吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1499-1511.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240603
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
草苁蓉多糖对THP-1巨噬细胞炎症反应的抑制作用及其机制
- 1.延边大学附属医院检验科,吉林 延吉 133000
2.延边大学医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,吉林 延吉 133000
Inhibitory effect of Boschnikia rossica polysaccharides on THP-1 macrophage inflammation and its mechanism
Xinyue MA1,2,Hui XU2,Jiawen DIAO2,Aihua JIN1( ),Jishu QUAN2(
),Jishu QUAN2( )
)
- 1.Department of Clinical Laboratory,Affiliated Hospital,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China
2.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,School of Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China
摘要:
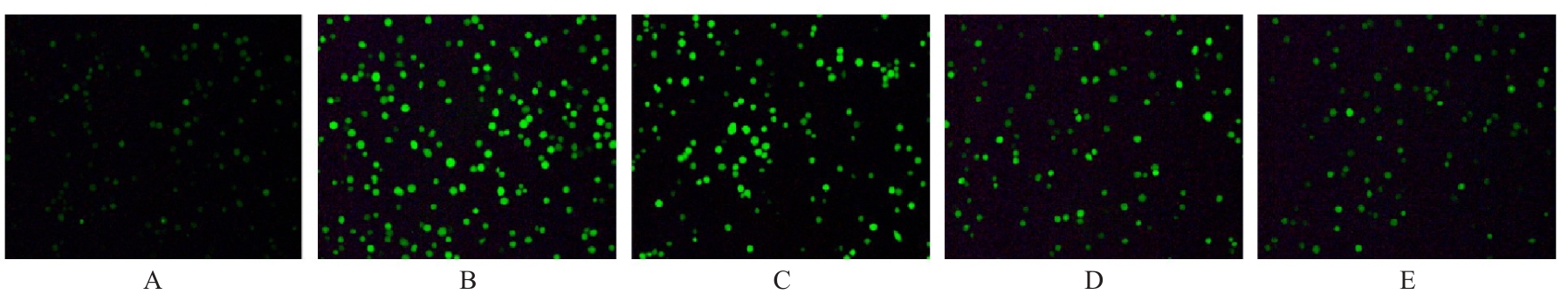
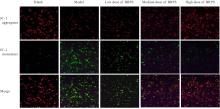
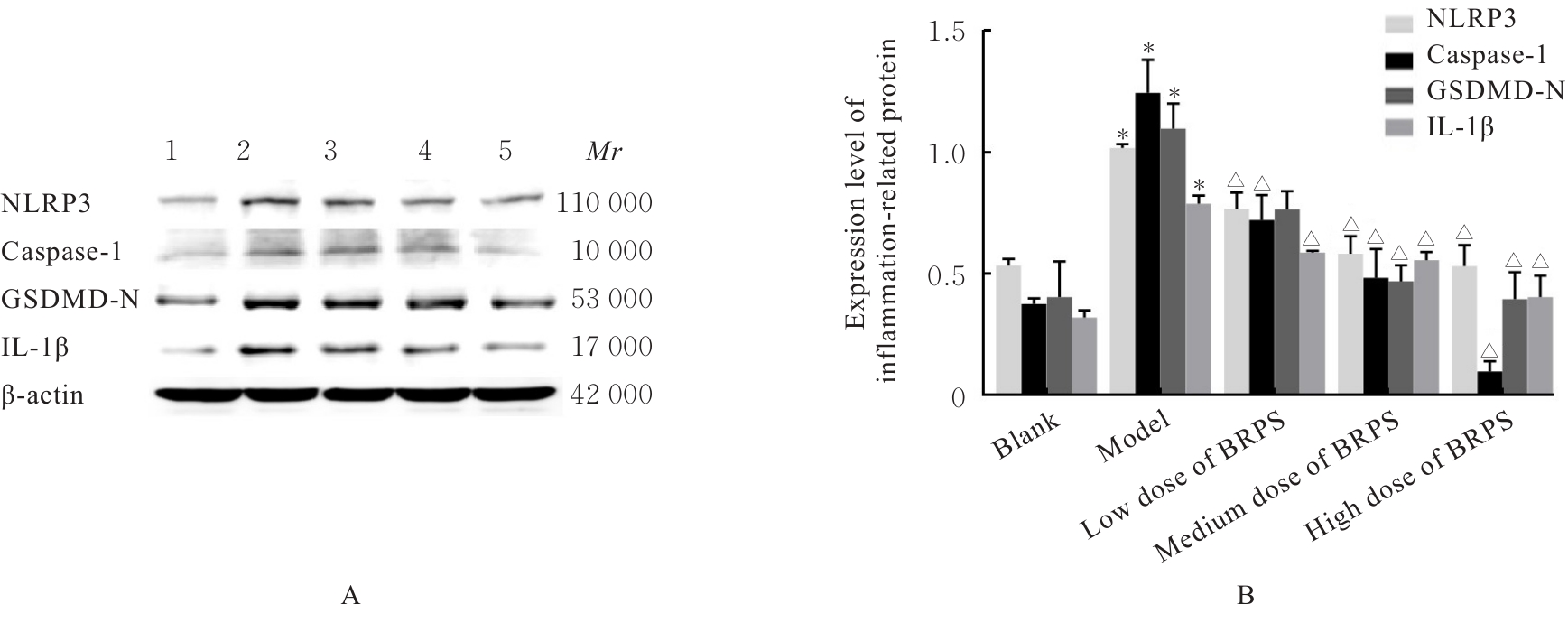
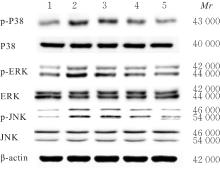
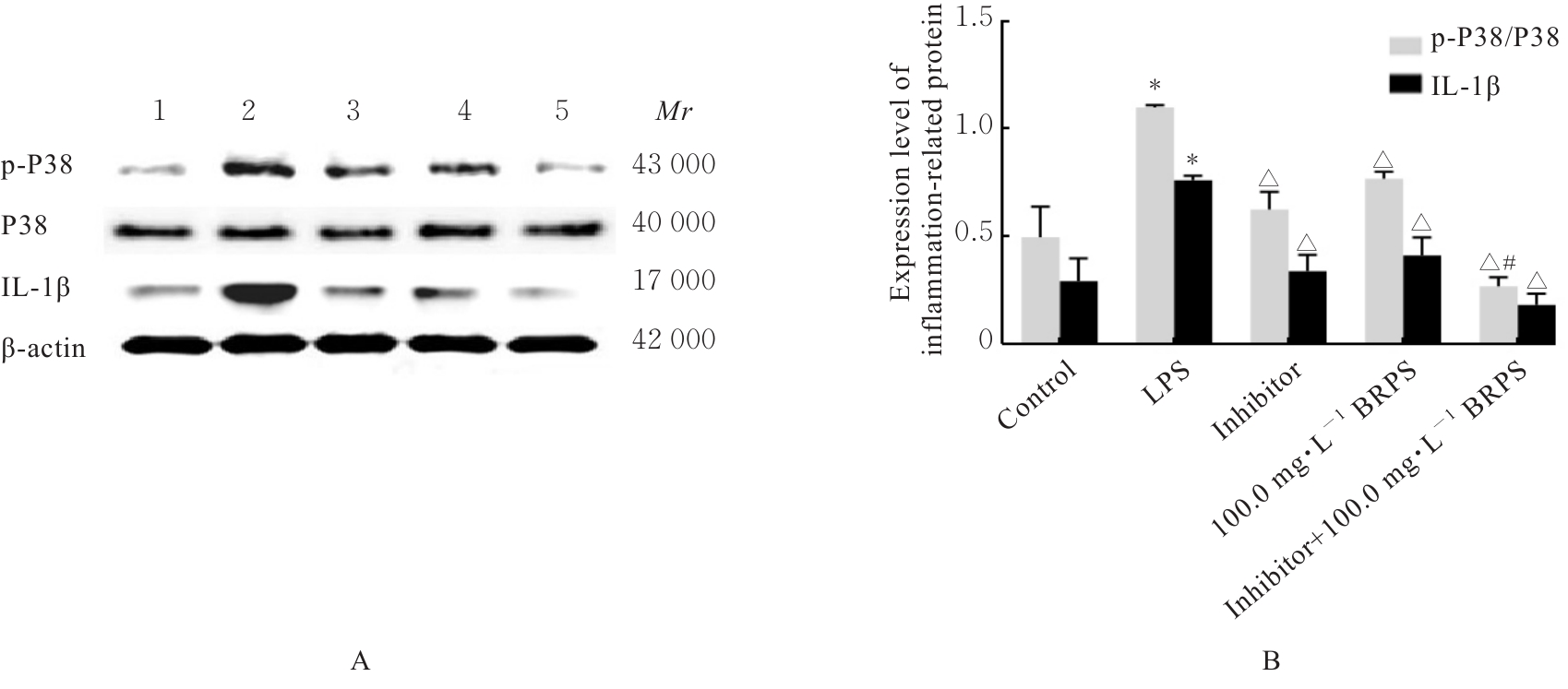
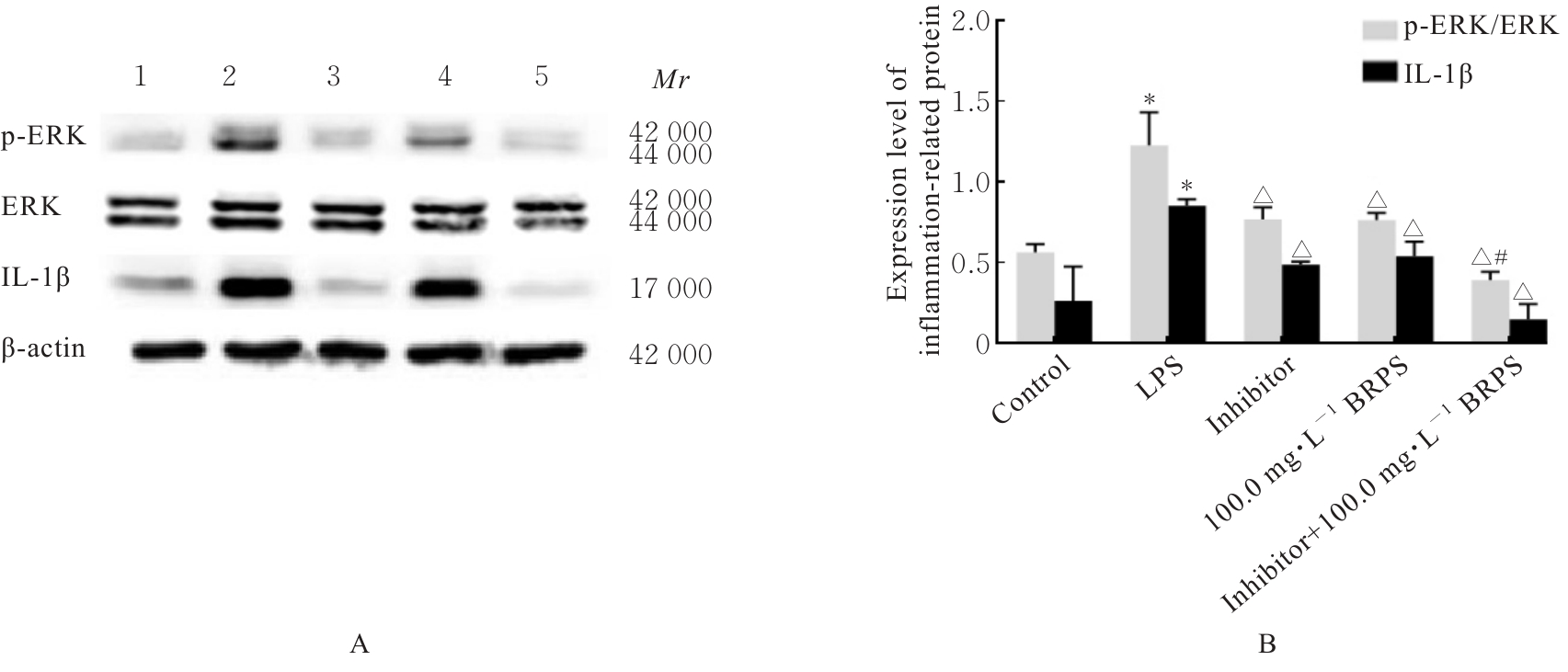
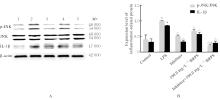
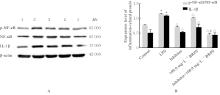
目的 探讨草苁蓉多糖(BRPS)对脂多糖(LPS)诱导的THP-1巨噬细胞炎症反应的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 将THP-1单核细胞分化为巨噬细胞,采用LPS诱导THP-1巨噬细胞,建立炎症模型。CCK-8法检测不同浓度(0、100、200、500、1 000和2 000 μg·L-1)LPS及不同浓度(0、12.5、25.0、50.0、100.0和200.0 mg·L-1)BRPS处理后THP-1巨噬细胞存活率,选取后续实验药物浓度。将THP-1巨噬细胞分为空白组、模型组、低剂量BRPS组(25.0 mg·L-1 BRPS)、中剂量BRPS组(50.0 mg·L-1 BRPS)和高剂量BRPS组(100.0 mg·L-1 BRPS)。采用P38抑制剂SB203580、ERK抑制剂U0126、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)抑制剂SP600125和核因子κB(NF-κB)抑制剂BAY11-7082对THP-1细胞进行验证。另取THP-1细胞,分为对照组、LPS组、抑制剂组、100.0 mg·L-1 BRPS组和抑制剂+100.0 mg·L-1 BRPS组。酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组THP-1巨噬细胞培养液中肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素(IL)-6和IL-1β水平,2,7-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)荧光探针法检测各组THP-1巨噬细胞中活性氧(ROS)水平,Hoechst33342/PI荧光染色法观察各组THP-1巨噬细胞膜损伤情况,JC-1荧光染色法观察各组THP-1巨噬细胞线粒体膜电位,蛋白印迹法检测各组THP-1巨噬细胞中环氧合酶2(COX-2)、高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)、NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NLRP3)、含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白酶(Caspase)-1、消皮素D(GSDMD)-N、IL-1β、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)和NF-κB相关蛋白表达水平。 结果 CCK-8法检测,LPS浓度为100~2 000 μg·L-1时,THP-1巨噬细胞存活率均>90%;与0 μg·L-1 LPS组比较,100、200、500、1 000和2 000 μg·L-1 LPS组THP-1巨噬细胞培养液中IL-6水平均明显升高(P<0.05),提示巨噬细胞炎症反应明显增强,因此选用100 μg·L-1 LPS构建炎症模型;12.5、25.0、50.0、100.0和200.0 mg·L-1 BRPS处理THP-1巨噬细胞,THP-1巨噬细胞存活率分别为91.2%、93.8%、91.4%、90.6%和91.8%,选取25.0、50.0和100.0 mg·L-1 BRPS作为后续实验中低、中和高剂量BRPS组药物浓度。ELISA法检测,与空白组比较,模型组THP-1巨噬细胞培养液中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞培养液中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。DCFH-DA荧光探针法检测,与空白组比较,模型组THP-1巨噬细胞中ROS水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞中ROS水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。Hoechst33342/PI荧光染色法观察,与空白组比较,模型组THP-1巨噬细胞膜损伤程度明显增加;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞膜损伤程度明显减少。JC-1荧光染色法观察,空白组THP-1巨噬细胞线粒体膜电位较高;与空白组比较,模型组THP-1巨噬细胞线粒体跨膜电位明显降低;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞线粒体跨膜电位逐渐升高。蛋白印迹法检测,与空白组比较,模型组THP-1巨噬细胞中COX-2、HMGB1、NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD-N和IL-1β蛋白表达水平及p-P38/P38、p-ERK/ERK、p-JNK/JNK和p-NF-κB/NF-κB比值均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,中和高剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞中HMGB1、NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD-N和IL-1β蛋白表达水平及p-P38/P38、p-ERK/ERK、p-JNK/JNK和p-NF-κB/NF-κB比值均明显降低(P<0.05),低剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞中NLRP3、Caspase-1和IL-1β蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),高剂量BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞中COX-2蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与对照组比较,LPS组THP-1巨噬细胞p-P38/P38、p-ERK/ERK、p-JNK/JNK和p-NF-κB/NF-κB比值及IL-1β蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与LPS组比较,抑制剂组、100 mg·L-1 BRPS组和抑制剂+100 mg·L-1 BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞中p-P38/P38、p-ERK/ERK、p-JNK/JNK和p-NF-κB/NF-κB比值及IL-1β蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与抑制剂组比较,抑制剂+ 100 mg·L-1 BRPS组THP-1巨噬细胞p-P38/P38、p-ERK/ERK、p-JNK/JNK和p-NF-κB/NF-κB比值均明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 BRPS抑制THP-1细胞巨噬细胞的炎症反应,其机制可能与BRPS调控MAPK和NF-κB信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5