吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 632-641.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250308
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
鹿茸多肽对C2C12成肌细胞分化的调控作用及机制
- 长春中医药大学药学院临床药学与中药药理教研室, 吉林 长春 130117
Regulatory effect of velvet antler polypeptides on differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts and its mechanism
- Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Chinese Medicine Pharmacology,School of Pharmacy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
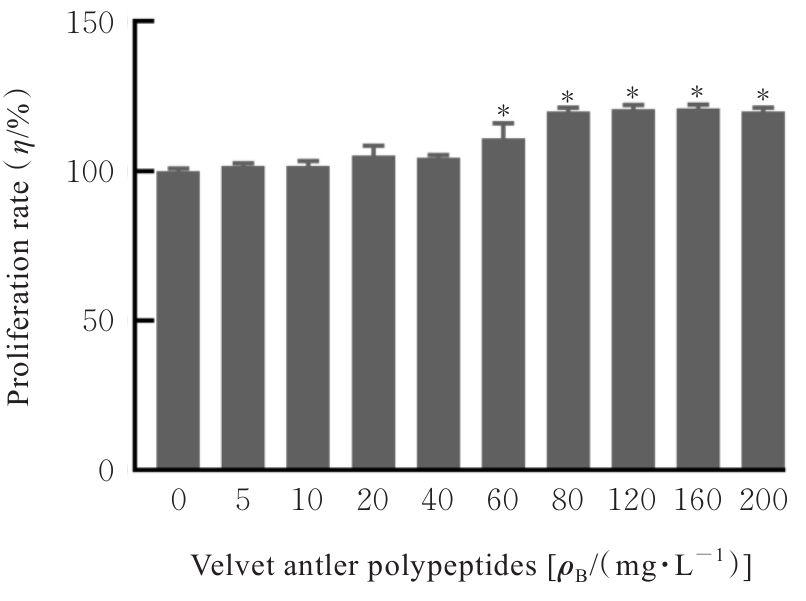
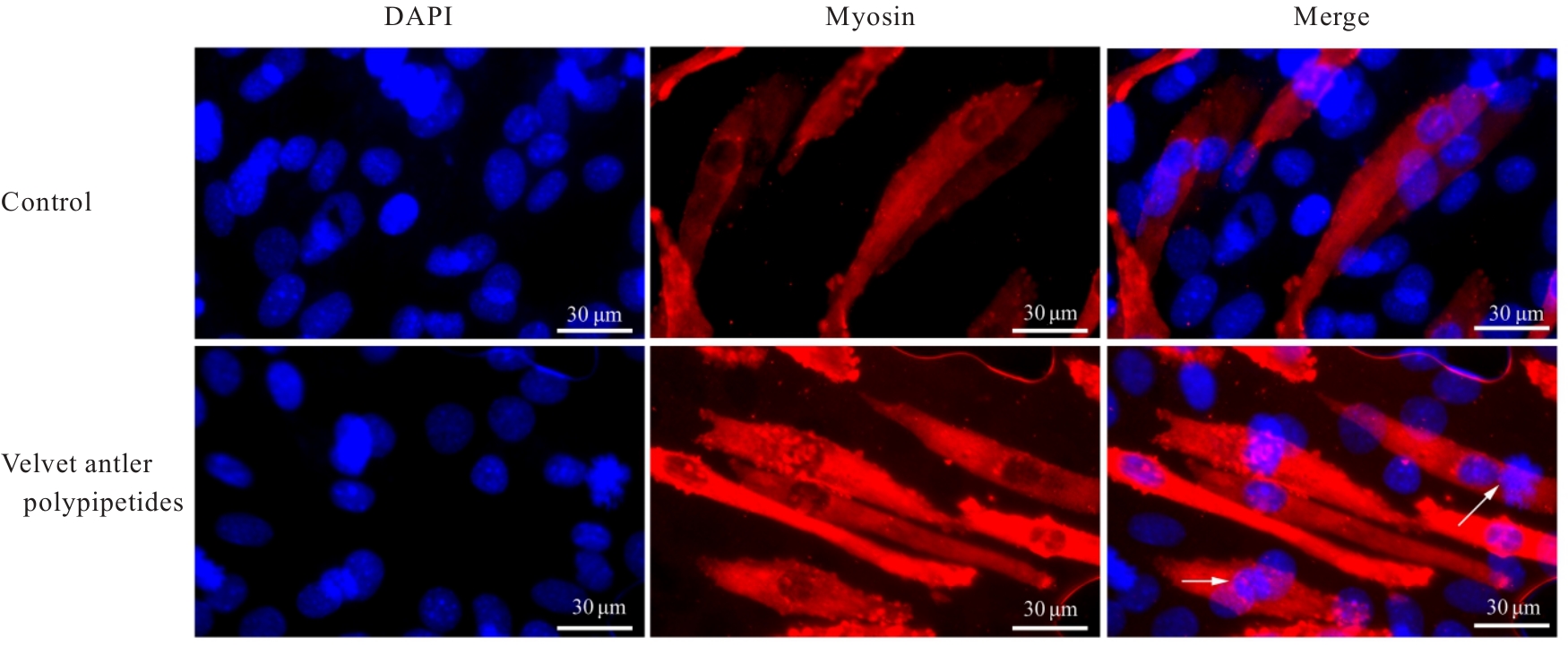
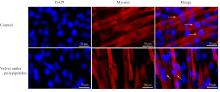
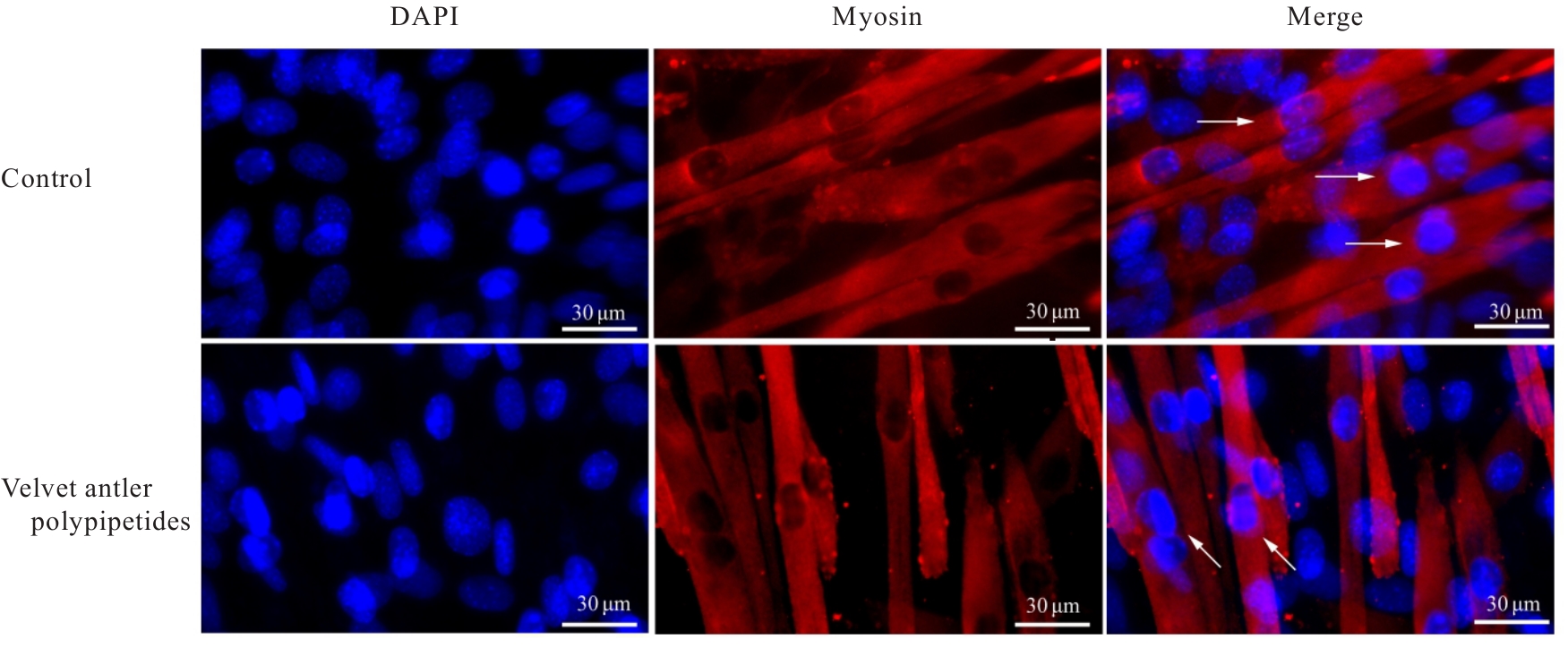
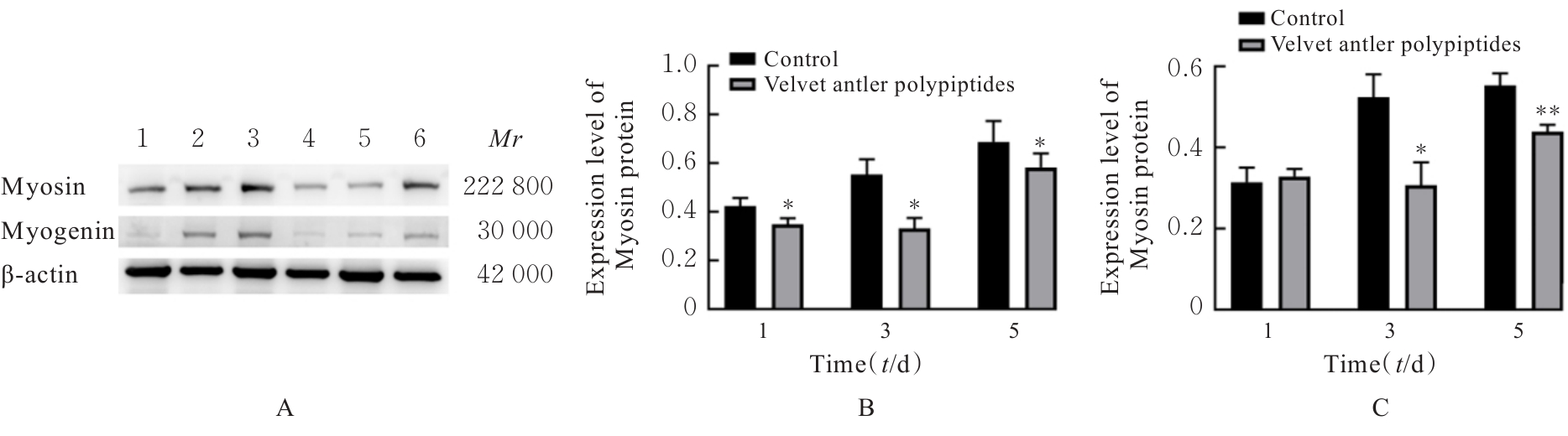
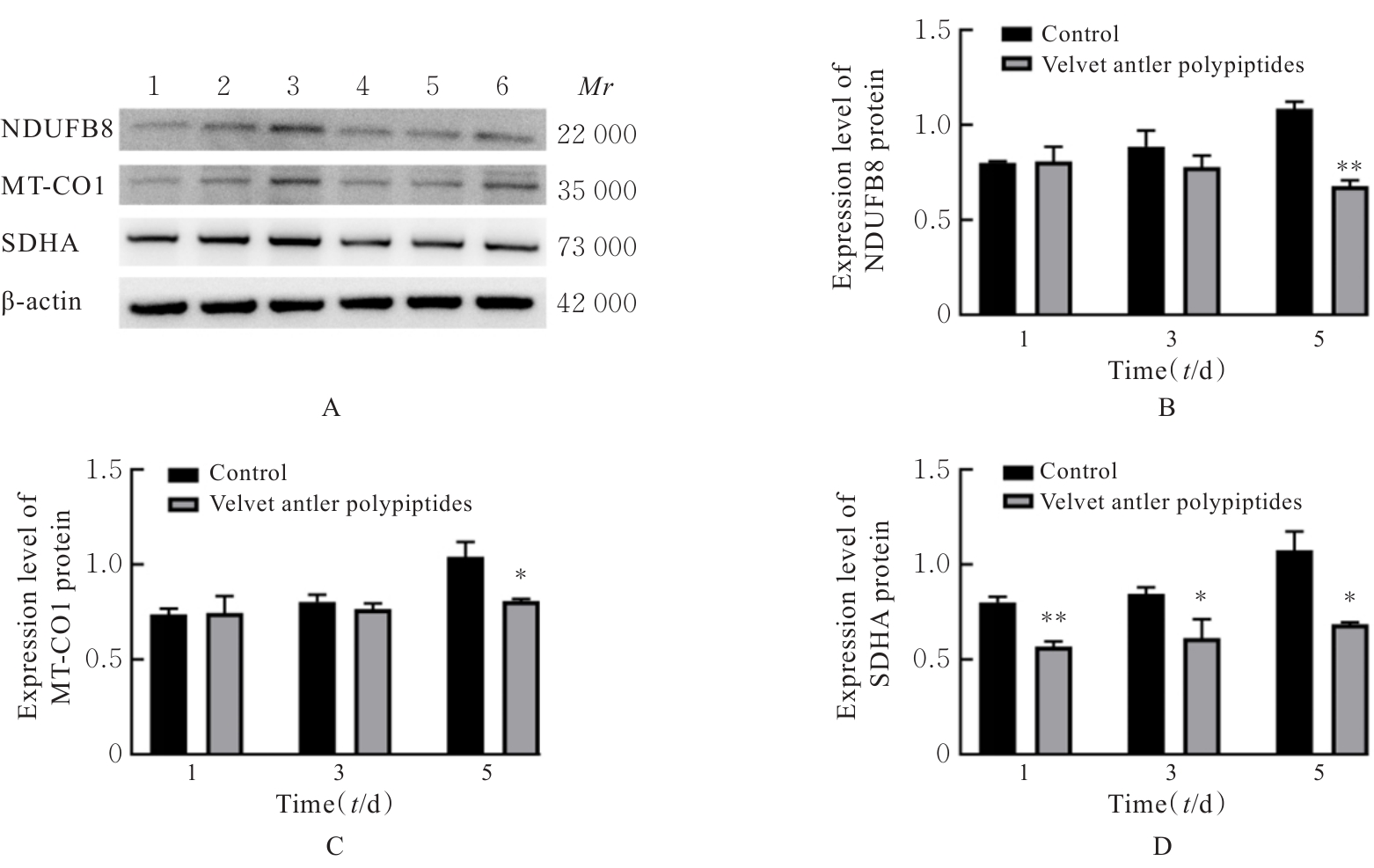
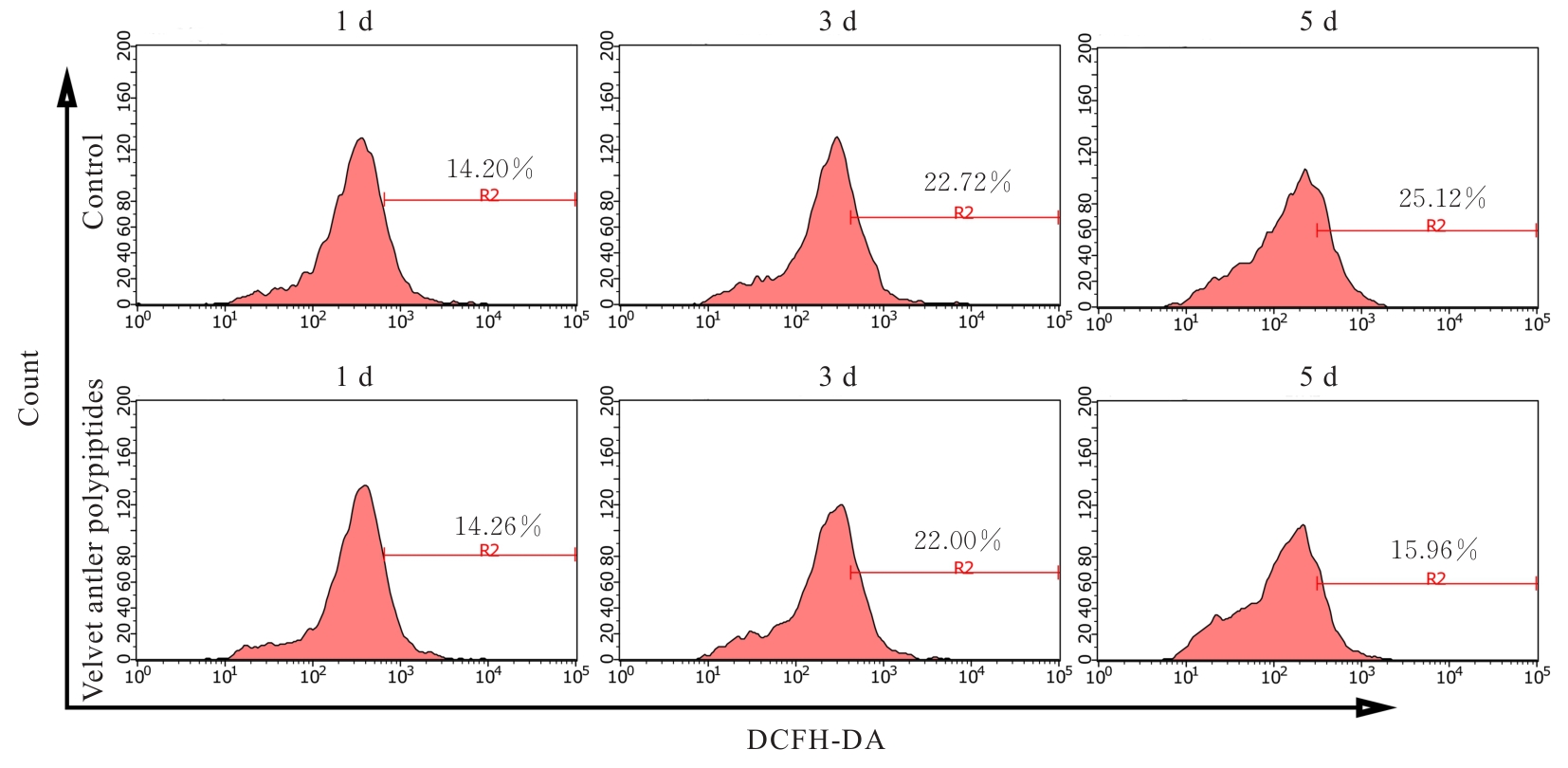
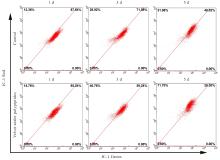
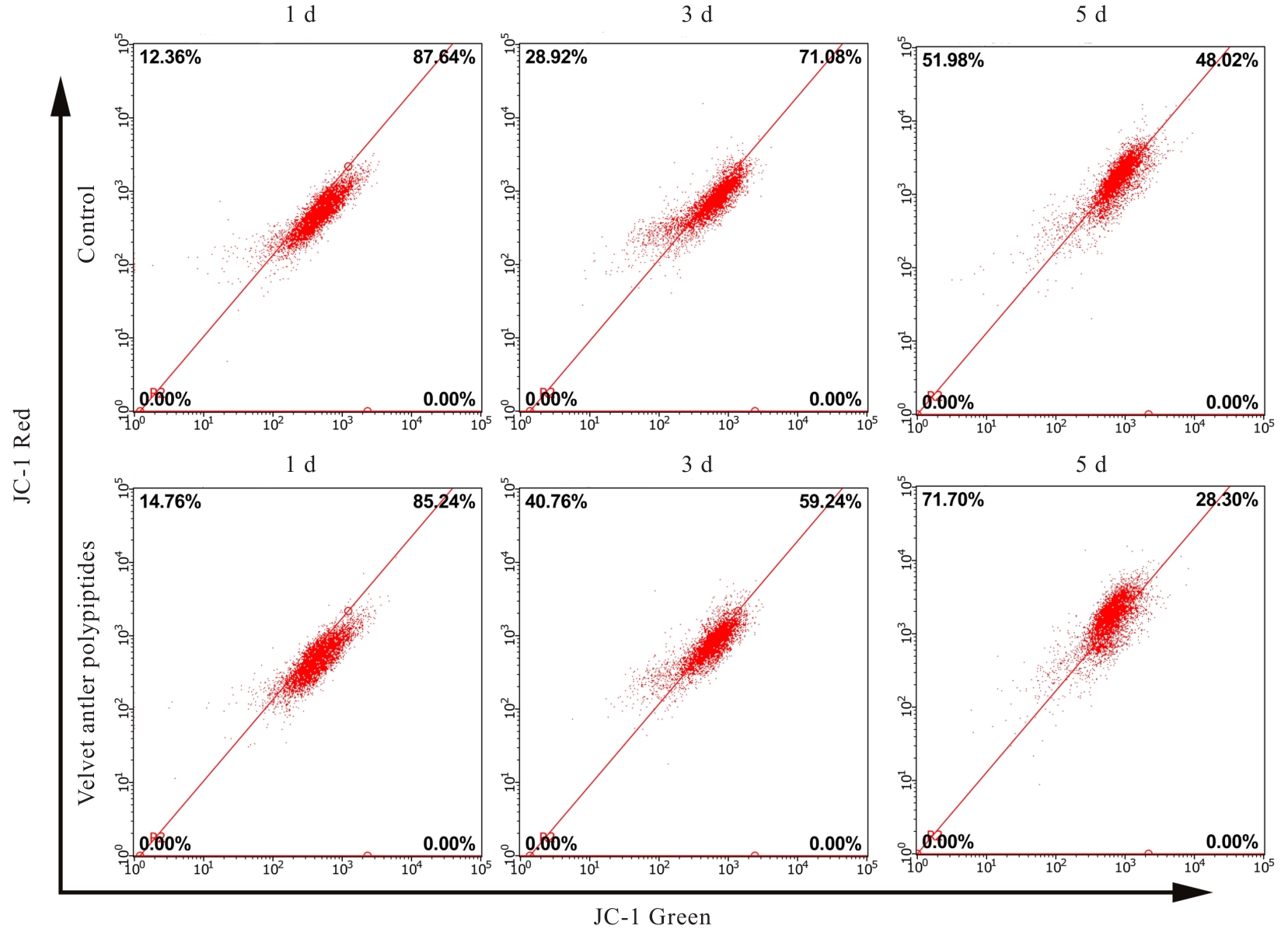
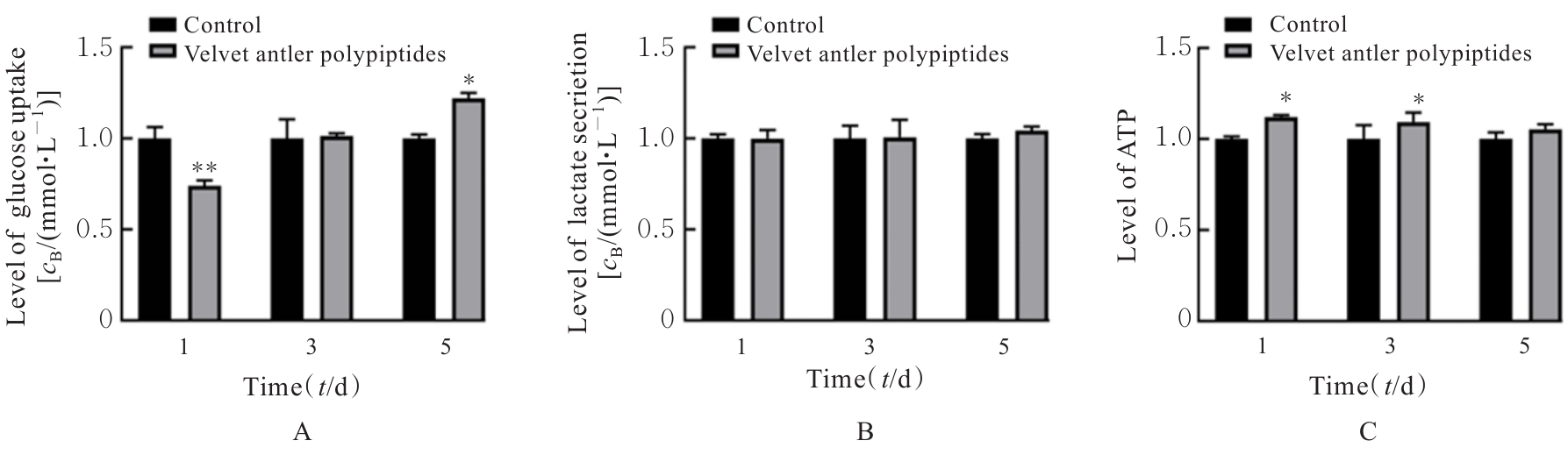
目的 探讨鹿茸多肽对C2C12成肌细胞分化过程中线粒体能量代谢效率的调控作用,并阐明其相关机制。 方法 采用生长培养基(GM)维持C2C12成肌细胞增殖,加入分化培养基(DM)诱导细胞分化,分化时间为1、3和5 d,分化的C2C12成肌细胞分为对照组和鹿茸多肽组,鹿茸多肽组加入80 mg·L-1鹿茸多肽,对照组给予同等体积磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)。采用细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测0、5、10、20、40、60、80、120、160和200 mg·L-1鹿茸多肽处理后各组未分化细胞增殖率,免疫荧光法检测各组细胞融合指数,Western blotting法检测各组细胞中肌球蛋白、肌细胞生成素、泛醌氧化还原酶B8(NDUFB8)、线粒体编码细胞色素C氧化酶1(MT-CO1)和琥珀酸脱氢酶复合体黄蛋白亚基A(SDHA)蛋白表达水平,2',7'-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)荧光探针法检测各组细胞中活性氧(ROS)水平,线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒(JC-1)检测各组细胞线粒体膜电位,试剂盒检测各组细胞中三磷酸腺苷(ATP)水平、葡萄糖摄取量和乳酸水平。 结果 与 0 mg·L-1 鹿茸多肽处理组比较,60、80、120、160和200 mg·L-1鹿茸多肽处理组未分化C2C12成肌细胞增殖率均明显升高(P<0.05)。免疫荧光法检测,与分化同期对照组比较,分化3和5 d鹿茸多肽处理组C2C12成肌细胞融合指数均明显降低(P<0.05),多核肌管细胞数量明显减少。Western blotting法,与分化同期对照组比较,分化1、3和5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞中肌球蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),分化3和5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞中肌细胞生成素蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与分化同期对照组比较,分化5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞中NDUFB8和MT-CO1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),分化1、3和5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞SDHA蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。DCFH-DA荧光探针法,与分化同期对照组比较,分化5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞ROS水平明显降低(P<0.01)。JC-1试剂盒检测,与分化同期对照组比较,分化3和5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞线粒体膜电位均明显升高(P<0.05)。与分化同期对照组比较,分化1 d鹿茸多肽组细胞葡萄糖摄取量明显降低(P<0.01),分化5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞葡萄糖摄取量明显升高(P<0.05),分化1、3和5 d鹿茸多肽组细胞乳酸水平差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);分化1和3 d鹿茸多肽组细胞ATP水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 鹿茸多肽对C2C12成肌细胞分化具有抑制作用,其机制可能与鹿茸多肽降低线粒体氧化磷酸化复合体亚基表达,提高线粒体氧化磷酸化效率有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5