吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1084-1093.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250424
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
基于甾醇酯与肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤发生的因果关系的孟德尔随机化分析
- 1.华北理工大学公共卫生学院分子遗传学研究室,河北 唐山 063210
2.华北理工大学生命科学学院分子遗传学研究室,河北 唐山 063210
Mendelian randomization analysis based on causal association of sterol esters with occurrence of intrahepatic ductal, biliary, and gallbladder malignancy
Xianlei ZHOU1,Zimo YAN2,Liwen GUO2,Xuemei ZHANG1,2( )
)
- 1.Laboratory of Molecular Genetics,School of Public Health,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063210,China
2.Laboratory of Molecular Genetics,School of Life Sciences,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063210,China
摘要:
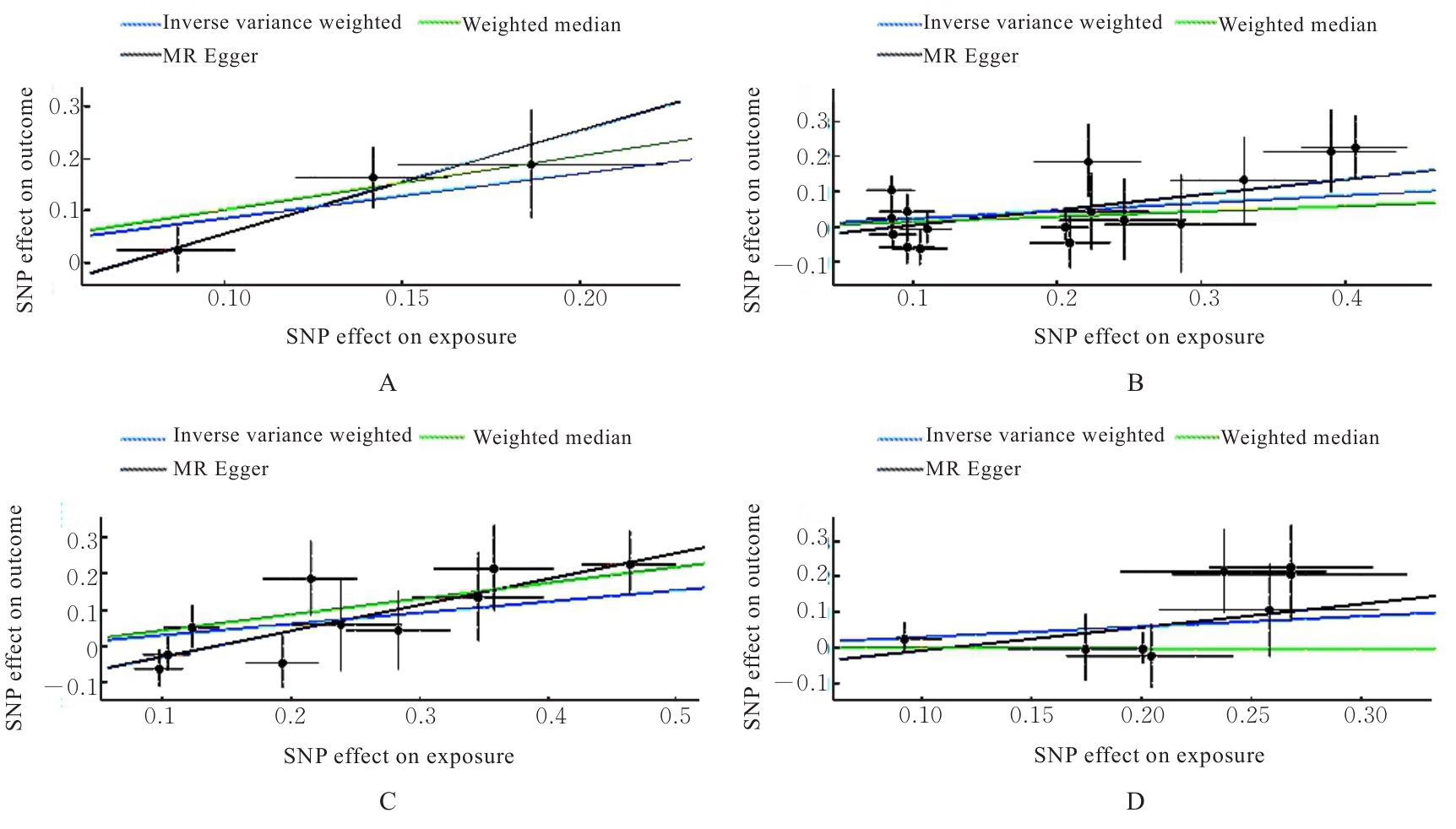
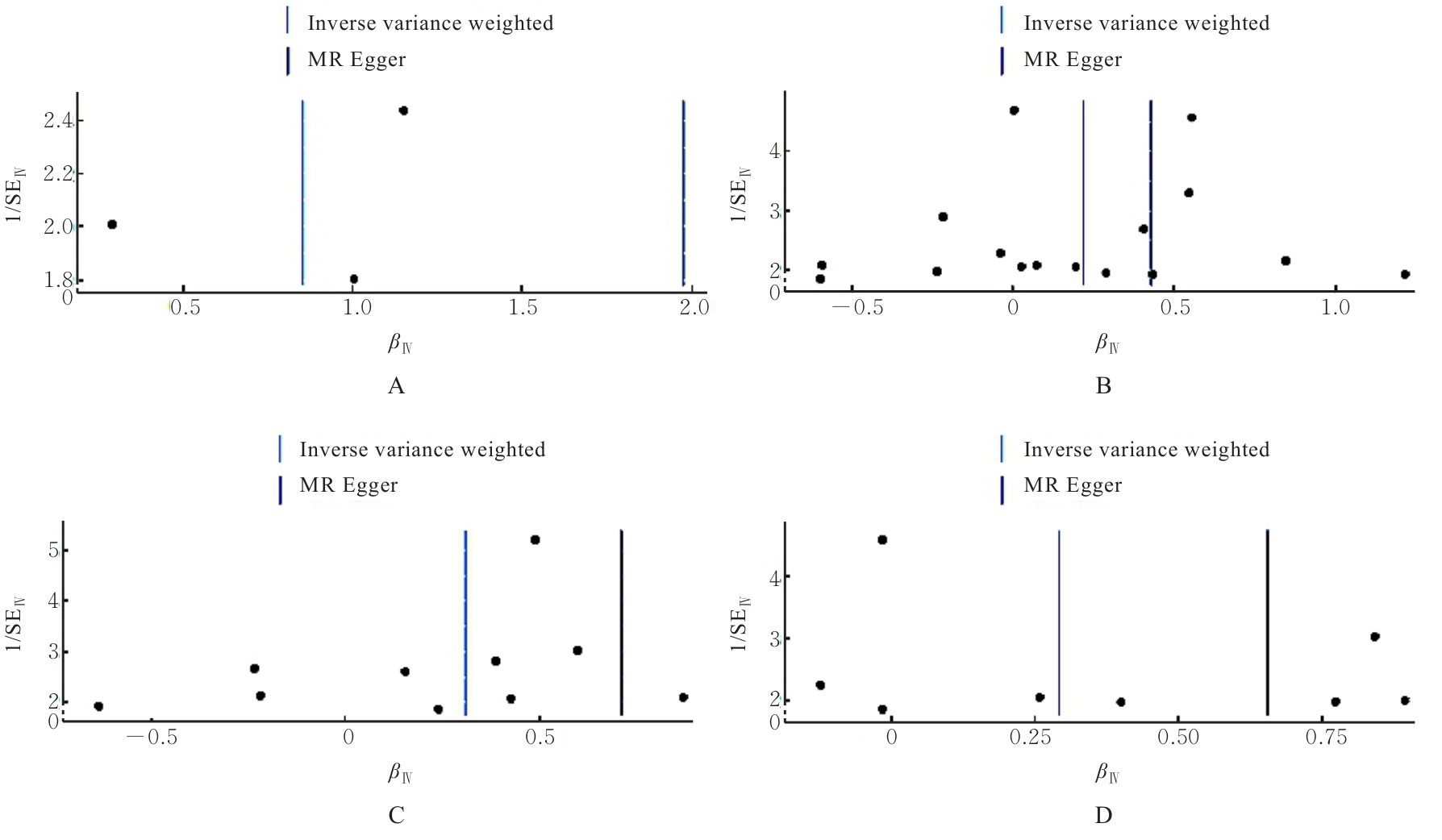
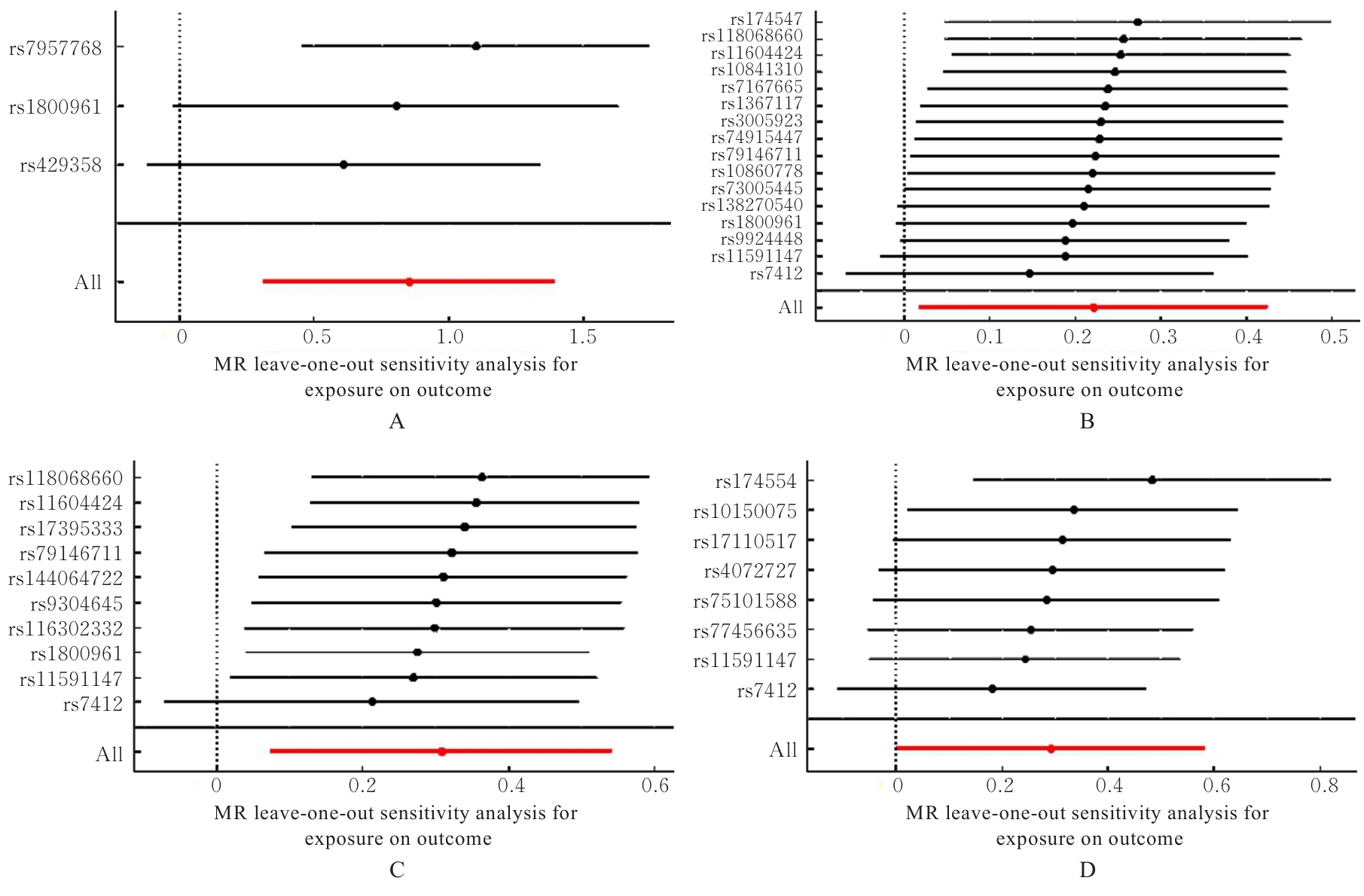
目的 采用两样本孟德尔随机化(MR)分析,探讨甾醇酯与肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤发生的因果关联,为甾醇酯的生物学机制研究以及探索肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤的早期防治提供依据。 方法 15种不同种类的甾醇酯特征的工具变量数据来自芬兰数据库(FinnGen),肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤全基因组数据来自全基因组关联研究(GWAS)数据库,以甾醇酯、肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤为关键词进行检索,下载编号为ICD-O-3和GCST90277238-GCST9027725,采用逆方差加权法(IVW)、MR-Egger回归法和加权中位数(WM)法评价甾醇酯与肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤发生的因果关联,采用MR-Egger截距法进行多效性检验,Cochran Q检验进行异质性检验,留一法进行敏感性分析,综合评估结果的可靠性和稳健性。 结果 IVW分析,甾醇酯(27:1/14:0)[比值比(OR)=2.349,95%置信区间(CI)=1.371~4.025,P=0.002]、甾醇酯(27:1/16:0)(OR=1.248,95%CI=1.018~1.523,P=0.033)、甾醇酯(27:1/18:2)(OR=1.361,95%CI=1.078~1.718,P=0.009)和甾醇酯(27:1/22:6)(OR=1.339,95%CI=1.001~1.791,P=0.049)增加患肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤的风险。MR-Egger回归分析,甾醇酯(27:1/18:2)(OR=2.038,95%CI=1.337~3.105,P=0.011)是肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤的危险因素。WM分析,甾醇酯(27:1/14:0)(OR=2.786,95%CI=1.419~5.468,P=0.003),甾醇酯(27:1/18:2)(OR=1.548,95%CI=1.148~2.088,P=0.004)是肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤的危险因素。MR-Egger截距分析和Cochran Q检验,本研究无水平多效性和异质性。留一法敏感性分析未发现影响较大的异常单核苷酸多态性(SNPs),确保本研究可靠性。 结论 甾醇酯(27:1/14:0)、甾醇酯(27:1/16:0)、甾醇酯(27:1/18:2)和甾醇酯(27:1/22:6)与肝内导管、胆道和胆囊恶性肿瘤之间存在因果关联且促进该类恶性肿瘤的发生发展。
中图分类号:
- R735