吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1547-1556.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240608
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
白藜芦醇对颞下颌关节骨关节炎的治疗作用及其机制
孙高1,2,何静1,赵琪1,石剑虹1,廖智羚1,田原野1,吴国民1( )
)
- 1.吉林大学口腔医院口腔颌面外一科与整形美容外科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学口腔医院 吉林省牙发育及颌骨重塑与再生重点实验室,吉林 长春 130021
Therapeutic effect of resveratrol on osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint and its mechanism
Gao SUN1,2,Jing HE1,Qi ZHAO1,Jianhong SHI1,Zhiling LIAO1,Yuanye TIAN1,Guomin WU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Ⅰand Oral Plastic Surgery,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Jilin Provincal Key Laboratory of Tooth Development and Bone Remodeling and Regeneration,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
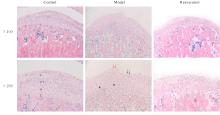
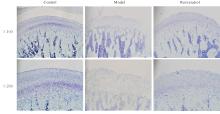
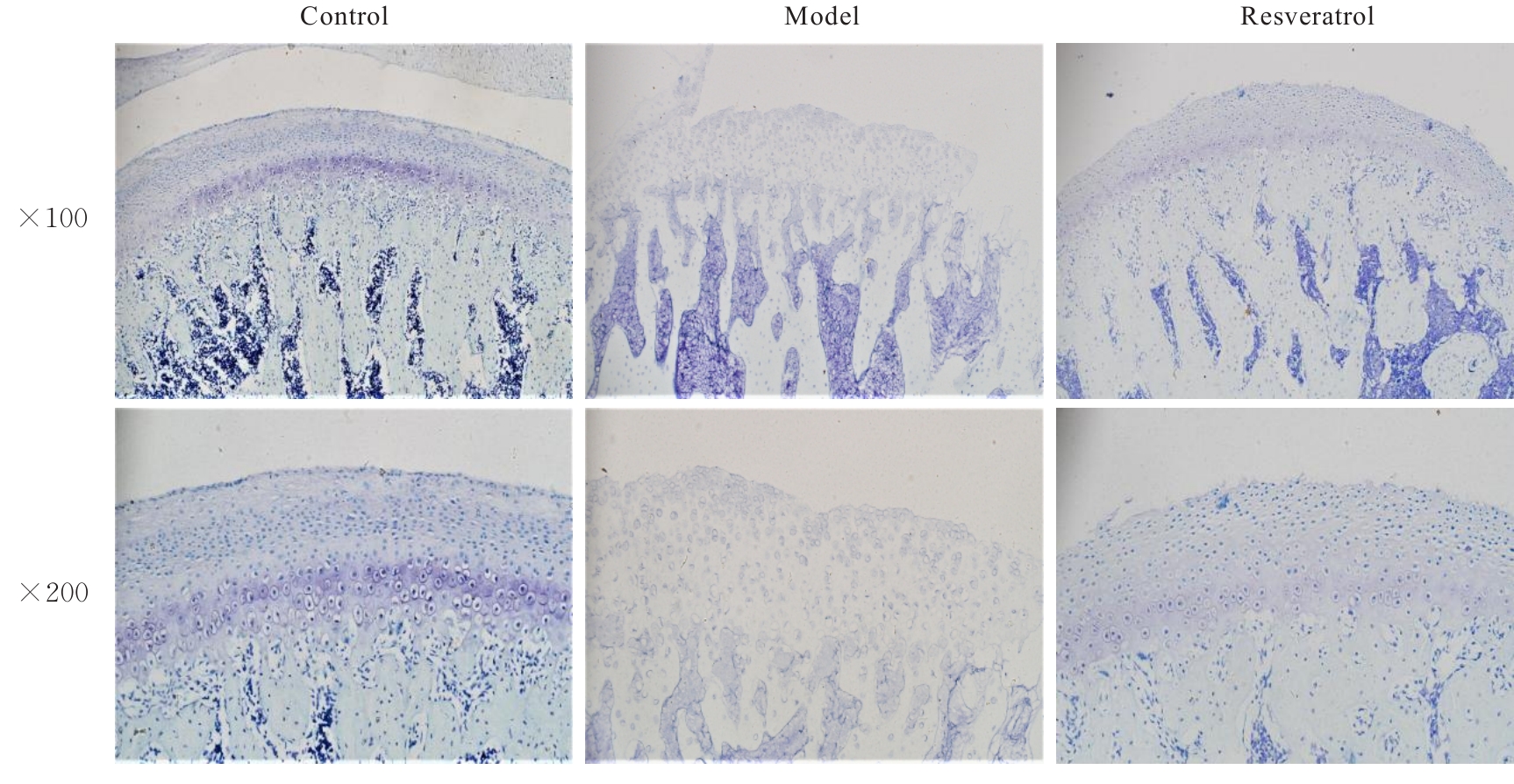
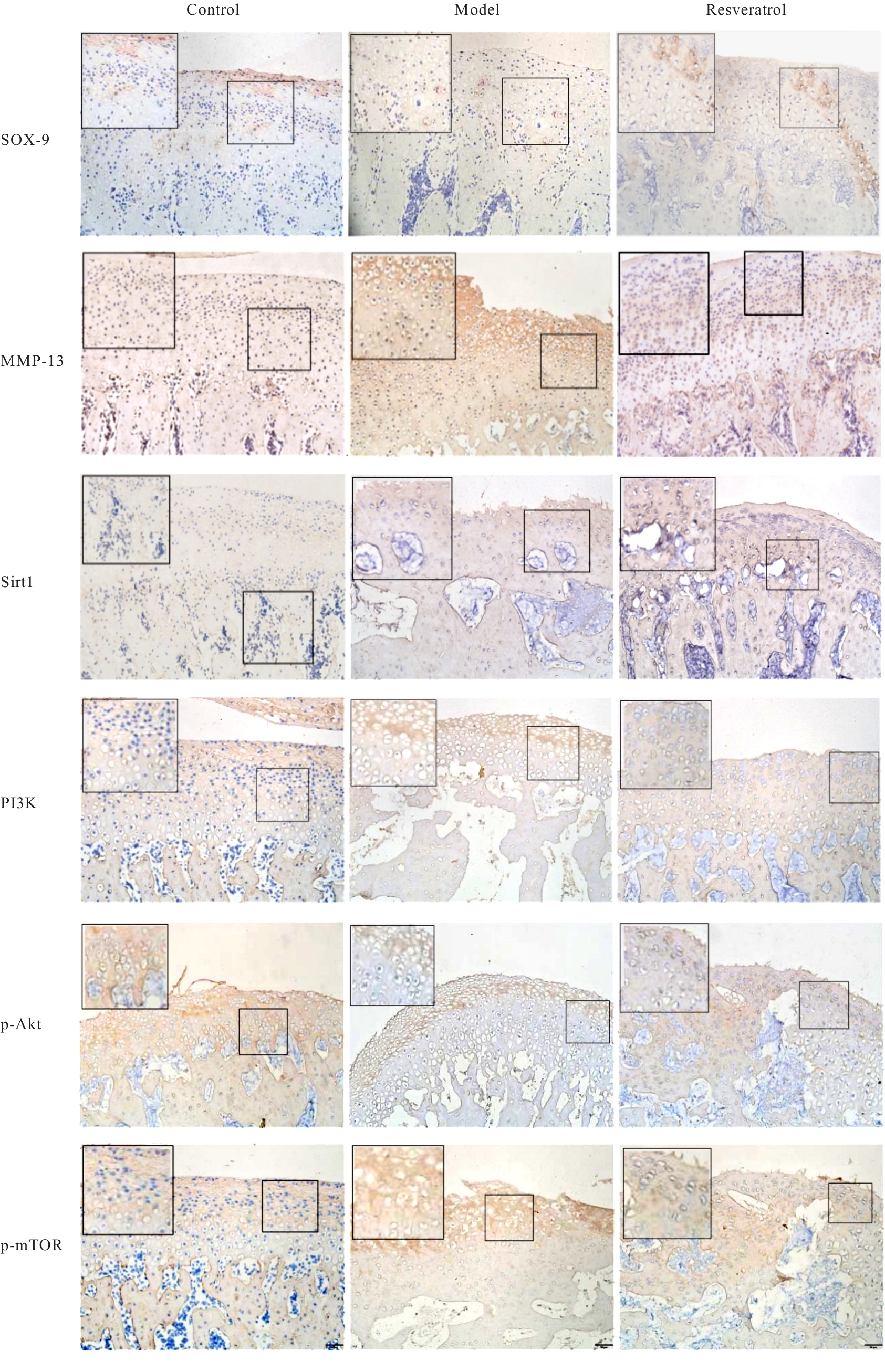
目的 探讨白藜芦醇对颞下颌关节骨关节炎(TMJOA)的治疗作用,并阐明相关作用机制。 方法 45只SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组和白藜芦醇组,每组15只。模型组和白藜芦醇组大鼠关节腔内注射20 g·L-1碘乙酸钠(MIA)50 μL,构建TMJOA大鼠模型;对照组大鼠注射等量生理盐水。造模3周后,白藜芦醇组大鼠注射80 μL白藜芦醇溶液,每周1次,连续3周,对照组和模型组大鼠注射等量生理盐水。微型计算机断层扫描技术(Micro-CT)系统检测各组大鼠髁突结构,计算感兴趣区的骨体积分数(BV/TV)、骨小梁厚度(Tb.Th)、骨小梁间距(Tb.p)和骨小梁数(Tb.N)。HE染色和甲苯胺蓝染色观察各组大鼠颞下颌关节(TMJ)组织病理形态表现,免疫组织化学法检测各组大鼠TMJ组织中性别决定区Y框蛋白(SOX)-9、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-13、沉默信息调节因子(Sirt)1、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)、磷酸化蛋白激酶B(p-Akt)和磷酸化哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(p-mTOR)蛋白表达水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组大鼠TMJ组织中SOX-9、MMP-13、Sirt1、PI3K、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)和蛋白激酶B(Akt)mRNA表达水平。 结果 造模3周后,大鼠髁突骨质破坏明显,表面粗糙不平,延续性中断,表明TMJOA大鼠模型造模成功。Micro-CT系统检测,对照组大鼠髁突表面光滑,形态规则,骨质连续完整;模型组大鼠髁突破坏明显,骨质连续性受到不同程度破坏,表面粗糙可伴有不同程度骨质缺损;白藜芦醇组大鼠髁突病变减轻,髁突形态外观得到一定的改善。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠BV/TV和Tb.Th均明显降低(P<0.05),Tb.Sp明显增加(P<0.05);与模型组比较,白藜芦醇组大鼠BV/TV和Tb.Th均明显升高(P<0.05),Tb.Sp明显减少(P<0.05)。HE染色观察,对照组大鼠髁突层次清晰,软骨细胞排列规则,整齐有序;模型组大鼠髁突表面粗糙不平,缺损明显,呈现典型的TMJOA表现;白藜芦醇组大鼠髁突表面略微粗糙,整体分层大致清晰,细胞排列较为有序。甲苯胺蓝染色观察,对照组大鼠髁突肥大层软骨细胞呈蓝紫色,染色明显且均匀;模型组大鼠髁突肥大层软骨细胞淡染,部分区域甚至失染;白藜芦醇组大鼠髁突肥大细胞层染色基本明显且较为均匀。免疫组织化学法检测,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠TMJ组织中MMP-13、PI3K、p-Akt和p-mTOR蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),SOX-9和Sirt1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,白藜芦醇组大鼠TMJ组织中SOX-9和Sirt1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),MMP-13、PI3K、p-Akt和p-mTOR蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。RT-qPCR法检测,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠TMJ组织中MMP-13、PI3K、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),SOX-9和Sirt1 mRNA表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,白藜芦醇组大鼠TMJ组织中SOX-9和Sirt1 mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),MMP-13、PI3K、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 白藜芦醇对TMJOA有治疗作用,其作用机制可能是通过激活Sirt1、抑制PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路实现的。
中图分类号:
- R684.3