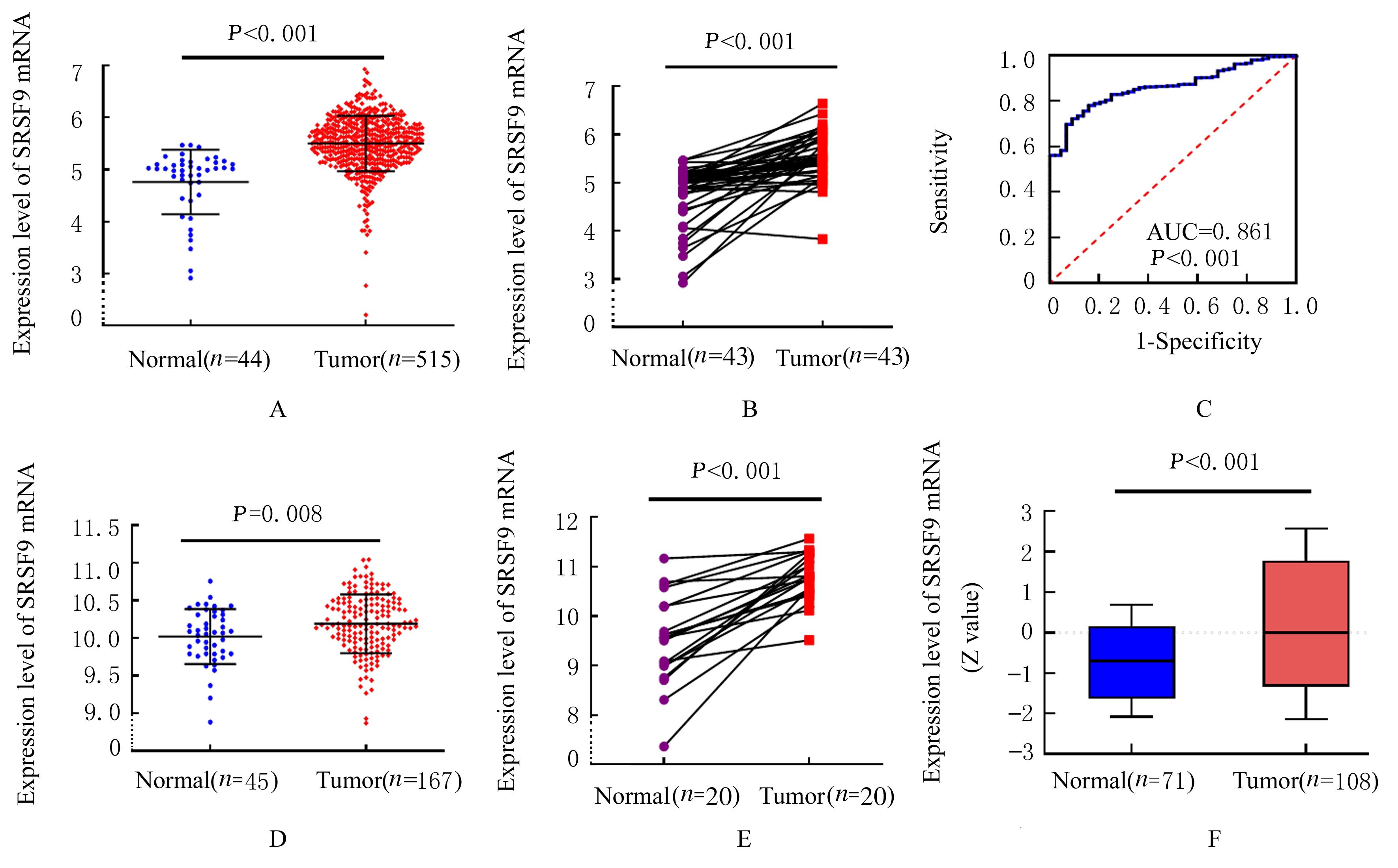
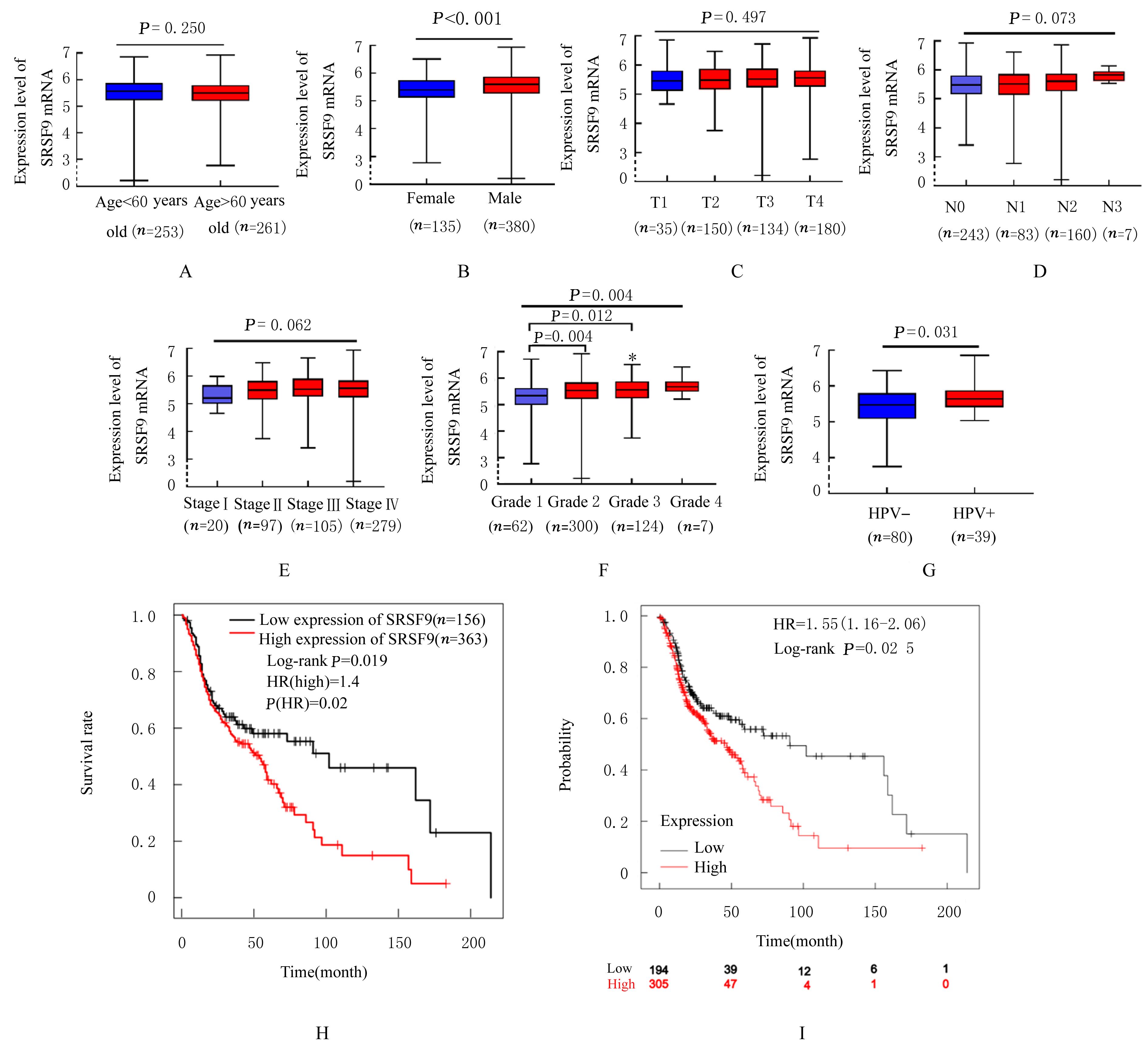
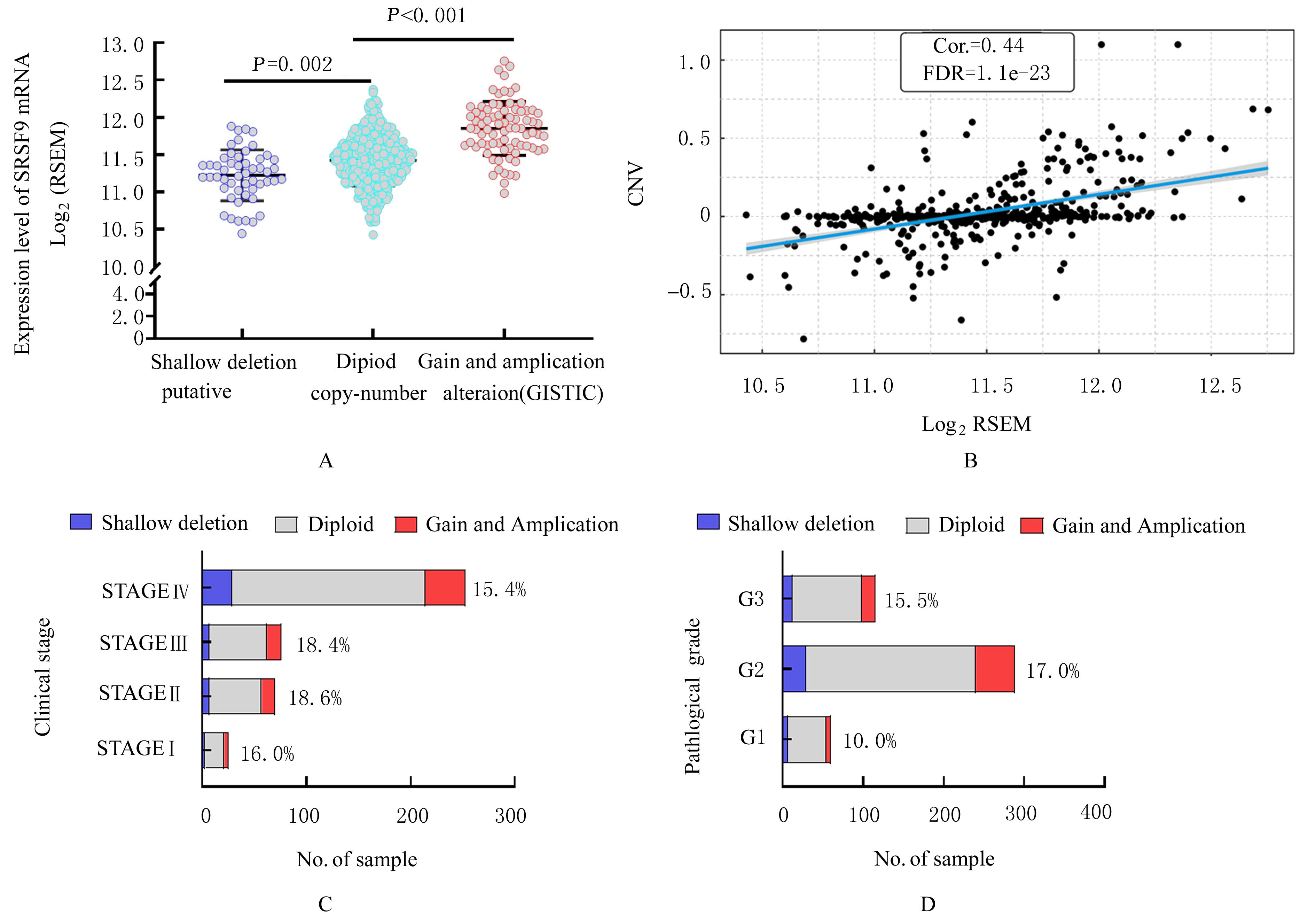
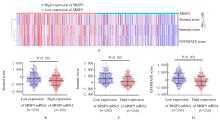
| 1 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249.
|
| 2 |
SCIARRILLO R, WOJTUSZKIEWICZ A, ASSARAF Y G, et al. The role of alternative splicing in cancer: from oncogenesis to drug resistance[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2020, 53:100728.
|
| 3 |
FACKENTHAL J D. Alternative mRNA splicing and promising therapies in cancer [J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13(3):561.
|
| 4 |
FU Y, HUANG B L, SHI Z, et al. SRSF1 and SRSF9 RNA binding proteins promote Wnt signalling-mediated tumorigenesis by enhancing β-catenin biosynthesis[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2013, 5(5):737-750.
|
| 5 |
WANG X Y, LU X S, WANG P, et al. SRSF9 promotes colorectal cancer progression via stabilizing DSN1 mRNA in an m6A-related manner[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1):198.
|
| 6 |
ZHANG G S, LIU B, SHANG H, et al. High expression of serine and arginine-rich splicing factor 9 (SRSF9) is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression and a poor prognosis[J]. BMC Med Genomics, 2022, 15(1):180.
|
| 7 |
HUI J Y. Regulation of mammalian pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Sci China C Life Sci, 2009,52(3): 253-260.
|
| 8 |
CHOI S, CHO N, KIM K K. The implications of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in cell signal transduction[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2023, 55(4):755-766.
|
| 9 |
KOZLOVSKI I, SIEGFRIED Z, AMAR-SCHWARTZ A, et al. The role of RNA alternative splicing in regulating cancer metabolism[J]. Hum Genet, 2017, 136(9):1113-1127.
|
| 10 |
BRADLEY R K, ANCZUKÓW O. RNA splicing dysregulation and the hallmarks of cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23(3):135-155.
|
| 11 |
FRANKIW L, BALTIMORE D, LI G D. Alternative mRNA splicing in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19(11):675-687.
|
| 12 |
CHENG R, XU Z C, LUO M, et al. Identification of alternative splicing-derived cancer neoantigens for mRNA vaccine development[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2022, 23(2): bbab553.
|
| 13 |
KUMAR K, SINHA S K, MAITY U, et al. Insights into established and emerging roles of SR protein family in plants and animals[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2023, 14(3): e1763.
|
| 14 |
LUO C L, CHENG Y M, LIU Y G, et al. SRSF2 regulates alternative splicing to drive hepatocellular carcinoma development[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(5): 1168-1178.
|
| 15 |
WAN L D, DENG M, ZHANG H H. SR splicing factors promote cancer via multiple regulatory mechanisms[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(9): 1659.
|
| 16 |
ZHENG X, PENG Q, WANG L J, et al. Serine/arginine-rich splicing factors: the bridge linking alternative splicing and cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2020, 16(13):2442-2453.
|
| 17 |
JIANG L Y, HUANG J Q, HIGGS B W, et al. Genomic landscape survey identifies SRSF1 as a key oncodriver in small cell lung cancer [J]. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(4): e1005895.
|
| 18 |
DU J X, LUO Y H, ZHANG S J, et al. Splicing factor SRSF1 promotes breast cancer progression via oncogenic splice switching of PTPMT1[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1):171.
|
| 19 |
LIU Y D, MAO X, MA Z C, et al. Aberrant regulation of LncRNA TUG1-microRNA-328-3p-SRSF9 mRNA Axis in hepatocellular carcinoma: a promising target for prognosis and therapy[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1):36.
|
| 20 |
WANG R, SU Q, YIN H Z, et al. Inhibition of SRSF9 enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer to erastin-induced ferroptosis by reducing glutathione peroxidase 4 expression[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2021, 134:105948.
|
| 21 |
TACHEZY R, KLOZAR J, RUBENSTEIN L, et al. Demographic and risk factors in patients with head and neck tumors[J]. J Med Virol, 2009, 81(5): 878-887.
|
| 22 |
MOLE S, FAIZO A A A, HERNANDEZ-LOPEZ H, et al. Human papillomavirus type 16 infection activates the host serine arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1)- splicing factor axis[J]. J Gen Virol, 2020, 101(5): 523-532.
|
| 23 |
SOMBERG M, LI X Z, JOHANSSON C, et al. Serine/arginine-rich protein 30c activates human papillomavirus type 16 L1 mRNA expression via a bimodal mechanism[J]. J Gen Virol, 2011, 92(Pt 10):2411-2421.
|
| 24 |
TAN E S, KNEPPER T C, WANG X, et al. Copy number alterations as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(9): 2223.
|
| 25 |
ESSERS P B M, VAN DER HEIJDEN M, VOSSEN D, et al. Ovarian cancer-derived copy number alterations signatures are prognostic in chemoradiotherapy-treated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 147(6):1732-1739.
|
| 26 |
TURLEY S J, CREMASCO V, ASTARITA J L. Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment[J]. Nat Rev Immunol,2015,15(11): 669-682.
|
| 27 |
CHEN B, LAI J G, DAI D N, et al. JAK1 as a prognostic marker and its correlation with immune infiltrates in breast cancer[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(23):11124-11135.
|
| 28 |
SCHMIDT D R, PATEL R, KIRSCH D G, et al. Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in clinical oncology[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(4): 333-358.
|
| 29 |
BIAN X L, LIU R, MENG Y, et al. Lipid metabolism and cancer[J]. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(1):1-17.
|
| 30 |
MIAO X W, WANG B L, CHEN K L, et al. Perspectives of lipid metabolism reprogramming in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an overview[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12:1008361.
|
| 31 |
LIN X H, ZHOU W K, LIU Z Q, et al. Targeting cellular metabolism in head and neck cancer precision medicine era: a promising strategy to overcome therapy resistance[J]. Oral Dis, 2023, 29(8): 3101-3120.
|
 )
)