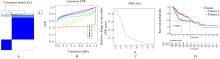
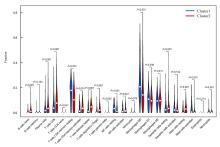
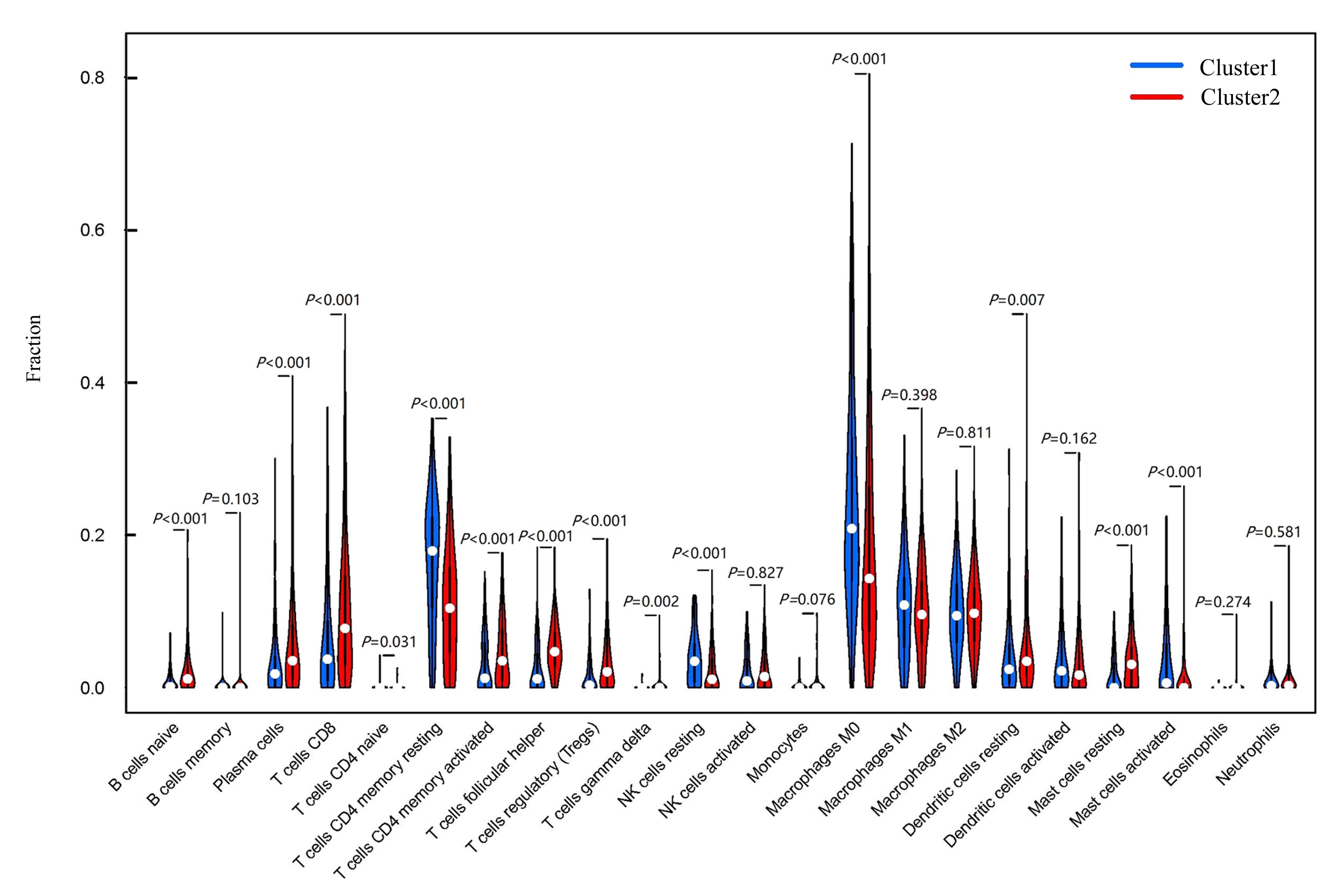
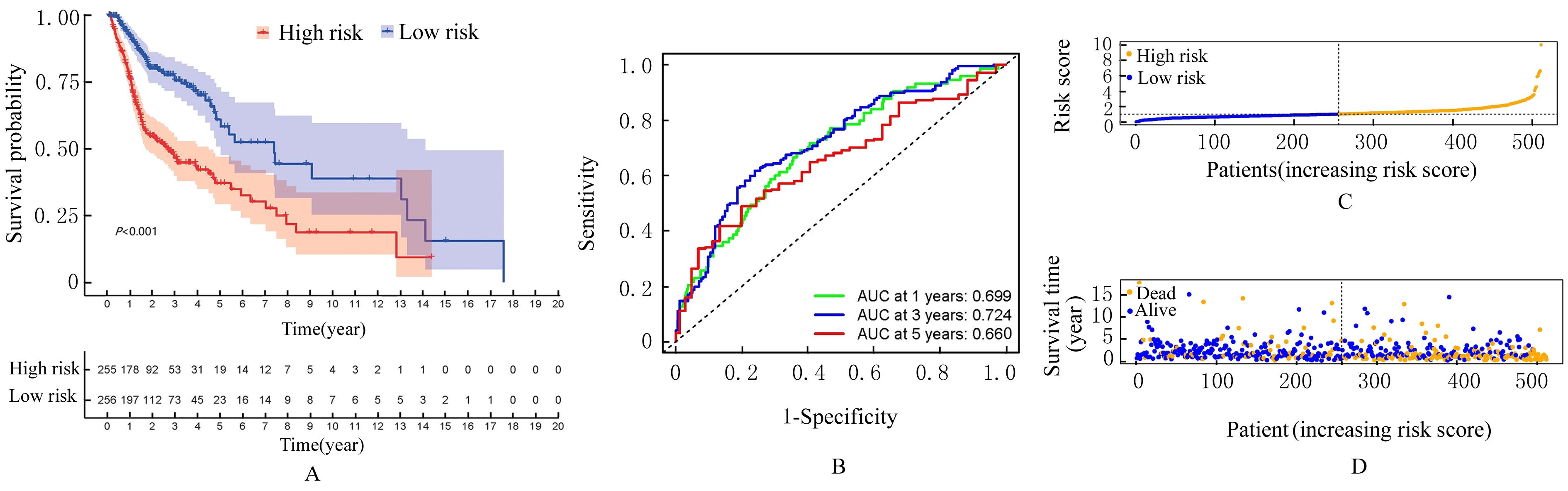
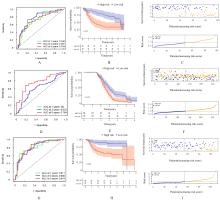
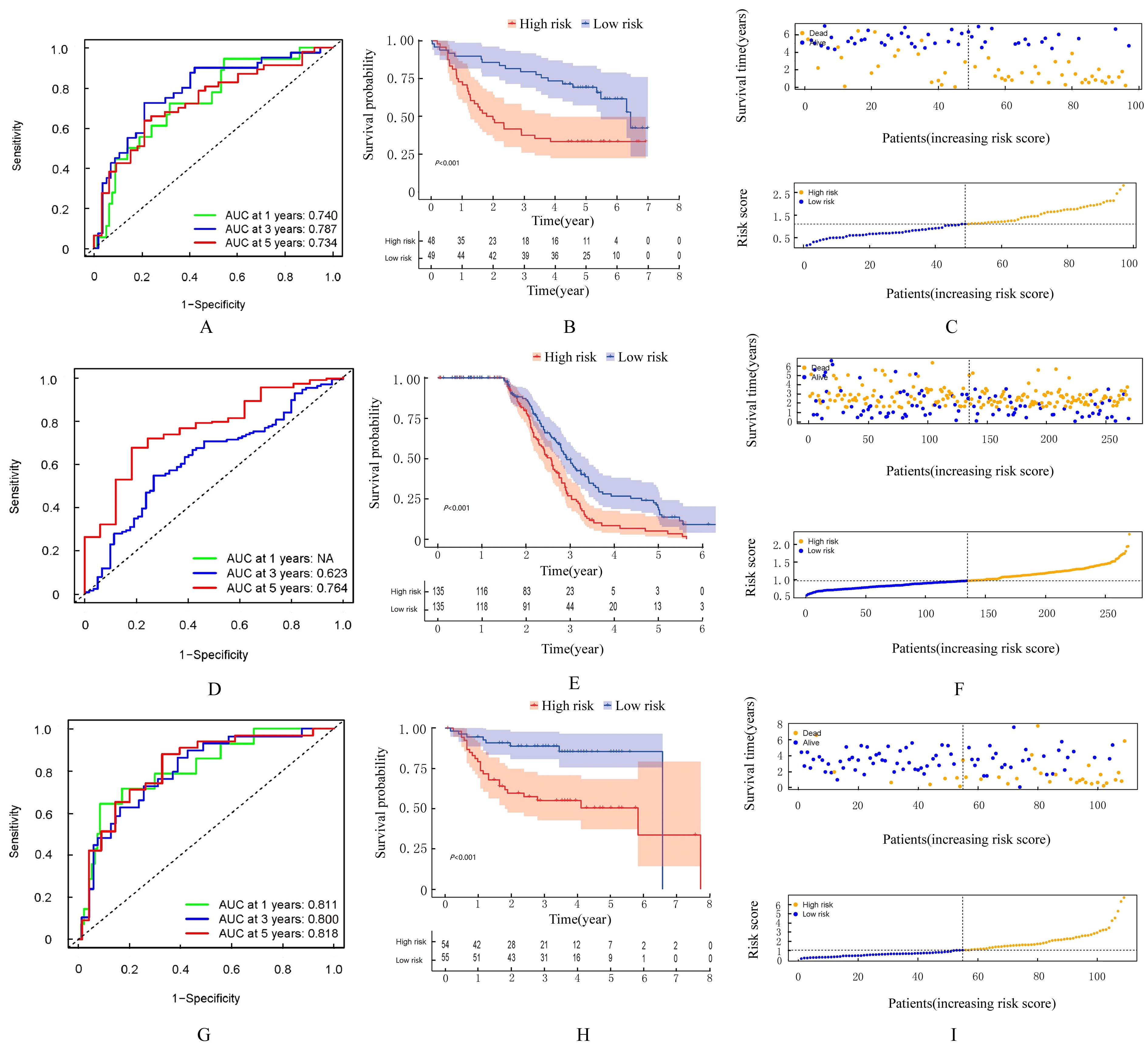
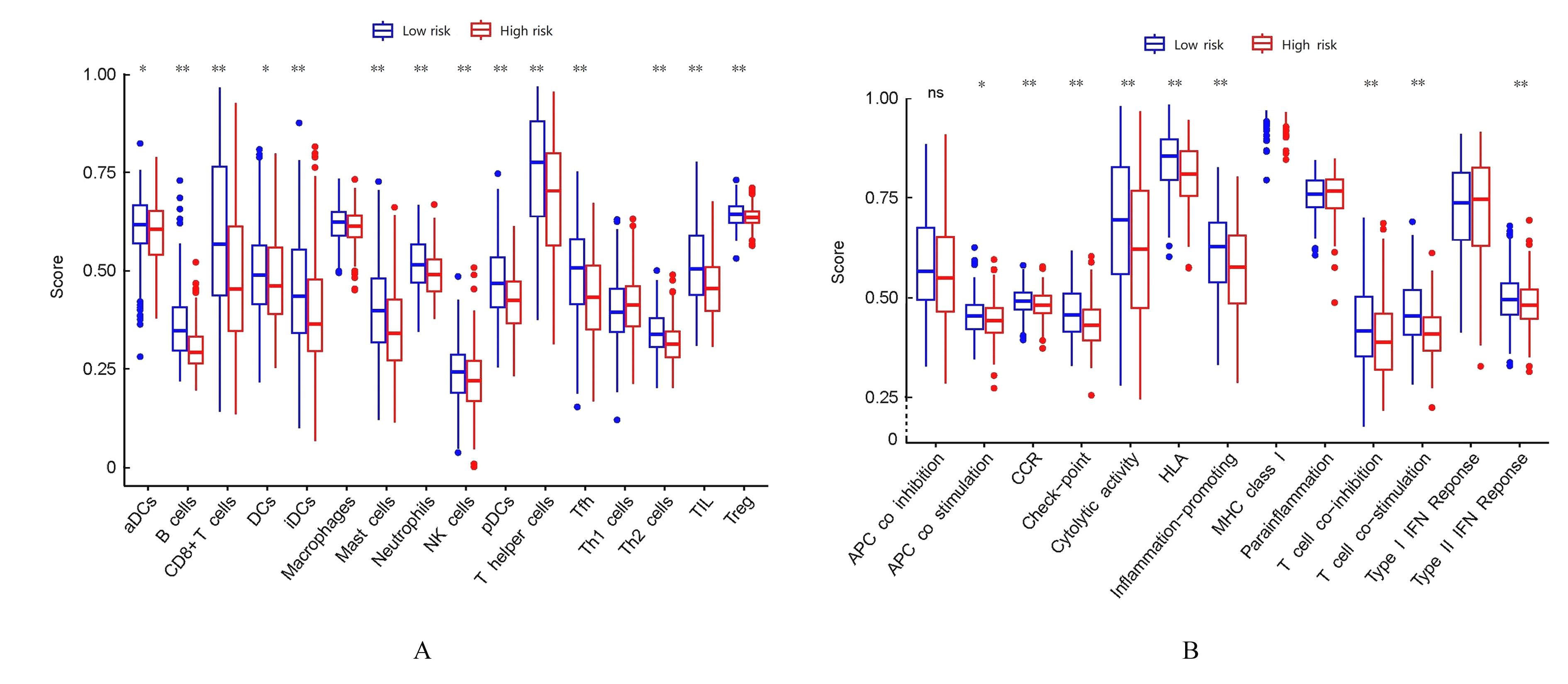
| 1 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249.
|
| 2 |
NAMAYANDEH S M, KHAZAEI Z, LARI NAJAFI M, et al. GLOBAL leukemia in children 0-14 statistics 2018, incidence and mortality and human development index (HDI): GLOBOCAN sources and methods[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21(5): 1487-1494.
|
| 3 |
JOHNSON D E, BURTNESS B, LEEMANS C R,et al.Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 92.
|
| 4 |
LEEMANS C R, BRAAKHUIS B J M, BRAKENHOFF R H. Response to correspondence on the molecular biology of head and neck cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011, 11(5): 382.
|
| 5 |
CHAUHAN S S, KAUR J, KUMAR M, et al. Prediction of recurrence-free survival using a protein expression-based risk classifier for head and neck cancer[J]. Oncogenesis, 2015, 4(4): e147.
|
| 6 |
CHEN Y J, MAHIEU N G, HUANG X J, et al. Lactate metabolism is associated with mammalian mitochondria[J].Nat Chem Biol,2016,12(11): 937-943.
|
| 7 |
FAUBERT B, LI K Y, CAI L, et al. Lactate metabolism in human lung tumors[J]. Cell, 2017,171(2): 358-371.e9.
|
| 8 |
CHEN L H, HUANG L X, GU Y,et al.Lactate-lactylation hands between metabolic reprogramming and immunosuppression[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022,23(19): 11943.
|
| 9 |
MAI S J, LIANG L P, MAI G H, et al. Development and validation of lactate metabolism-related lncRNA signature as a prognostic model for lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Endocrinol,2022,13: 829175.
|
| 10 |
SUN Z L, TAO W, GUO X D, et al. Construction of a lactate-related prognostic signature for predicting prognosis, tumor microenvironment, and immune response in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 818984.
|
| 11 |
ZHANG Z H, FANG T, LV Y G. A novel lactate metabolism-related signature predicts prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment of breast cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 934830.
|
| 12 |
FISHILEVICH S, NUDEL R, RAPPAPORT N,et al. GeneHancer: genome-wide integration of enhancers and target genes in GeneCards[J]. Database, 2017, 2017: bax028.
|
| 13 |
HIRSCHHAEUSER F, SATTLER U G, MUELLER-KLIESER W. Lactate: a metabolic key player in cancer[J].Cancer Res,2011,71(22):6921-6925.
|
| 14 |
CHALMERS Z R, CONNELLY C F, FABRIZIO D, et al. Analysis of 100, 000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden[J]. Genome Med, 2017, 9(1): 34.
|
| 15 |
MARABELLE A, FAKIH M, LOPEZ J, et al. Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab: prospective biomarker analysis of the multicohort, open-label, phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(10): 1353-1365.
|
| 16 |
WU T, JIAO Z, LI Y X, et al. HPRT1 promotes chemoresistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via activating MMP1/PI3K/akt signaling pathway[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(4): 855.
|
| 17 |
JIANG Z H, SHEN X F, WEI Y H,et al. A pan-cancer analysis reveals the prognostic and immunotherapeutic value of stanniocalcin-2 (STC2)[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 927046.
|
| 18 |
XIE W, LI X Y, YANG C X, et al. The pyroptosis-related gene prognostic index associated with tumor immune infiltration for pancreatic cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11): 6178.
|
| 19 |
BURR M L, SPARBIER C E, CHAN K L, et al. An evolutionarily conserved function of polycomb silences the MHC class I antigen presentation pathway and enables immune evasion in cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 36(4): 385-401.e8.
|
| 20 |
GUO X Y, LIN W Q, WEN W Q, et al. Identifying novel susceptibility genes for colorectal cancer risk from a transcriptome-wide association study of 125,478 subjects[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(4): 1164-1178.
|
| 21 |
XU J W, LIU X Y, LIU X T, et al. Long noncoding RNA KCNMB2-AS1 promotes the development of esophageal cancer by modulating the miR-3194-3p/PYGL axis[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1):6687-6702.
|
| 22 |
GAO Y, ZHANG E C, FEI X, et al. Identification of novel metabolism-associated subtypes for pancreatic cancer to establish an eighteen-gene risk prediction model[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 691161.
|
| 23 |
ZHONG H, LIU S, CAO F, et al. Dissecting tumor antigens and immune subtypes of glioma to develop mRNA vaccine[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 709986.
|
| 24 |
WEI M Q, LI H, LI Q F, et al. Based on network pharmacology to explore the molecular targets and mechanisms of Gegen Qinlian Decoction for the treatment of ulcerative colitis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 5217405.
|
| 25 |
HU B, YANG X B, SANG X T. Development and verification of the hypoxia-related and immune-associated prognosis signature for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2020, 7: 315-330.
|
| 26 |
WU M, WEI B, DUAN S L, et al. Methylation-driven gene PLAU as a potential prognostic marker for differential thyroid carcinoma[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 819484.
|
| 27 |
AI C, ZHANG J X, LIAN S Y, et al. FOXM1 functions collaboratively with PLAU to promote gastric cancer progression[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(4): 788-794.
|
| 28 |
VISHNUBALAJI R, ALAJEZ N M. Epigenetic regulation of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) by TGF-β signaling[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 15410.
|
| 29 |
XIONG X X, CHEN S Y, SHEN J F, et al. Cannabis suppresses antitumor immunity by inhibiting JAK/STAT signaling in T cells through CNR2[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 99.
|
| 30 |
EKE I, HEHLGANS S, CORDES N. There’s something about ilk[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2009,85(11): 929-936.
|
| 31 |
KATOH M, KATOH M. Human FOX gene family (Review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2004, 25(5): 1495-1500.
|
 )
)