吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5): 1101-1108.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220501
• 基础研究 •
黄芪甲苷对低氧诱导小鼠血管损伤的保护作用及其机制
- 锦州医科大学 辽宁省心脑血管药物重点实验室,辽宁 锦州 121001
Protective effect of astragaloside Ⅳ on hypoxia-induced vascular injury and its mechanism
Yue WANG,Meili LU,Hongxin WANG( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Drug of Liaoning Province,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121001,China
摘要:
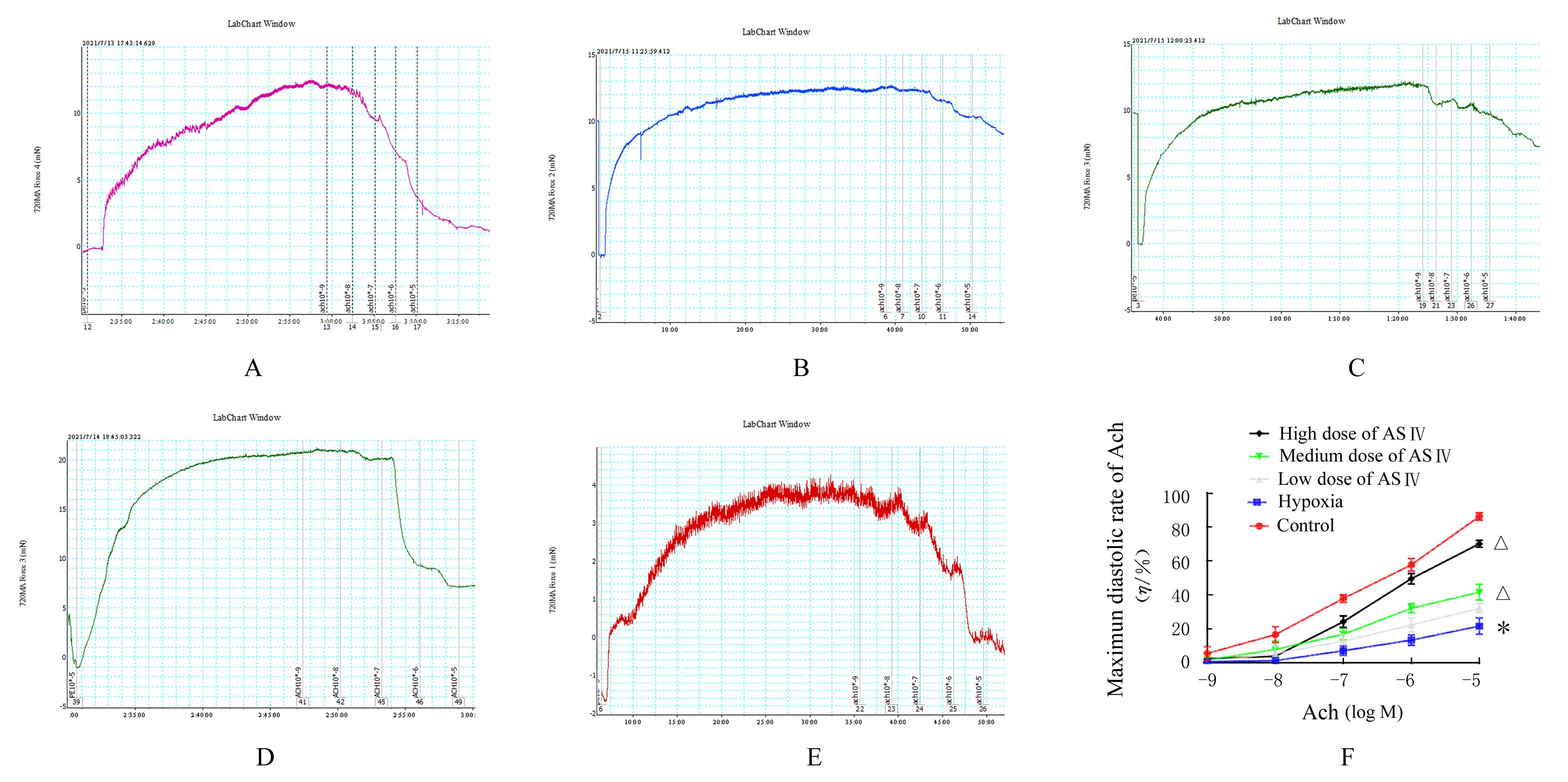
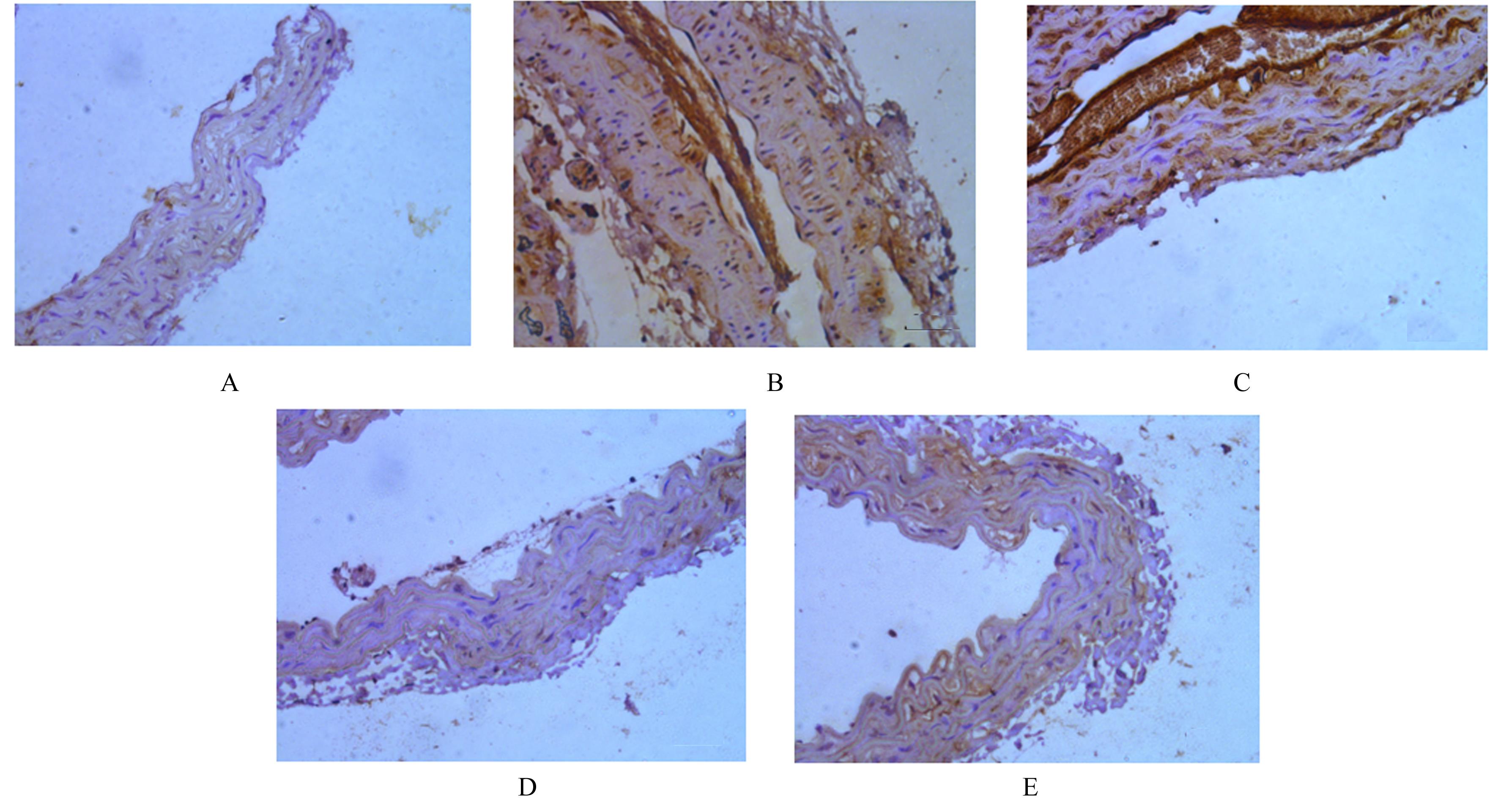
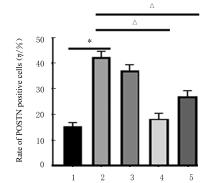
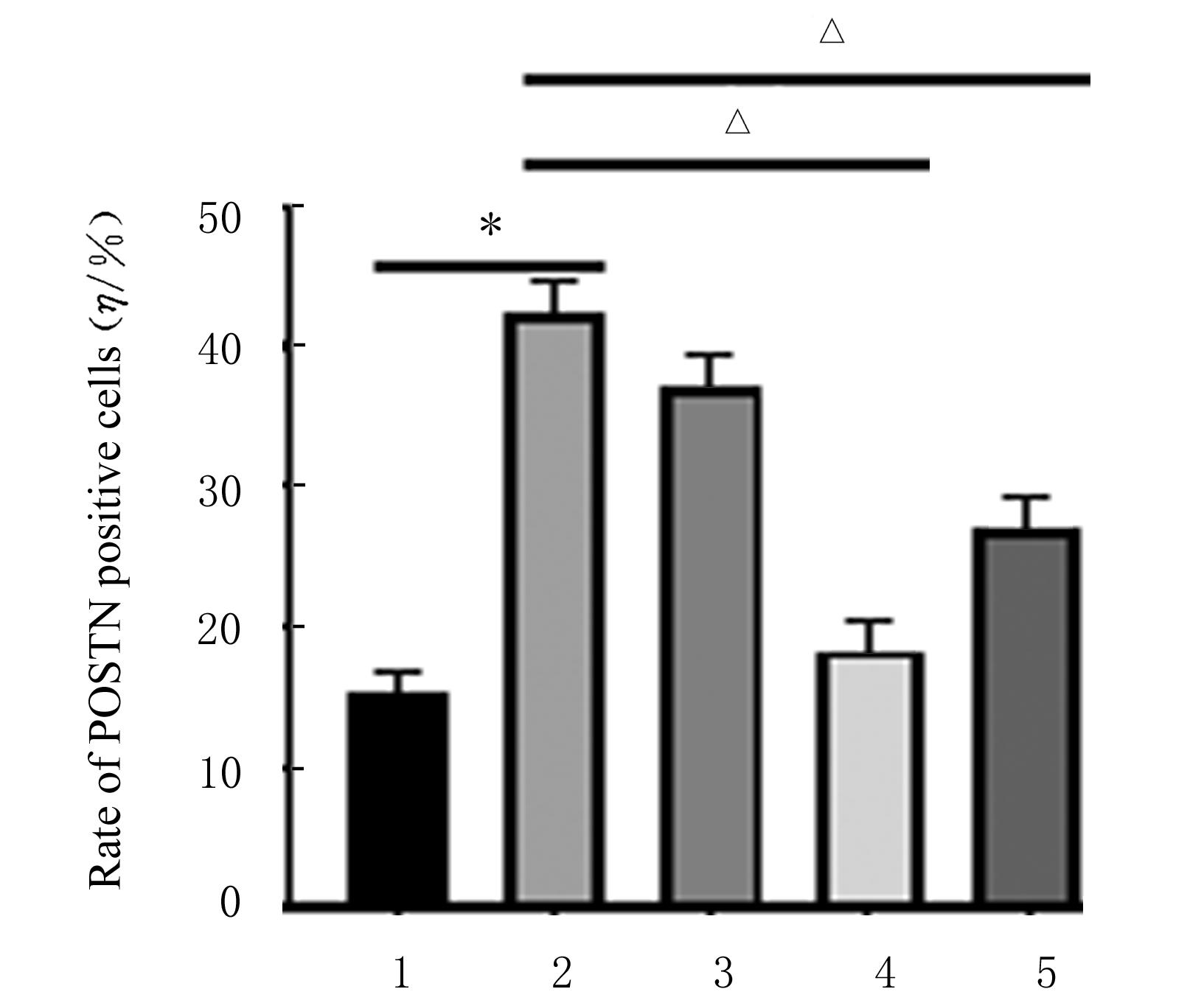
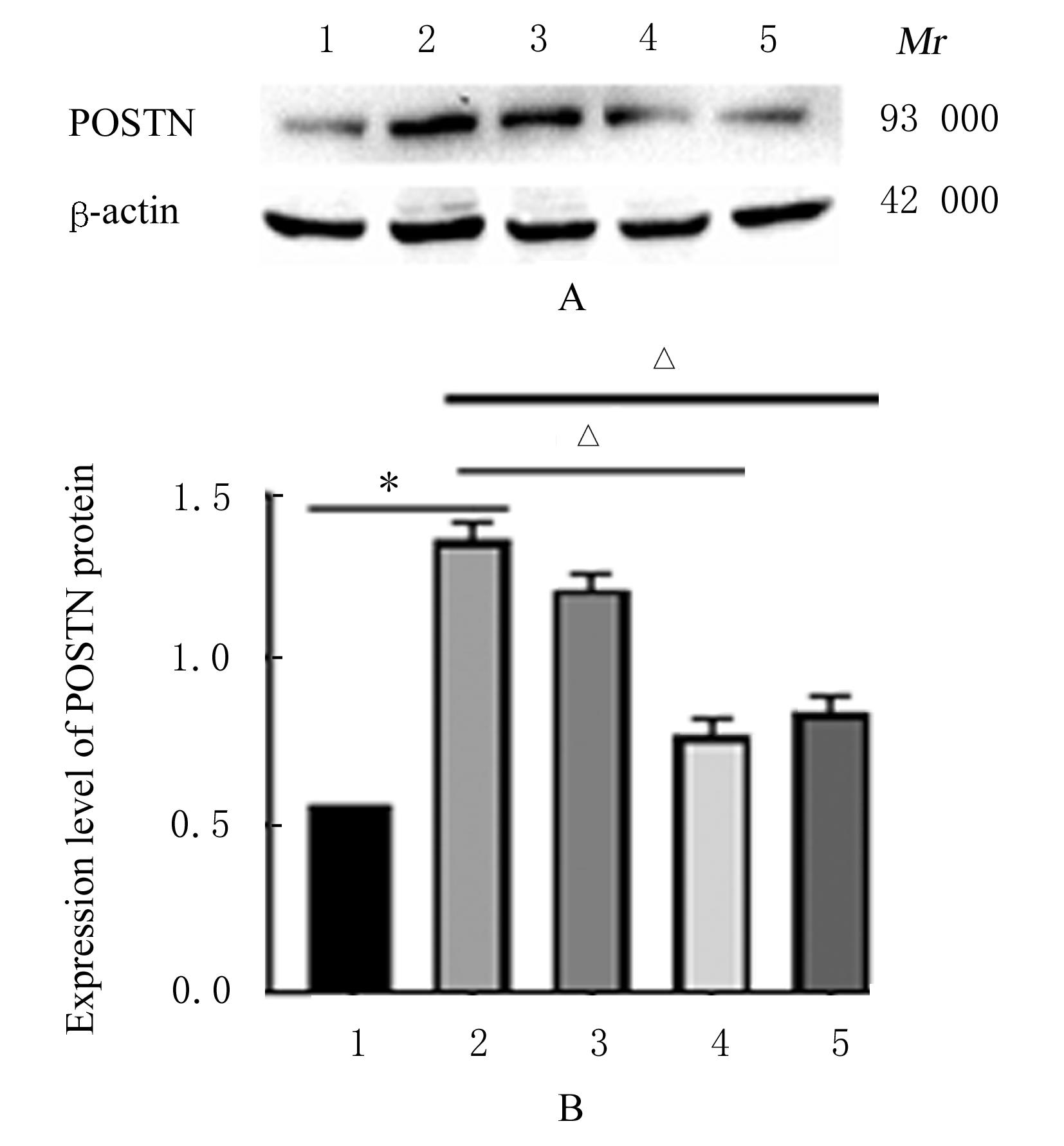
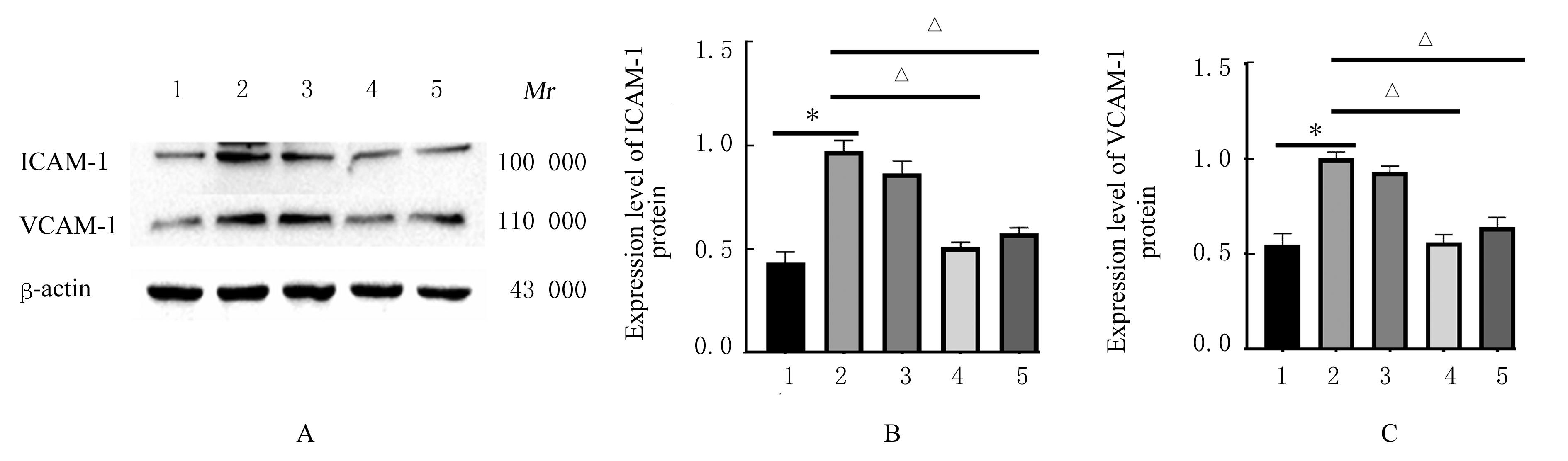
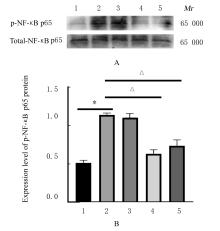
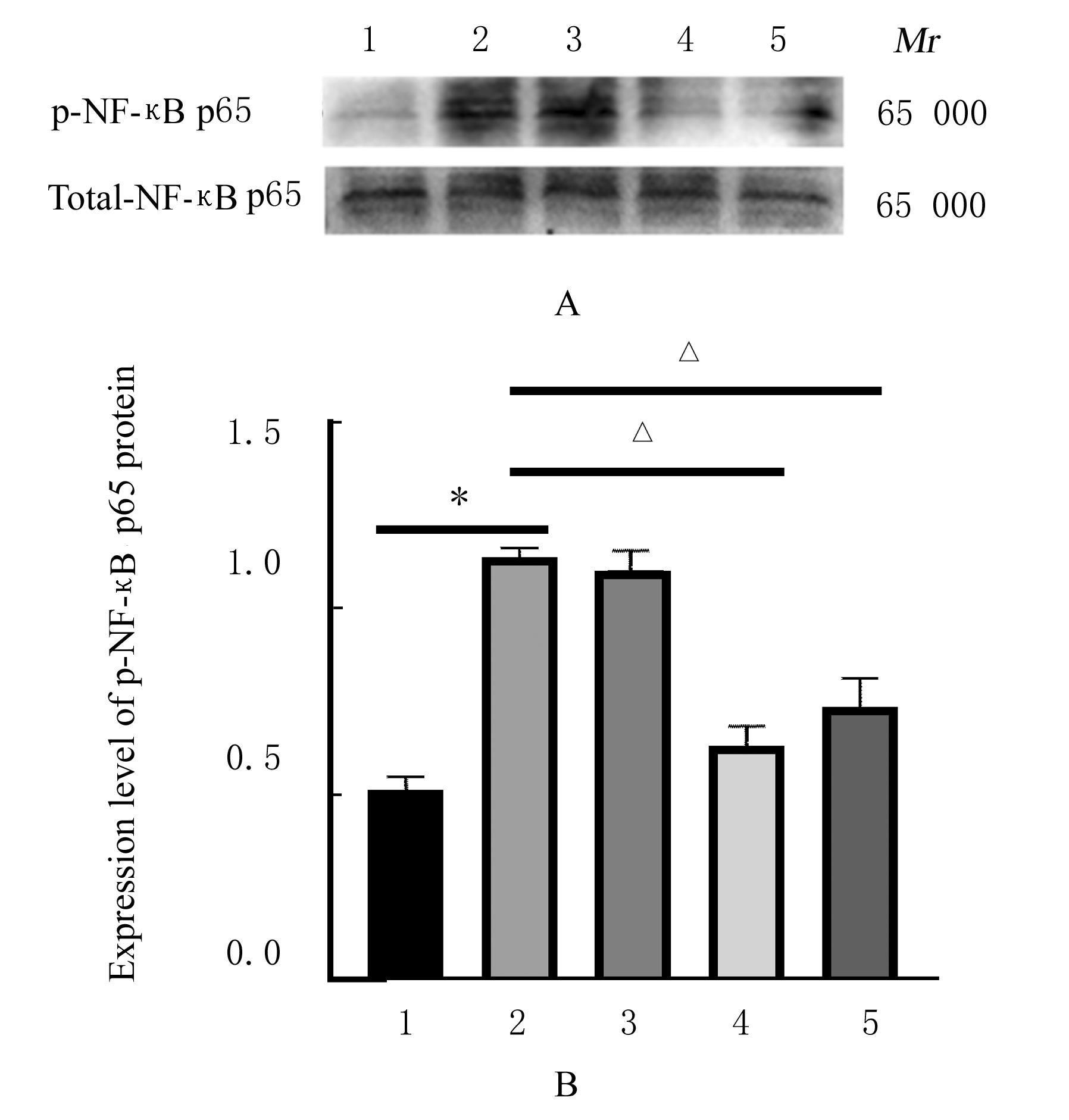
目的 探讨黄芪甲苷(ASⅣ)对低氧诱导的小鼠血管损伤的保护作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 60只雄性健康昆明小鼠随机分为对照组,低氧组,低、中和高剂量(40、80和120 mg·kg-1)ASⅣ组。低氧组和不同剂量ASⅣ组小鼠在低氧舱(氧浓度10%)中饲养,连续4周,低、中和高剂量ASⅣ组小鼠于低氧第2天灌胃给药,连续4周。离体血管环实验检测各组小鼠血管张力,酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法检测各组小鼠血清中白细胞介素6(IL-6)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,免疫组织化学法检测各组小鼠胸主动脉组织中骨膜蛋白(POSTN)阳性细胞率,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN、细胞间黏附分子1(ICAM-1)、血管细胞黏附分子1(VCAM-1)和磷酸化核因子κB(p-NF-κB)p65蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,低氧组小鼠乙酰胆碱(Ach)最大舒张率明显降低(P<0.01);与低氧组比较,低剂量ASⅣ组小鼠Ach最大舒张率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),中和高剂量ASⅣ组小鼠Ach最大舒张率明显升高(P<0.01)。ELISA法检测,与对照组比较,低氧组小鼠血清中IL-6和TNF-α水平明显升高(P<0.01);与低氧组比较,低、中和高剂量ASⅣ组小鼠血清中IL-6和TNF-α水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。免疫组织化学法,对照组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN阳性细胞率极低;与对照组比较,低氧组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN阳性细胞率明显升高(P<0.01);与低氧组比较,低剂量ASⅣ组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN阳性细胞率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),中和高剂量ASⅣ组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN阳性细胞率明显降低(P<0.01)。Western blotting法检测,与对照组比较,低氧组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN、ICAM-1、VCAM-1 和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与低氧组比较,低剂量ASⅣ组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN、ICAM-1、VCAM-1 和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),中和高剂量ASⅣ组小鼠胸主动脉组织中POSTN、ICAM-1、VCAM-1和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。 结论 ASⅣ可改善低氧诱导小鼠血管内皮功能障碍和炎症反应,其作用机制可能与调控POSTN/NF-κB信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R543