吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 610-620.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250306
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
骨髓来源的间充质干细胞移植通过ROS/Nrf2信号对血管性痴呆大鼠线粒体自噬的影响及其机制
孙烈乾1,顾梦宇1,杨杰2,王凯漪1,郭高帅1,3,张宏博1,3,张思怡1,3,王堂龙3,杨志伟1,3,贺延妮1,3,杨超1,3( )
)
- 1.湖北中医药大学第一临床学院, 湖北 武汉 430065
2.湖北省中医院肿瘤科,湖北 武汉 430061
3.湖北省中西医结合医院老年病科,湖北 武汉 430015
Effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on mitochondrial autophagy in rats with vascular dementia through ROS/Nrf2 signaling and its mechanism
Lieqian SUN1,Mengyu GU1,Jie YANG2,Kaiyi WANG1,Gaoshuai GUO1,3,Hongbo ZHANG1,3,Siyi ZHANG1,3,Tanglong WANG3,Zhiwei YANG1,3,Yanni HE1,3,Chao YANG1,3( )
)
- 1.First Clinical Medical College,Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,Wuhan 430065,China
2.Department of Oncology,Hubei Provincial Hospital of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine,Wuhan 430061,China
3.Department of Geriatrics,Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan 430015,China
摘要:
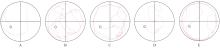
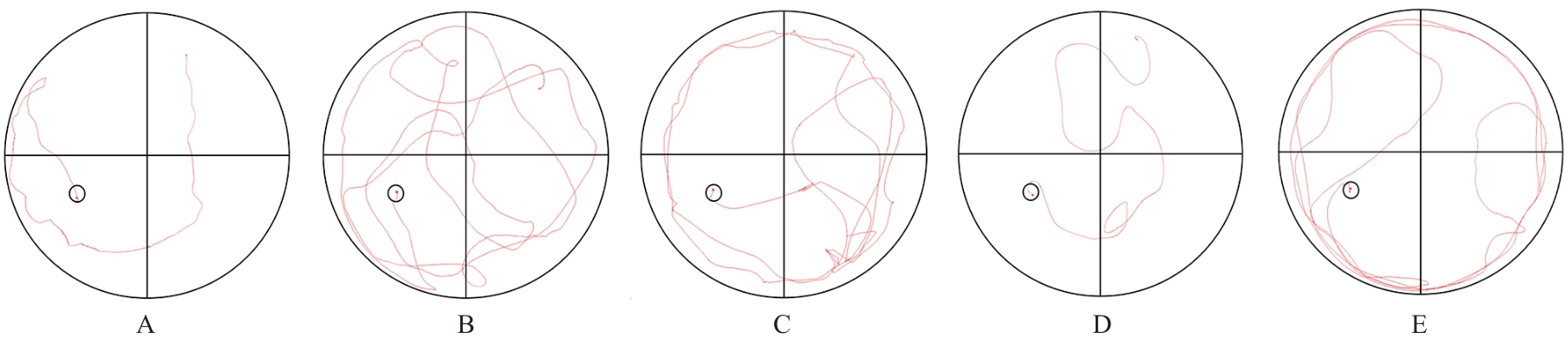
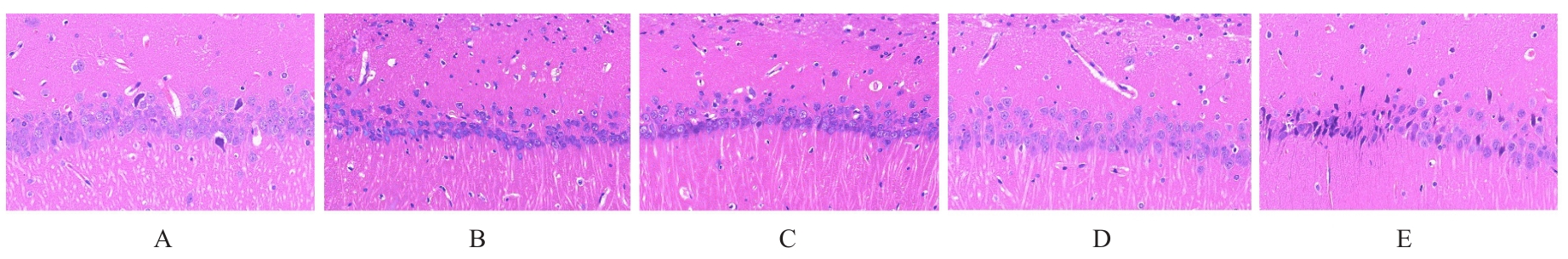
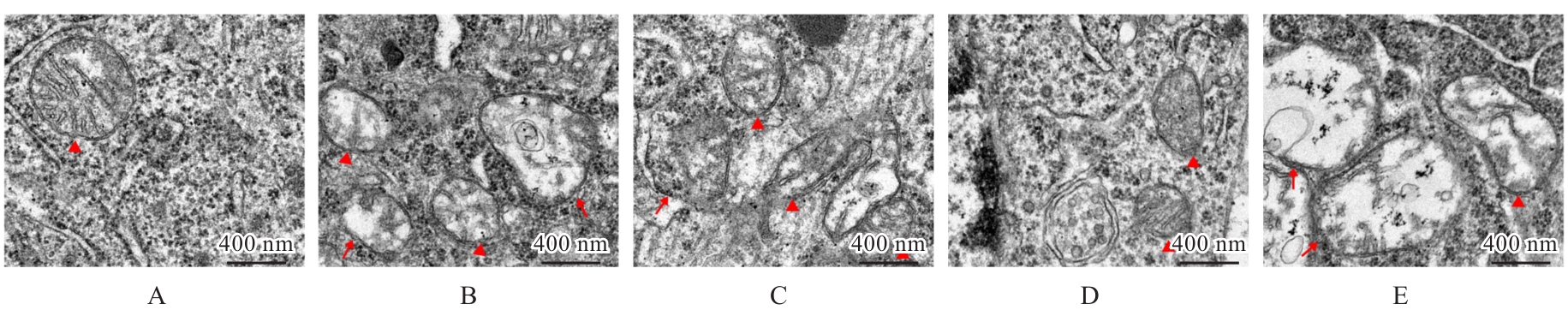
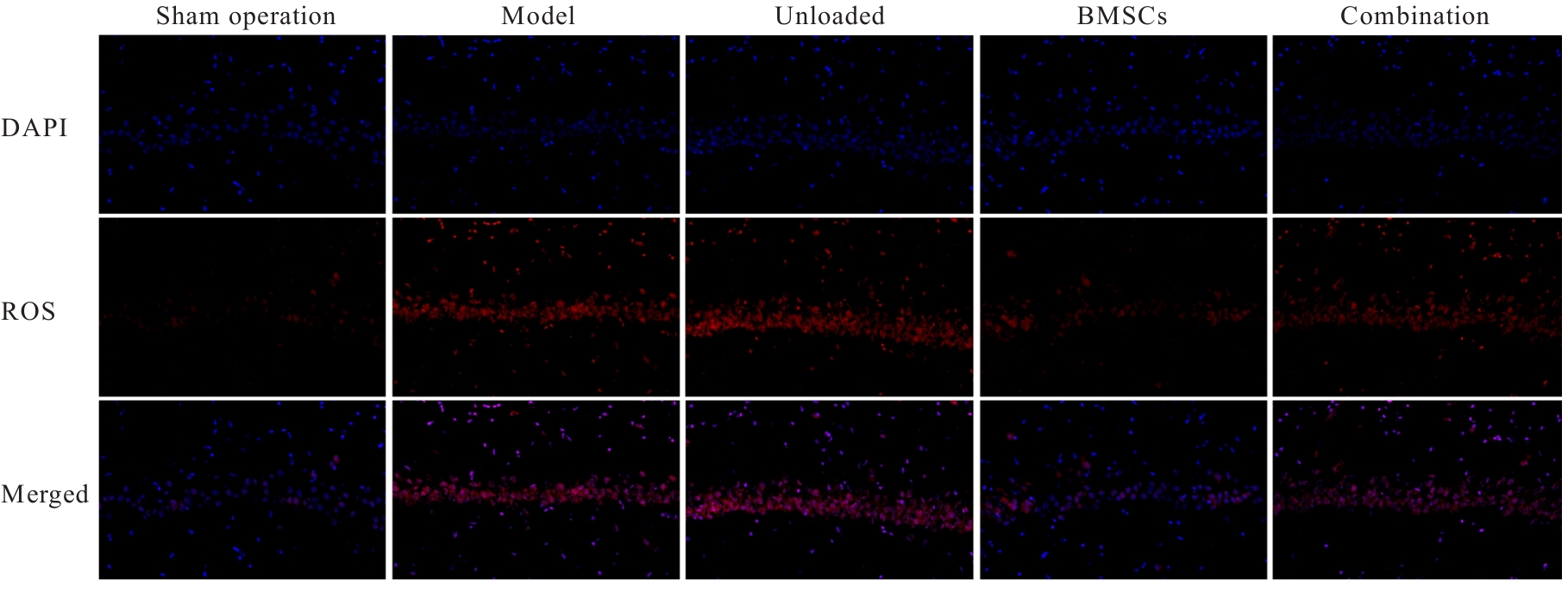
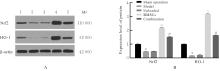
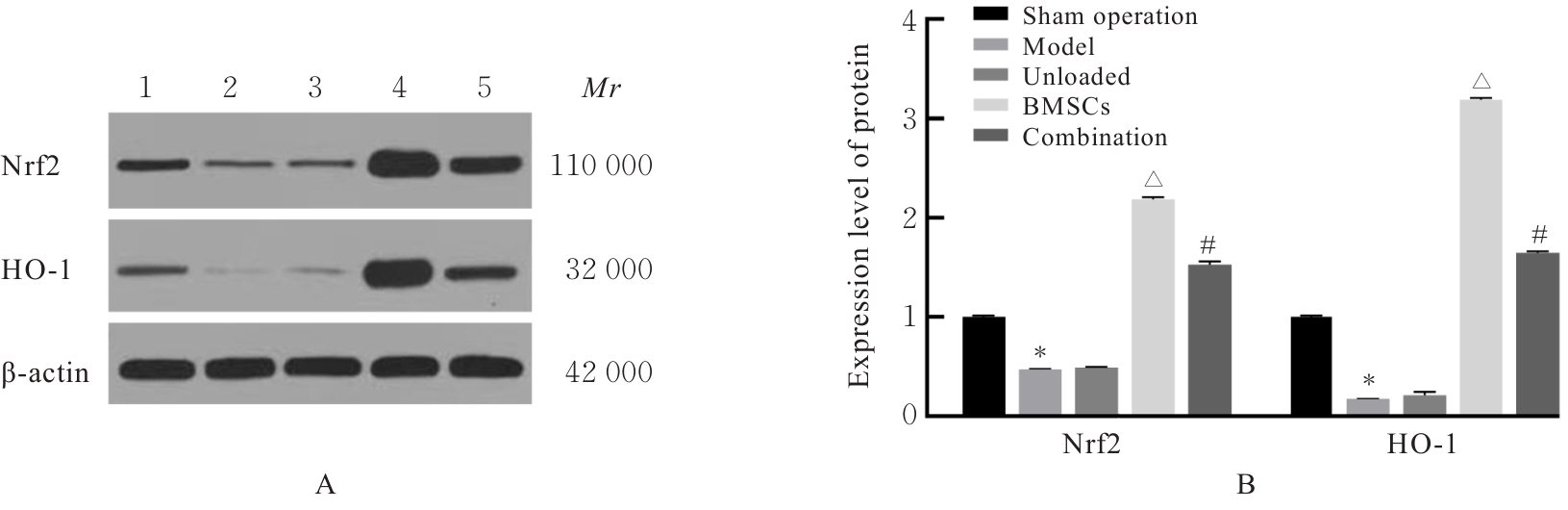
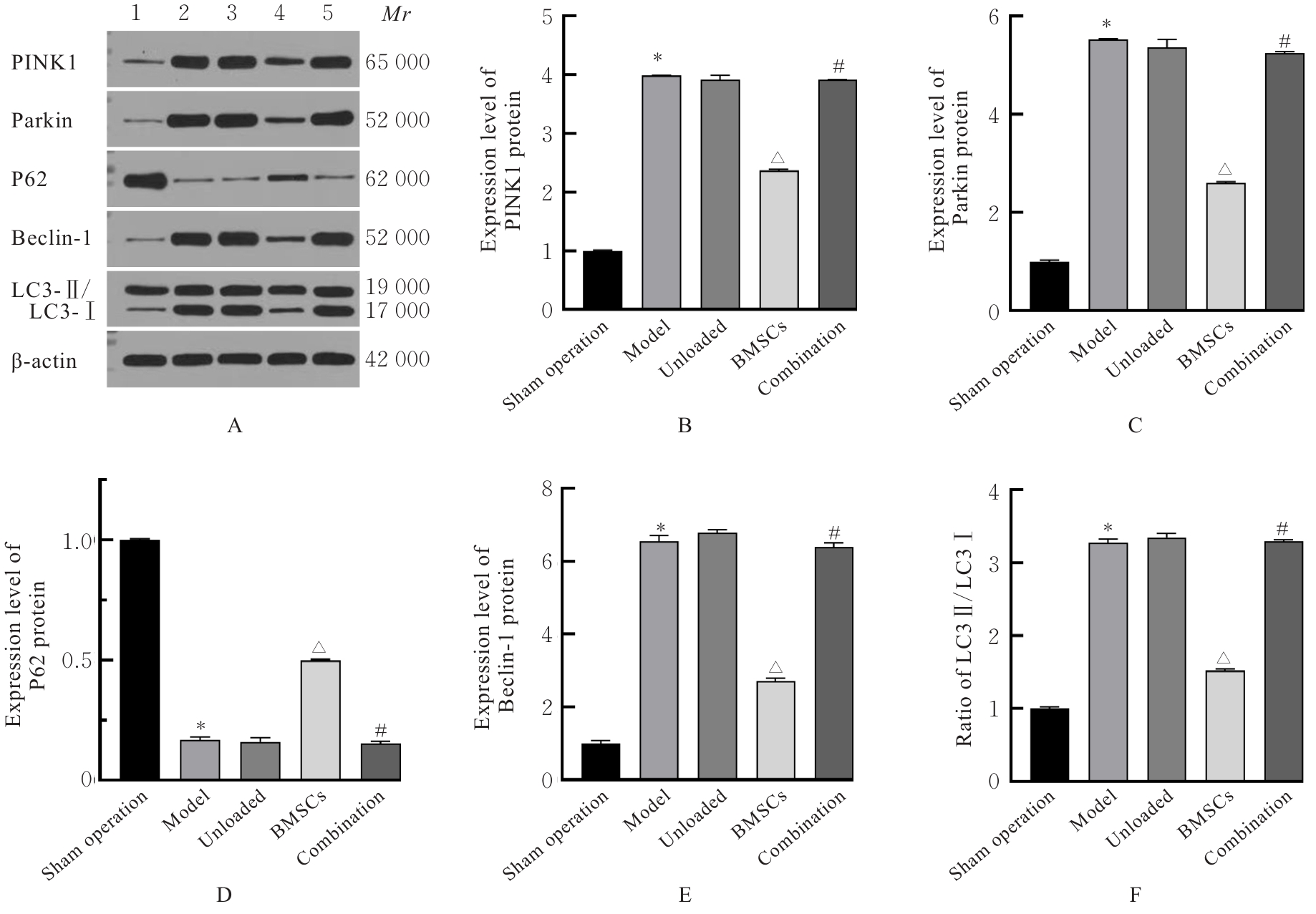
目的 探讨骨髓来源的间充质干细胞(BMSCs)移植通过活性氧(ROS)/核因子E2相关因子2(Nrf2)信号对血管性痴呆(VaD)大鼠线粒体自噬的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 将45只SD雄性成年大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、空载组、BMSCs组和BMSCs+ML385(Nrf2抑制剂)组(联合组),每组9只。各组大鼠腹腔注射麻醉后,除假手术组外,其余各组大鼠制备VaD模型。采用Morris水迷宫实验检测各组大鼠的学习记忆能力,HE染色观察各组大鼠脑组织病理形态表现,尼氏染色观察各组大鼠脑组织海马区尼氏体变化情况,透射电镜观察各组大鼠脑组织海马区超微结构,荧光探针法检测各组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元中ROS水平,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠脑组织中Nrf2、血红素加氧酶1(HO-1)、磷酸酶与张力蛋白同源物诱导激酶1(PINK1)、E3泛素蛋白连接酶parkin(Parkin)、苄氯素1(Beclin-1)和泛素结合蛋白P62(P62)蛋白表达水平及微管相关蛋白1A/1B轻链3(LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ)比值。 结果 Morris水迷宫实验,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠逃避潜伏期明显延长(P<0.01),穿越原平台次数和停留时间均明显减少(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BMSCs组大鼠逃避潜伏期明显缩短(P<0.01),穿越原平台次数和停留时间均明显增加(P<0.01);与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠逃避潜伏期明显延长(P<0.01),穿越原平台次数和停留时间均明显减少(P<0.01)。HE染色观察,假手术组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元数量和形态正常,染色均匀,结构清晰,未见明显病变;与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑组织海马区组织稀疏,结构紊乱,神经元数量减少且形态不一,染色不均匀,核固缩,可见部分坏死的神经元;与模型组比较,空载组大鼠脑组织海马区可见组织结构紊乱、神经元减少和染色不均等损伤表现,BMSCs组大鼠海马区神经元损伤减轻,形态恢复正常,排列较为整齐,神经元丢失情况明显改善;与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠海马区神经元形态不规则,组织结构紊乱,细胞边界不清,染色不均匀,核固缩。尼氏染色观察,假手术组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元排列整齐紧密,形态规则完整,核仁明显,尼氏小体着色深且数量多;与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元固缩,呈空泡状,尼氏小体着色少且数量稀少;与模型组比较,空载组大鼠脑组织海马区可见尼氏小体着色少且数量稀少等损伤表现,BMSCs组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元固缩减少,细胞形态相对完整,尼氏小体数量相对增多;与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠脑组织神经元固缩,形态完整性丧失,尼氏小体破碎且数量减少。透射电镜观察,假手术组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元线粒体呈椭圆形,双层膜结构清晰可见,内部嵴完整;与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元线粒体肿胀变形,双层膜结构破坏,内部嵴断裂消失,结构模糊,胞质中可见大量自噬小体;与模型组比较,空载组大鼠脑组织海马区线粒体损伤表现仍较明显,胞质中自噬小体数量较多,BMSCs组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元线粒体膜和内部结构有明显改善,损伤程度减轻,胞质中可见少量自噬小体;与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元线粒体肿胀,双层膜结构破坏,内部嵴断裂消失,胞质中可见自噬小体。荧光探针法,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元中ROS水平明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BMSCs组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元中ROS水平明显降低(P<0.01);与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠脑组织海马区神经元中ROS水平明显升高(P<0.01)。Western blotting法,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BMSCs组大鼠脑组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01);与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠脑组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑组织中Parkin、PINK1和Beclin-1蛋白表达水平及LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值均明显升高(P<0.01),P62蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BMSCs组大鼠脑组织中Parkin、PINK1和Beclin-1蛋白表达水平及LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值均明显降低(P<0.01),P62蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与BMSCs组比较,联合组大鼠脑组织中Parkin、PINK1和Beclin-1蛋白表达水平及LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值均明显升高(P<0.01),P62蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。 结论 BMSCs可以减轻大鼠脑组织海马区神经元病理改变,改善VaD大鼠的认知功能,其作用机制可能与调控ROS/Nrf2信号通路抑制线粒体自噬有关。
中图分类号:
- R743.9