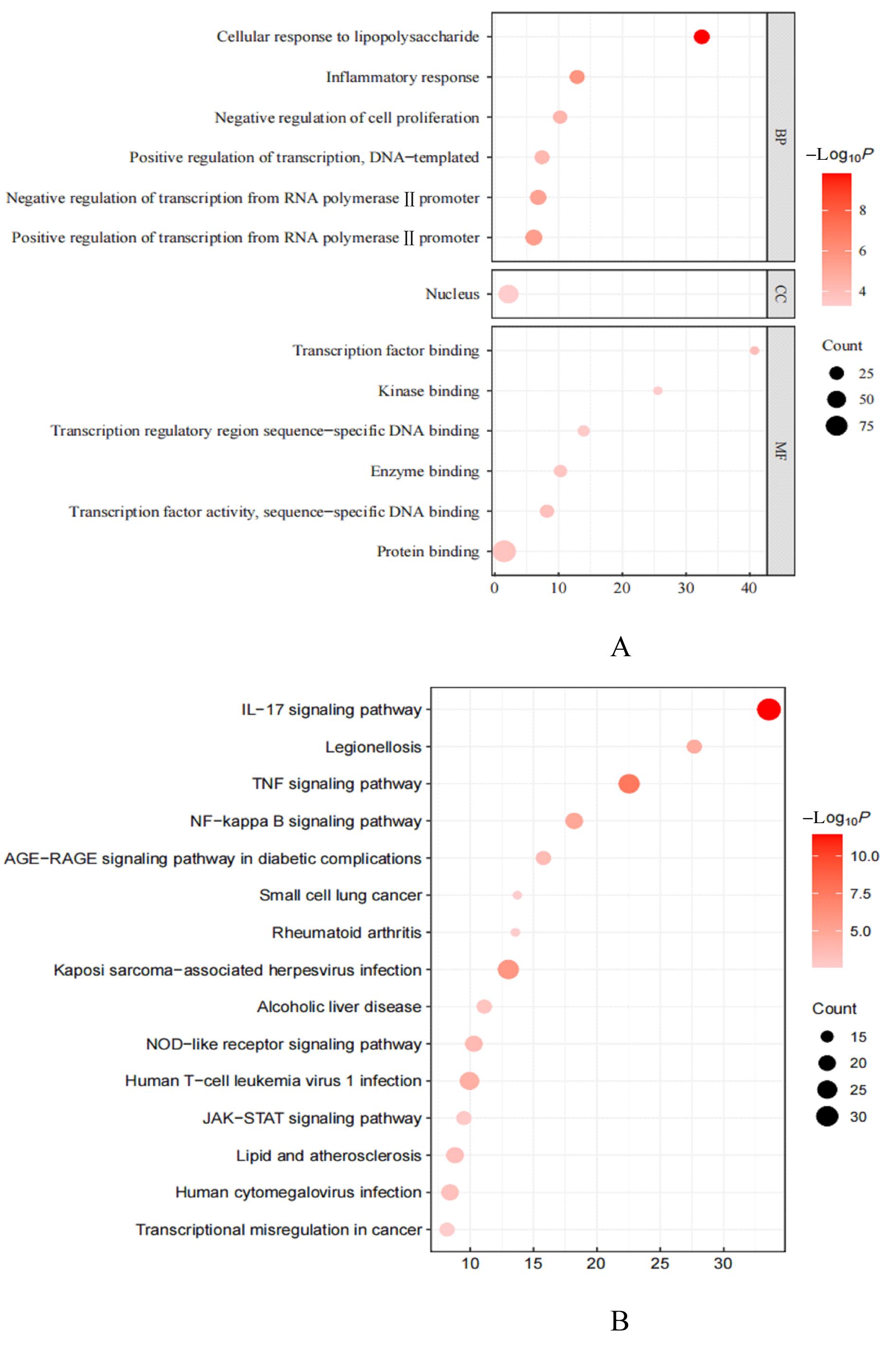
ZHAO Y, XIA Z J, LIN T, et al. Significance of hub genes and immune cell infiltration identified by bioinformatics analysis in pelvic organ prolapse[J]. Peer J, 2020, 8: e9773.
|
| 5 |
ZHOU Q, HONG L, WANG J. Identification of key genes and pathways in pelvic organ prolapse based on gene expression profiling by bioinformatics analysis[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2018, 297(5): 1323-1332.
|
| 6 |
RITCHIE M E, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47.
|
| 7 |
NEWMAN A M, LIU C L, GREEN M R, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles[J].Nat Methods,2015,12(5):453-457.
|
| 8 |
LINDEN A. Measuring diagnostic and predictive accuracy in disease management: an introduction to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis[J]. J Eval Clin Pract, 2006, 12(2): 132-139.
|
| 9 |
李志毅, 朱 兰, 徐 涛, 等. 中国城市地区女性盆腔器官脱垂临床流行病学调查[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2019, 99(11): 857-861.
|
| 10 |
CHEN X X, GILES J, YAO Y, et al. The path to healthy ageing in China: a Peking University-Lancet Commission[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400(10367):1967-2006.
|
| 11 |
RUIZ-ZAPATA A M, KERKHOF M H, GHAZANFARI S, et al. Vaginal fibroblastic cells from women with pelvic organ prolapse produce matrices with increased stiffness and collagen content[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 22971.
|
| 12 |
LANG J H, ZHU L, SUN Z J, et al. Estrogen levels and estrogen receptors in patients with stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2003, 80(1): 35-39.
|
| 13 |
侯 睿, 樊少磊. 盆腔器官脱垂患者子宫主韧带组织中炎性因子、氧化损伤标志物水平的研究[J]. 中国妇产科临床杂志, 2021, 22(3): 270-272.
|
| 14 |
VIROLLE T, MONTHOUEL M N, DJABARI Z,et al.Three activator protein-1-binding sites bound by the Fra-2.JunD complex cooperate for the regulation of murine laminin alpha3A (lama3A) promoter activity by transforming growth factor-beta[J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273(28): 17318-17325.
|
| 15 |
ZEISBERG M, NEILSON E G. Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions[J]. J Clin Invest, 2009, 119(6): 1429-1437.
|
| 16 |
DONGRE A, RASHIDIAN M, REINHARDT F,et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to immunosuppression in breast carcinomas[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(15): 3982-3989.
|
| 17 |
LIU J, WU Z S, HAN D, et al. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor inhibits liver cancer through small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)ylation-related suppression of NF-κB/snail signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(4): 1262-1278.
|
| 18 |
HSIEH C H, TAI S K, YANG M H. Snail-overexpressing cancer cells promote M2-like polarization of tumor-associated macrophages by delivering miR-21-abundant exosomes[J].Neoplasia,2018,20(8): 775-788.
|
| 19 |
BERASAIN C, AVILA M A. Amphiregulin[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2014, 28: 31-41.
|
| 20 |
ZAISS D M W, GAUSE W C, OSBORNE L C, et al. Emerging functions of amphiregulin in orchestrating immunity, inflammation, and tissue repair[J]. Immunity, 2015, 42(2): 216-226.
|
| 21 |
CHICHE A, ROUX I L, VON JOEST M, et al. Injury-induced senescence enables in vivo reprogramming in skeletal muscle[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2017, 20(3): 407-414.
|
| 22 |
BURZYN D, KUSWANTO W, KOLODIN D, et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair[J]. Cell, 2013, 155(6): 1282-1295.
|
| 23 |
PERUGORRIA M J, LATASA M U, NICOU A, et al. The epidermal growth factor receptor ligand amphiregulin participates in the development of mouse liver fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48(4): 1251-1261.
|
| 24 |
CONNEELY K N, CAPELL B C, ERDOS M R,et al. Human longevity and common variations in the LMNA gene: a meta-analysis[J].Aging Cell, 2012,11(3): 475-481.
|
| 25 |
RAGNAUTH C D, WARREN D T, LIU Y W, et al. Prelamin A acts to accelerate smooth muscle cell senescence and is a novel biomarker of human vascular aging[J]. Circulation, 2010, 121(20): 2200-2210.
|
| 26 |
VITERI G, CHUNG Y W, STADTMAN E R. Effect of progerin on the accumulation of oxidized proteins in fibroblasts from Hutchinson Gilford progeria patients[J]. Mech Ageing Dev, 2010, 131(1): 2-8.
|
| 27 |
OSORIO F G, BÁRCENA C, SORIA-VALLES C, et al. Nuclear lamina defects cause ATM-dependent NF-κB activation and link accelerated aging to a systemic inflammatory response[J]. Genes Dev, 2012, 26(20): 2311-2324.
|
| 28 |
BORRELLI A, SCHIATTARELLA A, BONELLI P, et al. The functional role of MnSOD as a biomarker of human diseases and therapeutic potential of a new isoform of a human recombinant MnSOD[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2014, 2014: 476789.
|
| 29 |
SUN G G, WANG Y D, HU W N, et al. Effects of manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) expression on regulation of esophageal cancer cell growth and apoptosis in vitro and in nude mice[J]. Tumour Biol, 2013, 34(3): 1409-1419.
|
| 30 |
LI P F, XIONG F, XING H Y, et al. Retinoic acid inhibits the pyroptosis of degenerated nucleus pulposus cells by activating Sirt1-SOD2 signaling[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2023, 64(4): 337-349.
|
| 31 |
HU W S, LIAO W Y, CHANG C H, et al. Paracrine IGF-1 activates SOD2 expression and regulates ROS/p53 axis in the treatment of cardiac damage in D-galactose-induced aging rats after receiving mesenchymal stem cells[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(15): 4419.
|
 )
)
 )
)