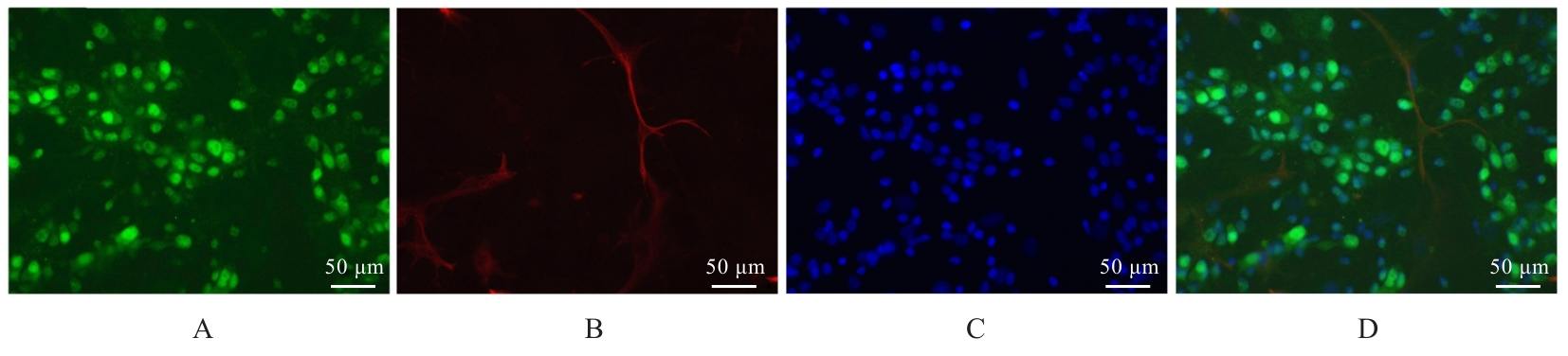
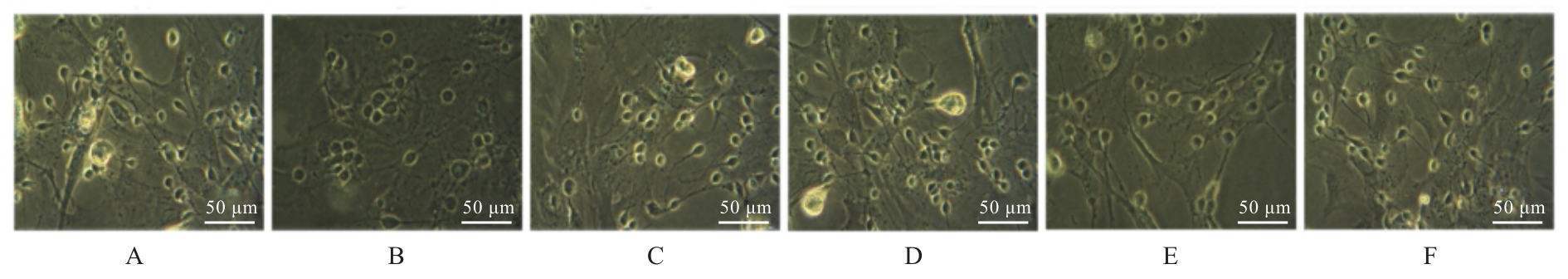
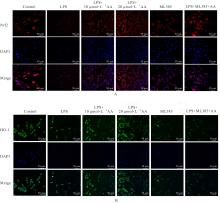
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 85-95.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250111
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Improvement effect of asiatic acid on damage of lipopolysaccharide-induced hippocampum neuron in rats through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Yanyan BAI,Yutong ZHOU,Haijuan SUI,Zhuo LIU( )
)
- Department of Pharmacology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
-
Received:2024-03-25Accepted:2024-05-14Online:2025-01-28Published:2025-03-06 -
Contact:Zhuo LIU E-mail:liuz@jzmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R742
Cite this article
Yanyan BAI,Yutong ZHOU,Haijuan SUI,Zhuo LIU. Improvement effect of asiatic acid on damage of lipopolysaccharide-induced hippocampum neuron in rats through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 85-95.
share this article
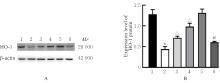
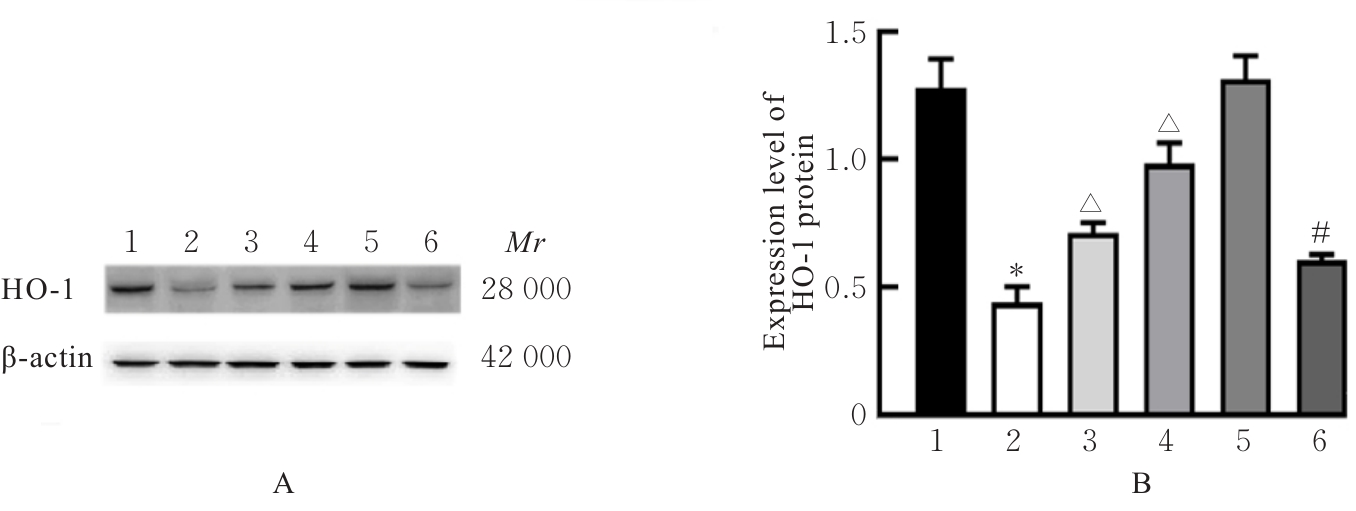
Tab.1
Survival rates and LDH leakage rates of hippocampus neurons of rats in various groups"
| Group | Surival rate | LDH leakage rate |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 100.00±4.82 | 14.41±0.70 |
| LPS | 31.39±2.65* | 38.77±5.85* |
| LPS+10 μmol·L-1 AA | 73.27±5.39△△ | 28.53±4.31△△ |
| LPS+20 μmol·L-1 AA | 95.49±6.18△△ | 19.57±5.36△△ |
| LPS+40 μmol·L-1 AA | 76.90±9.04△△ | 30.02±6.30△ |
| AA | 99.54±7.44 | 15.52±1.09 |
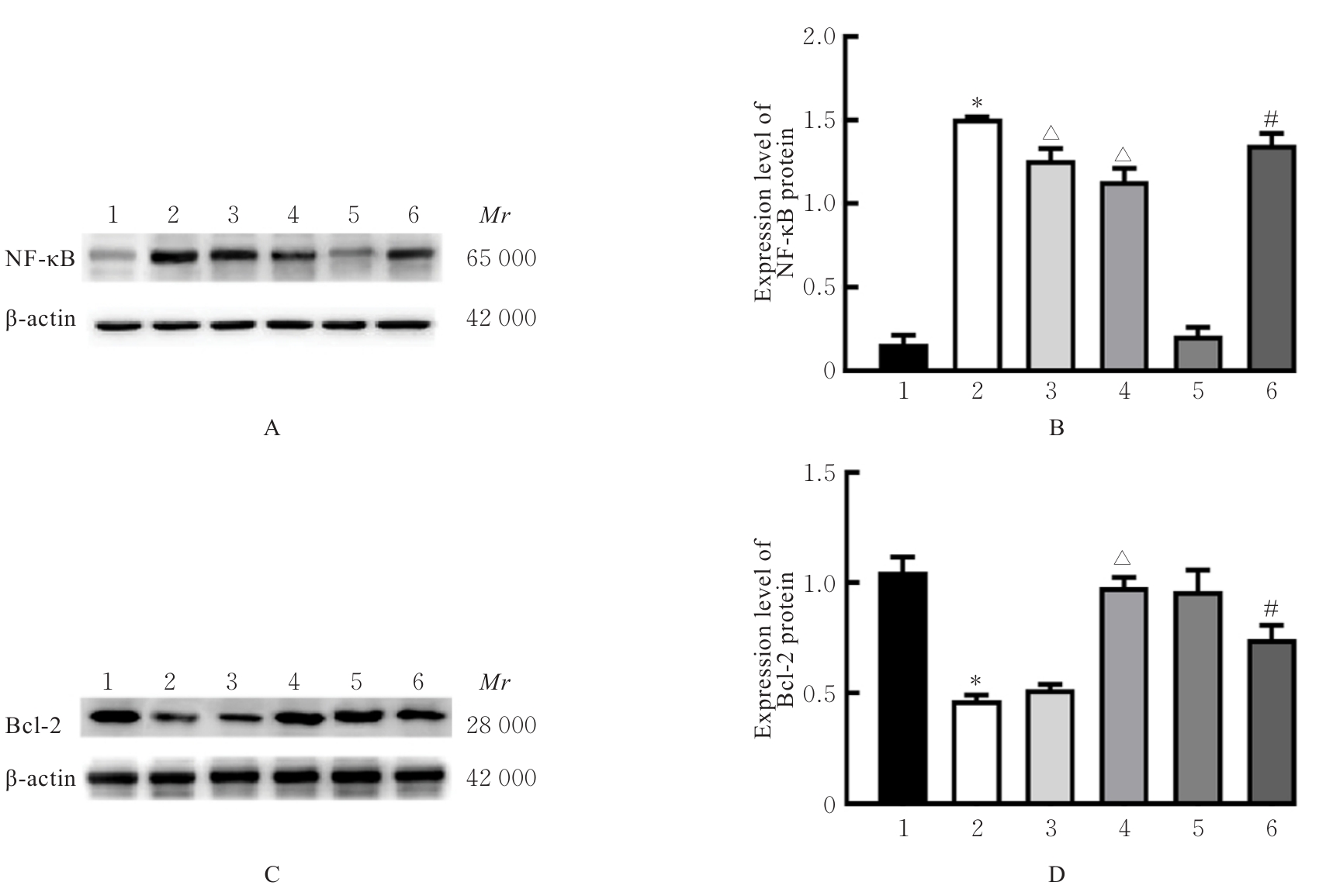
Tab.2
Levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in culture supernatant of hippocampus neurons of rats in various groups [n=6, x±s, ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | IL-1β | TNF-α |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 10.25±1.35 | 2.93±0.16 |
| LPS | 125.15±19.98* | 16.37±2.46* |
| LPS+10 μmol·L-1 AA | 99.98±15.44△ | 13.59±1.48△ |
| LPS+20 μmol·L-1 AA | 81.89±10.46△△ | 8.42±0.60△△ |
| LPS+40 μmol·L-1 AA | 97.34±11.17△ | 15.97±3.02 |
| AA | 11.75±0.31 | 3.81±0.75 |
Tab.3
SOD activities and MDA levels in hippocampus neurons of rats in various groups"
| Group | SOD [λB/(U·mg-1)] | MDA [mB/(μmol·g-1)] |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 147.17±19.96 | 6.94±0.26 |
| LPS | 86.45±5.67* | 14.25±1.38* |
| LPS+10 μmol·L-1 AA | 101.92±14.93△ | 10.59±0.74△ |
| LPS+20 μmol·L-1 AA | 122.69±13.82△ | 8.55±0.47△ |
| LPS+40 μmol·L-1 AA | 91.76±10.54 | 13.12±2.92 |
| AA | 138.24±16.61 | 6.77±0.64 |
| 1 | TIWARI S, ATLURI V, KAUSHIK A, et al. Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2019, 14: 5541-5554. |
| 2 | DENG M, YAN W L, GU Z C, et al. Anti-neuroinflammatory potential of natural products in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(3): 1486. |
| 3 | DEARDORFF W J, GROSSBERG G T. Targeting neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence for NSAIDs and novel therapeutics [J]. Expert Rev Neurother, 2017, 17(1): 17-32. |
| 4 | ZHOU X D, TANG L Y, XU Y L, et al. Towards a better understanding of medicinal uses of carthamus tinctorius L. in traditional Chinese medicine: a phytochemical and pharmacological review[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2014, 151(1): 27-43. |
| 5 | GUO T T, ZHANG D H, ZENG Y Z, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2020, 15(1): 40. |
| 6 | DING L Y, LIU T, MA J. Neuroprotective mechanisms of Asiatic acid[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(5): e15853. |
| 7 | ISLAMIE R, MYINT S L L, ROJANARATHA T, et al. Neuroprotective effect of nose-to-brain delivery of Asiatic acid in solid lipid nanoparticles and its mechanisms against memory dysfunction induced by Amyloid Beta1-42 in mice [J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2023, 23(1): 294. |
| 8 | HALDER T, PATEL B, ACHARYA N. Asiatic acid fabricated nanoconstructs to mitigate amyloid Beta1-42 induced injury in SH-SY5Y cells in-vitro and ameliorates cognitive impairment by dual cholinesterase inhibition and attenuation of oxidative stress in-vivo [J]. Pharm Res, 2023, 40(1): 197-213. |
| 9 | XU Y, YAO J, ZOU C, et al. Asiatic acid protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by inactivation of Kupffer cells via PPARγ/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway [J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(49): 86339-86355. |
| 10 | 张亚苹, 隋海娟, 闫恩志. 迷迭香酸通过激活Nrf2/HO-1通路对Aβ1-42 所致星形胶质细胞损伤的保护作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49(1): 22-30. |
| 11 | LEE W, LEE C H, LEE J, et al. Botanical formulation, TADIOS, alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced acute lung injury in mice via modulation of the Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 270: 113795. |
| 12 | BUENDIA I, MICHALSKA P, NAVARRO E, et al. Nrf2-ARE pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 157: 84-104. |
| 13 | CAI Z Y, HUSSAIN M D, YAN L J. Microglia, neuroinflammation, and beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2014, 124(5): 307-321. |
| 14 | CALSOLARO V, EDISON P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: current evidence and future directions[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2016, 12(6): 719-732. |
| 15 | 王亚楠, 任 凌, 韩 伟, 等. 阿尔茨海默病病理生理机制及诊断研究进展[J/OL]. 解放军医学杂志, 1-13[2025-03-01]. . |
| 16 | KESIKA P, SUGANTHY N, SIVAMARUTHI B S, et al. Role of gut-brain axis, gut microbial composition, and probiotic intervention in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 264: 118627. |
| 17 | KAMETANI F, HASEGAWA M. Reconsideration of amyloid hypothesis and tau hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Front Neurosci, 2018, 12: 25. |
| 18 | AMINZADEH M, ROGHANI M, SARFALLAH A, et al. TRPM2 dependence of ROS-induced NLRP3 activation in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 54: 78-85. |
| 19 | XIN Y W, TIAN M, DENG S X, et al. The key drivers of brain injury by systemic inflammatory responses after sepsis: microglia and neuroinflammation[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 60(3): 1369-1390. |
| 20 | 胡承平, 陶凤芝, 王 灿, 等. 星形胶质细胞在阿尔茨海默病中的研究进展[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2023, 44(5): 740-746. |
| 21 | BATEMAN R J, AISEN P S, DE STROOPER B, et al. Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease: a review and proposal for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2011, 3(1): 1. |
| 22 | PARK Y J, YANG H J, LI W, et al. Menthae herba attenuates neuroinflammation by regulating CREB/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in BV2 microglial cells [J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(4): 649. |
| 23 | WU Q, ZHANG X S, WANG H D, et al. Astaxanthin activates nuclear factor erythroid-related factor 2 and the antioxidant responsive element (Nrf2-ARE) pathway in the brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats and attenuates early brain injury[J]. Mar Drugs, 2014, 12(12): 6125-6141. |
| 24 | WANG Y, PEI H Y, CHEN W J, et al. Palmatine protects PC12 cells and mice from Aβ25-35-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(24): 7955. |
| 25 | XU M F, XIONG Y Y, LIU J K, et al. Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene in Centella asiatica, attenuates glutamate-induced cognitive deficits in mice and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2012, 33(5): 578-587. |
| 26 | CHENG W J, CHEN W M, WANG P, et al. Asiatic acid protects differentiated PC12 cells from Aβ25-35-induced apoptosis and tau hyperphosphorylation via regulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 208: 96-101. |
| [1] | Chaohe ZHANG,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG. Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 105-114. |
| [2] | Xingqi SU,Lingmin ZHAO,Di MA,Jiulin YOU,Ying CHEN,Liangshu FENG,Jing WANG,Jiachun FENG,Chuan WANG. Analysis on correlation of cerebral infarct area with cytokines and immune status in patients with acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 124-132. |
| [3] | Kuai WANG,Yu YANG. Research progress in microglia-related susceptibility genes in Alzheimer’s disease and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 255-265. |
| [4] | Siqi LI,Guangdao CHEN,Qiyi ZENG. Improvement effect of chrysophanol on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of EA. hy926 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1512-1518. |
| [5] | Meng QU,Rui HUANG,Xinda JU,Yuxin LIU,Jichen XIA,Jiaxin HUANG,Chunyan YU,Zhiheng DONG. Ameliorative effect of ginsenoside Rh1 on kidney injury in diabetic mice through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1565-1571. |
| [6] | Yi LONG,Ziyi YOU,Xiuying TAN,Rou ZHANG,Yuhan ZHANG,Lina YANG. Protective effect of sodium butyrate on acute liver injury in mice induced by lipopolysaccharide combined with D-galactosamine and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1614-1620. |
| [7] | Haixia CHEN,Hongru LI,Jingyi LIU,Zhifang XU,Shuwen LIU,Yuan YANG,Yang CHEN,Yu LUO,Yinjie CUI. Research progress in changes of intestinal flora after spinal cord injury and their effects on spinal neuroinflammation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1751-1756. |
| [8] | Haoyu WANG,Yuqi WANG,Bingqian WANG,Jinhan NIE,Jiaqing YAN,Min HU. Inhibitory effect of mesalazine on pro-inflammatory factors and peroxides in RAW264.7 cells and its therapeutic effect on periodontitis model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1250-1258. |
| [9] | Fengmei XIONG,Yuxiang CAI,Zhuo LIU,Na SUN,Yang LI. Alleviatory effect of curcumin on cardiomyocyte toxicity induced by doxorubicin by regulating SIRT3/SOD2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1339-1347. |
| [10] | Wenhui LIU,Miao YU,Ying GUO,Yupeng LIU,Yang XING,Xinyu HONG,Jiale CUI. Research progress in effect of CXC chemokine receptor 3 on occurrence and development of nervous system diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1474-1480. |
| [11] | Xiaoyu WANG,Bing LI,Guohui LIU. Research progress in application of inflammatory markers in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1173-1181. |
| [12] | Xueting CHI,Fangyuan CHEN,Zifeng PI,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Yinqing LI,Xiaowei HUANG,Zhe LIN. Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 963-969. |
| [13] | Jianan HAN,Zhuorui LIU,Peiyong ZENG,Shuang JIANG,Hongyu LI. Anti-fatigue effect of Wujia Shengmai Yin in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 689-696. |
| [14] | Jing TANG,Huan LI,Shuo ZHANG,Ligang JING. Analysis on association between serum homocysteine and inflammatory response and oxidative stress in patients with acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 786-790. |
| [15] | Yiyan YU,Zhimin ZHANG,Jiawen CHEN,Xin LIU,Yan LI,Hongyan ZHAO. Research progress in relationship between macrophage polarization and oral diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 864-871. |
|
||