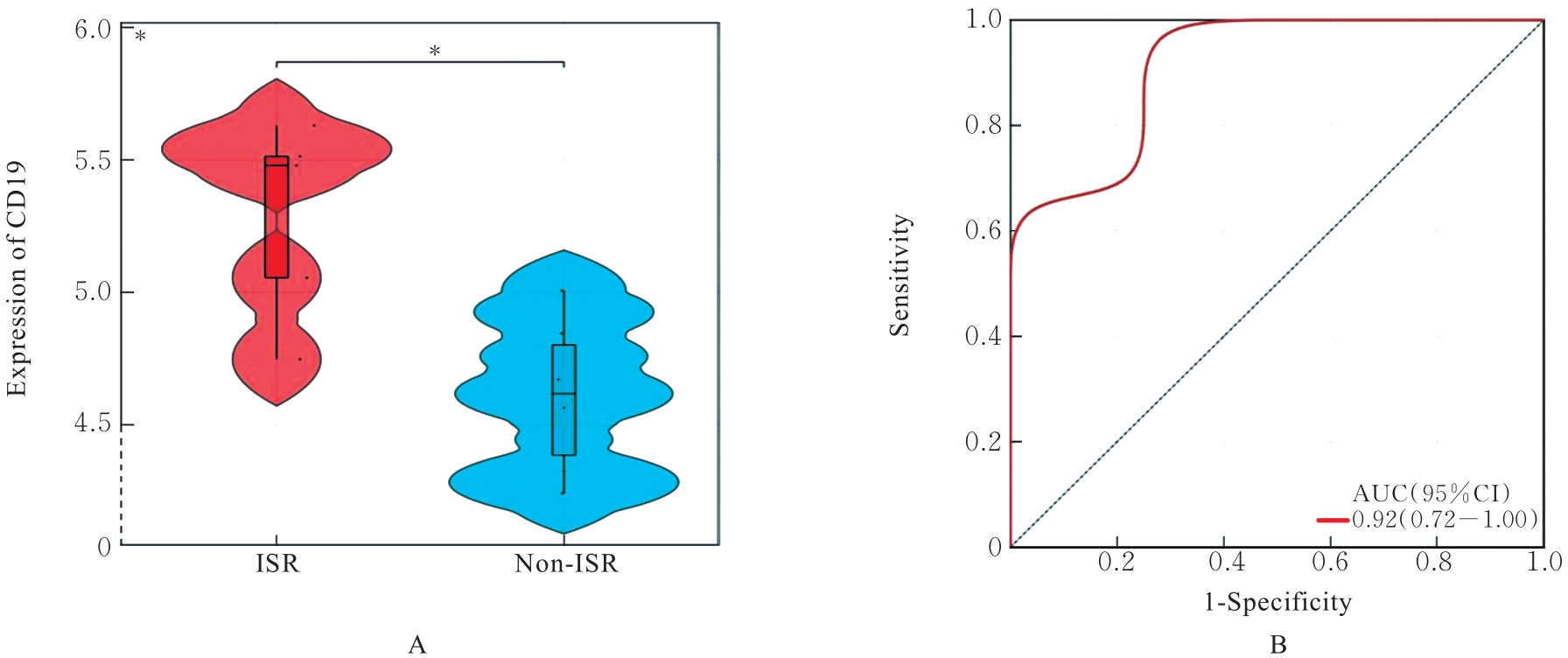
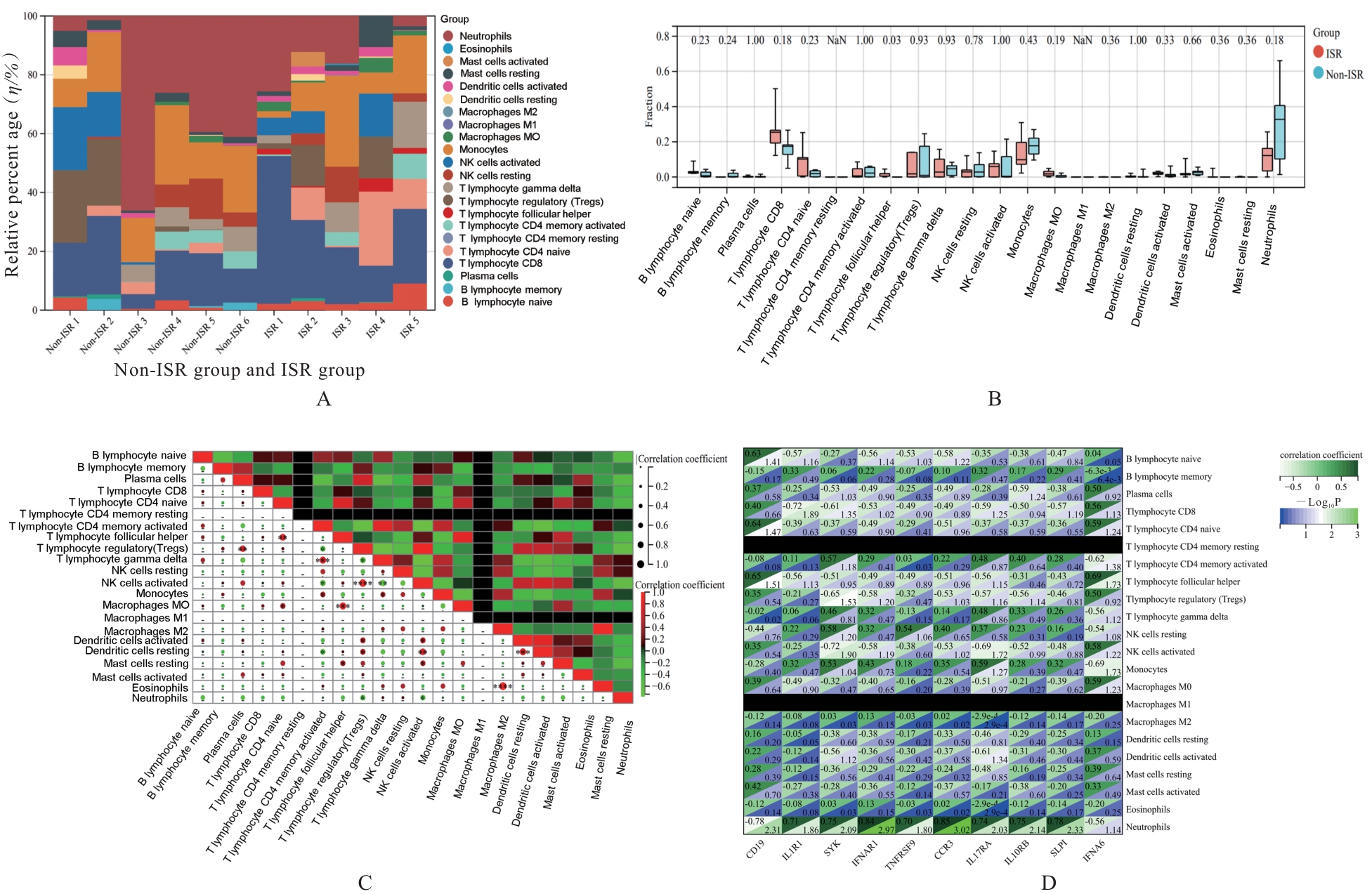
| 1 |
HOARE D, BUSSOOA A, NEALE S, et al. The future of cardiovascular stents: bioresorbable and integrated biosensor technology[J]. Adv Sci, 2019, 6(20): 1900856.
|
| 2 |
ALFONSO F, GONZALO N, RIVERO F, et al. The year in cardiovascular medicine 2020: interventional cardiology[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(10): 985-1003.
|
| 3 |
ULLRICH H, OLSCHEWSKI M, MÜNZEL T, et al. Coronary In-stent restenosis: predictors and treatment[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2021, 118(38): 637-644.
|
| 4 |
YERASI C, CASE B C, FORRESTAL B J, et al. Drug-coated balloon for De Novo Coronary artery disease: JACC state-of-the-art review[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 75(9): 1061-1073.
|
| 5 |
NICCOLI G, MONTONE R A, SABATO V, et al. Role of allergic inflammatory cells in coronary artery disease[J]. Circulation, 2018, 138(16): 1736-1748.
|
| 6 |
BANAI S, FINKELSTEIN A, ALMAGOR Y, et al. Targeted anti-inflammatory systemic therapy for restenosis: The Biorest Liposomal Alendronate with Stenting Study (BLAST)-a double blind, randomized clinical trial[J]. Am Heart J, 2013, 165(2): 234-240.
|
| 7 |
YAO Y, YAN Z Y, LIAN S L, et al. Prognostic value of novel immune-related genomic biomarkers identified in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2020, 8(2): e000444.
|
| 8 |
范吉林, 朱婷婷, 田晓玲, 等. 基于房颤中circRNA-miRNA-mRNA网络构建和免疫细胞浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(6): 1535-1545.
|
| 9 |
FAN J X, CAO S, CHEN M Y, et al. Investigating the AC079305/DUSP1axis as oxidative stress-related signatures and immune infiltration characteristics in ischemic stroke[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 8432352.
|
| 10 |
张德洪, 郑明珠, 李家秋, 等. 基于MSR1 mRNA和蛋白在泛癌组织中表达的生物信息学分析及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49(2): 425-439.
|
| 11 |
赵志娟, 孟 莲, 刘春霞. 基于融合基因作用于横纹肌肉瘤的miRNA-mRNA调控网络的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(1): 154-162.
|
| 12 |
GIUSTINO G, COLOMBO A, CAMAJ A, et al. Coronary In-stent restenosis: JACC state-of-the-art review[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 80(4): 348-372.
|
| 13 |
COLLET C, GRUNDEKEN M J, ASANO T, et al. State of the art: coronary angiography[J]. EuroIntervention, 2017, 13(6): 634-643.
|
| 14 |
DEMYANETS S, TENTZERIS I, JARAI R, et al. An increase of interleukin-33 serum levels after coronary stent implantation is associated with coronary in-stent restenosis[J]. Cytokine, 2014, 67(2): 65-70.
|
| 15 |
SCHILLINGER M, MINAR E. Restenosis after percutaneous angioplasty: the role of vascular inflammation[J]. Vasc Health Risk Manag, 2005, 1(1): 73-78.
|
| 16 |
DEL PORTO F, CIFANI N, PROIETTA M, et al. Lag3+ regulatory T lymphocytes in critical carotid artery stenosis[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2019, 19(4): 463-468.
|
| 17 |
DEL PORTO F, CIFANI N, PROIETTA M, et al. Regulatory T CD4+ CD25+ lymphocytes increase in symptomatic carotid artery stenosis[J]. Ann Med, 2017, 49(4): 283-290.
|
| 18 |
LI Q Q, LI Y T, HUANG W, et al. Loss of lipocalin 10 exacerbates diabetes-induced cardiomyopathy via disruption of Nr4a1-mediated anti-inflammatory response in macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 930397.
|
| 19 |
HAOHAN S, PUSSADHAMMA B, JUMNAINSONG A, et al. Association of major histocompatibility complex class I related chain A/B positive microparticles with acute myocardial infarction and disease severity[J]. Diagnostics, 2020, 10(10): 766.
|
| 20 |
GORCZYNSKI R M. IL-17 signaling in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1240: 47-58.
|
| 21 |
DI SALVO T G, YANG K C, BRITTAIN E, et al. Right ventricular myocardial biomarkers in human heart failure[J]. J Card Fail, 2015, 21(5): 398-411.
|
| 22 |
ALIMADADI A, MUNROE P B, JOE B, et al. Meta-analysis of dilated cardiomyopathy using cardiac RNA-seq transcriptomic datasets[J]. Genes, 2020, 11(1): 60.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG B, YAO R J, HU C, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate mediated sandwich-like coating for mimicking endothelium with sustained therapeutic nitric oxide generation and heparin release[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 269: 120418.
|
| 24 |
LU H K, HUANG Y, LIANG X Y, et al. Pinellia ternata attenuates carotid artery intimal hyperplasia and increases endothelial progenitor cell activity via the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in wire-injured rats[J]. Pharm Biol, 2020, 58(1): 1184-1191.
|
| 25 |
TANG Z H, WANG Y, FAN Y B, et al. Suppression of c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits neointimal formation in balloon-injured rat arteries[J]. Circulation, 2008, 118(7): 764-772.
|
| 26 |
KHAN R, AGROTIS A, BOBIK A. Understanding the role of transforming growth factor-beta1 in intimal thickening after vascular injury[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2007, 74(2): 223-234.
|
| 27 |
WANG S X, LINCOLN T M, MURPHY-ULLRICH J E. Glucose downregulation of PKG-I protein mediates increased thrombospondin1-dependent TGF-{beta}activity in vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2010, 298(5): C1188-C1197.
|
| 28 |
LI X C, DING Y, ZI M T, et al. CD19, from bench to bedside[J]. Immunol Lett, 2017, 183: 86-95.
|
| 29 |
WENG R Q, LIU S D, GU X D, et al. Clonal diversity of the B cell receptor repertoire in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis and type 2 diabetes[J]. Open Life Sci, 2021, 16(1): 884-898.
|
| 30 |
FUJIMOTO M, POE J C, HASEGAWA M, et al. CD19 regulates intrinsic B lymphocyte signal transduction and activation through a novel mechanism of processive amplification[J]. Immunol Res, 2000, 22(2/3): 281-298.
|
| 31 |
FUJIMOTO M, FUJIMOTO Y, POE J C, et al. CD19 regulates Src family protein tyrosine kinase activation in B lymphocytes through processive amplification[J]. Immunity, 2000, 13(1): 47-57.
|
| 32 |
DEVEZA R C, ELKINS M, SARAGIOTTO B T. PEDro systematic review update: exercise for coronary heart disease[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2017, 51(9): 755-756.
|
| 33 |
CHOE N, KWON J S, KIM Y S, et al. The microRNA miR-34c inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia by targeting stem cell factor[J]. Cell Signal, 2015, 27(6): 1056-1065.
|
| 34 |
CROTTY S. T follicular helper cell biology: a decade of discovery and diseases[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50(5): 1132-1148.
|
| 35 |
PREITE S, HUANG B, CANNONS J L, et al. PI3K orchestrates T follicular helper cell differentiation in a context dependent manner: implications for autoimmunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 3079.
|
 ),刘克坚1(
),刘克坚1( )
)
 ),Kejian LIU1(
),Kejian LIU1( )
)