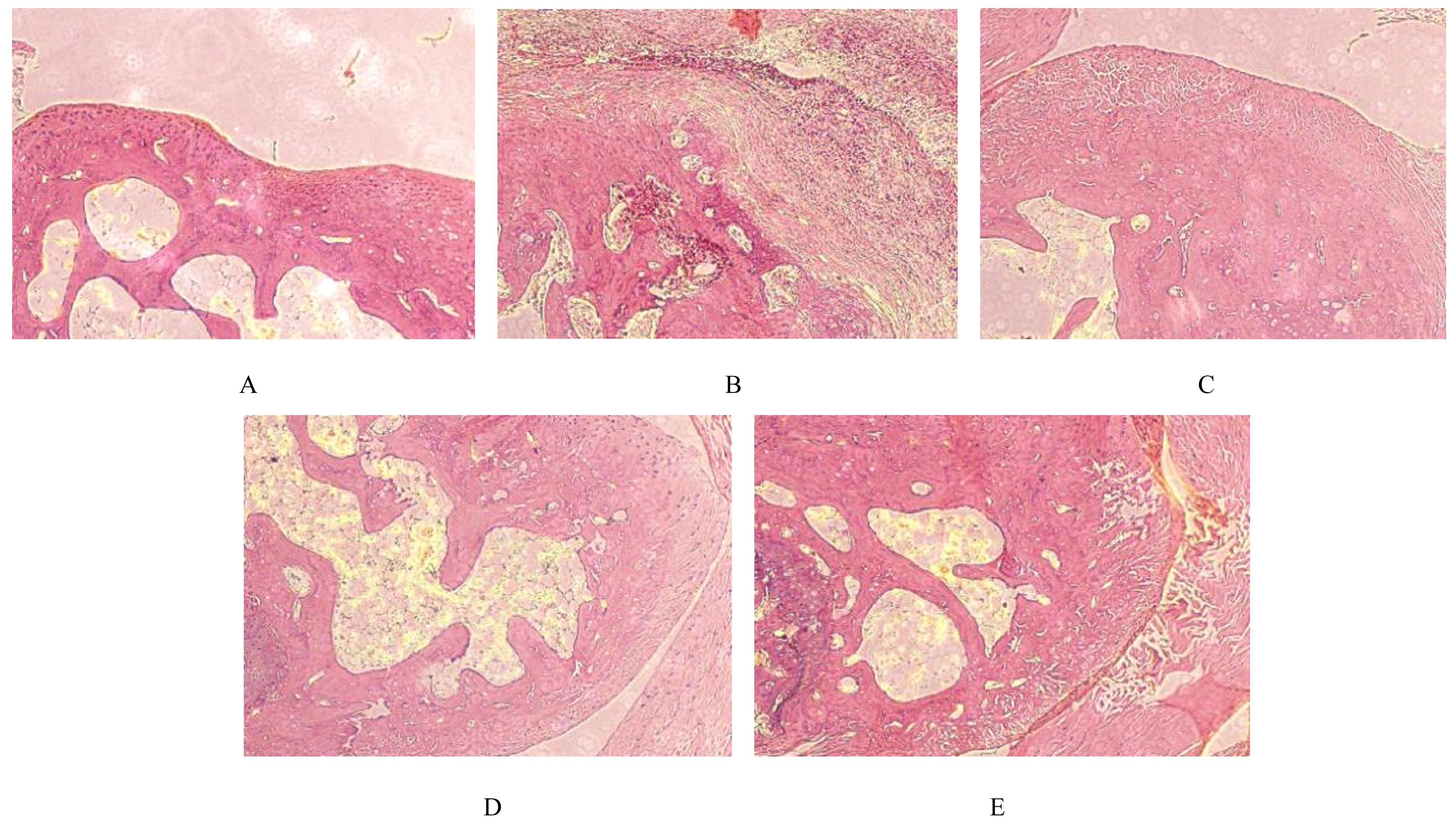
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 617-624.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230309
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Improvement effect of Saposhnikoviae Radix wild product on rheumatoid arthritis in rats and its mechanism
Zhe LIN1,Taidong WANG1,Xiaowei HUANG1,Chao MA1,Xuefeng ZHUANG1,Yuchen WANG1,He LIN1,Junqi GUO1( ),Guangfu LYU2(
),Guangfu LYU2( )
)
- 1.Labratory of Pharmacology of Chinese Medicine,School of Pharmacy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Department of Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jilin Ginseng Academy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
-
Received:2022-07-08Online:2023-05-28Published:2023-06-20 -
Contact:Junqi GUO,Guangfu LYU E-mail:kjcchgk@163.com;message219@163.com
CLC Number:
- R965.1
Cite this article
Zhe LIN,Taidong WANG,Xiaowei HUANG,Chao MA,Xuefeng ZHUANG,Yuchen WANG,He LIN,Junqi GUO,Guangfu LYU. Improvement effect of Saposhnikoviae Radix wild product on rheumatoid arthritis in rats and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 617-624.
share this article
Tab. 2
Swelling degrees of feet of rats in various groups"
| Group | Foot circum ference | |
|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 2.49±0.09 | 2.44±0.05 |
| Model | 3.03±0.19* | 2.76±0.21* |
| Dexamethasone | 3.04±0.24* | 2.30±0.10△△ |
| Low dose of SaposhnikoviaeRadix | 3.01±0.17* | 2.54±0.05△ |
| High dose of SaposhnikoviaeRadix | 3.04±0.21* | 2.56±0.09△ |
Tab. 3
Organ indexes of rats in various groups (n=10,xˉ±s,mg·100 g-1)"
| Group | Spleen index | Thymus index |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.017 6±0.001 2 | 0.004 7±0.003 2 |
| Model | 0.017 6±0.002 5 | 0.013 1±0.002 9* |
| Dexamethasone | 0.017 7±0.001 9 | 0.005 6±0.003 1△ |
| Low dose of Saposhnikoviae Radix | 0.015 3±0.001 9 | 0.012 3±0.002 3△ |
| High dose of Saposhnikoviae Radix | 0.017 0±0.002 1 | 0.011 0±0.003 1△ |
Tab. 4
Levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in serum of rats in various groups [n=10,xˉ±s,ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 30.46±2.48 | 48.36±3.67 | 23.85±1.68 |
| Model | 85.67±9.25* | 105.62±15.71* | 70.93±8.31* |
| Dexamethasone | 45.58±5.63△ | 60.92±5.78△ | 38.10±2.76△ |
| Low dose of Saposhnikoviae Radix | 65.72±7.52△ | 77.23±8.03△ | 59.34±6.53△ |
| High dose of Saposhnikoviae Radix | 60.45±6.83△ | 69.55±7.36△ | 46.88±5.08△ |
| 1 | 马媛媛. 蒙医沙疗治疗类风湿性关节炎研究进展[J]. 中国民族医药杂志, 2020, 26(4): 60-62. |
| 2 | 蒙兴文, 张 政, 舒 川. 中药熏蒸疗法治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J]. 当代医药论丛, 2022, 20(9): 16-19. |
| 3 | 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(2020年版 一部)[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020:156. |
| 4 | 史 磊, 孟祥才, 曹思思, 等. 防风的本草溯源[J]. 现代中药研究与实践, 2021, 35(4): 93-97. |
| 5 | 代雪双, 卜凡优. 基于古代文献探讨类风湿性关节炎辨治特点[J]. 亚太传统医药, 2017, 13(16): 69-70. |
| 6 | 王 浩, 郭凌阁, 尚兴朴, 等. 基于防风外观性状和内在指标性成分划分防风药材商品规格等级研究[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(20): 5320-5327. |
| 7 | 潘秀和, 刘超波, 孙 俊, 等. 核因子κB信号通路在炎症性肺部疾病中的作用[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2016, 30(7): 762-769. |
| 8 | 袁 娟, 胡 玲, 宋小鸽, 等. 艾灸对类风湿性关节炎大鼠关节滑膜组织Toll样受体4-骨髓样分化因子88-核转录因子-κB信号通路的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2015, 40(3): 199-204. |
| 9 | 刘 静, 燕丽君. 雷公藤内酯醇对类风湿性关节炎模型大鼠血管新生和PTEN/PI3K/AKT通路的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(6): 1227-1233. |
| 10 | 韩隆胤, 魏赈权, 潘东梅, 等. 断藤益母汤对胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠的治疗作用及对血清IL-1β和MMP-1表达影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2020, 38(2): 33-37. |
| 11 | YOUNG H O LEE M D P, BAE S C. Correlation between circulating VEGF levels and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis[J]. Z Rheumatol, 2018, 77(3): 240-248. |
| 12 | 王慧莲, 展俊平, 苗喜云, 等. 丹酚酸B对人类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖与凋亡的影响及其作用机制[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2022, 47(4): 334-339. |
| 13 | 沈婷婷, 李光耀, 罗 琼, 等. 类风湿性关节炎患者应用雷公藤制剂及合并用药所致药物性肝损伤的临床特征分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(9): 2067-2072. |
| 14 | 王 波, 何友武, 赵 璐, 等. 附子汤对类风湿性关节炎大鼠抗炎及关节影响研究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2020, 58(21): 40-44, 193. |
| 15 | 许冰馨, 王琪珊, 范凯健, 等. 地塞米松改善胶原性关节炎大鼠免疫功能与其血药浓度的相关性研究[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2021, 24(3): 198-203. |
| 16 | 贾 琳, 王亚利, 张明全, 等. 卫气虚证大鼠模型的建立及玉屏风散的反证效果[J]. 中医杂志,2015,56(8): 690-693. |
| 17 | LI G M, ZHAO J, LI B, et al. Associations between CCL21gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2017, 37(10): 1673-1681. |
| 18 | 符传恭, 陆志夫, 宋世锋, 等. MiR-424-5p靶向PHD2对骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡及炎症因子分泌的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2021, 56(1): 1-5. |
| 19 | 蔡 辉, 张群燕, 郭郡浩, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者外周血血浆中TNF-α、IL-1β及IL-10的表达及临床意义[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2017, 35(3): 519-521. |
| 20 | GOPAL K, THEVARAJAH M, NG C M, et al. Effects of vitamin D on disease activity and serum interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2019, 22(5): 834-841. |
| 21 | BAS D B, SU J, WIGERBLAD G, et al. Pain in rheumatoid arthritis: models and mechanisms[J]. Pain Manag, 2016, 6(3): 265-284. |
| 22 | 赵泽明, 张 柳. NF-κB信号通路与骨关节炎的关系研究进展[J]. 华北理工大学学报(医学版), 2021,23(3): 232-238. |
| 23 | 阚玉娜, 谢佳明, 马立威, 等. 中药活性成分改善类风湿性关节炎作用机制研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2021, 23(10): 139-145. |
| 24 | 刘湜桦, 管洪宇, 黎孟枫. 肿瘤细胞“炎化”与NF-κB信号通路的非编码RNA调控[J]. 生命科学, 2018, 30(2): 157-168. |
| 25 | RIGOGLOU S, PAPAVASSILIOU A G. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2013, 45(11): 2580-2584. |
| 26 | 陈 俊, 林 洁, 赵忠胜, 等. 乌头汤对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠滑膜组织TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(27): 4381-4386. |
| 27 | 蒋耀平, 肖 敬, 赵先锋, 等. 壮医药线点灸联合甲氨蝶呤对佐剂关节炎大鼠NF-κB/IκB信号通路的影响[J]. 中医药学报, 2018, 46(5): 18-24. |
| 28 | 李 丽, 张小兵. 核因子κB信号通路与变应性鼻炎的关系[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(7): 1266-1271. |
| [1] | Zhou YANG,Shudian LIN,Yuwei ZHAN,Lu XIAO,Keying FU,Xiaodie HUANG. Effects of down-regulation of ROCK2 expression targeted by miR-94-5p on proliferation, migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 665-674. |
| [2] | Yan YU,Chengcheng YU,Yakun HAN. Analysis on phenotypes of plasma cells of gingiva and expression characteristics of RANKL in patients with periodontitis complicated with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 757-764. |
| [3] | Xiong LIN,Linghang QU,Jing XU,Chunlian LIU,Shuiqing LI,Yanju LIU. Improvement effects of Atractylodes rhizome oil and Atractylodes rhizome ethanol extract on ulcerative colitis model mice and comparison of their curative effects [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1247-1255. |
| [4] | Yinong LIU,Qiang ZHANG,Li XU. Improvement effect of atorvastatin on vascular endothelial dysfunction induced by Ox-LDL/β2GPⅠ/anti-β2GPⅠ complex and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 317-323. |
| [5] | Na HAN,Fanping LIU,Yanqing TIAN,Zhiqing ZHENG,Weiming LANG,Qian WANG,Yatao LIU,Jianguang ZHU. Regulatory effect of miRNA-27a on immune function in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 104-110. |
| [6] | Qin WANG, Chunlin LIN, Zhibin CHENG, Ruofan HE, Penghang LIN, Hui CHEN, Jianxin YE, Guangwei ZHU. Construction of TRAF6 ubiquitination site mutation vectors and identification of its functional ubiquitination sites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 551-558. |
| [7] | Lijun YAN,Shengquan TONG,Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Nanfang CHEN,Jie HU. Therapeutic effect of total glucosides of paeony in model rats with rheumatoid arthritis by mediating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and its mechanisim [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 390-396. |
| [8] | Jie WU,Xuehua YANG,Ling MA,Wenqiang FAN,Dongdong FU,Xiao GAO,Shufei ZUO,Shu LIANG,Yilu QIN,Peishan WANG,Jinyan GUO. Effect of miR-26a-5p on apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 460-468. |
| [9] | Jing LIU,Lijun YAN. Effects of triptolide on angiogenesis and PTEN / PI3K / AKT pathway in model rats with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1227-1233. |
| [10] | Lijun YAN,Shengquan TONG,Jing LIU,Dongmei GAO,Ping WU,Xi WANG. Effect of total saponins of clematis on T lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood of rats with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1241-1246. |
| [11] | Hui LI,Minghe LI,Cong ZHAO,Chang SU. Effect of minocycline hydrochloride on periodontitis in postmenopausal women and its influence in inflammatory and bone metabolism factors in gingival crevicular fluid [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1304-1308. |
| [12] | WANG Yingying, SUN Lijuan, FAN Ziwei, GU Hong, YOU Xianmei, GUAN Tianhao, ZHANG Chengyi, CHEN Xi. Inhibitory effect of baicalin on autophagy of synovial RSC-364 cells of rats induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 498-503. |
| [13] | QIN Chao, DAI Xi, YANG Xiaoqiong, WANG Rongli, WANG Xing, LI Guoping. Intervention effect of honokiol on inflammatory response in lung tissue of asthma mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 214-220. |
| [14] | ZHANG Heng, GUO Bin, TIAN Hao, LI Lan, WU Jing, MEN Xiuli. Effect of lithium chloride on apoptosis of islet β cells in rats induced by dexamethasone and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1231-1237. |
| [15] | WANG Ye, WANG Hong, ZHANG Shujian, JI Huayi, JIN Zhengyong. Intervention effect of glutamine on hyperoxia lung injury in neonatal rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 747-751. |