吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1019-1027.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250418
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
Rh 家族 C 糖蛋白在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中的表达及其临床意义
周紫如1,孙梦菲2,张华坤1,孙淑妍1,孙琦2,李锋1,3,陈云昭4,禹洁4,曹玉文1( ),崔晓宾1,2(
),崔晓宾1,2( )
)
- 1.石河子大学医学院病理学系,新疆 石河子 832002
2.南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院病理科,江苏 南京 210008
3.首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院病理科,北京 100020
4.浙江省人民医院 杭州医学院附属人民医院病理科,浙江 杭州 310014
Expression of Rh family C glycoprotein in esophageal squamous carcinoma and its clinical significance
Ziru ZHOU1,Mengfei SUN2,Huakun ZHANG1,Shuyan SUN1,Qi SUN2,Feng LI1,3,Yunzhao CHEN4,Jie YU4,Yuwen CAO1( ),Xiaobin CUI1,2(
),Xiaobin CUI1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology,School of Medicial Sciences,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832002,China
2.Department of Pathology,Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital,School of Medical Sciences,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210008,China
3.Department of Pathology,Affilicated Beijing Chaoyang Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100020,China
4.Department of Pathology,Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital,Affiliated People’s Hospital,Hangzhou Medical College,Hangzhou 310014,China
摘要:
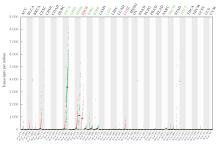
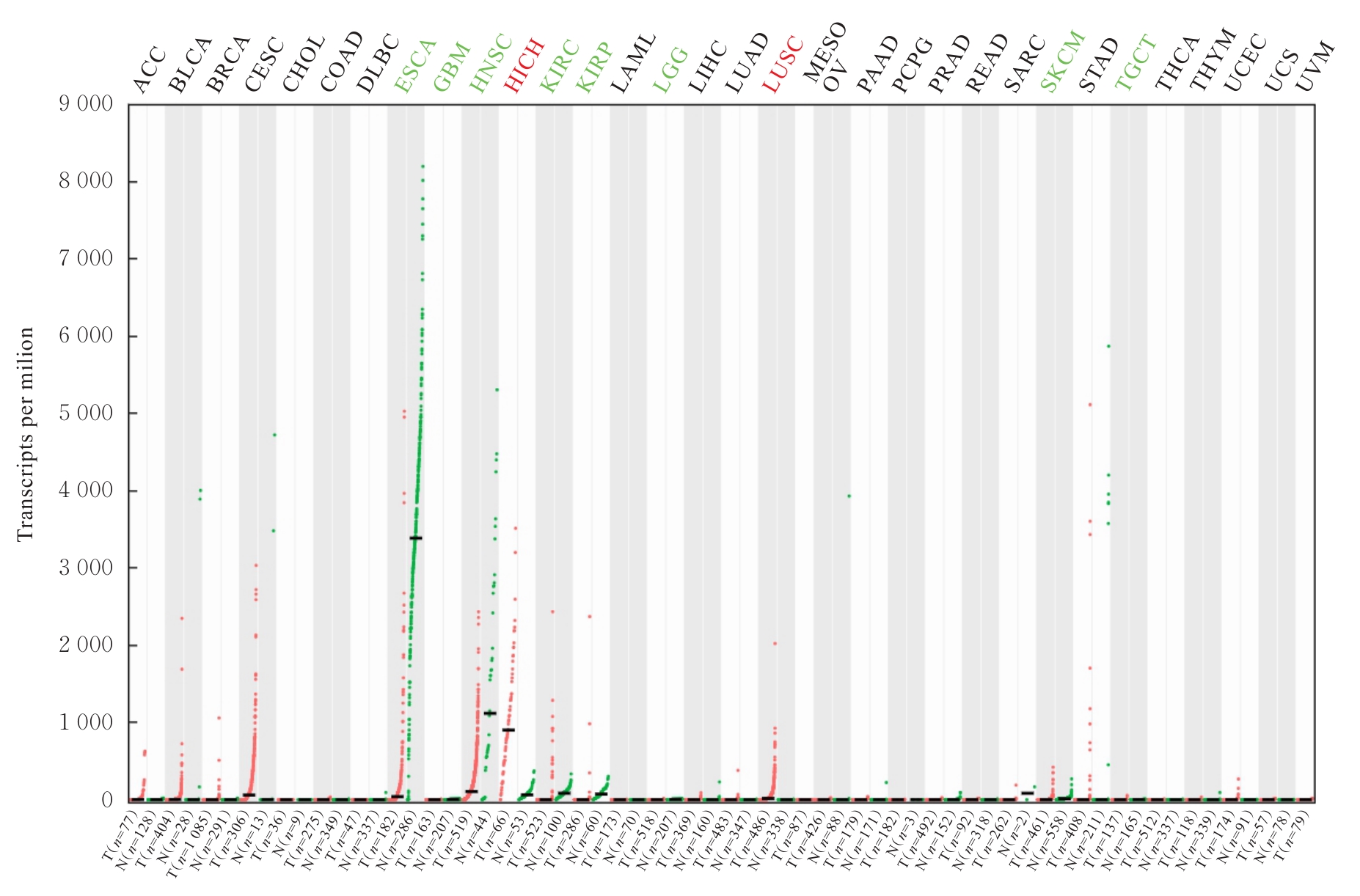
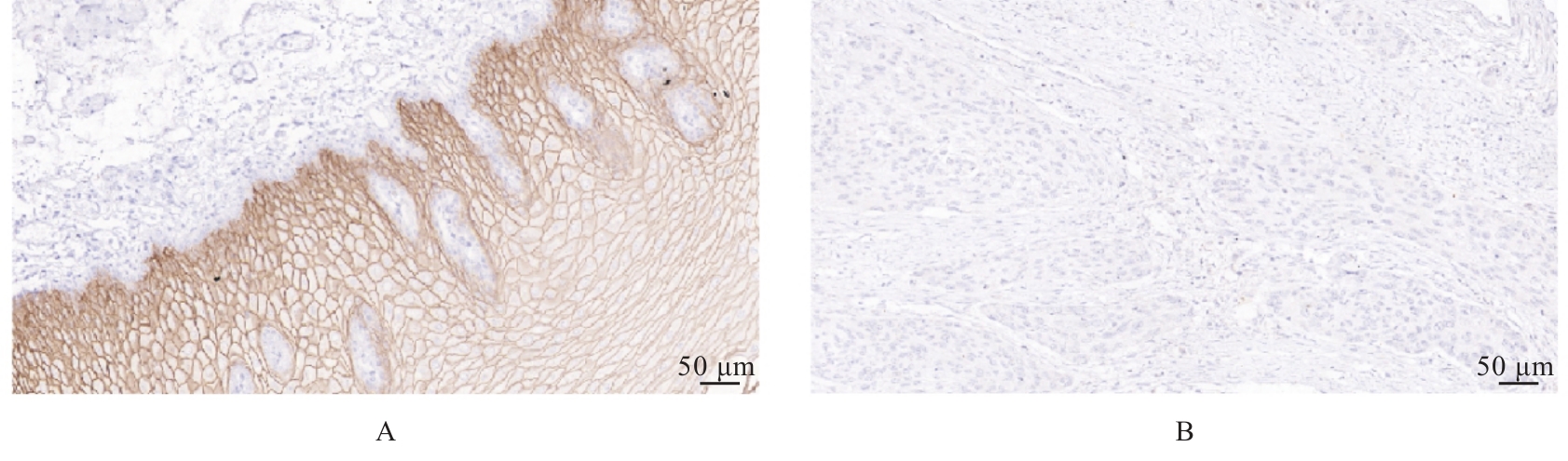
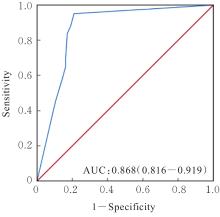
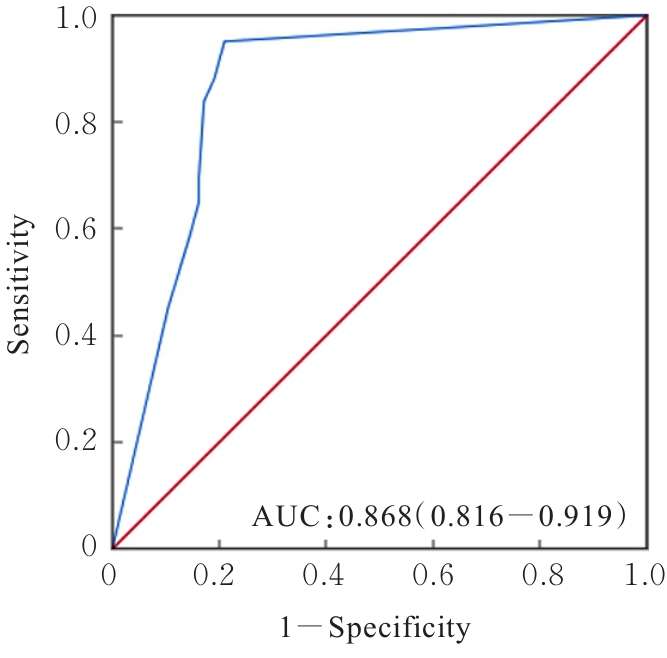
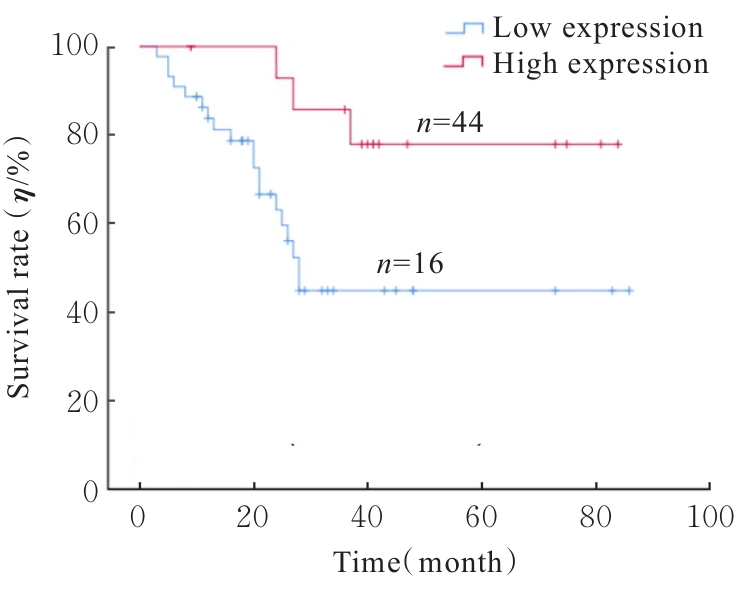
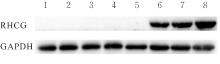
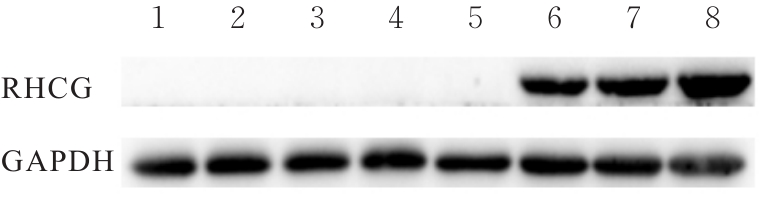
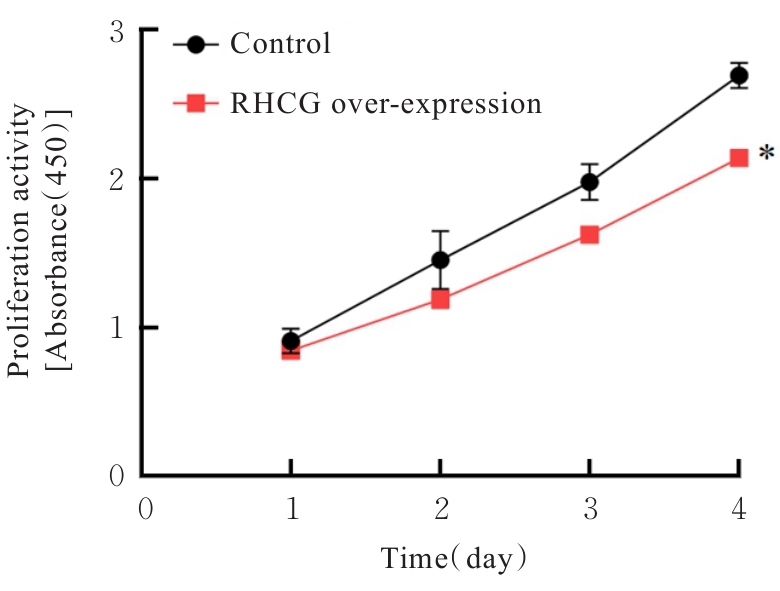
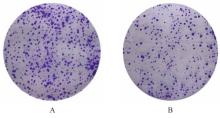
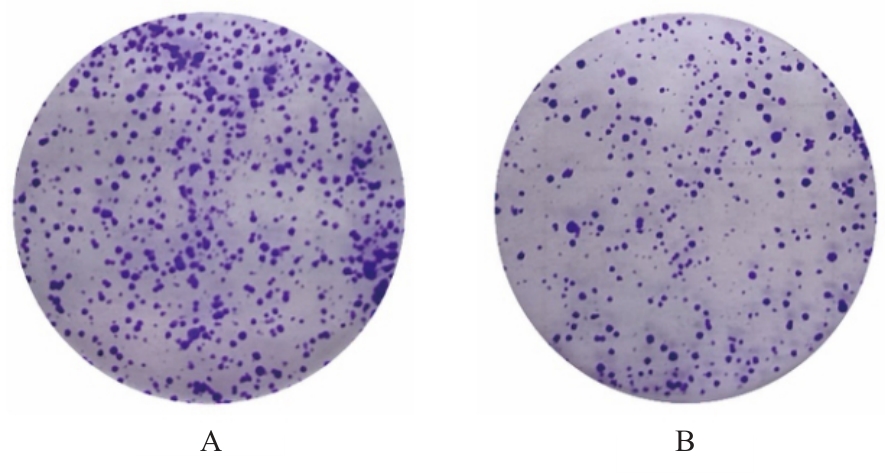
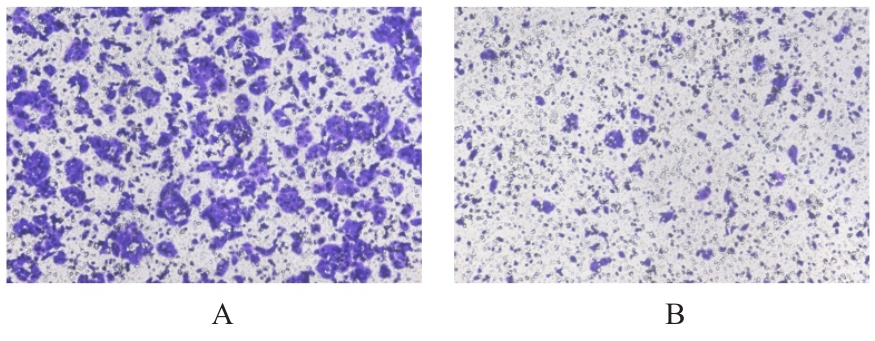
目的 探讨Rh家族C糖蛋白(RHCG)在食管鳞状细胞癌(ESCC)癌组织中的表达及其对ESCC细胞恶性生物学行为的影响,阐明RHCG作为ESCC患者诊断和预后标志物的价值。 方法 收集ESCC组织样本143例,癌旁正常组织样本105例。采用免疫组织化学染色法将143例ESCC样本分为2组,免疫组织化学评分≤6分为RHCG低表达组,免疫组织化学评分>6分为RHCG高表达组。免疫组织化学染色法检测143例ESCC组织和105例正常组织中RHCG蛋白表达情况,并分析其与ESCC患者临床病理特征的关系。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和Kaplan-Meier生存分析评估RHCG蛋白在ESCC患者诊断和预后判断中的价值,单因素与多因素COX回归分析确定影响ESCC患者预后的独立危险因素。采用基因表达谱动态分析(GEPIA)2数据库分析多种肿瘤组织中RHCG mRNA表达情况。培养ESCC TE-1细胞,设置不同Lipofectamine 2000∶RHCG比例,在6孔细胞培养板中转染TE-1细胞,RHCG转染组质粒添加量分别为2.0、2.5和3.0 μg,分别转染24和48 h,转染空载体的正常对照作为对照组,采用Western blotting法检测不同浓度转染后各组TE-1细胞中RHCG蛋白表达量并验证最佳转染条件,细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)实验检测2组TE-1细胞增殖活性,平板克隆实验检测2组TE-1细胞克隆形成数,Transwell小室实验检测2组TE-1细胞迁移细胞数。 结果 与癌旁正常组织比较,ESCC、多形性胶质母细胞瘤和头颈部鳞状细胞癌等多种癌组织中RHCG mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05)。RHCG蛋白主要位于正常食管鳞状上皮细胞的胞膜上,ESCC组织中RHCG蛋白表达强度低于癌旁正常食管组织(χ2=109.373,P<0.001),且RHCG低表达组患者分化程度差于RHCG高表达组(P=0.041)。RHCG诊断ESCC的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)值为0.86,灵敏度和特异度分别为95.1%及75.0%;Kaplan-Meier生存分析,与RHCG高表达组比较,RHCG低表达组患者生存期更短,预后较差[风险比(HR)=0.269,95%置信区间(CI)=0.113~0.639,P=0.020];COX回归分析,RHCG低表达可作为影响ESCC预后的独立危险因素(HR=4.569,95%CI=1.315~15.877,P=0.017)。Western blotting法验证,最佳转染条件为RHCG质粒3.0 μg转染48 h,此时RHCG过表达效果最佳,RHCG蛋白表达量最高。CCK-8实验,与对照组比较,接种细胞第4天时,过表达RHCG组细胞增殖活性降低(P<0.001)。在TE-1细胞中,过表达RHCG组TE-1细胞克隆形成数低于对照组(t=17.70,P<0.001)。Transwell小室实验,与对照组比较,过表达RHCG组TE-1细胞迁移数减少(t=23.74,P<0.001)。 结论 RHCG在ESCC组织中低表达且与ESCC患者预后不良相关,过表达RHCG可以抑制TE-1细胞的增殖和迁移,RHCG有望成为ESCC新的诊断和预后标志物及治疗靶点。
中图分类号:
- R735.1