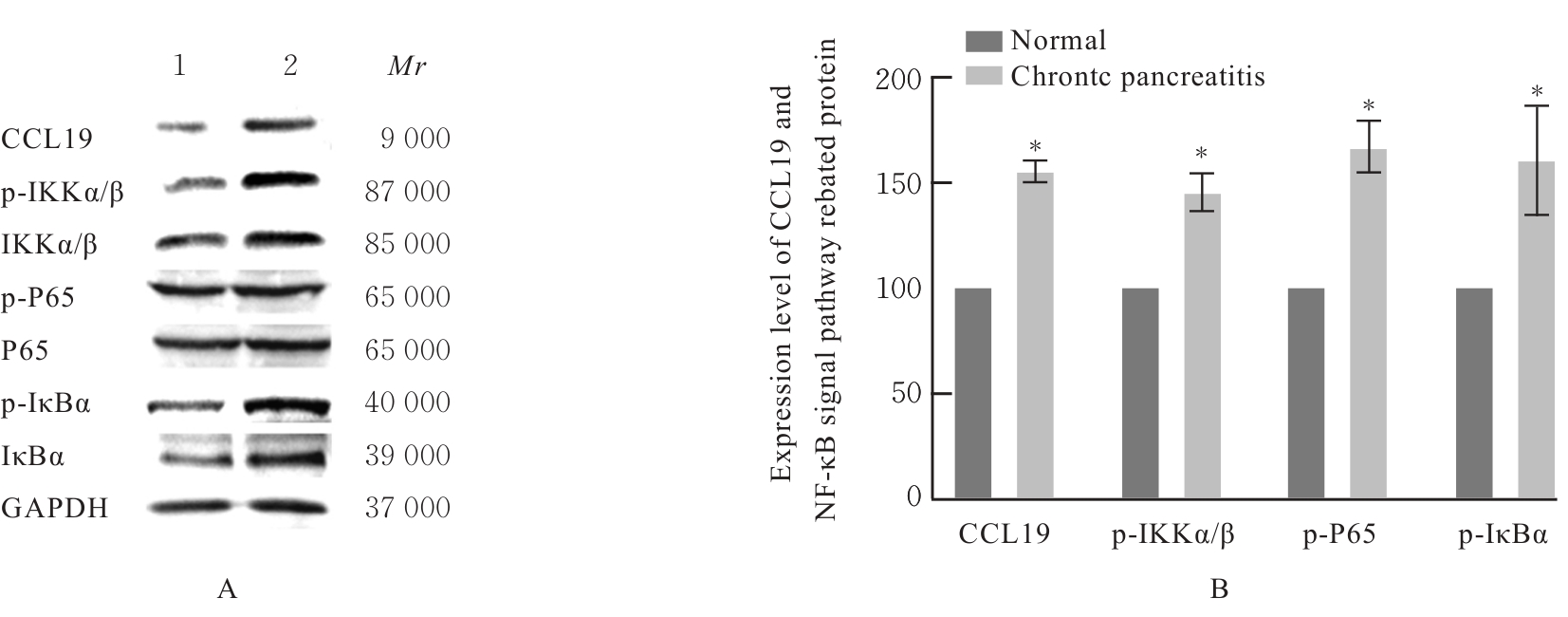
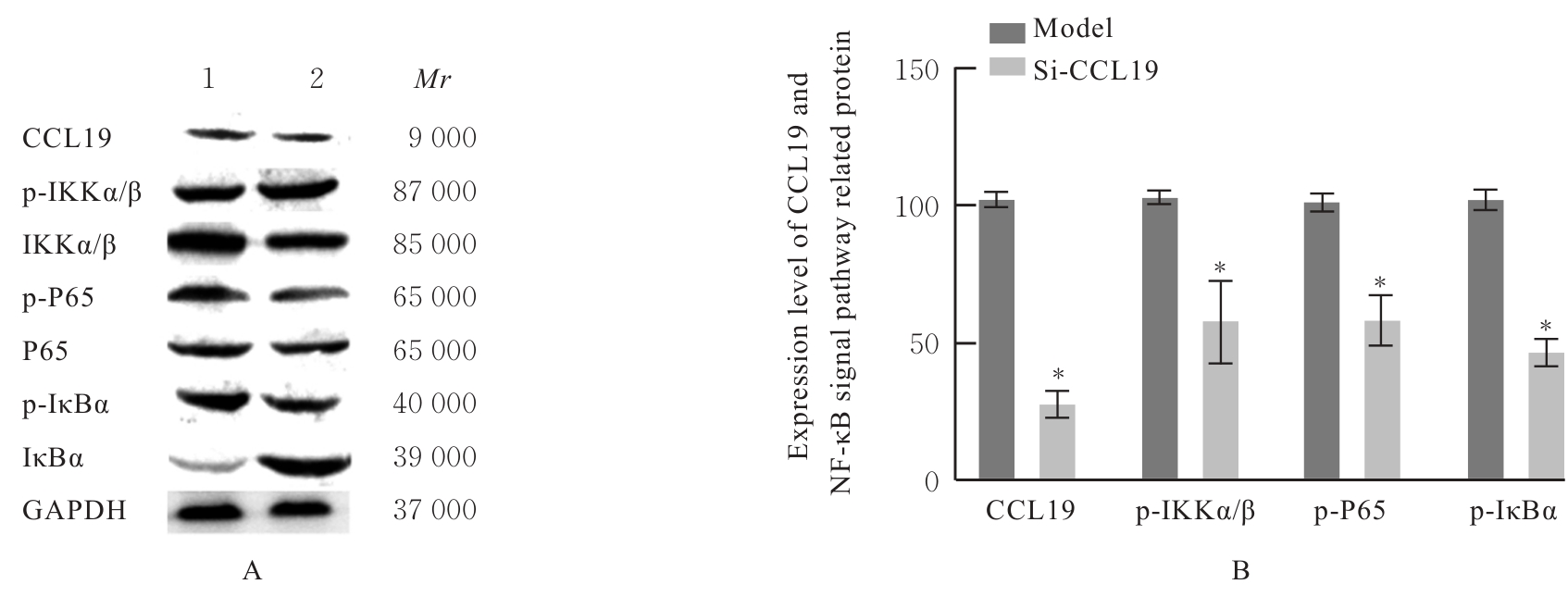
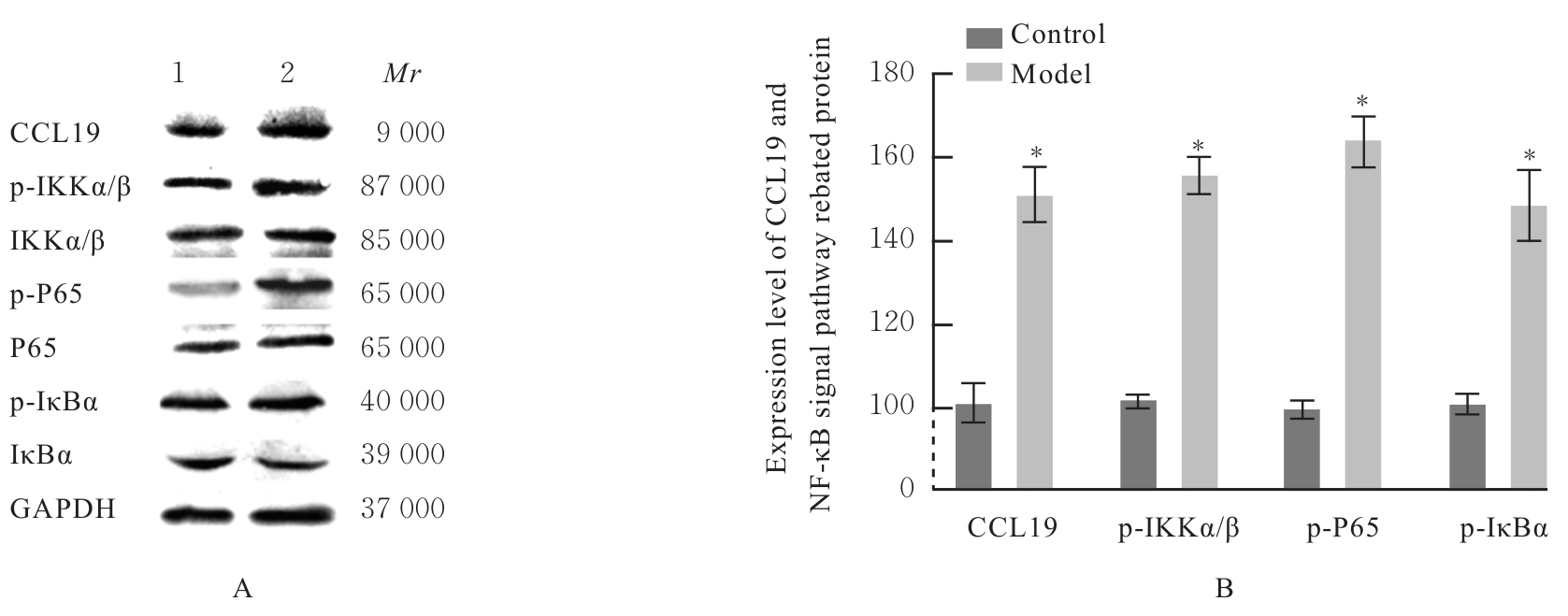
| [1] |
Xinyue MA,Hui XU,Jiawen DIAO,Aihua JIN,Jishu QUAN.
Inhibitory effect of Boschnikia rossica polysaccharides on THP-1 macrophage inflammation and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1499-1511.
|
| [2] |
Xuejun JIN,Chuyuan LU.
Inhibitory effect of leucovorin on growth and angiogenesis of subcutaneous transplanted tumors in mouse lung cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 612-619.
|
| [3] |
Bo YUAN,Jiayi XIE,Siyu JIANG,Yajun MENG,Qinghua ZHU,Xiaofei LI,Xiumei FU,Lide XIE.
Effect of adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes on migration ability of macrophages in vitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 718-727.
|
| [4] |
Shuang CHEN,Hong LI.
Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378.
|
| [5] |
Xuebing ZHOU,Qianqian LIN,Yanchun LI.
Effect of polysaccharides from porphyra on inflammatory factors secreted by macrophages in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1452-1456.
|
| [6] |
Xue DONG, Jinfeng ZANG, Caifeng XU, Hebing LIU, Zhaohua CHENG.
Construction and validation of risk prediction model of enteral nutrition feeding intolerance of patients with severe acute pancreatitis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1586-1592.
|
| [7] |
Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI.
Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226.
|
| [8] |
Chuanlong SONG,Hongjie JIAO, HAILIQIGULI·Nuriding,Yingbin YUE,Mei YAN.
Improvement effect of hydatid antigen B on immune thrombocytopenia in mice by regulating macrophage polarization through tumor necrosis factor receptor 2
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 858-866.
|
| [9] |
Haitao LI, Qin LI, Fei CAI, Guofu HU, Yunfei TENG.
Effect of apigenin on polarization and inflammation of mouse RAW264.7 macrophages and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 549-556.
|
| [10] |
Yan YU,Chengcheng YU,Yakun HAN.
Analysis on phenotypes of plasma cells of gingiva and expression characteristics of RANKL in patients with periodontitis complicated with rheumatoid arthritis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 757-764.
|
| [11] |
Xinghong GAO,Hongmei TANG,Yuejiao LI,Xiaoyun WANG,Xing WANG,Xiefang YUAN,Min WU.
Attenuating effect of translocator protein ligand XBD173 on pulmonary inflammatory response induced by cigarette smoke extraction in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 272-279.
|
| [12] |
Xiaojuan ZHU,Haitao DAI,Yan LI,Lingxin CUI,Ya WANG,Jiang XU,Nan WU.
Improvement effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on periodontal inflammation in diabetic periodontitis rats and its influence on expression levels of TLR4 and NF-κB in periodontal tissue
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 31-38.
|
| [13] |
Xuechun DU,Baosheng LI,Shuwei QIAO,Yanzhen OU,Zhen LI,Weiyan MENG.
Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis-LPS on expression levels of ferroptosis-related factors in macrophages
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1148-1155.
|
| [14] |
Hang YANG,Jiaqi CHEN,Shouhan WANG,Hongjun YANG,Bin WANG.
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on cardiac injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1175-1181.
|
| [15] |
Wei CHEN,Nan SHEN,Wanna HAN,Yanli XI,Kuang REN,Lianhai JIN,Na XU.
Effect of adapters of Toll-like receptor 4 on M2 polarization of macrophages induced by lactate and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1190-1199.
|
 )
)