吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 879-886.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250403
血清总胆汁酸水平在ApoE-/-小鼠心律失常发生中的作用
岳星,李雪梅,张寒潇,左川弋,朱莉娟,吕菁,张承舜,曹新( )
)
- 成都中医药大学针灸推拿学院针灸学美容教研室,四川 成都 610075
Role of serum total bile acid level in development of arrhythmia in ApoE-/- mice
Xing YUE,Xuemei LI,Hanxiao ZHANG,Chuanyi ZUO,Lijuan ZHU,Jing LYU,Chengshun ZHANG,Xin CAO( )
)
- Department of Acupuncture&Aesthetic Medicine,School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina,Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu 610075,China )
摘要:
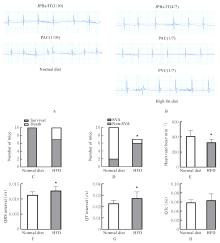
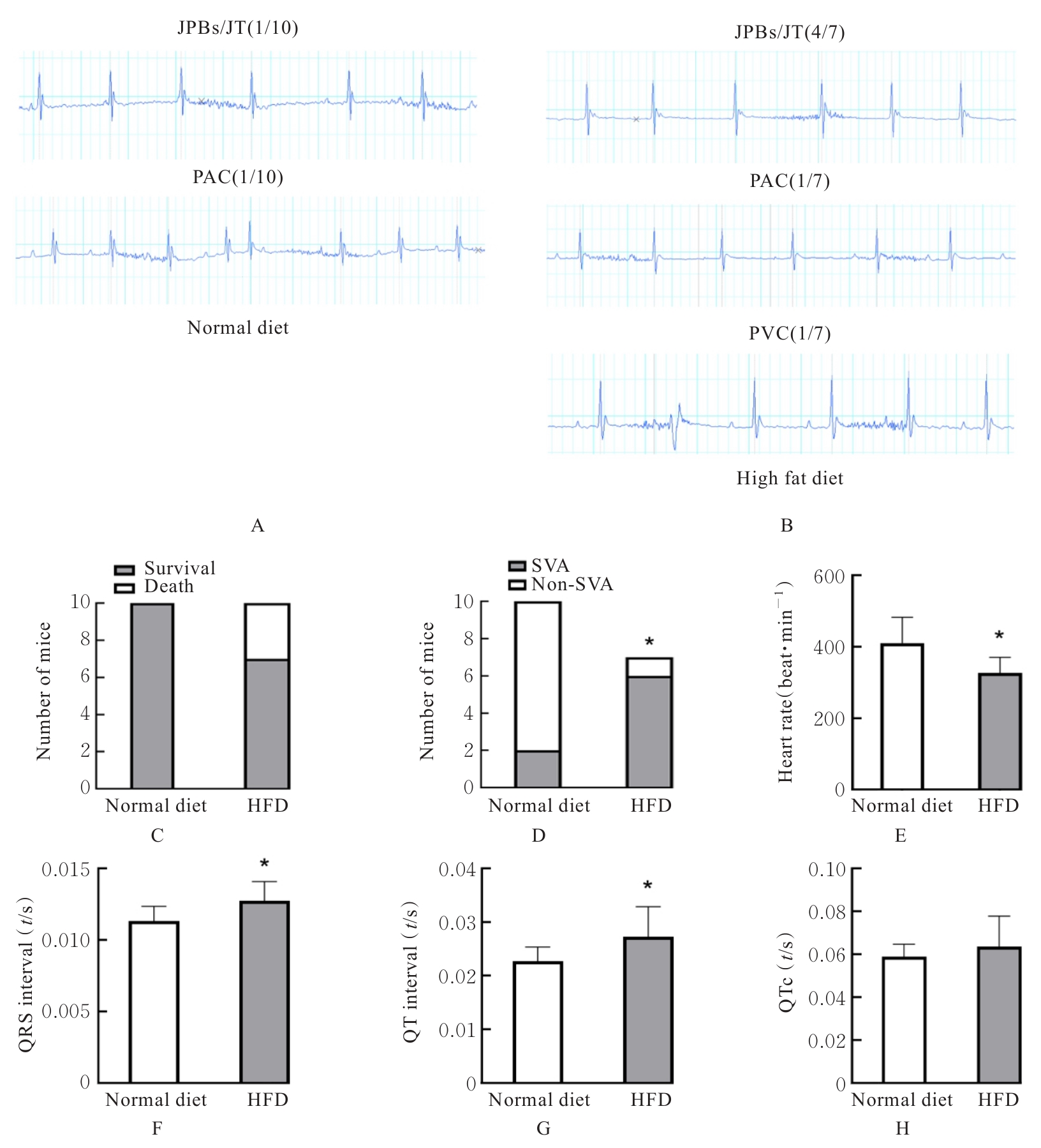
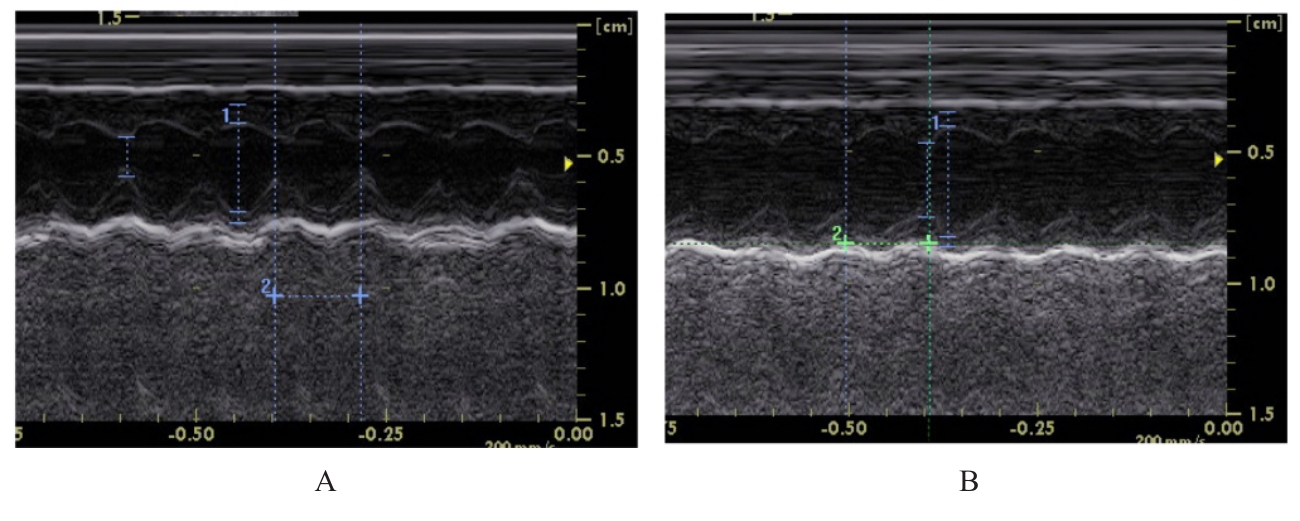
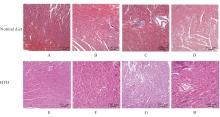
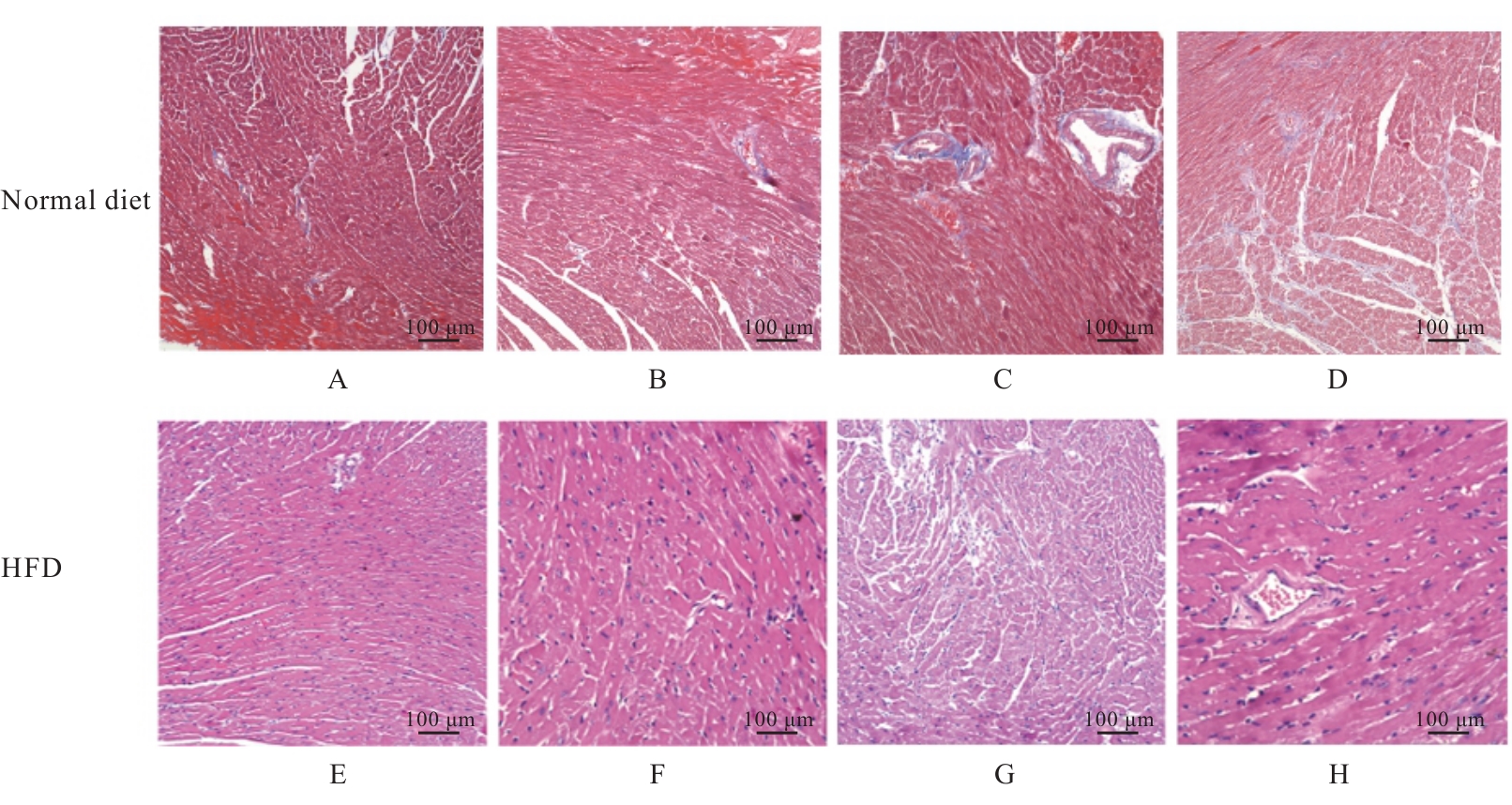
目的 探讨长期高脂饮食引起载脂蛋白E敲除(ApoE-/-)小鼠血清胆汁酸水平改变在室上心律失常(SVA)发生中的作用,并探讨其作用机制。 方法 将20只ApoE-/-小鼠随机分为正常饲料组和高脂饲料(HFD)组,每组10只,饲养20周后,采用体表心电图检查2组小鼠心脏电生理,超声心动图检测2组小鼠心脏收缩功能和结构,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测2组小鼠血清中血脂、总胆汁酸(TBA)和炎症因子水平,苏木精-伊红(HE)染色检测2组小鼠心脏炎症反应,Masson染色观察2组小鼠心肌纤维化程度。 结果 HFD组小鼠出现交界区早搏(JPB)/交界区心动过速(JT)4例、房性早搏(PAC)1例和室性早搏(PVC)1例,而正常饲料组小鼠仅出现JPB/JT和PAC各1例。与正常饲料组比较,HFD组小鼠心率明显降低(P<0.05),收缩末期容积(ESV)、心室去极时间(QRS)和心室去极和复极总时间(QT)间期明显延长(P<0.05),射血分数(EF)和短轴缩短率(FS)降低(P<0.05),舒张末期容积(EDV)升高(P<0.05),但组间收缩末期容积(ESV)比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),左心室舒张末期内径(LVIDd)和左心室收缩末期内径(LVIDs)增加(P<0.05),血浆中总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白(HDL-c)、低密度脂蛋白(LDL-c)水平和体质量差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),TBA水平升高(P<0.05),白细胞介素6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、单核细胞趋化蛋白(MCP-1)和趋化因子C-X-C基序配体1(CXCL-1)差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与正常饲料组比较,HFD组小鼠白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。HE染色,HFD与正常饲料组小鼠炎性细胞浸润相似。Masson染色,与正常饲料组比较,HFD组小鼠纤维化有增加趋势,但心肌纤维化面积组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 长期高脂饮食可升高ApoE-/-小鼠血清TBA水平,可能引起SVA。
中图分类号:
- R542.22