吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 797-803.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240325
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
系统性红斑狼疮患者妊娠期血清CCL19和sCD163水平及其对母婴结局的影响
- 1.山东省青岛市妇女儿童医院产科,山东 青岛 266000
2.康复大学青岛医院 青岛市市立医院产科,山东 青岛 266011
3.山东省青岛市妇女儿童医院生殖医学中心,山东 青岛 266000
4.青岛大学附属医院产科,山东 青岛 266003
5.康复大学青岛医院 青岛市市立医院风湿免疫科,山东 青岛 266011
Expression levels of serum CCL19 and sCD163 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy and their impact on maternal and infant outcomes
Yu LIU1,Baolai LI2,Chenxi YANG3,Ping TAN4,Qian XU1,Qian XING5( )
)
- 1.Department of Obstetrics,Women and Children Hospital,Qingdao City,Shandong Province,Qingdao 266000,China
2.Department of Obstetrics,Qingdao Municipal Hospital,Qingdao Hospital,University of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences,Qingdao 266011,China
3.Reproductive Medicine Center,Women and Children’s Hospital,Qingdao City,Shandong Province,Qingdao 266000,China
4.Department of Obstetrics,Affiliated Hospital,Qingdao University,Qingdao 266003,China
5.Department of Rheumatology,Qingdao Municipal Hospital,Qingdao Hospital,University of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences,Qingdao 266011,China
摘要:
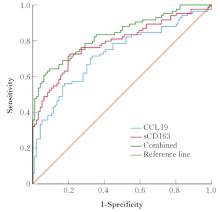
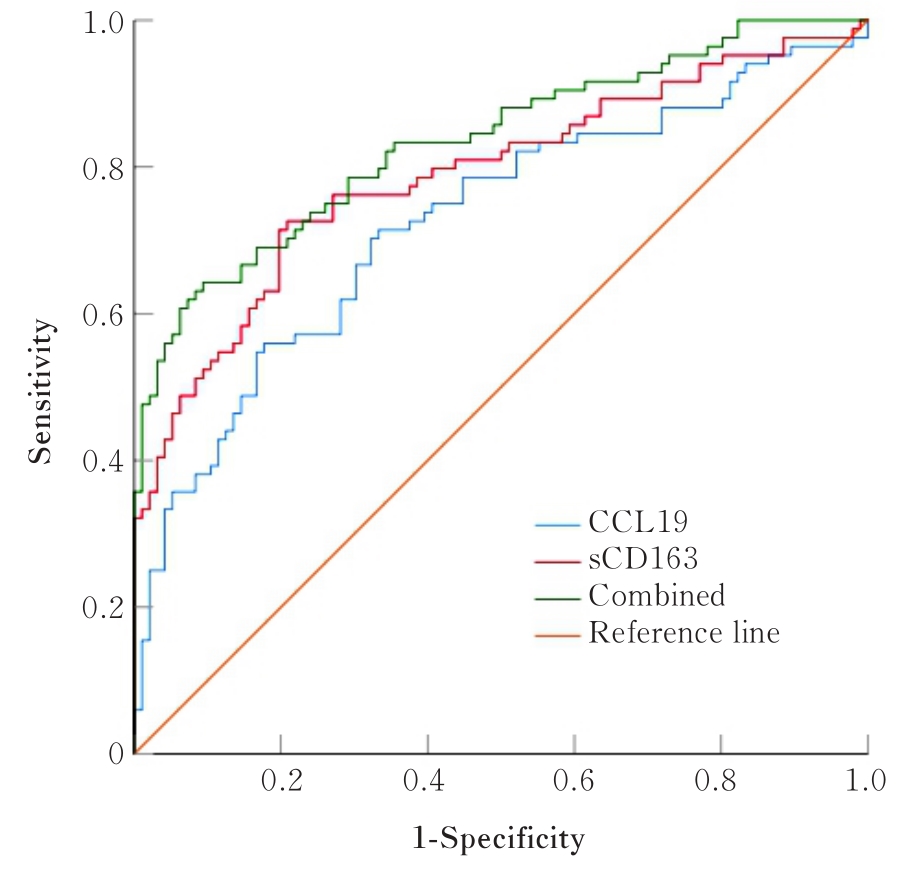
目的 探讨外周血趋化因子配体19(CCL19)和可溶性CD163(sCD163)在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者妊娠期血清中的水平变化,并阐明其对母婴结局的影响。 方法 选取180例妊娠期SLE患者作为SLE组,根据母婴结局分为妊娠成功组(n=132)和妊娠失败组(n=48);另外随机选取同期产检的180例健康孕妇作为对照组。收集2组研究对象一般资料,试剂盒检测2组研究对象血清中CCL19和sCD163水平及相关血清因子水平。采用多因素Logistic回归分析检测SLE患者妊娠失败的影响因素,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析SLE组血清中CCL19和sCD163水平预测妊娠结局的效果。 结果 与对照组比较,SLE组患者血清中补体C3和补体C4水平明显降低(P<0.05),血清中红细胞沉降率(ESR)、肌酐(CR)、抗心磷脂抗体(ACA)-IgG、抗β2糖蛋白Ⅰ(anti-β2GPⅠ)、CCL19和sCD163水平明显升高(P<0.01)。与妊娠成功组比较,妊娠失败组患者血清中补体C3和补体C4水平明显降低(P<0.01),血清中ESR、CR、ACA-IgG、anti-β2GPⅠ、CCL19和sCD163水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。血清中CCL19、sCD163、ESR、CR、ACA-IgG和anti-β2GPⅠ水平是妊娠期SLE患者妊娠失败的危险因素(P<0.05或P<0.01),补体C3和补体C4水平是妊娠期SLE患者妊娠失败的保护因素(P<0.01)。血清CCL19水平预测妊娠期SLE患者妊娠失败的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.726,血清sCD163水平预测妊娠期SLE患者妊娠失败预后的AUC为0.789,二者联合预测妊娠期SLE患者妊娠失败的AUC为0.835。二者联合预测妊娠期SLE患者妊娠失败的效能优于CCL19和sCD163水平各自单独预测(Z联合检测-CCL19=3.066,P=0.002;Z联合检测-sCD163=2.087,P=0.037)。 结论 SLE患者妊娠期血清中CCL19和sCD163水平明显升高,可能导致患者母婴结局不良。
中图分类号:
- R593.24