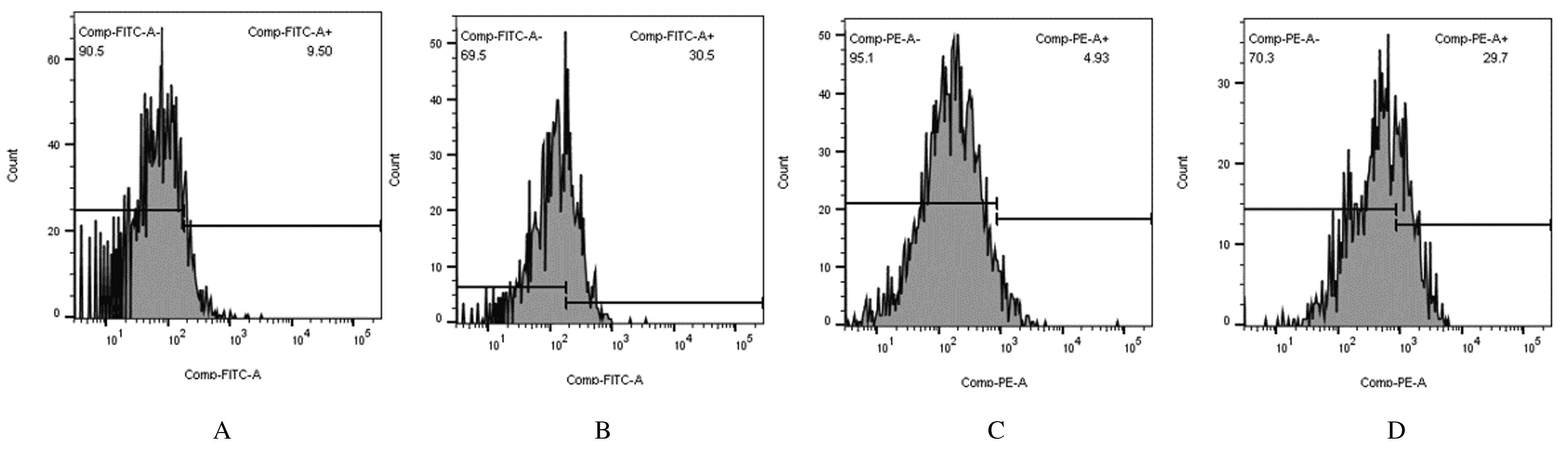
| 1 |
NAVARRETE M, GARCÍA J, DUTZAN N, et al. Interferon-γ, interleukins-6 and -4, and factor -A as indirect markers of the classical and alternative macrophage activation pathways in chronic periodontitis[J].J Periodontol, 2014, 85(5): 751-760.
|
| 2 |
FRETWURST T, GARAICOA-PAZMINO C, NELSON K, et al. Characterization of macrophages infiltrating peri-implantitis lesions[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2020, 31(3): 274-281.
|
| 3 |
王莉新, 吴文斌, 胥孜杭, 等. 黄芪甲苷通过诱导M1型巨噬细胞极化发挥抗肿瘤作用的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019, 25(14): 19-24.
|
| 4 |
王琳源, 靳 赢, 林晓萍. CD4+T细胞在不同菌株诱导小鼠牙周炎中的表达[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2014, 23(1): 20-25.
|
| 5 |
CHOI G E, HYUN K Y. Inhibitory effect of Acer tegmentosum maxim extracts on P. gingivalis LPS-induced periodontitis[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2020, 109: 104529.
|
| 6 |
KOBAYASHI R, KONO T, BOLERJACK B A, et al. Induction of IL-10-producing CD4+ T-cells in chronic periodontitis[J]. J Dent Res, 2011, 90(5): 653-658.
|
| 7 |
SUH J S, KIM S, BOSTRÖM K I, et al. Periodontitis-induced systemic inflammation exacerbates atherosclerosis partly via endothelial-mesenchymal transition in mice[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2019, 11(3): 21.
|
| 8 |
TAMURA H, MAEKAWA T, DOMON H, et al. Peptides from rice endosperm protein restrain periodontal bone loss in mouse model of periodontitis[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2019, 98: 132-139.
|
| 9 |
王琳源, 靳 赢, 林晓萍. 适应性免疫应答在牙周炎发生中的作用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2013, 48(2): 115-118.
|
| 10 |
SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J].J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440.
|
| 11 |
YU T, ZHAO L, HUANG X, et al. Enhanced activity of the macrophage M1/M2 phenotypes and phenotypic switch to M1 in periodontal infection[J]. J Periodontol, 2016, 87(9): 1092-1102.
|
| 12 |
SONG P, REN H. Macrophages in microenvironment of liver metastases [J].Int J Immunol,2019,42(5):528-531.
|
| 13 |
TU J J, WANG X M, GONG X, et al. Synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: the past, present, and future[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2020, 2020: 1583647.
|
| 14 |
KUO P C, WENG W T, SCOFIELD B A, et al. Dimethyl itaconate, an itaconate derivative, exhibits immunomodulatory effects on neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 138.
|
| 15 |
JAGANNATHAN R, LAVU V, RAO S R. Comparison of the proportion of non-classic (CD14+CD16+) monocytes/macrophages in peripheral blood and gingiva of healthy individuals and patients with chronic periodontitis[J]. J Periodontol, 2014, 85(6): 852-858.
|
| 16 |
LAM R S, O'BRIEN-SIMPSON N M, LENZO J C, et al. Macrophage depletion abates Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone resorption in mice[J]. J Immunol, 2014, 193(5): 2349-2362.
|
| 17 |
SEYEDIZADE S S, AFSHARI K, BAYAT S, et al. Current status of M1 and M2 macrophages pathway as drug targets for inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 2020, 68(2): 10.
|
| 18 |
ZANG X L, ZHANG X X, HU H Y, et al. Targeted delivery of zoledronate to tumor-associated macrophages for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Mol Pharm, 2019, 16(5): 2249-2258.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU L N, BI C S, GAO L N, et al. Macrophage polarization in human gingival tissue in response to periodontal disease[J]. Oral Dis, 2019, 25(1): 265-273.
|
| 20 |
WANG P P, WANG H H, HUANG Q Q, et al. Exosomes from M1-polarized macrophages enhance paclitaxel antitumor activity by activating macrophages-mediated inflammation[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(6): 1714-1727.
|
| 21 |
FOEY A D, HABIL N, AL-SHAGHDALI K, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis-stimulated macrophage subsets exhibit differential induction and responsiveness to interleukin-10[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2017, 73: 282-288.
|
| 22 |
JONES K J, EKHLASSI S, MONTUFAR-SOLIS D, et al. Differential cytokine patterns in mouse macrophages and gingival fibroblasts after stimulation with Porphyromonas gingivalis or Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide[J]. J Periodontol, 2010, 81(12): 1850-1857.
|
| 23 |
GONZALEZ O A, NOVAK M J, KIRAKODU S, et al. Differential gene expression profiles reflecting macrophage polarization in aging and periodontitis gingival tissues[J]. Immunol Invest, 2015, 44(7): 643-664.
|
 )
)