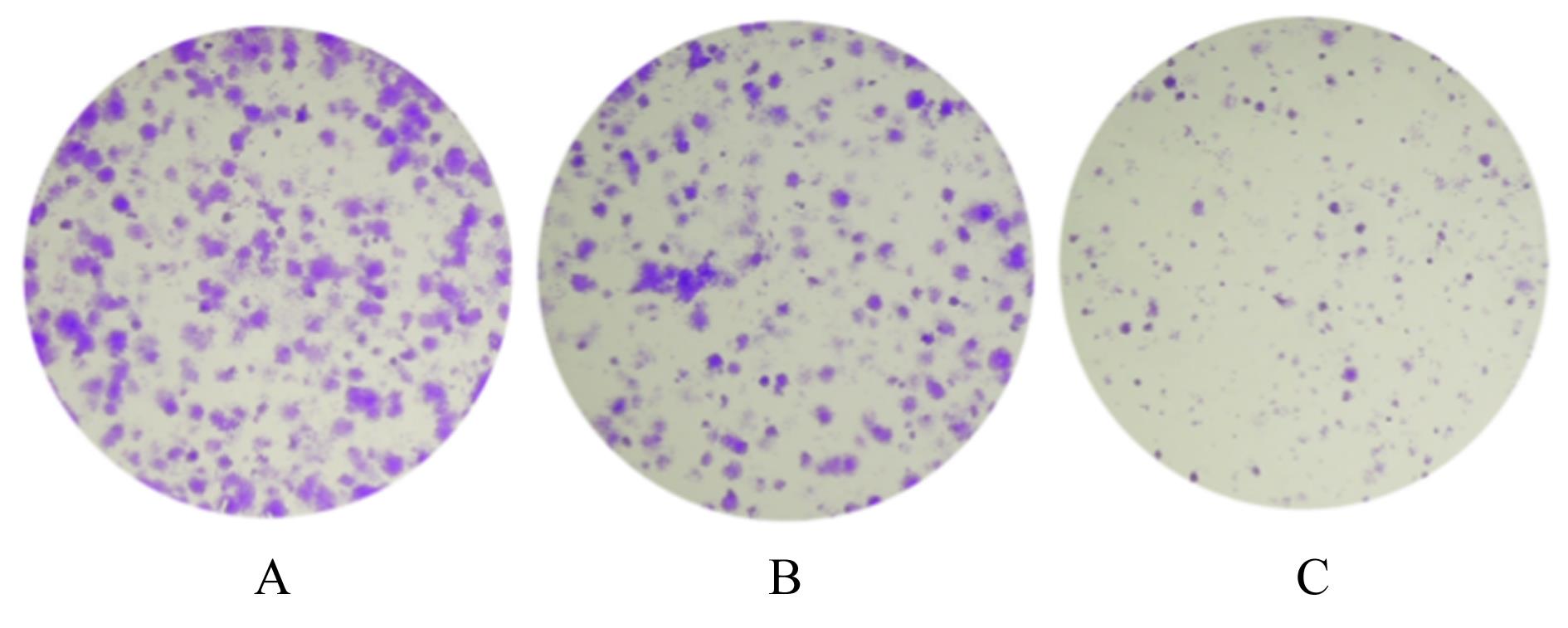
| 1 |
AL-DALAHMAH O, ARGENZIANO M G, KANNAN A, et al. Re-convolving the compositional landscape of primary and recurrent glioblastoma reveals prognostic and targetable tissue states[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 2586.
|
| 2 |
WANG L M, ENGLANDER Z K, MILLER M L,et al. Malignant glioma[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2023, 1405: 1-30.
|
| 3 |
GRUBE S, DÜNISCH P, FREITAG D, et al. Overexpression of fatty acid synthase in human gliomas correlates with the WHO tumor grade and inhibition with Orlistat reduces cell viability and triggers apoptosis[J]. J Neurooncol, 2014, 118(2): 277-287.
|
| 4 |
YASUMOTO Y, MIYAZAKI H, VAIDYAN L K,et al.Inhibition of fatty acid synthase decreases expression of stemness markers in glioma stem cells[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0147717.
|
| 5 |
TAN W, ZHONG Z F, WANG S P, et al. Berberine regulated lipid metabolism in the presence of C75, compound C, and TOFA in breast cancer cell line MCF-7[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2015, 2015: 396035.
|
| 6 |
WANG X Y, ZHANG J M, WANG S S, et al. Berberine modulates gut microbiota to attenuate cerebral ferroptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion in mice[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2023, 953: 175782.
|
| 7 |
SUN Y X, HUANG H Y, ZHAN Z X, et al. Berberine inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by suppressing TGF-β1/COL11A1 pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 625: 38-45.
|
| 8 |
LIU Z Q, CHEN Y, GAO H J, et al. Berberine inhibits cell proliferation by interfering with wild-type and mutant P53 in human glioma cells[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 12151-12162.
|
| 9 |
TSUJI S, NAKAMURA S, SHODA K, et al. NMDA receptor signaling induces the chemoresistance of temozolomide via upregulation of MGMT expression in glioblastoma cells[J].J Neurooncol,2022,160(2):375-388.
|
| 10 |
RÖHRIG F, SCHULZE A. The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2016, 16(11): 732-749.
|
| 11 |
FLÖTER J, KAYMAK I, SCHULZE A. Regulation of metabolic activity by p53[J].Metabolites,2017,7(2): 21.
|
| 12 |
BRAULT C, SCHULZE A. The role of glucose and lipid metabolism in growth and survival of cancer cells[J]. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2016, 207: 1-22.
|
| 13 |
FLAVENY C A, GRIFFETT K, EL-GENDY B E L D,et al. Broad anti-tumor activity of a small molecule that selectively targets the Warburg effect and lipogenesis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2015, 28(1): 42-56.
|
| 14 |
ZHAN Y, QIAO W, YI B L, et al. Dual role of pseudogene TMEM198B in promoting lipid metabolism and immune escape of glioma cells[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(40): 4512-4523.
|
| 15 |
SCHWAIGER-HABER M, STANCLIFFE E, ANBUKUMAR D S, et al. Using mass spectrometry imaging to map fluxes quantitatively in the tumor ecosystem[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 2876.
|
| 16 |
GUO D L, PRINS R M, DANG J L, et al. EGFR signaling through an Akt-SREBP-1-dependent, rapamycin-resistant pathway sensitizes glioblastomas to antilipogenic therapy[J]. Sci Signal, 2009, 2(101): ra82.
|
| 17 |
LI L, PILO G M, LI X L, et al. Inactivation of fatty acid synthase impairs hepatocarcinogenesis driven by AKT in mice and humans[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(2): 333-341.
|
| 18 |
ZAYTSEVA Y Y, RYCHAHOU P G, GULHATI P, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase attenuates CD44-associated signaling and reduces metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72(6): 1504-1517.
|
| 19 |
OSBORNE T F. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): key regulators of nutritional homeostasis and insulin action[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(42): 32379-32382.
|
| 20 |
HORTON J D, GOLDSTEIN J L, BROWN M S. SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver[J]. J Clin Invest, 2002, 109(9): 1125-1131.
|
| 21 |
DAMIANO F, GIANNOTTI L, GNONI G V, et al. Quercetin inhibition of SREBPs and ChREBP expression results in reduced cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in C6 glioma cells[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2019, 117: 105618.
|
| 22 |
RUSH J, MORITZ A, LEE K A, et al. Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2005, 23(1): 94-101.
|
| 23 |
HAN L Y, DAI W X, LUO W Q, et al. Enhanced de novo lipid synthesis mediated by FASN induces chemoresistance in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(3): 562.
|
| 24 |
ZHU L, DU W, LIU Y P, et al. Prolonged high-glucose exposure decreased SREBP-1/FASN/ACC in Schwann cells of diabetic mice via blocking PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(4): 5777-5789.
|
 )
)
 )
)