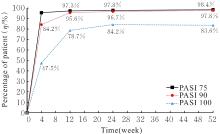
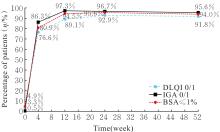
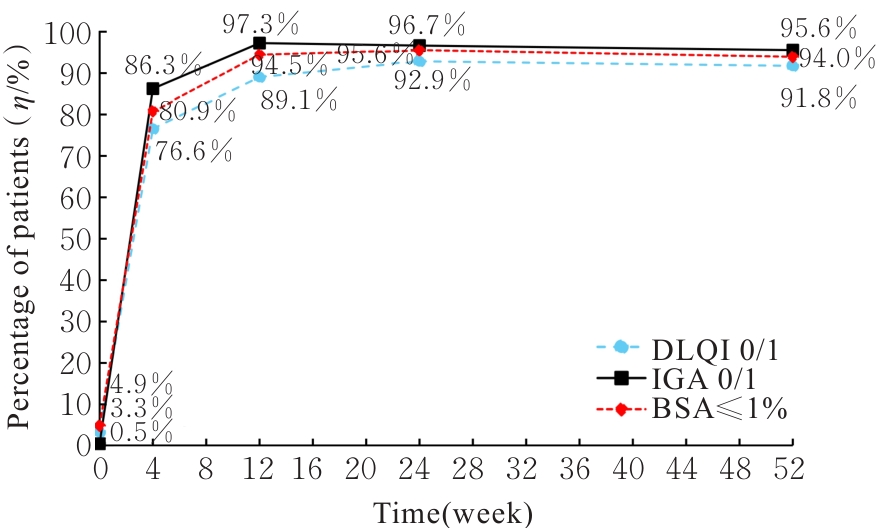
| 1 |
ARMSTRONG A W, READ C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(19): 1945-1960.
|
| 2 |
FURUE M, FURUE K, TSUJI G, et al. Interleukin-17A and keratinocytes in psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(4): 1275.
|
| 3 |
中华医学会皮肤性病学分会银屑病专业委员会. 中国银屑病诊疗指南(2023版)[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2023, 56(7): 573-625.
|
| 4 |
FRIEDER J, KIVELEVITCH D, MENTER A. Secukinumab: a review of the anti-IL-17A biologic for the treatment of psoriasis[J]. Ther Adv Chronic Dis, 2018, 9(1): 5-21.
|
| 5 |
CAI L, ZHANG J Z, YAO X, et al. Secukinumab demonstrates high efficacy and a favorable safety profile over 52 weeks in Chinese patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis[J]. Chin Med J, 2020, 133(22): 2665-2673.
|
| 6 |
TADA Y, MORITA A, YAMANAKA K, et al. Real-world retention rates and effectiveness of secukinumab in psoriasis: results from a multicenter cohort study (RAILWAY)[J]. J Dermatol, 2023, 50(11): 1415-1426.
|
| 7 |
KIM B S, KIM D H, SHIN B S, et al. Real-world safety and effectiveness of secukinumab in adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results from postmarketing surveillance in Korea[J]. Ther Adv Chronic Dis, 2024, 15: 20406223241230180.
|
| 8 |
GALLUZZO M, TALAMONTI M, SIMONE C D, et al. Secukinumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a multi-center, retrospective, real-life study up to 52 weeks observation[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2018, 18(7): 727-735.
|
| 9 |
ORTIZ-SALVADOR J M, SANELEUTERIO-TEMPORAL M, MAGDALENO-TAPIAL J, et al. A prospective multicenter study assessing effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in a real-life setting in 158 patients[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2019, 81(2): 427-432.
|
| 10 |
ROMPOTI N, SIDIROPOULOU P, PANAGAKIS P, et al. Real-world data from a single Greek centre on the use of secukinumab in plaque psoriasis: effectiveness, safety, drug survival, and identification of patients that sustain optimal response[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2020, 34(6): 1240-1247.
|
| 11 |
STROBER B, GREENBERG J D, KARKI C, et al. Impact of psoriasis severity on patient-reported clinical symptoms, health-related quality of life and work productivity among US patients: real-world data from the Corrona Psoriasis Registry[J]. BMJ Open, 2019, 9(4): e027535.
|
| 12 |
KIM J, BISSONNETTE R, LEE J, et al. The spectrum of mild to severe psoriasis vulgaris is defined by a common activation of IL-17 pathway genes, butwith key differences in immune regulatory genes[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2016, 136(11): 2173-2182.
|
| 13 |
ZHOU J, YUAN Y, LIU Y H, et al. Effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in Chinese patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in real-world practice[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2024, 33(1): e14890.
|
| 14 |
NOTARIO J, DEZA G, VILARRASA E, et al. Treatment of patients with plaque psoriasis with secukinumab in a real-life setting: a 52-week, multicenter, retrospective study in Spain[J]. J Dermatolog Treat, 2019, 30(5): 424-429.
|
| 15 |
CHIRICOZZI A, BALATO A, CONRAD C, et al. Secukinumab demonstrates improvements in absolute and relative psoriasis area severity indices in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: results from a European, multicentric, retrospective, real-world study[J]. J Dermatolog Treat, 2020, 31(5): 476-483.
|
| 16 |
ZWEEGERS J, ROOSENBOOM B, VAN DE KERKHOF P C, et al. Frequency and predictors of a high clinical response in patients with psoriasis on biological therapy in daily practice: results from the prospective, multicenter BioCAPTURE cohort[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2017, 176(3): 786-793.
|
| 17 |
GOTTLIEB A B, DEODHAR A, MCINNES I B, et al. Long-term safety of secukinumab over five years in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: update on integrated pooled clinical trial and post-marketing surveillance data[J]. Acta Derm Venereol, 2022, 102: adv00698.
|
| 18 |
ESHWAR V, KAMATH A, SHASTRY R, et al. A review of the safety of interleukin-17A inhibitor secukinumab[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2022, 15(11): 1365.
|
| 19 |
YIN Y F, WANG M J, LIU M R, et al. Efficacy and safety of IL-17 inhibitors for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2020, 22(1): 111.
|
| 20 |
AL-JANABI A, FOULKES A C, MASON K, et al. Phenotypic switch to eczema in patients receiving biologics for plaque psoriasis: a systematic review[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2020, 34(7): 1440-1448.
|
 )
)