吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 191-201.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250123
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
自分泌运动因子和溶血磷脂酸受体3在慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血清及肺组织中的表达及其意义
- 1.石河子大学第一附属医院呼吸与危重症医学科,新疆 石河子 832000
2.石河子大学第一附属 医院急诊医学中心,新疆 石河子 832000
Expressions of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 in serum and lung tissue of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their significances
Peiqin JIANG1,Zheng ZHANG1,Zhong HUANG2( ),Xianling LU1(
),Xianling LU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
2.Emergency Medical Center,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
摘要:
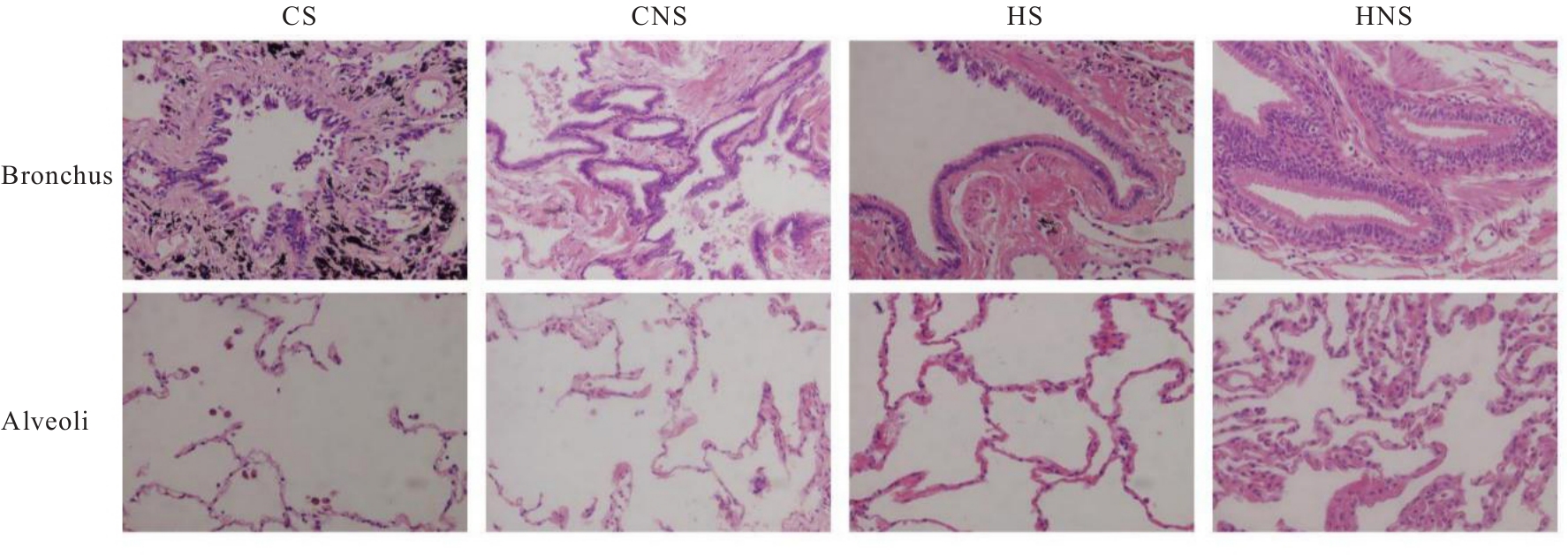
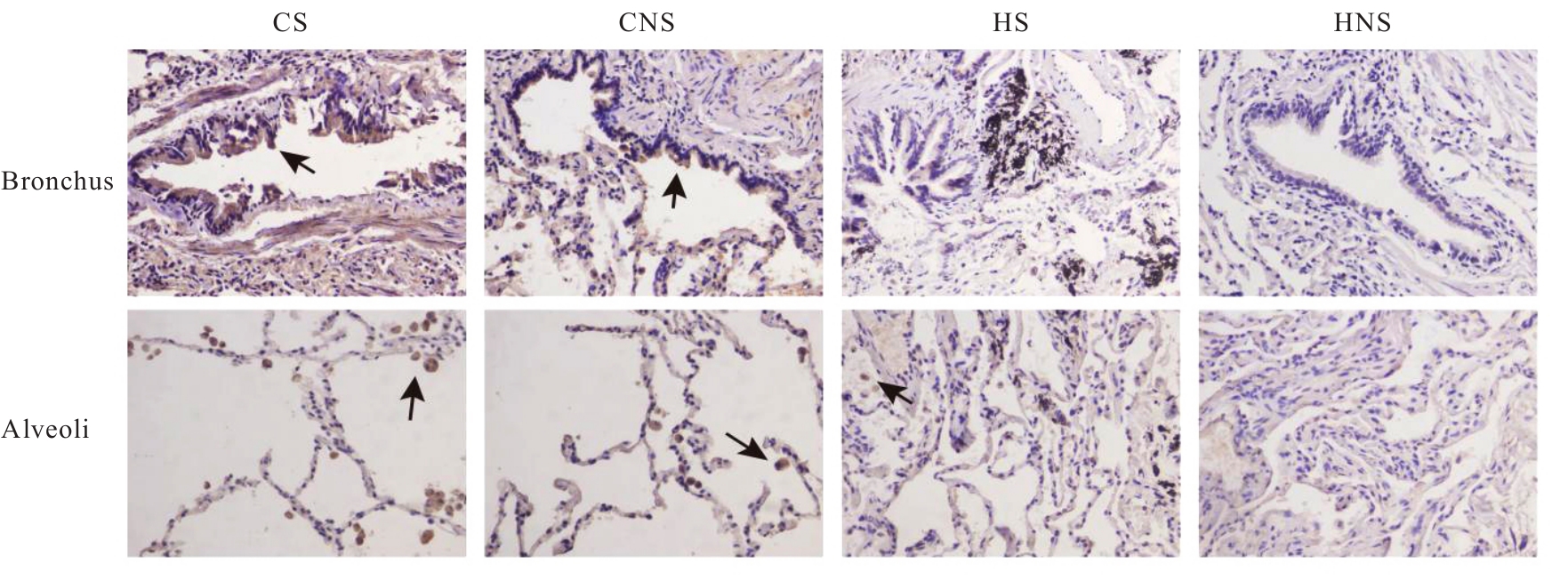
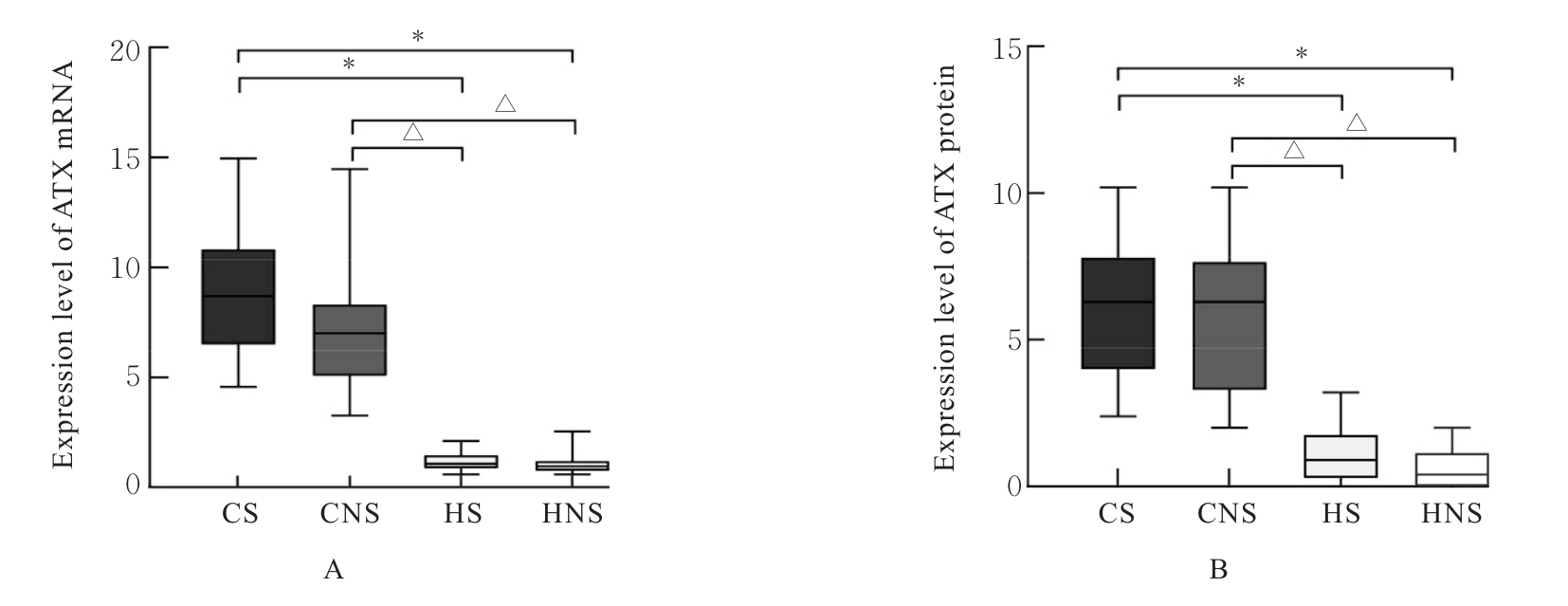
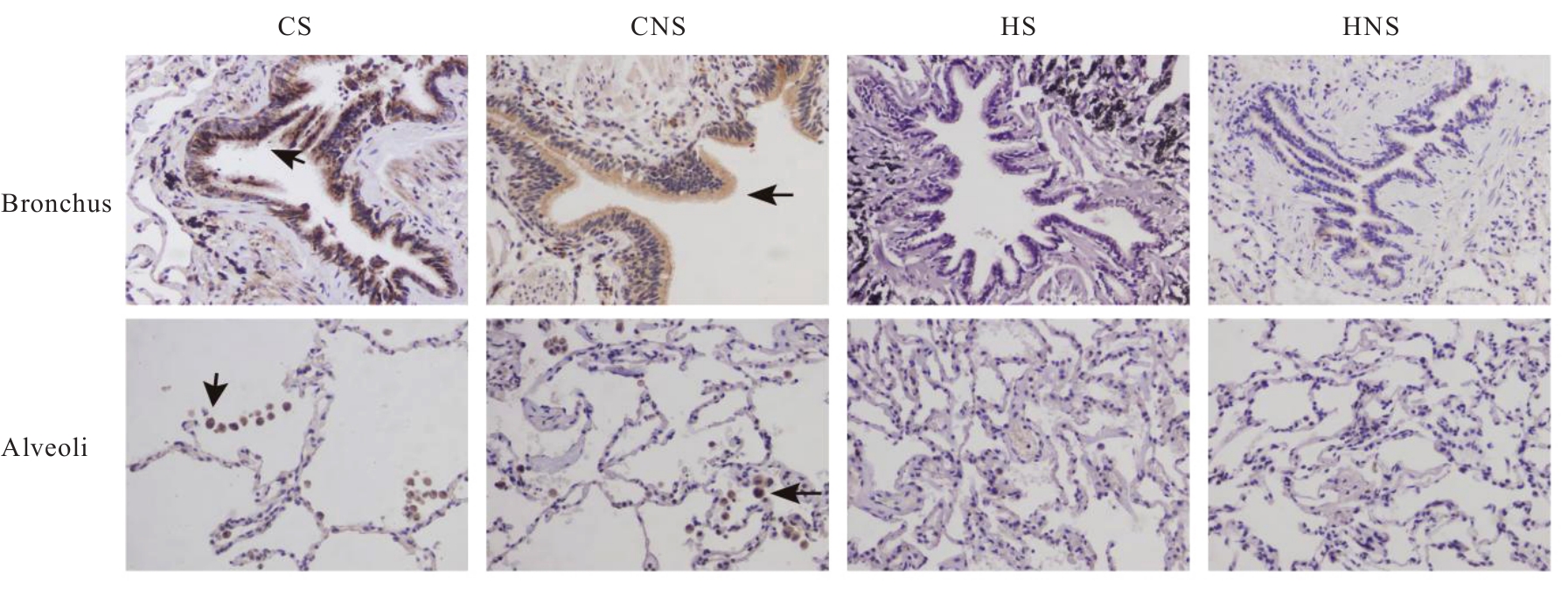
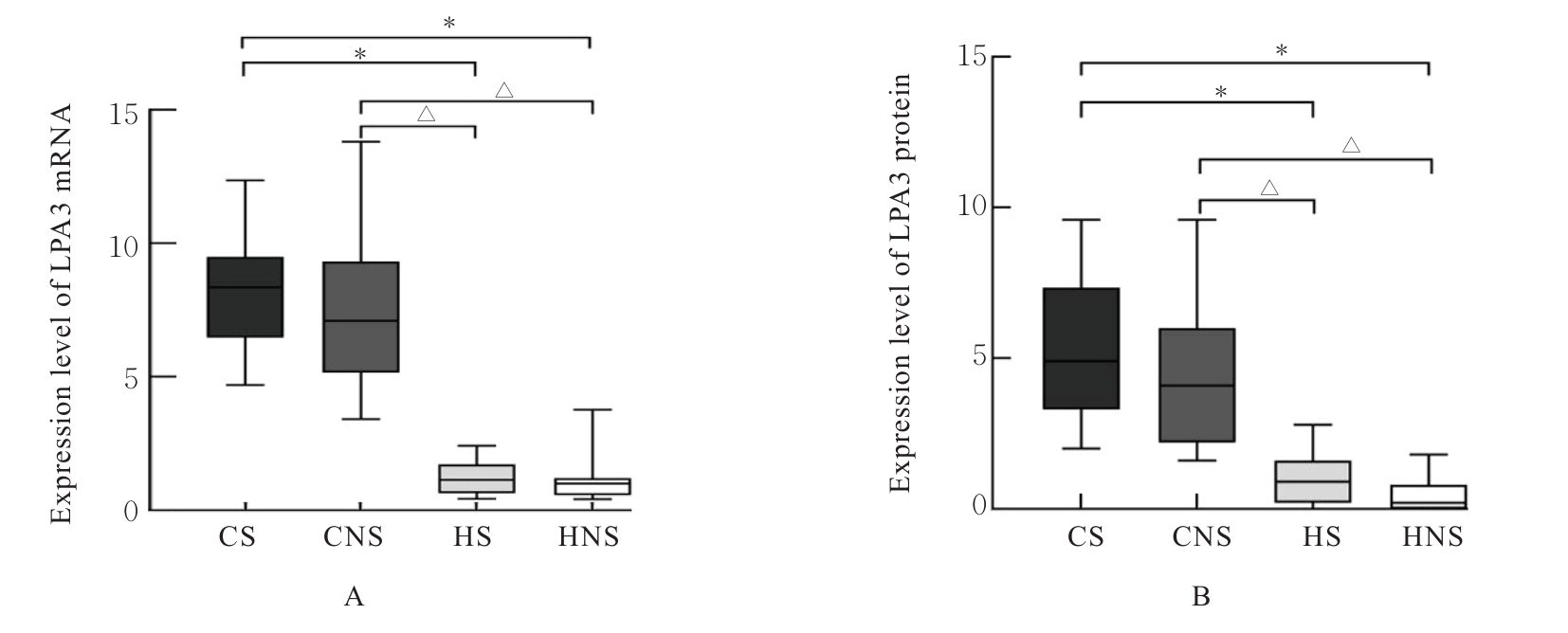
目的 探讨自分泌运动因子(ATX)和溶血磷脂酸受体3(LPA3)在慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)患者血清及肺组织中的表达情况,阐明ATX和LPA3在COPD发生发展过程中的作用。 方法 收集40例COPD患者纳入急性加重期组(AECOPD组),经治疗后处于稳定期者纳入COPD稳定期组,共计40例,并收集40名健康体检者纳入对照组,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测各组研究对象血清中ATX水平。另收集80例行肺叶切除术的患者,分为COPD吸烟组(CS组,n=20)、COPD不吸烟组(CNS组,n=20)、非COPD吸烟组(HS组,n=20)和非COPD不吸烟组(HNS组,n=20),收集各组研究对象的一般资料,HE染色观察各组患者肺组织的病理形态表现,免疫组织化学染色法检测各组患者肺组织中ATX和LPA3蛋白表达水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组患者肺组织中ATX和LPA3 mRNA表达水平,Pearson相关分析符合正态分布的连续变量的相关性,Spearman相关分析评估其他变量间的相关性。 结果 与对照组比较,COPD稳定期组研究对象第1秒用力呼气容积占预计值百分比(FEV1%pred)和第1秒用力呼气容积占用力肺活量百分比(FEV1/FVC)均明显降低(P<0.05)。与COPD稳定期组和对照组比较,AECOPD组患者血清中ATX水平升高(P<0.05);与对照组比较,COPD稳定期组患者血清中ATX水平升高(P<0.05)。AECOPD组患者血清中ATX水平与COPD评估测试量表(CAT)评分呈正相关关系(r=0.581,P<0.001),与吸烟史、白细胞计数(WBC)、中性粒细胞百分比(NEUT%)、中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)和体质量指数(BMI)无相关性(P>0.05);COPD稳定期组患者血清中ATX水平与WBC和CAT评分均呈正相关关系(r=0.384,P=0.014;r=0.463,P=0.003),与FEV1%pred和FEV1/FVC均呈负相关关系(r=
中图分类号:
- R563.9