吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1358-1364.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240520
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
MEIS1表达对胃癌根治术后患者生存期的影响及其在预后评估中的价值
易嘉欣,张扬雨,付颖利,潘禹辰,韩永杰,姜晶( ),吴燕华(
),吴燕华( )
)
- 吉林大学第一医院临床流行病学研究室,吉林 长春 130021
Effect of MEIS1 expression on survival in patients after radical gastrectomy and its value in prognostic evaluation
Jiaxin YI,Yangyu ZHANG,Yingli FU,Yuchen PAN,Yongjie HAN,Jing JIANG( ),Yanhua WU(
),Yanhua WU( )
)
- Department of Clinical Epidemiology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
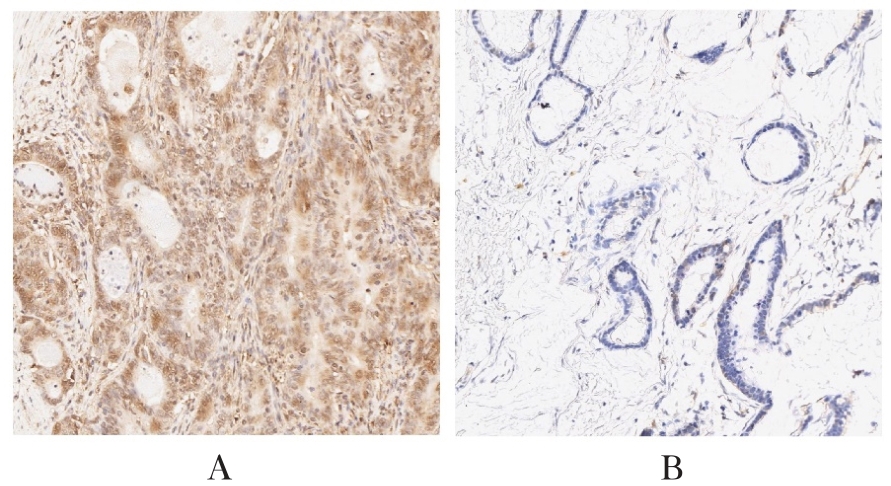
目的 探讨不同表达水平骨髓嗜病毒整合位点1(MEIS1)胃癌患者的术后生存情况,分析MEIS1表达在胃癌患者预后评估中的预测价值。 方法 在胃癌生存队列中选取215例行胃癌根治术的患者。免疫组织化学染色法检测胃癌和癌旁正常组织中MEIS1表达水平。采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法分析MEIS1表达水平与患者临床病理特征的关系;采用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,采用Log-rank检验比较MEIS1高表达组和MEIS1低表达组胃癌患者生存差异;采用多因素Cox比例风险回归模型计算风险比(HR)及其95%置信区间(CI),评价MEIS1表达水平与胃癌患者生存的关系。 结果 免疫组织化学染色,MEIS1在胃癌组织中表达水平降低;单因素分析,MEIS1高表达患者比MEIS1低表达患者总生存期长(P=0.049),预后更好;多因素Cox比例风险回归分析,MEIS1低表达和TNM分期高是胃癌患者预后的独立危险因素(HR=1.577,95%CI:1.011~2.460,P=0.045;HR=2.709,95%CI:1.708~4.297,P<0.001)。 结论 MEIS1低表达胃癌患者术后总生存期短,MEIS1有望成为胃癌根治术后患者预后评估的生物标志物。
中图分类号:
- R735.2