吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1312-1317.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250518
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
大疱性类天疱疮患者发生感染的临床转归及危险因素分析
李晓1,王莉2,武文3,王瑞1,张爱英2,张烁2,姜汝佳2,孟亚宁2( )
)
- 1.山东大学齐鲁医院德州医院皮肤科,山东 德州 253000
2.山东大学齐鲁医院德州医院医院感染 管理科,山东 德州 253000
3.山东大学齐鲁医院德州医院神经外科,山东 德州 253000
Clinical outcomes and risk factors analysis on infection in patients with bullous pemphigoid
Xiao LI1,Li WANG2,Wen WU3,Rui WANG1,Aiying ZHANG2,Shuo ZHANG2,Rujia JIANG2,Yaning MENG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Dermatology,Dezhou Hospital,Qilu Hospital,Shandong University,Dezhou 253000,China
2.Department of Hospital Infection Management,Dezhou Hospital,Qilu Hospital,Shandong University,Dezhou 253000,China
3.Department of Neurosurgery,Dezhou Hospital,Qilu Hospital,Shandong University,Dezhou 253000,China
摘要:
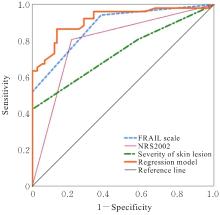
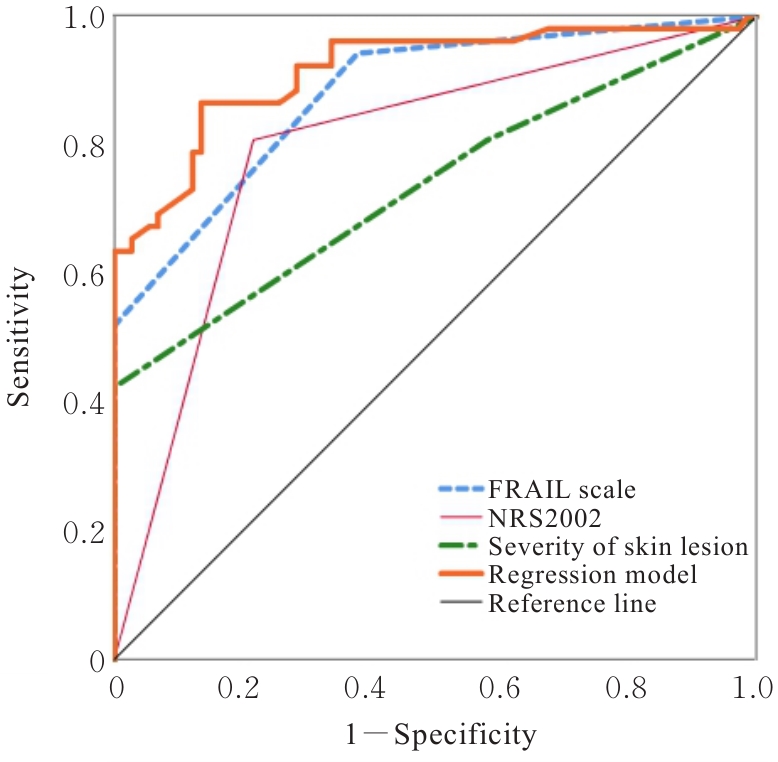
目的 探讨大疱性类天疱疮(BP)患者的感染情况及临床转归,分析BP住院患者发生感染的危险因素,构建并评价风险预测模型。 方法 选择首次确诊为BP的住院患者126例,根据BP患者是否发生感染分为感染组52例和未感染组74例,记录2组患者感染情况及转归情况,对2组患者的一般资料、实验室检查结果、衰弱筛查FRAIL量表评分、NRS2002评分和皮损严重程度进行统计学分析,采用多因素Logistic回归模型识别患者发生感染的危险因素,采用拟合优度检验评价模型,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价模型对感染的预测价值。 结果 126例BP住院患者中,发生感染52例,感染率41.27%。感染组患者死亡率高于未感染组(P<0.05),未感染组患者缓解率高于感染组(P<0.05)。未感染组和感染组患者衰弱筛查FRAIL量表评分、NRS2002评分、血清白蛋白水平、前白蛋白水平、住院次数及皮损严重程度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);多因素Logistic回归分析回归方程:Logistic(P)=-7.63+0.922×皮损严重程度+2.565×衰弱筛查FRAIL量表评分+1.214×NRS2002评分,Logistic回归模型曲线下面积为0.916。 结论 衰弱筛查FRAIL量表评分、NRS2002评分和皮损严重程度是BP住院患者发生感染的危险因素,据此构建的感染风险预测模型具有良好预测价值,可为预防BP住院患者发生感染提供新的防控思路。
中图分类号:
- R758.66