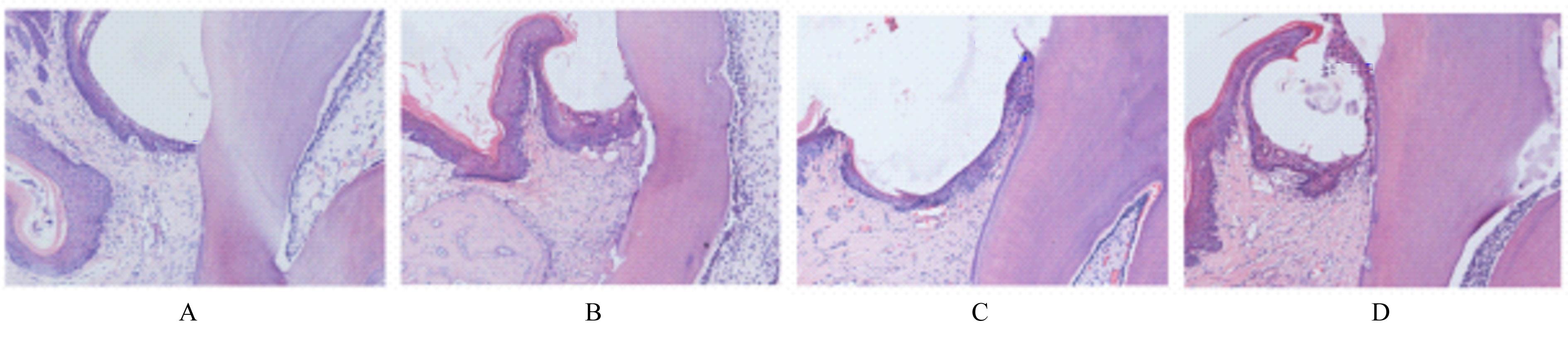
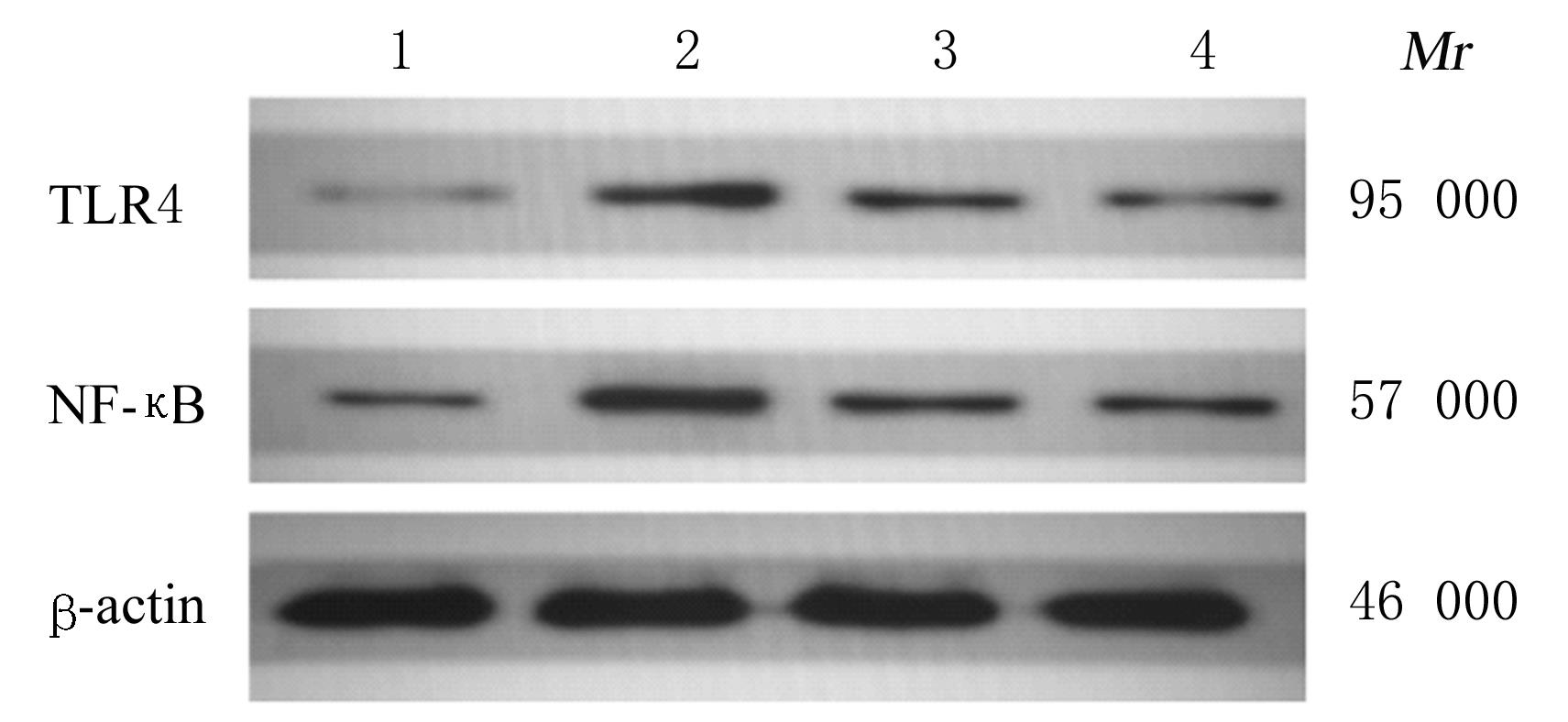
| 1 |
陈 飞, 史金先, 焦 鹏, 等. 牙周炎患者血清中内脂素和PGE2水平检测及其与牙周炎活动性的关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(3): 563-567.
|
| 2 |
张叶茁, 杨岳峰, 杨野仝, 等. 茯苓复合提取物对2型糖尿病大鼠血糖和血脂水平的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(5): 937-941.
|
| 3 |
孟焕新. 牙周炎与糖尿病的关系[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2007, 39(1): 18-20.
|
| 4 |
HEDGPETH D C, ZHANG X M, JIN J F, et al. Periodontal CD14 mRNA expression is downregulated in patients with chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2015, 15: 145.
|
| 5 |
PROMSUDTHI A, POOMSAWAT S, LIMSRICHAROEN W. The role of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 in gingival tissues of chronic periodontitis subjects with type 2 diabetes[J]. J Periodontal Res,2014,49(3): 346-354.
|
| 6 |
LV J S, JIANG X W, ZHANG Y, et al. Effect of resveratrol on expression of TLR4 and inflammatory factors in gingival epithelial cells under high glucose environment[J]. Shanghai J Stomatol, 2017, 26(1): 32-36.
|
| 7 |
YONGUC G N, DODURGA Y, ADIGUZEL E, et al. Grape seed extract has superior beneficial effects than vitamin E on oxidative stress and apoptosis in the hippocampus of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats[J]. Gene, 2015, 555(2): 119-126.
|
| 8 |
MOON S W, SHIN Y U, CHO H, et al. Effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on hard exudates in patients with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(21): e15515.
|
| 9 |
GAO Z L, LIU G Y, HU Z, et al. Grape seed proanthocyanidins protect against streptozotocin‑induced diabetic nephropathy by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress‑induced apoptosis[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(2): 1447-1454.
|
| 10 |
程雨微, 王小云, 查红英, 等. 葡萄籽原花青素对糖尿病小鼠心室重构的保护作用[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2021, 56(6): 925-931.
|
| 11 |
顾丽芬, 杨 涛, 高 颖, 等. 原花青素B2对人牙周膜细胞炎症介质表达的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 39(2): 120-125.
|
| 12 |
郭晓雨, 李淑娟, 梁向阳, 等. 槲皮素脂质体对糖尿病牙周炎大鼠牙周组织的作用及血清AGEs的影响[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2021, 37(7): 628-631.
|
| 13 |
KARTHIK S J, ANOOP S, KUMAR R S, et al. Predictors for gingival index in middle-aged Asian indians with type 2 diabetes from south India: a cross-sectional observational study[J]. Sci World J, 2018, 2018: 9081572.
|
| 14 |
KIM H, KIM C, KIM D U, et al. Inhibitory effects of Boesenbergia pandurata on age-related periodontal inflammation and alveolar bone loss in Fischer 344 rats[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2018, 28(3): 357-366.
|
| 15 |
GRAVES D T, DING Z J, YANG Y M. The impact of diabetes on periodontal diseases[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2020, 82(1): 214-224.
|
| 16 |
BASCONES-MARTÍNEZ A, GONZÁLEZ-FEBLES J, SANZ-ESPORRN J. Diabetes and periodontal disease. review of the literature[J]. Am J Dent, 2014, 27(2): 63-67.
|
| 17 |
MAJUMDER P, THOU K, BHATTACHARYA M, et al. Association of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) gene promoter polymorphisms with aggressive and chronic periodontitis in the eastern Indian population[J]. Biosci Rep, 2018, 38(4): BSR20171212.
|
| 18 |
JIANG Z L, CUI Y Q, GAO R,et al. Study of TNF-α, IL-1β and LPS levels in the gingival crevicular fluid of a rat model of diabetes mellitus and periodontitis[J]. Dis Markers, 2013, 34(5): 295-304.
|
| 19 |
BALAJI A, CHANDRASEKARAN S C, SUBRAMANIUM D, et al. Salivary interleukin-6-A pioneering marker for correlating diabetes and chronic periodontitis: a comparative study[J]. Indian J Dent Res, 2017, 28(2): 133-137.
|
| 20 |
孙俊波, 高 达, 赵逸菲, 等. 丹皮酚对大鼠糖尿病视网膜病变的改善作用及其调节miR-802-5p表达的作用机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(1): 82-93.
|
| 21 |
FRACASSETTI D, COSTA C, MOULAY L, et al. Ellagic acid derivatives, ellagitannins, proanthocyanidins and other phenolics, vitamin C and antioxidant capacity of two powder products from camu-camu fruit (Myrciaria dubia)[J]. Food Chem, 2013, 139(1/2/3/4): 578-588.
|
| 22 |
毕 玲, 傅柏平. 葡萄籽原花青素提取物的研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2008, 17(17): 1478-1481.
|
| 23 |
SUN Y L, HUANG J, SONG K P. BET protein inhibition mitigates acute myocardial infarction damage in rats via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 10(6): 2319-2324.
|
| 24 |
WANG J, CUI Z Q, LIU L, et al. miR-146a mimic attenuates murine allergic rhinitis by downregulating TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway[J]. Immunotherapy, 2019, 11(13): 1095-1105.
|
| 25 |
陈思云, 欧阳军, 白晨倩, 等. 姜黄素预处理对顺铂诱导的急性肾损伤小鼠肾功能及肾组织TLR-4/NF-κB通路蛋白表达的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022,57(5): 694-698.
|
| 26 |
李云鹏, 杨玉丹. 萝卜硫素预处理通过TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB通路对缺氧/复氧大鼠心肌细胞的保护作用[J].郑州大学学报(医学版), 2021,56(2): 188-191.
|
| 27 |
张 询, 袁彩霞, 林园园, 等. 晚期糖基化终末产物AGEs通过牙周膜成纤维细胞的TLR4途径促进牙周炎症[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2020, 36(11): 1007-1011.
|
| 28 |
韩倩倩, 戚威娟, 刘 钊, 等. Toll样受体4抑制剂对糖尿病小鼠体内肿瘤坏死因子α及精氨酸酶1表达的影响[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2017,11(3): 142-148.
|
 )
)