吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 948-957.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250411
藏红花醛对体外高糖诱导的大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖、迁移和表型转变的抑制作用
高逸璇1,2,汪鹏1,2,张思龙3,高瑞娟4,马莹芳1,2,张可可1,2,冯丹1,2,黄宗奇1,2,马克涛1,2,李丽1,5,司军强1,2( )
)
- 1.石河子大学医学院新疆地方与民族高发病教育部重点实验室,新疆 石河子 832002
2.石河子大学医学院生理学教研室,新疆 石河子 832002
3.新疆维吾尔自治区昌吉州人民医院普外二科,新疆 昌吉 831100
4.石河子大学第一附属医院放射科,新疆 石河子 832002
5.嘉兴大学医学院生理学教研室,浙江 嘉兴 314000
Inhibitory effect of safranal on proliferation, migration and phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells of rats induced by high glucose in vitro
Yixuan GAO1,2,Peng WANG1,2,Silong ZHANG3,Ruijuan GAO4,Yingfang MA1,2,Keke ZHANG1,2,Dan FENG1,2,Zongqi HUANG1,2,Ketao MA1,2,Li LI1,5,Junqiang SI1,2( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Endemic and Ethnic Diseases,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832002,China
2.Department of Physiology,School of Medical Sciences,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832002,China
3.Department of General Surgery,Changji People’s Hospital,Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture,Xinjiang 831100,China
4.Department of Radiology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832002,China
5.Department of Physiology,School of Medical Sciences,Jiaxing University,Jiaxing 314000,China
摘要:
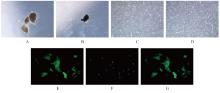
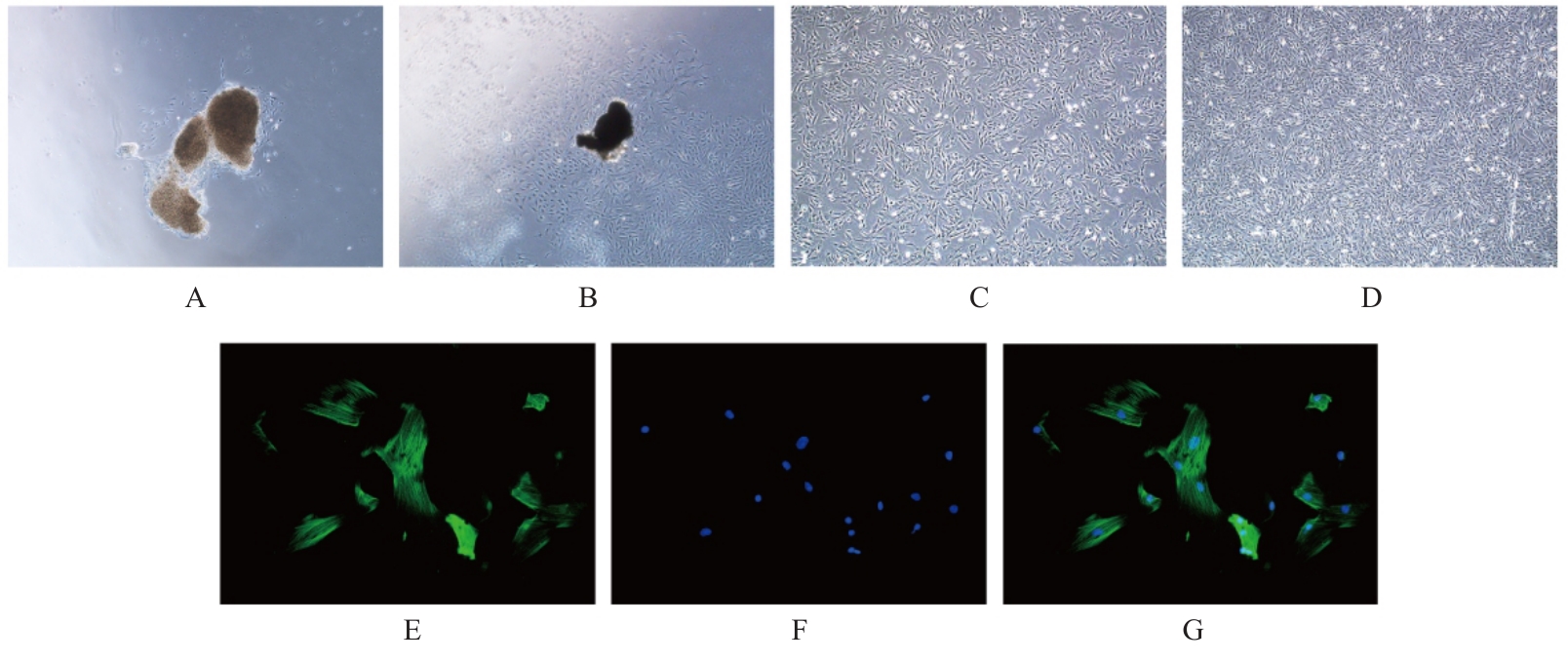
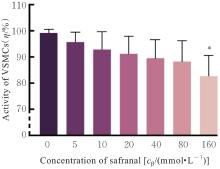
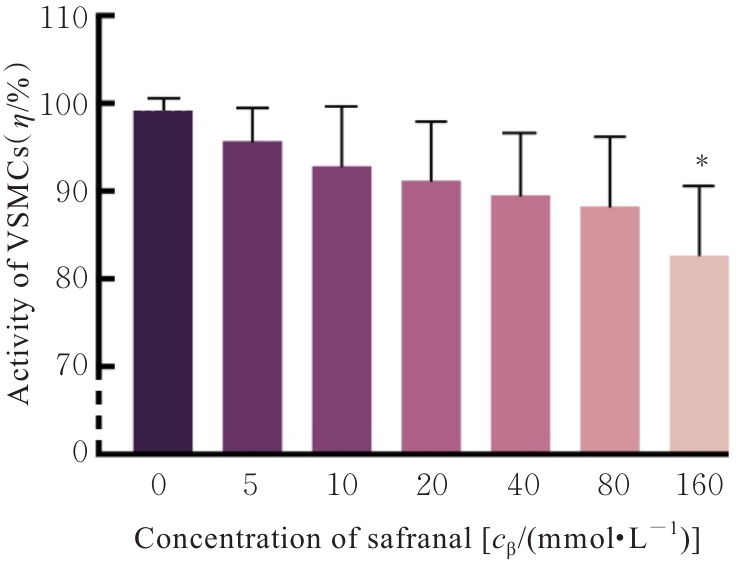
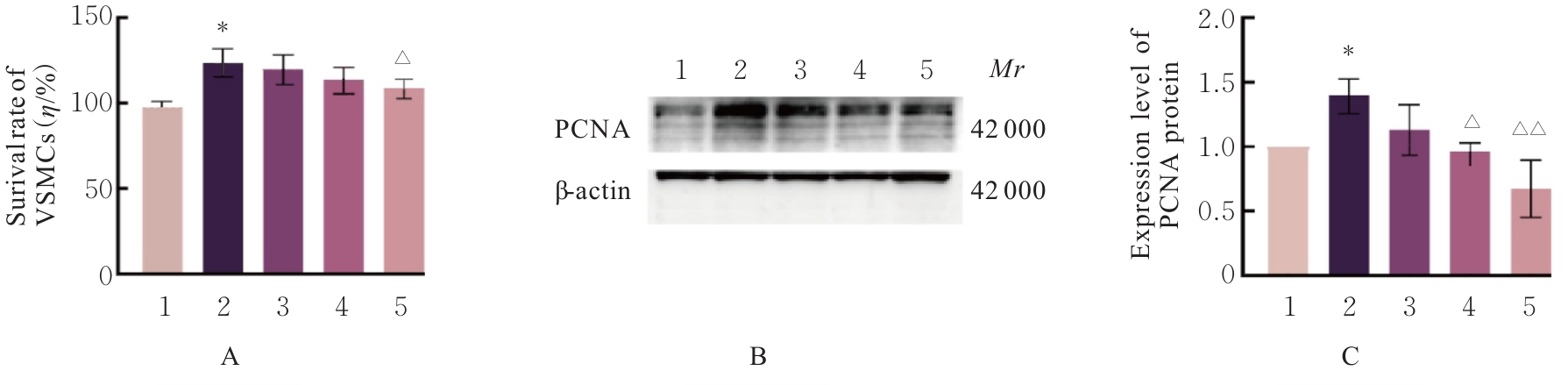
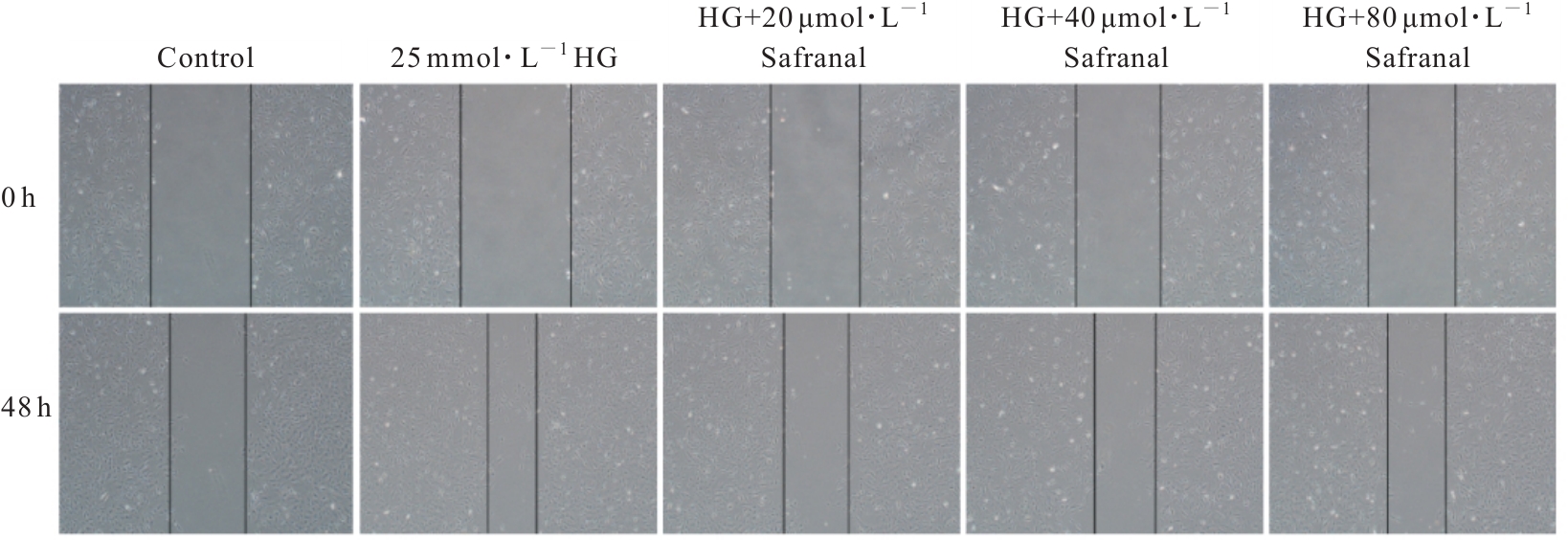
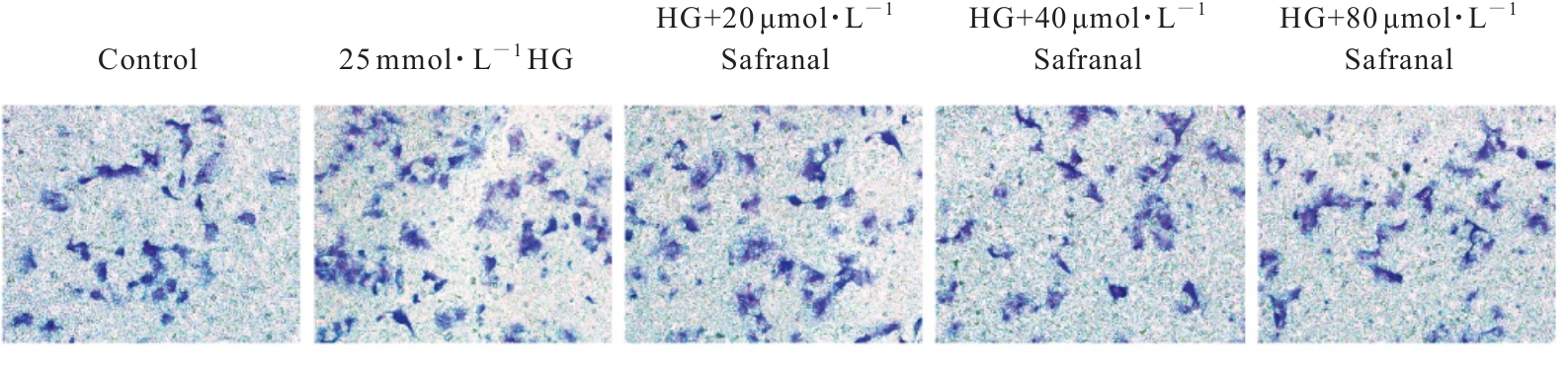
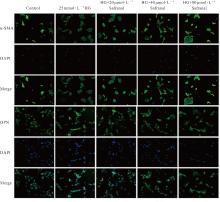
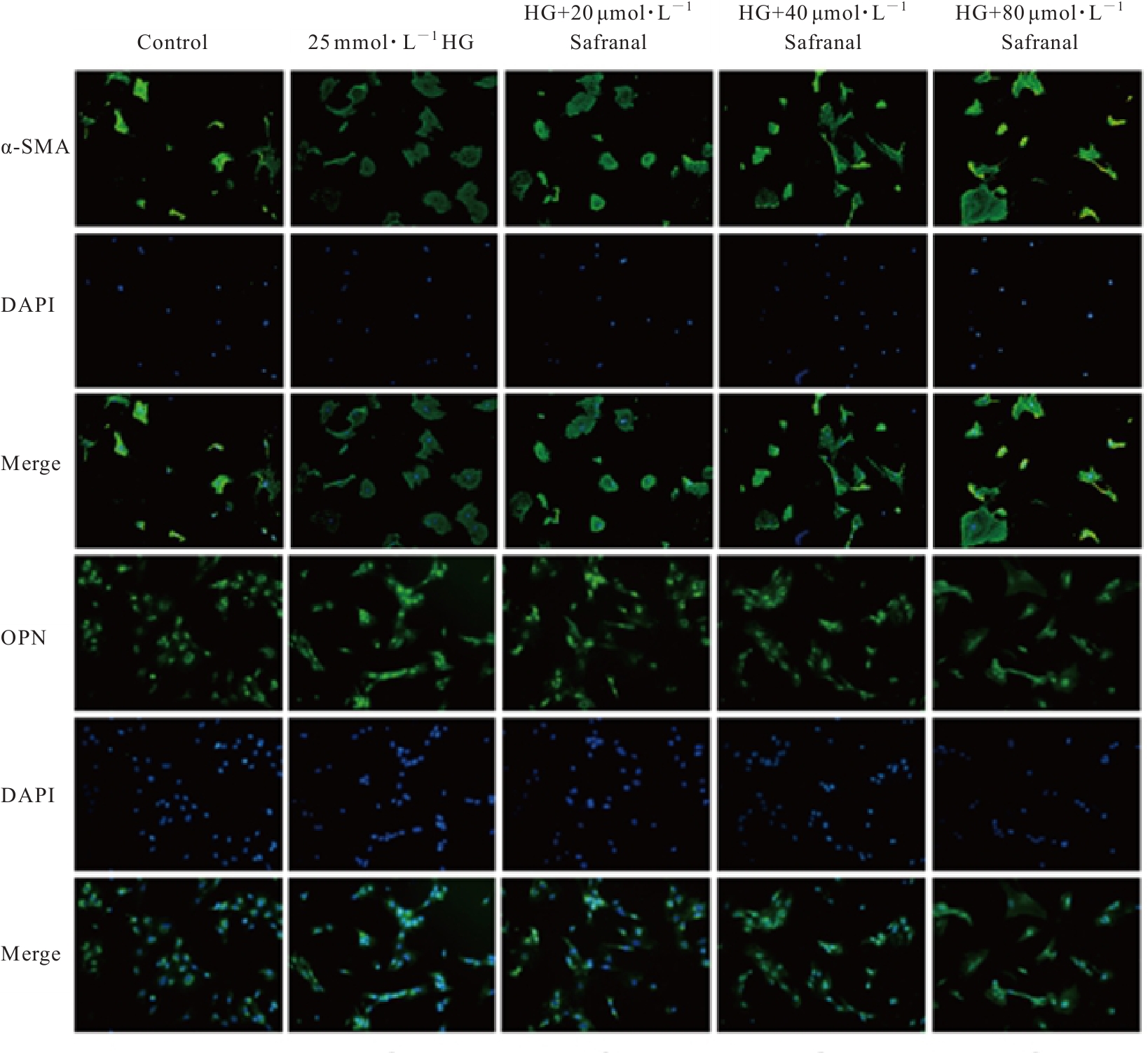
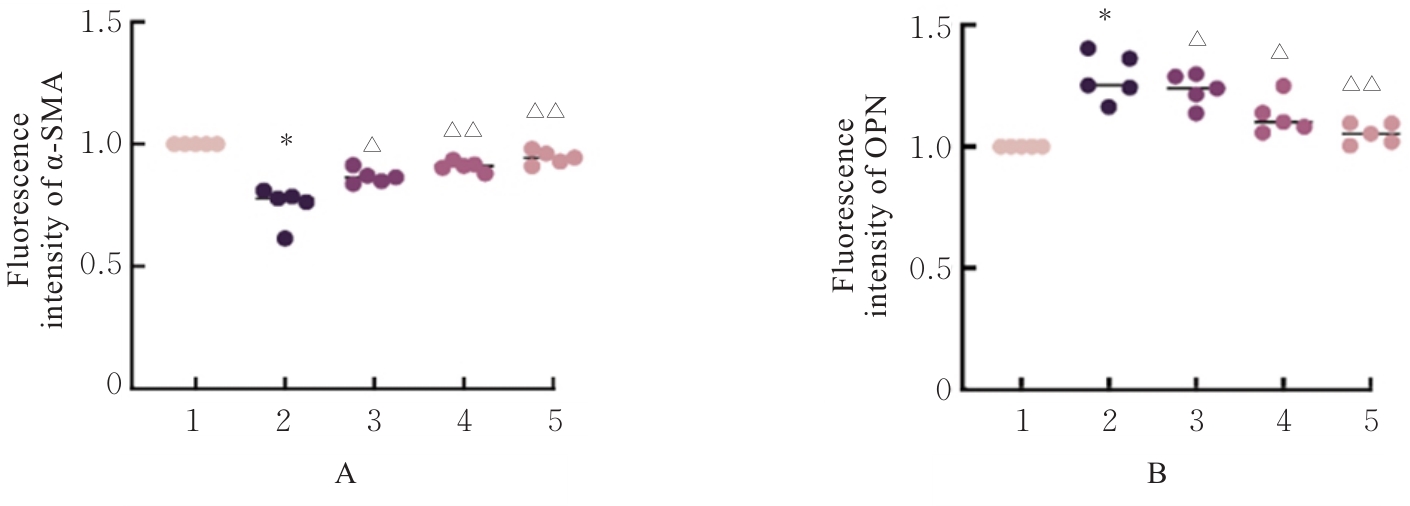
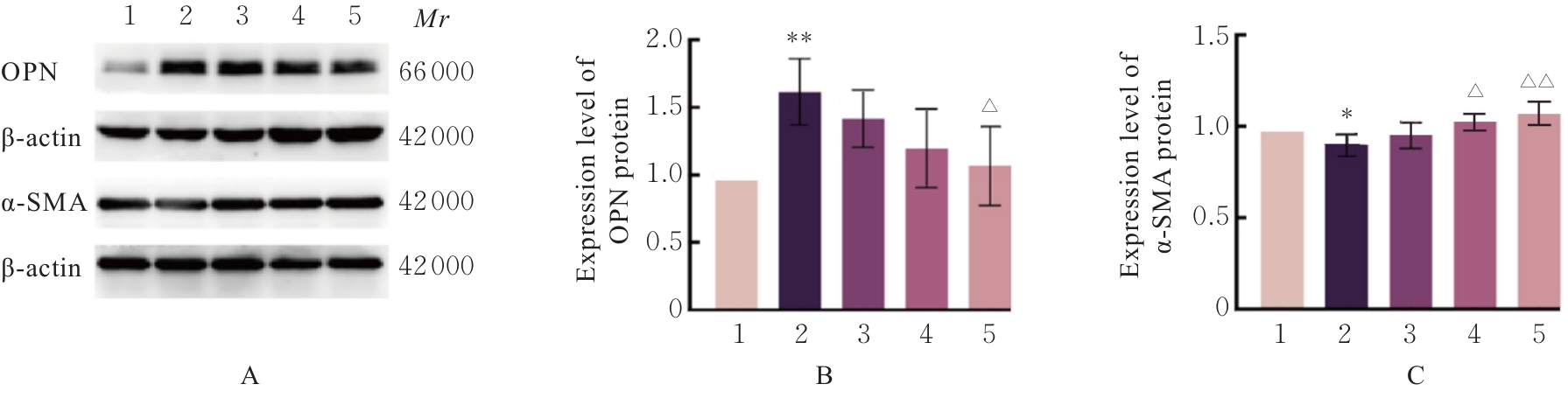
目的 探讨高糖诱导的藏红花醛对大鼠血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs)增殖、迁移和表型转化的影响,阐明藏红花醛在糖尿病(DM)血管病变防治中的作用。 方法 选择SD大鼠作为实验对象,取大鼠胸主动脉原代培养VSMCs,分为对照组、25 mmol·L-1高糖(HG)组和HG+20、40和80 μmol·L-1藏红花醛组。对照组VSMCs不进行处理,25 mmol·L-1 HG组VSMCs给予25 mmol·L-1 HG预处理,HG+20、40和80 μmol·L-1藏红花醛组VSMCs在25 mmol·L-1 HG组处理的基础上再分别用20、40和80 μmol·L-1藏红花醛进行48 h干预。采用细胞计数试剂盒-8(CCK-8)法确定藏红花醛合适浓度并检测各组VSMCs存活率,细胞划痕愈合实验检测各组VSMCs划痕愈合率,Transwell小室实验检测各组VSMCs迁移细胞数,免疫荧光法检测各组VSMCs中α平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)和兔抗骨桥蛋白(OPN)荧光强度,Western blotting法检测各组VSMCs中OPN、α-SMA和增殖细胞核抗原(PCNA)蛋白表达水平。 结果 显微镜下可见,体外培养4 d时,胸主动脉组织块边缘有梭形或三角形细胞爬出,其中长梭形为最常见的形态;第14天时细胞逐渐铺满皿底,当细胞密度达到80%~90%时,出现标志性的“谷峰状”生长状态。取第3代细胞进行免疫荧光法鉴定,采用VSMCs特异性标记物α-SMA蛋白进行细胞免疫荧光染色,原代培养VSMCs中α-SMA蛋白均表达为阳性。CCK-8实验,与对照组比较,160 μmol·L-1 藏红花醛组VSMCs活性明显降低(P<0.01),即对VSMCs产生了毒性损伤。20、40和80 μmol·L-1 藏红花醛干预48 h后,VSMCs活性无明显变化,综合考虑藏红花醛的作用效果和毒性后,采用上述3个浓度藏红花醛用于后续的细胞实验。经过48 h的干预,与对照组比较,25 mmol·L-1 HG组VSMCs活性升高(P<0.001);与25 mmol·L-1 HG组比较,HG+20、40和80 μmol·L-1 藏红花醛组VSMCs活性降低(P<0.05)。细胞划痕愈合实验和Transwell小室实验,干预48 h后,25 mmol·L-1 HG组VSMCs划痕愈合率明显高于对照组(P<0.01),穿过Transwell小室的穿膜细胞数明显增多(P<0.05);与25 μmol·L?1 HG组比较,HG+20、40和80 μmol·L-1藏红花醛组VSMCs划痕愈合率降低(P<0.05),穿膜细胞数减少(P<0.05)。免疫荧光染色,与对照组比较,25 mmol·L-1 HG组VSMCs中α-SMA蛋白荧光强度明显减弱(P<0.001),而OPN蛋白荧光强度明显增强(P<0.001);与25 mmol·L-1 HG组比较,HG+20、40和80 μmol·L-1 藏红花醛组VSMCs中α-SMA蛋白荧光强度逐渐增加(P<0.05),OPN蛋白荧光强度逐渐减弱(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与对照组比较,25 mmol·L-1 HG组VSMCs中α-SMA蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),PCNA和OPN蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01);与25 mmol·L-1 HG组比较,HG+20、40和80 μmol·L-1 藏红花醛组VSMCs中α-SMA蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),PCNA和OPN蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 藏红花醛能够抑制高糖诱导的大鼠VSMCs的增殖、迁移和表型转换。
中图分类号:
- R363.1