吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 341-351.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250208
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
IκB激酶相互作用蛋白在宫颈癌组织中的表达及其对宫颈癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响
- 石河子大学第一附属医院妇科,新疆 石河子 832000
Expression of I kappa B kinase-interacting protein in cervical cancer tissue and its effect on proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
Yan WANG,Zouyu ZHAO,Panpan YU,Ping YANG( )
)
- Department of Gynecology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
摘要:
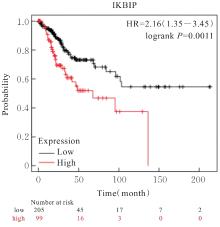
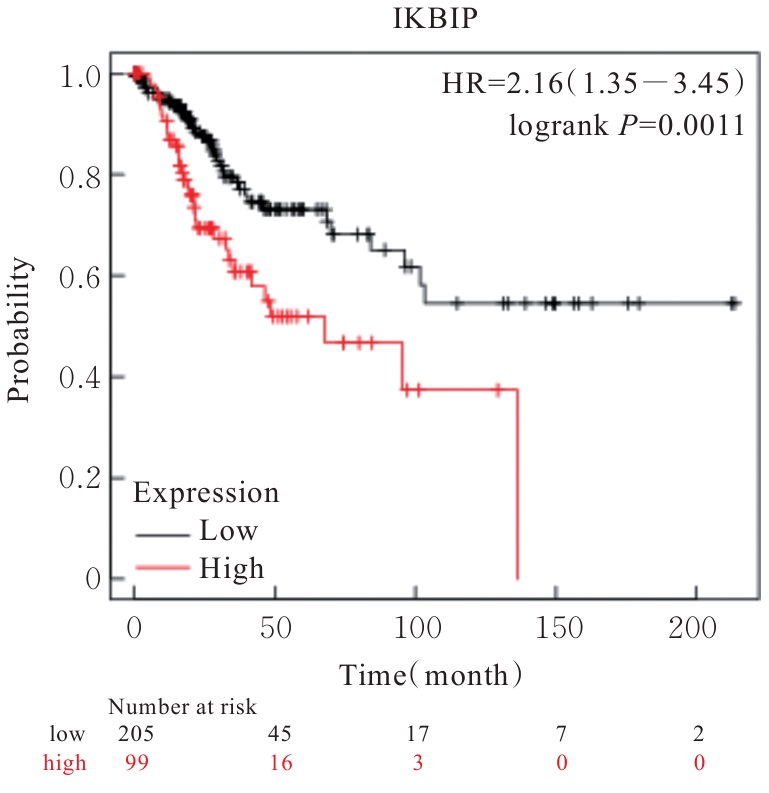
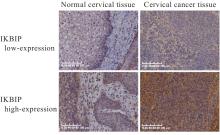
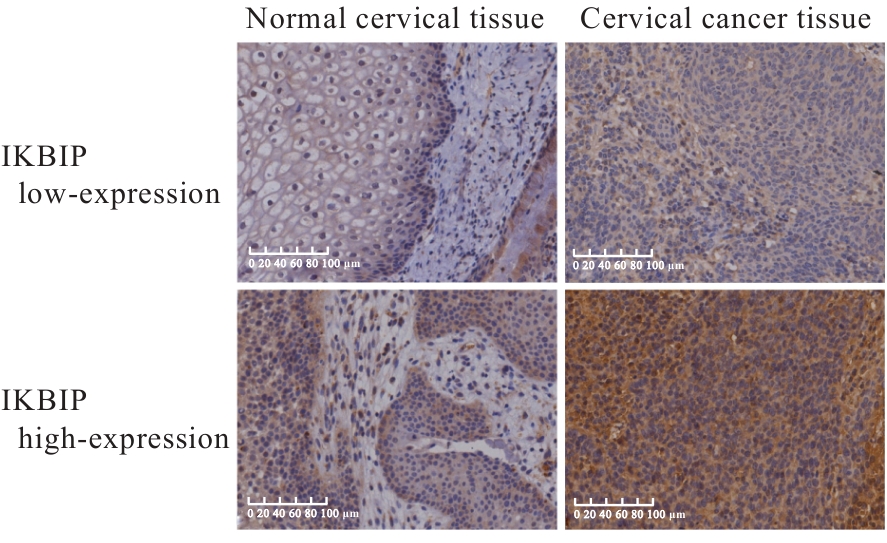
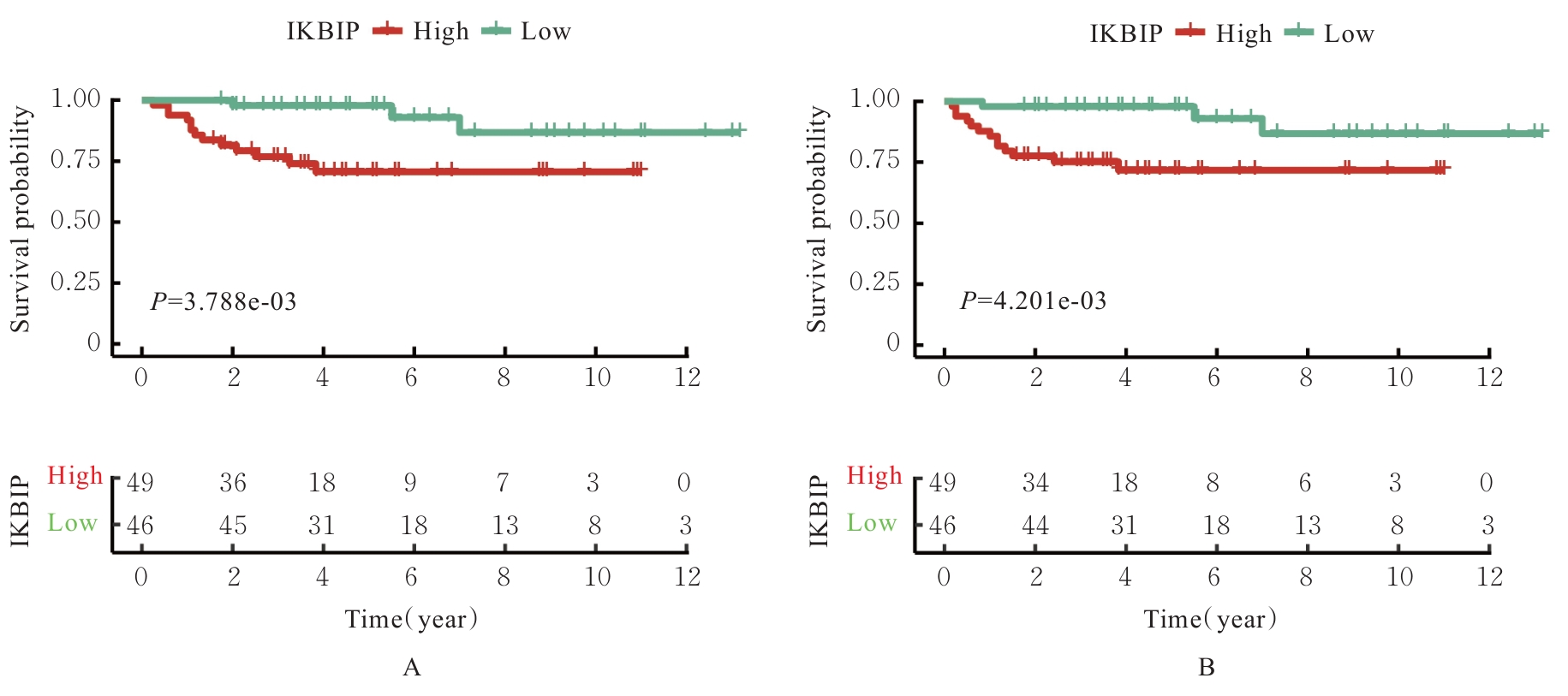
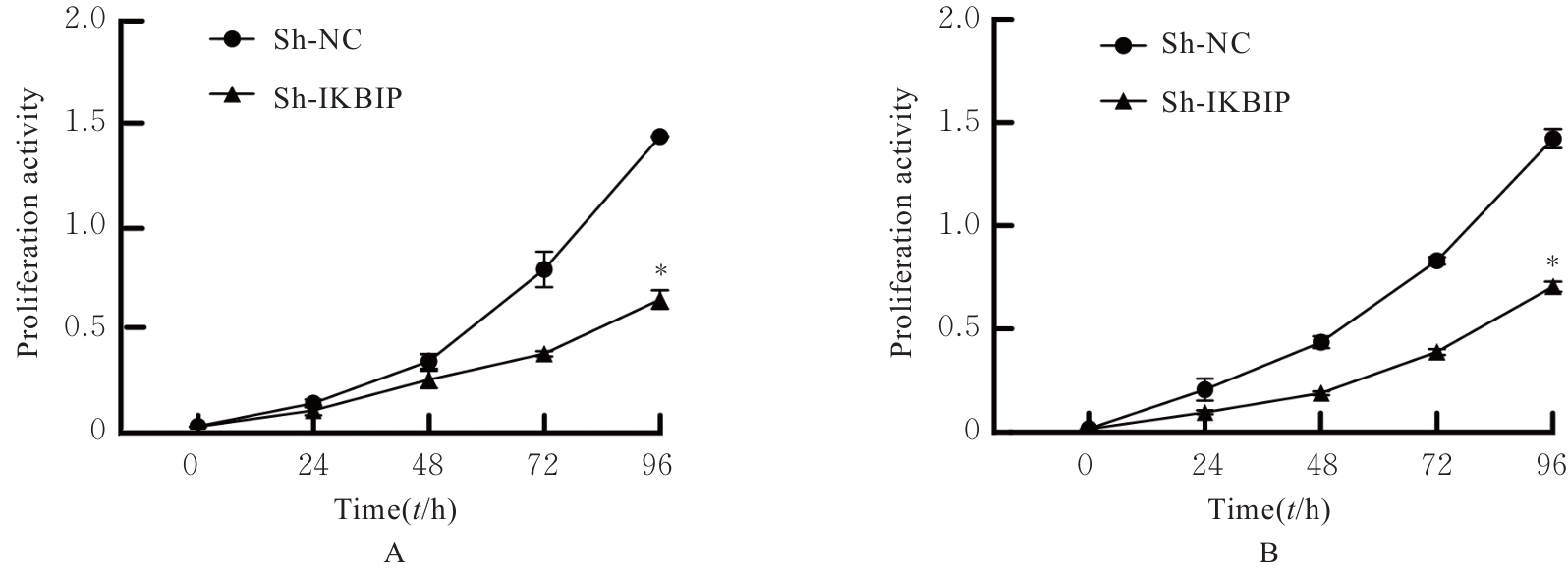
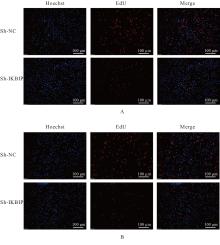
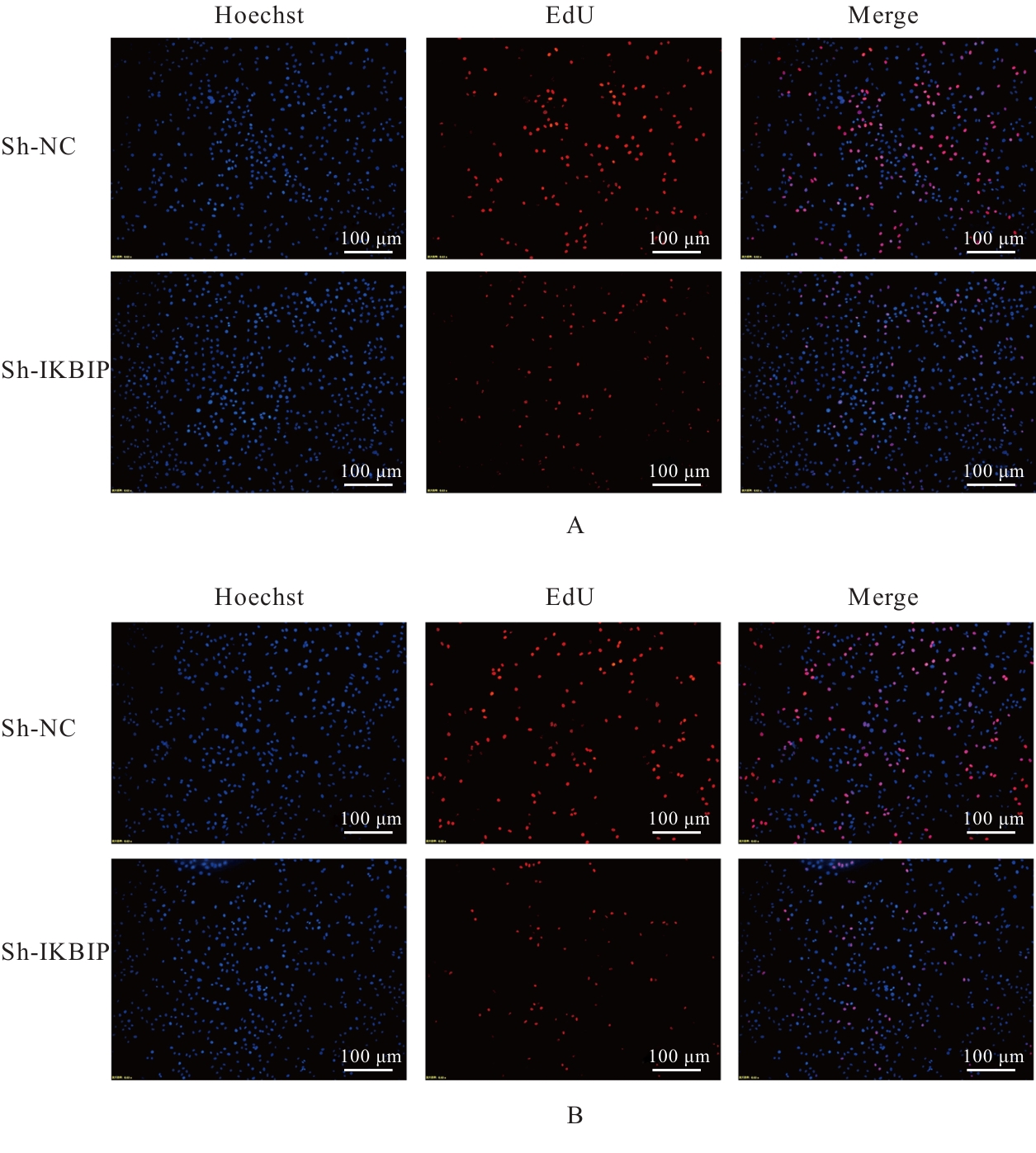
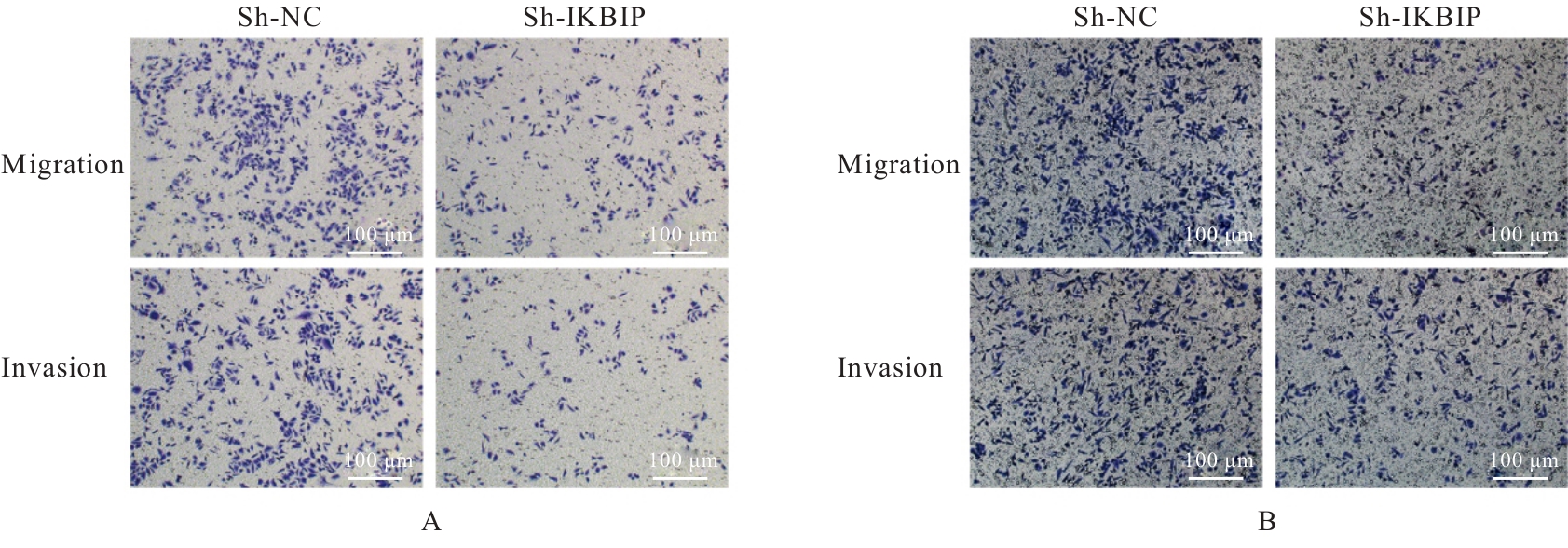
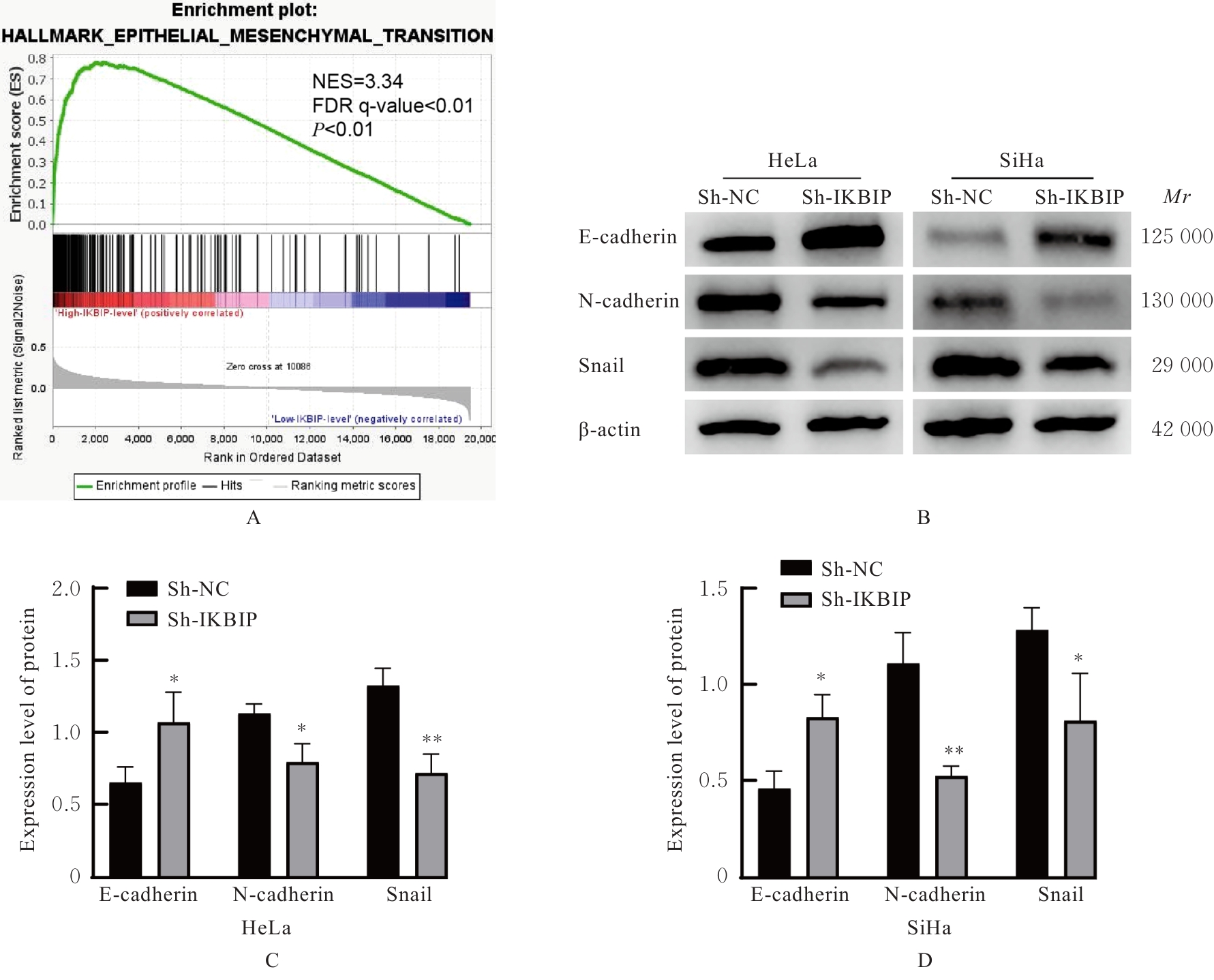
目的 探讨IκB激酶相互作用蛋白(IKBIP)在宫颈癌组织肿瘤细胞(TCCCT)中的表达与患者临床病理特征和预后的关系及其对宫颈癌(CC)HeLa和SiHa细胞生物学行为的影响,阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 采用GENT2数据库和Kaplan-Meier(K-M)plotter数据库分析CC及正常宫颈组织中的IKBIP mRNA表达水平差异以及其表达水平与CC患者临床预后的关系。基因集富集分析(GSEA)软件中选取参考基因集为Hallmark,进行相关通路富集。采用免疫组织化学法检测IKBIP蛋白在TCCCT和正常宫颈组织上皮细胞(ECNCT)中的表达情况,分析其表达水平与CC患者临床病理特征和预后的关系;单因素和多因素Cox回归分析影响CC患者预后的危险因素。构建IKBIP敲低的CC细胞(HeLa和SiHa细胞),实验分为sh-NC组和sh-IKBIP组;采用Western blotting法评估各组细胞中IKBIP蛋白表达情况;细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)和5-乙炔基-2'-脱氧尿苷(EdU)法检测各组细胞增殖活性及EdU阳性细胞率,Transwell小室实验检测各组迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数,Western blotting法检测各组细胞中E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)、N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)和Snail蛋白表达水平。 结果 GENT2数据库分析,CC组织中IKBIP mRNA表达水平高于正常宫颈组织(P<0.001)。GSEA富集分析,上皮-间质转化(EMT)通路位于IKBIP高表达组的第1位。免疫组织化学法,TCCCT中IKBIP蛋白阳性表达率高于ECNCT(50.5% vs 8.0%),且其过表达与FIGO分期(2018)和肿瘤分化程度有关联(P<0.05);单因素和多因素Cox回归分析,淋巴结转移(LNM)和IKBIP高表达是影响CC患者总生存期(OS)及无进展生存期(PFS)的独立危险因素(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与sh-NC组比较,sh-IKBIP组细胞IKBIP蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);CCK-8和EdU法,与sh-NC组比较,sh-IKBIP组细胞增殖活性和EdU阳性百分率均明显降低(P<0.05);Transwell小室实验,与sh-NC组比较,sh-IKBIP组迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数明显减少(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与sh-NC组比较,sh-IKBIP组细胞中E-cadherin蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),N-cadherin和Snail蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.05)。 结论 IKBIP蛋白在CC细胞中高表达,且与CC患者不良预后有密切关联。下调IKBIP蛋白表达可抑制CC细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力及EMT进程。
中图分类号:
- R711.74