吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 682-690.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230317
缺氧条件下HIF-1α/ROS对肺癌A549细胞凋亡和侵袭的作用及其机制
- 1.湖北省武汉市第三医院 武汉大学附属同仁医院呼吸与危重症医学科, 湖北 武汉 430070
2.湖北省武汉市第三医院 武汉大学附属同仁医院血液透析室, 湖北 武汉 430070
Effects of HIF-1α/ROS on apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer A549 cells under hypoxia and its mechanism
Bo HUANG1( ),Jie DING2,Hongrong GUO1,Hongjuan WANG1,Jianqun XU1,Quan ZHENG1
),Jie DING2,Hongrong GUO1,Hongjuan WANG1,Jianqun XU1,Quan ZHENG1
- 1.Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,Wuhan Third Hospital,Hubei Province,Affiliated Tongren Hospital,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430070,China
2.Hemodialysis Room,Wuhan Third Hospital,Hubei Province,Affiliated Tongren Hospital,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430070,China
摘要:
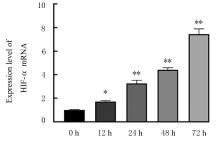
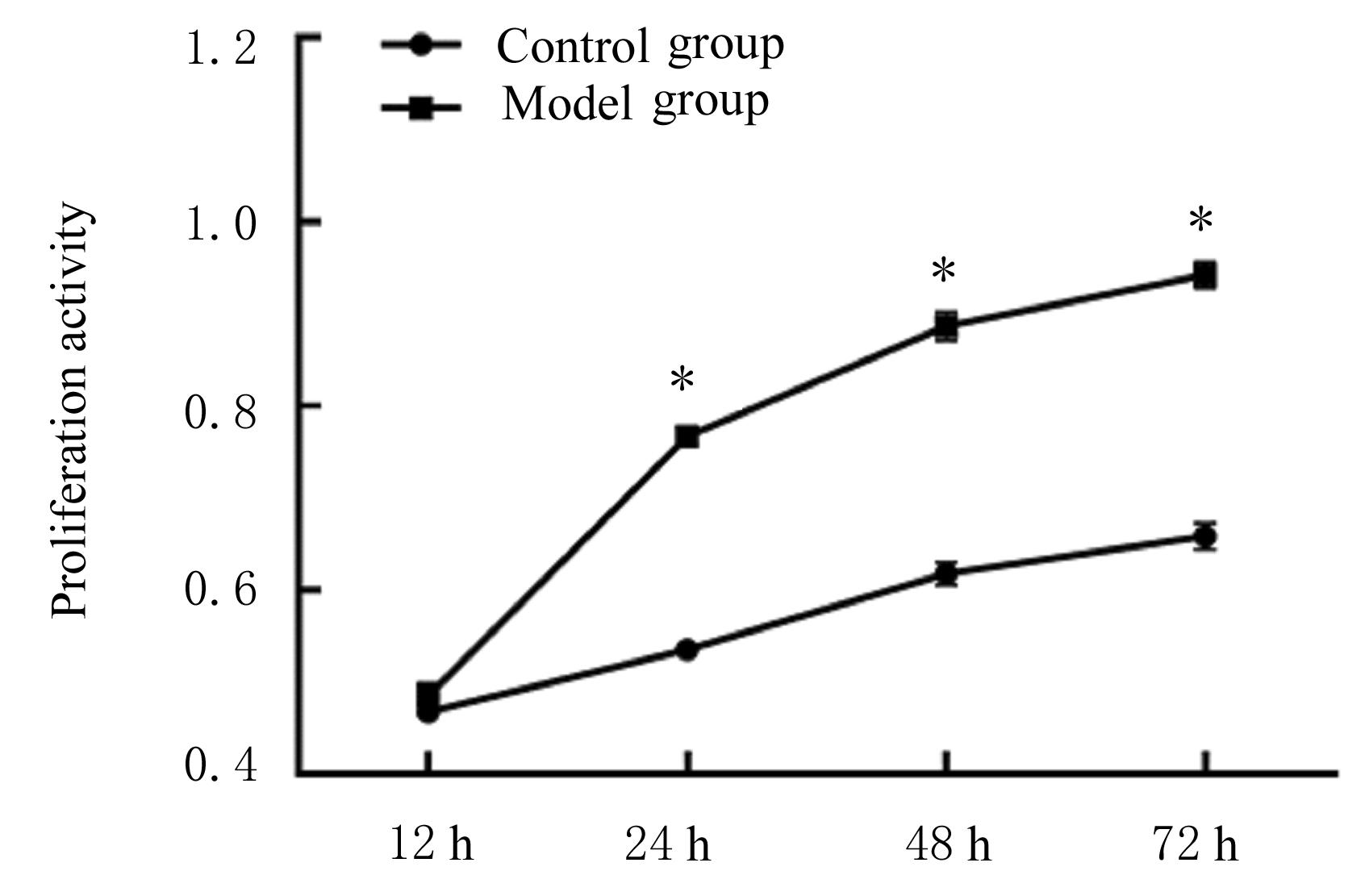
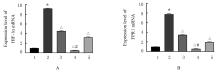
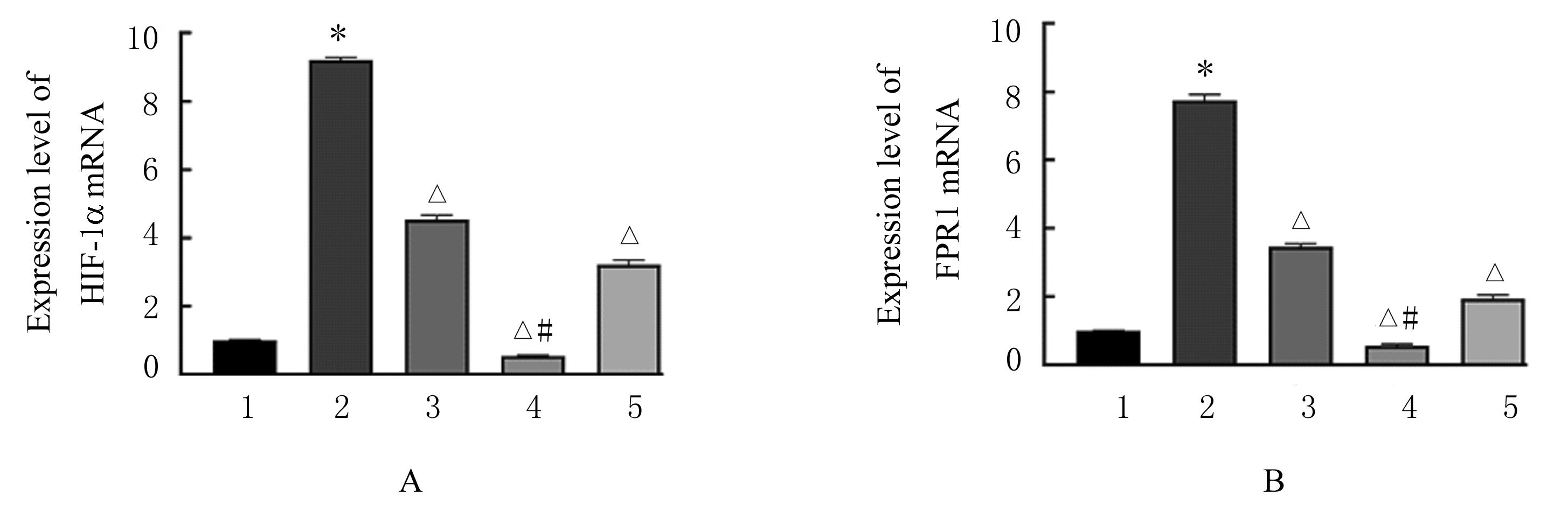
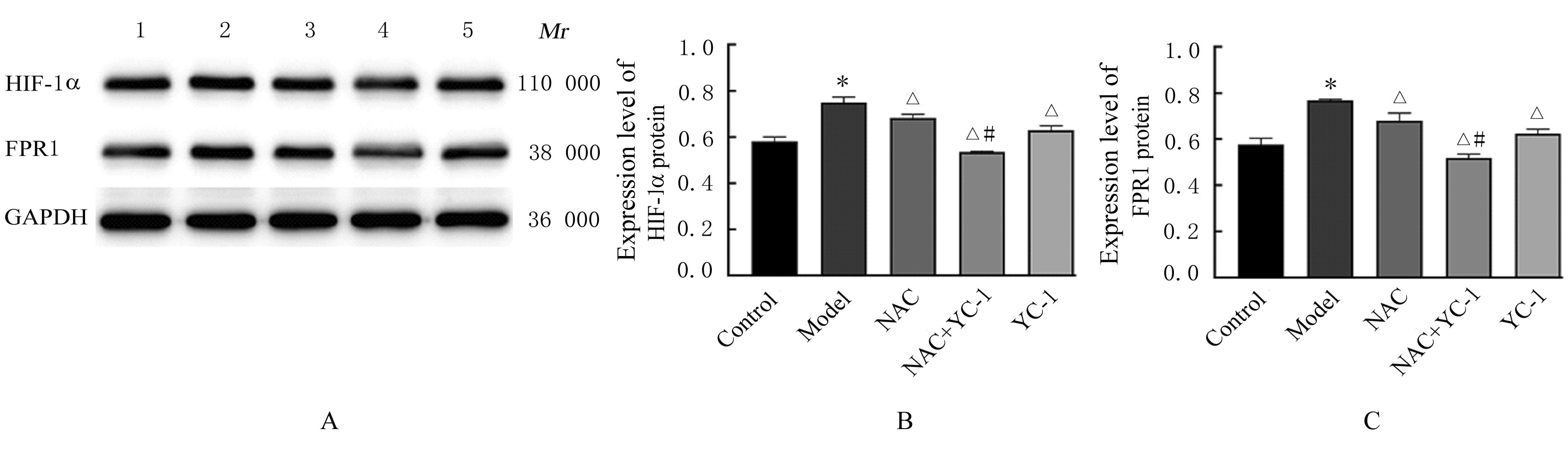
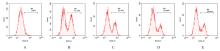
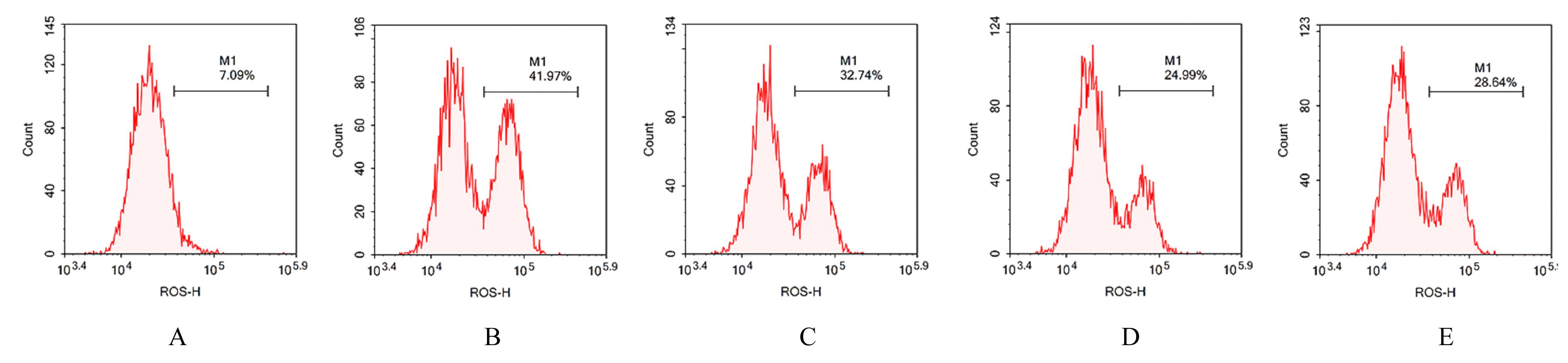
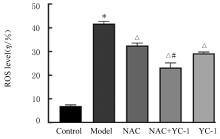
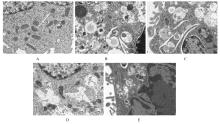
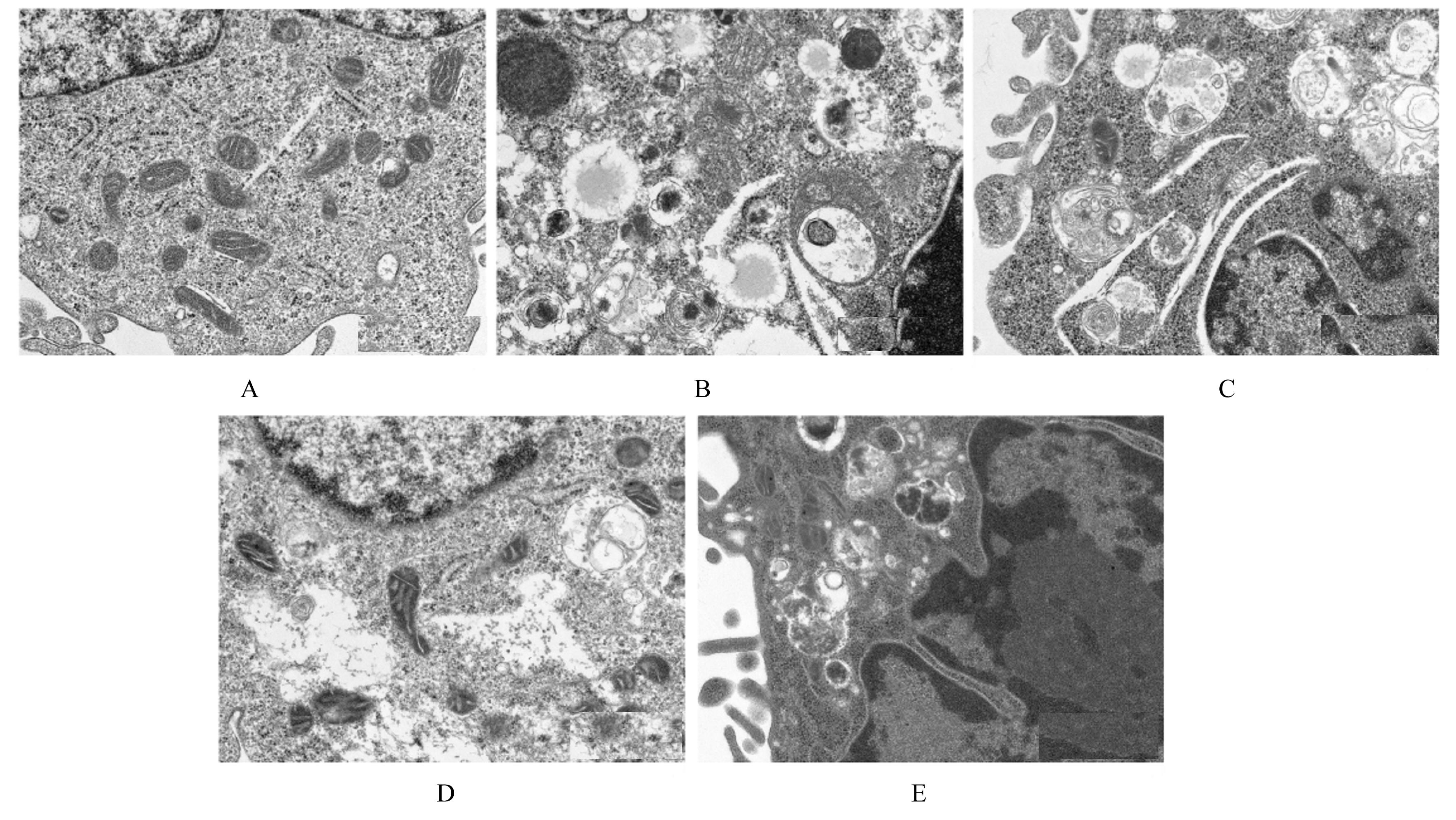
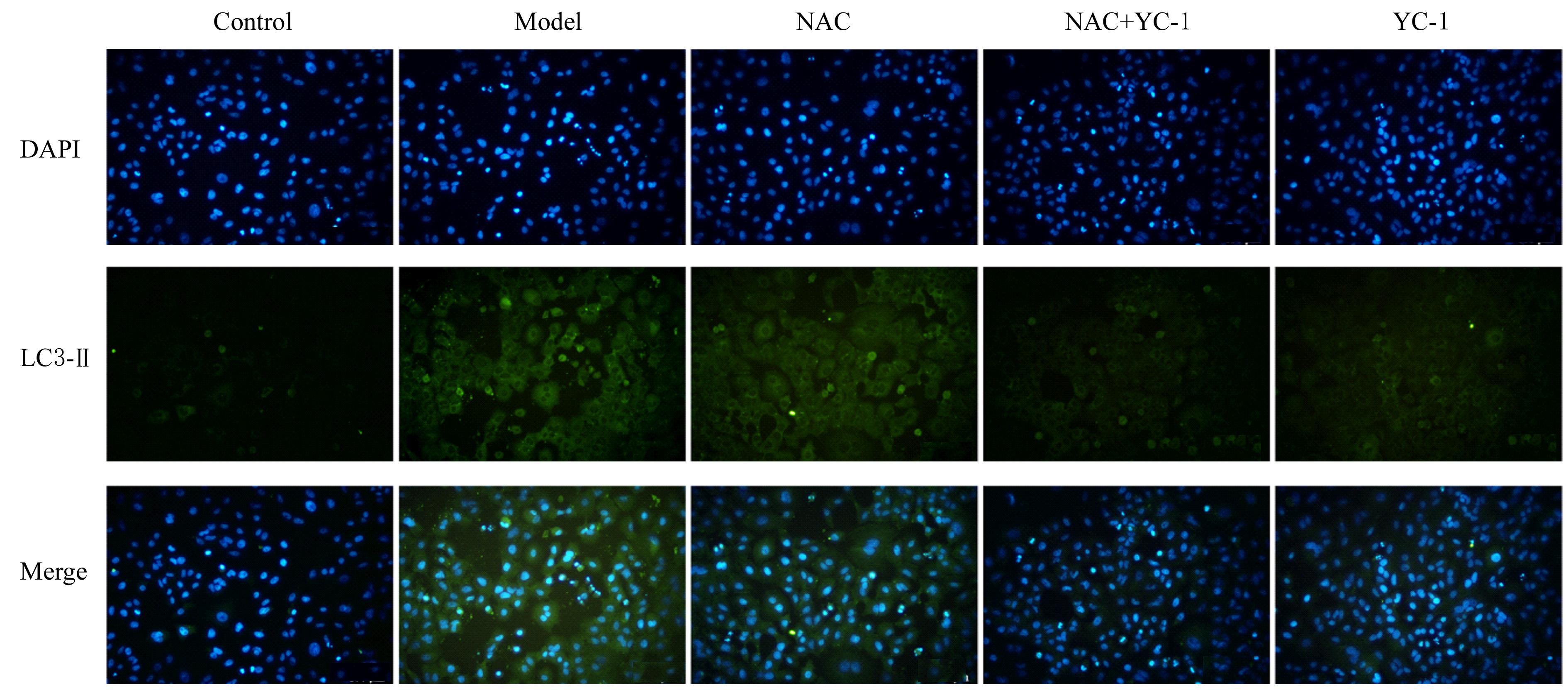
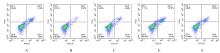
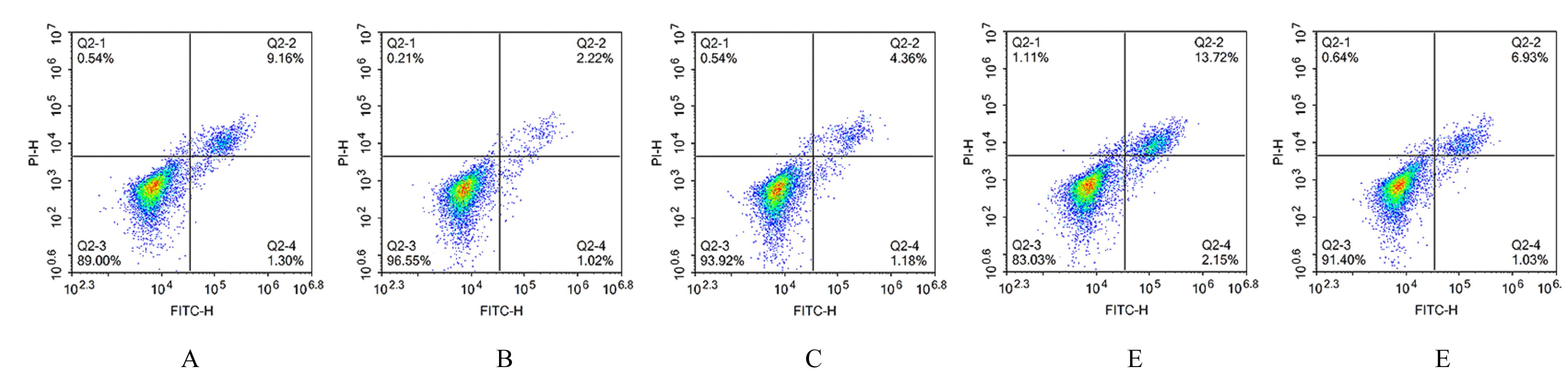
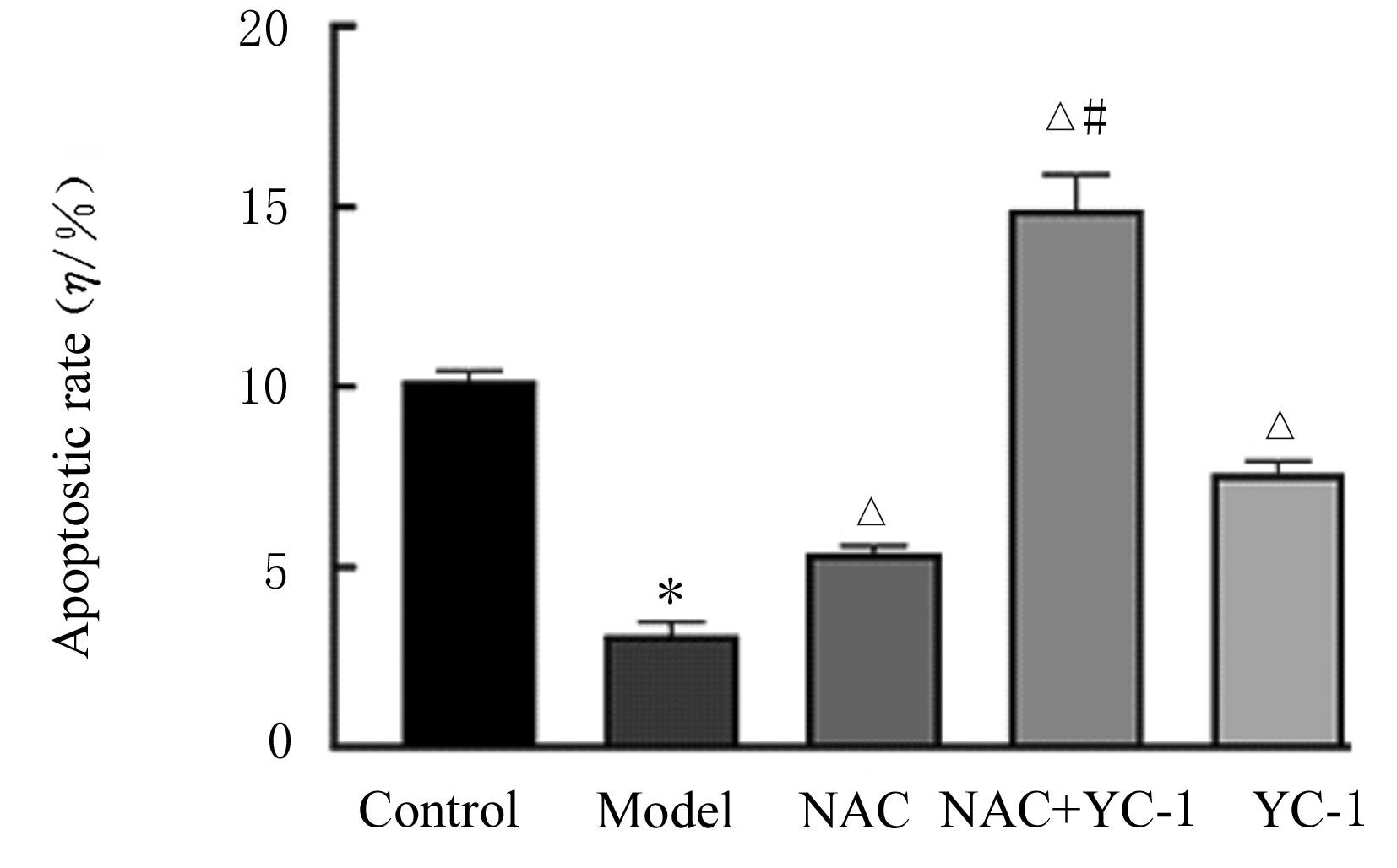
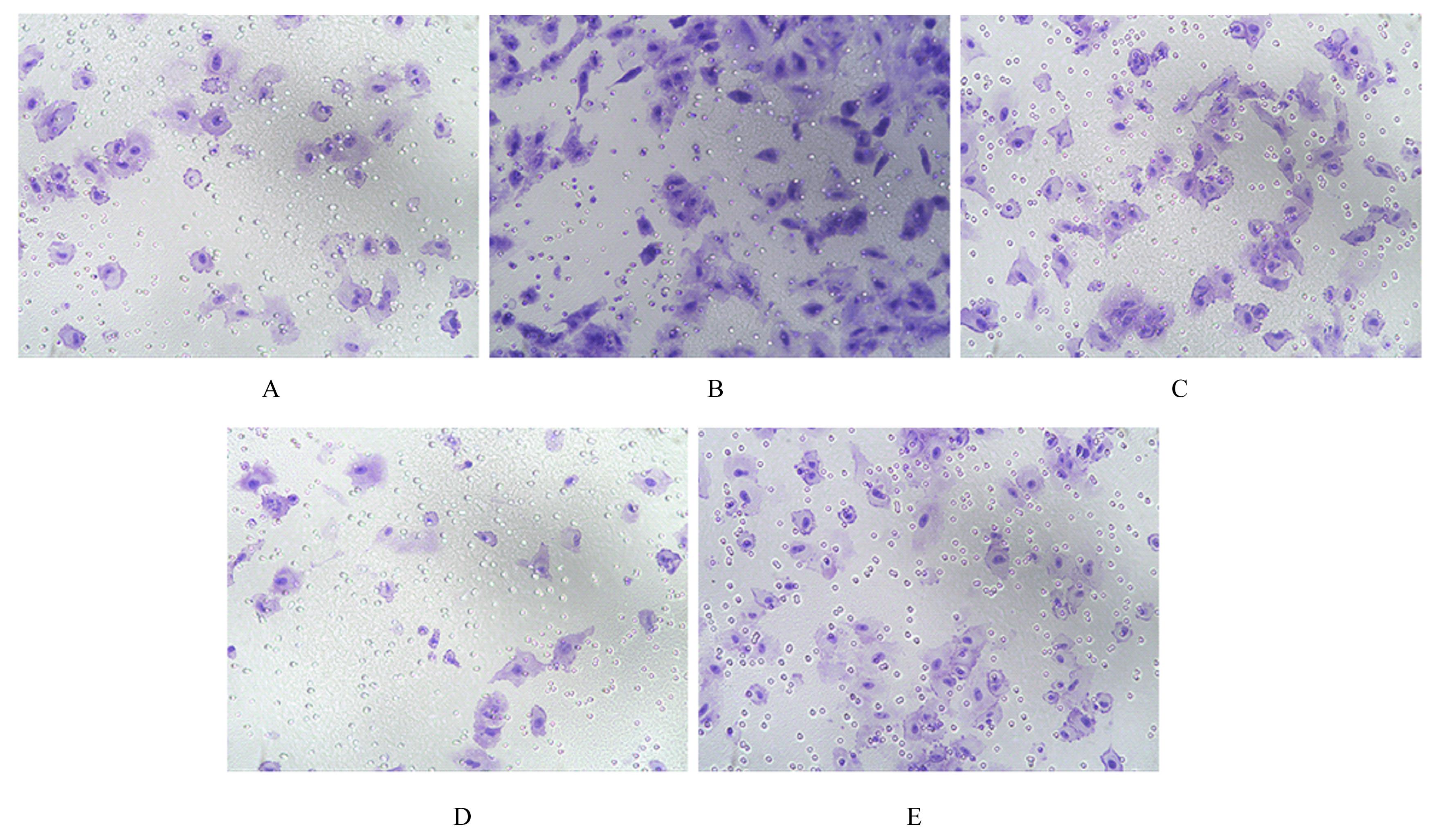
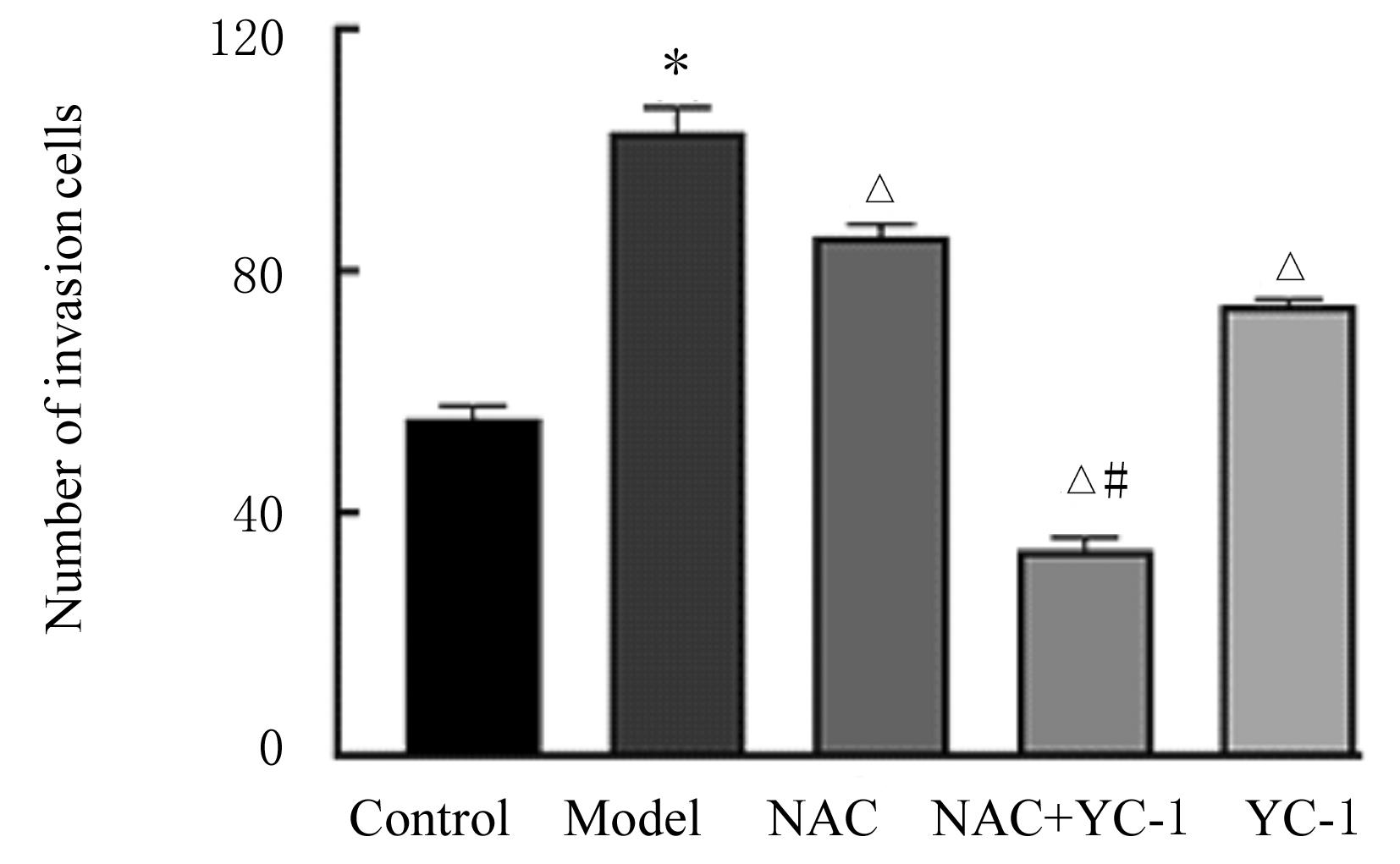
目的 探讨缺氧条件下缺氧诱导因子1α(HIF-1α)/活性氧(ROS)对非小细胞肺癌A549细胞凋亡和侵袭的作用,并阐明其相关机制。 方法 将A549细胞置于缺氧条件下培养12、24、48和72 h,构建缺氧细胞模型,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测不同处理时间细胞中HIF-1α mRNA表达水平,CCK-8法检测细胞增殖能力,鉴定缺氧细胞模型并确定最佳诱导时间。将A549细胞分为对照组(21%O2)、模型组(缺氧诱导)、N-乙酰半胱氨酸(NAC)组(20 mmol·L-1 NAC)、NAC+利非西呱(YC-1)组(20 mmol·L-1 NAC+100 μmol·L-1 YC-1)和YC-1组(100 μmol·L-1 YC-1)。RT-qPCR和Western blotting法检测各组细胞中HIF-1α和人甲酰肽受体1(FPR1) mRNA及蛋白表达水平,流式细胞术检测各组细胞中ROS水平,透射电镜观察各组细胞自噬体结构,免疫荧光法检测各组细胞中微管相关轻链3Ⅱ(LC3-Ⅱ)表达情况,流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率,Transwell小室实验检测各组侵袭细胞数。 结果 随着低氧诱导时间的延长,A549细胞中HIF-1α mRNA表达水平和细胞增殖能力均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),最佳低氧诱导时间为24 h。RT-qPCR和Western blotting法检测,与对照组比较,模型组细胞中HIF-1α和FPR1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,NAC组、NAC+YC-1组和YC-1组细胞中HIF-1α和FPR1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01);与NAC组比较,NAC+YC-1组细胞中HIF-1α和FPR1 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。流式细胞术检测,与对照组比较,模型组细胞中ROS水平明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,NAC组、NAC+YC-1组和YC-1组细胞中ROS水平均明显降低(P<0.01);与NAC组比较,NAC+YC-1组细胞中ROS水平明显降低(P<0.01)。透射电镜观察,对照组细胞中细胞器结构完整,未见自噬体结构;模型组细胞中可见大量自噬体和明显空泡,细胞中细胞器被降解;与模型组比较,NAC组、NAC+YC-1组和YC-1组细胞中自噬体减少,其中NAC+YC-1组细胞中自噬体最少。免疫荧光法检测,与对照组比较,模型组细胞中LC3-Ⅱ表达强度明显增加;与模型组比较,NAC组、NAC+YC-1组和YC-1组细胞中LC3-Ⅱ表达强度明显减少。流式细胞术检测,与对照组比较,模型组细胞凋亡率明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,NAC组、NAC+YC-1组和YC-1组细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.01);与NAC组比较,NAC+YC-1细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.01)。Transwell小室实验检测,与对照组比较,模型组侵袭细胞数明显增加(P<0.01);与模型组比较,NAC组、NAC+YC-1组和YC-1组侵袭细胞数均明显减少(P<0.01);与NAC组比较,NAC+YC-1组侵袭细胞数明显减少(P<0.01)。 结论 缺氧条件下抑制HIF-1α/ROS可促进肿瘤细胞凋亡,并抑制细胞侵袭,其作用机制与抑制肺癌细胞自噬有关。
中图分类号:
- R734.2