Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 479-485.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250222
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Two sample Mendelian randomization study on causal relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1 and colorectal cancer
Huaxia MU1,Weixiao BU1,Shuting DING1,Mengyao GAO1,Weiqiang SU1,Zhen ZHANG1,Qifu BO2,Feng LIU2,Fuyan SHI1,Qinghua WANG1,Yujia KONG1( ),Suzhen WANG1(
),Suzhen WANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Health Statistics,School of Public Health,Shandong Second Medical University,Weifang 261053,China
2.Department of Oncology,Affiliated Hospital,Shandong Second Medical University,Weifang 261041,China
-
Received:2024-05-30Accepted:2024-07-11Online:2025-03-28Published:2025-04-22 -
Contact:Yujia KONG,Suzhen WANG E-mail:yujia_kyj80@163.com;wangsz@wfmc.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R735.3
Cite this article
Huaxia MU,Weixiao BU,Shuting DING,Mengyao GAO,Weiqiang SU,Zhen ZHANG,Qifu BO,Feng LIU,Fuyan SHI,Qinghua WANG,Yujia KONG,Suzhen WANG. Two sample Mendelian randomization study on causal relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1 and colorectal cancer[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 479-485.
share this article
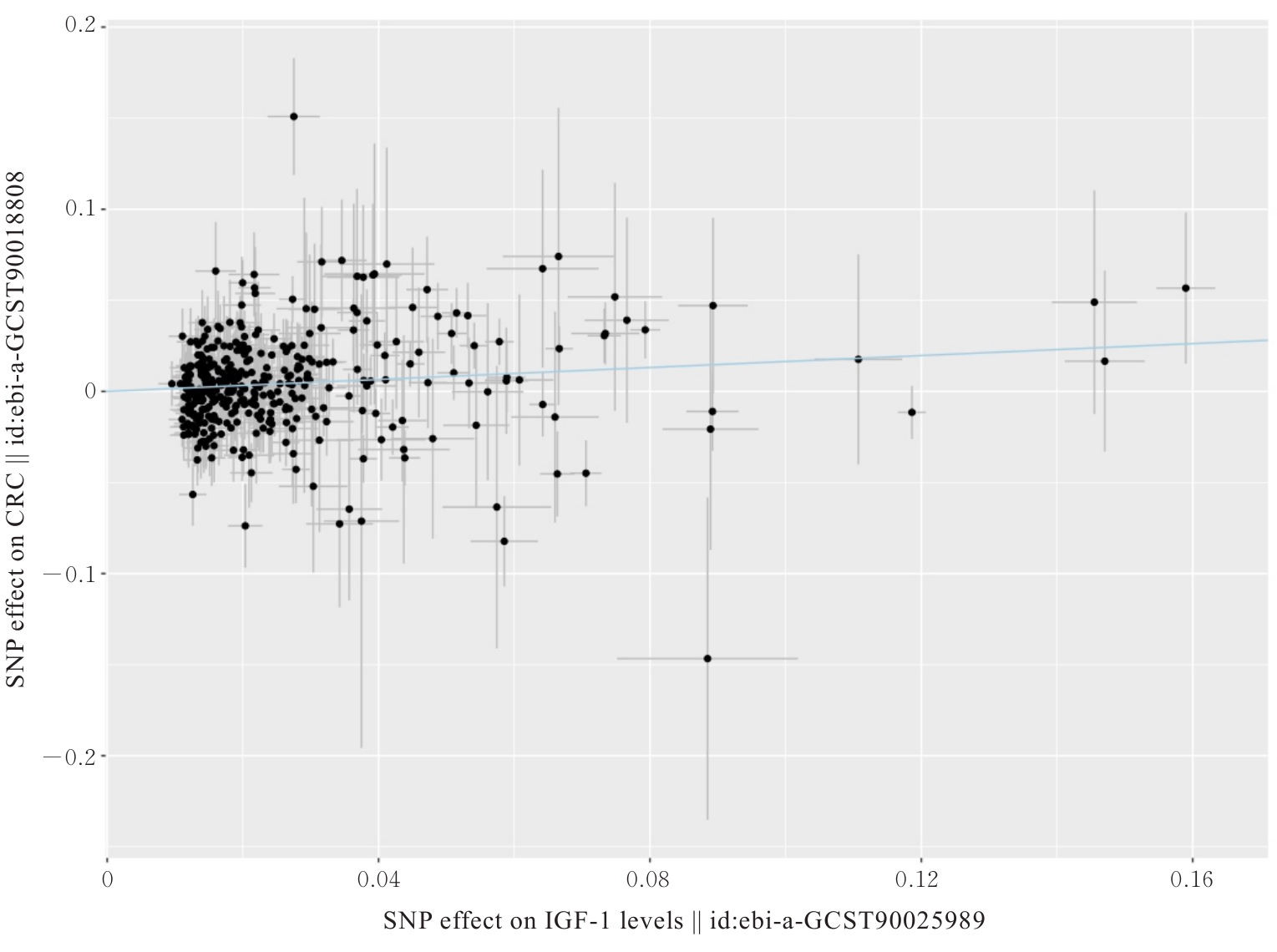
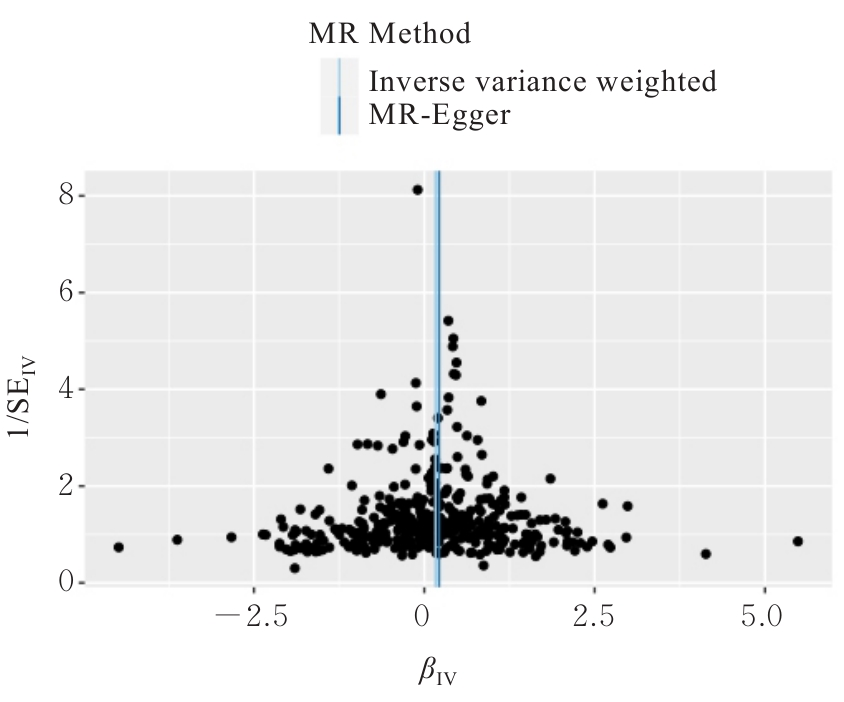
Tab.2
Estimates of causal effect in MR analysis results between IGF-1 level and CRC"
| Exposure | Outcome | Method | β | SE | OR (95%CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF-1 | CRC | Fixed effect IVW | 0.164 | 0.039 | 1.178(1.092,1.272) | <0.001 |
| Random effect IVW | 0.164 | 0.039 | 1.178(1.092,1.272) | <0.001 | ||
| WM | 0.200 | 0.057 | 1.222(1.092,1.367) | <0.001 | ||
| MR-Egger | 0.217 | 0.074 | 1.242(1.075,1.435) | 0.003 | ||
| SM | 0.198 | 0.153 | 1.219(0.902,1.645) | 0.198 | ||
| WME | 0.287 | 0.086 | 1.333(1.125,1.579) | 0.001 |
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | KNUPPEL A, FENSOM G K, WATTS E L, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations and risk of 30 cancers: prospective analyses in UK biobank[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(18): 4014-4021. |
| 3 | MURPHY N, CARRERAS-TORRES R, SONG M Y, et al. Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 associate with risk of colorectal cancer based on serologic and mendelian randomization analyses[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(5): 1300-1312.e20. |
| 4 | DEVESA J, ALMENGLÓ C, DEVESA P. Multiple effects of growth hormone in the body: is it really the hormone for growth?[J]. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes, 2016, 9: 47-71. |
| 5 | JENSEN-CODY S O, POTTHOFF M J. Hepatokines and metabolism: deciphering communication from the liver[J]. Mol Metab, 2021, 44: 101138. |
| 6 | MUKHERJEE A, ALZHANOV D, ROTWEIN P. Defining human insulin-like growth factor Ⅰ gene regulation[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 311(2): E519-E529. |
| 7 | ÁLVAREZ-NAVA F, LANES R. GH/IGF-1 signaling and current knowledge of epigenetics; a review and considerations on possible therapeutic options[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(10): 1624. |
| 8 | KASPRZAK A, SZAFLARSKI W. Role of alternatively spliced messenger RNA (mRNA) isoforms of the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) in selected human tumors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(19): 6995. |
| 9 | HU J X, LIU X Y, CHI J W, et al. Expressions of IGF-1, ERK, GLUT4, IRS-1 in metabolic syndrome complicated with colorectal cancer and their associations with the clinical characteristics of CRC[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2018, 21(4): 883-891. |
| 10 | ZELJKOVIC A, MIHAJLOVIC M, STEFANOVIC A, et al. Potential use of serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and E-cadherin as biomarkers of colorectal cancer[J]. Colorectal Dis, 2020, 22(12): 2078-2086. |
| 11 | CHOI Y J, LEE D H, HAN K D, et al. Adult height in relation to risk of cancer in a cohort of 22 809 722 Korean adults[J]. Br J Cancer, 2019, 120(6): 668-674. |
| 12 | ZHOU E, WANG L, SANTIAGO C N, et al. Adult-attained height and colorectal cancer risk: a cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2022, 31(4): 783-792. |
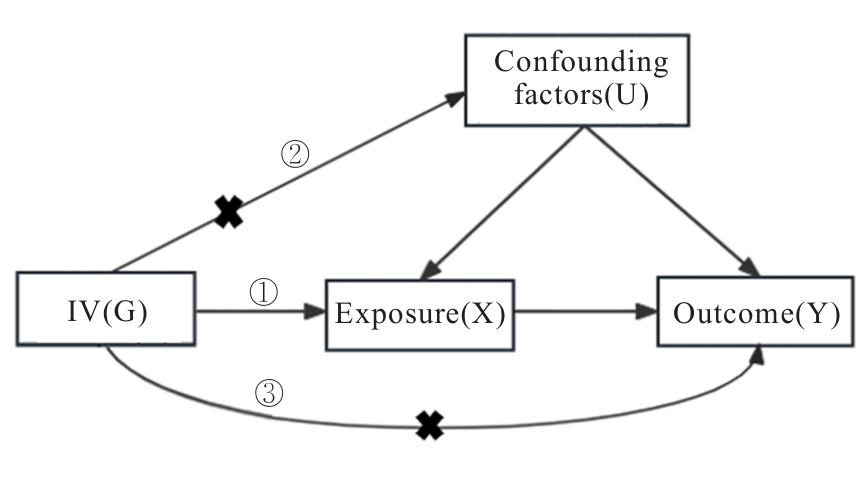
| 13 | 于天琦, 徐文涛, 苏雅娜, 等. 孟德尔随机化研究基本原理、方法和局限性[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2021, 21(10): 1227-1234. |
| 14 | HEMANI G, BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2018, 27(R2): R195-R208. |
| 15 | BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK P C, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted Median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2016, 40(4): 304-314. |
| 16 | BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2): 512-525. |
| 17 | 董朋涛, 王 峥, 李晓羽, 等. 炎症因子与糖尿病肾病的因果关系: 双向孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2024, 24(5): 543-549. |
| 18 | VERBANCK M, CHEN C Y, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(5): 693-698. |
| 19 | HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data[J]. PLoS Genet, 2017, 13(11): e1007081. |
| 20 | DURAIYARASAN S, ADEFUYE M, MANJUNATHA N, et al. Colon cancer and obesity: a narrative review[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(8): e27589. |
| 21 | JIANG B, ZHANG X, DU L L, et al. Possible roles of insulin, IGF-1 and IGFBPs in initiation and progression of colorectal cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(6): 1608-1613. |
| 22 | KAAKS R, TONIOLO P, AKHMEDKHANOV A, et al. Serum C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-Ⅰ, IGF-binding proteins, and colorectal cancer risk in women[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2000, 92(19): 1592-1600. |
| 23 | FUCHS C S, GOLDBERG R M, SARGENT D J, et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like binding protein-3, and outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from intergroup trial N9741[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(24): 8263-8269. |
| 24 | 曹欢易, 关海霞, 傅晓莹. 内分泌疾病与非酒精性脂肪性肝病[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(1): 11-16. |
| 25 | WALKIEWICZ K, NOWAKOWSKA-ZAJDEL E, KOZIEŁ P, et al. The role of some ADAM-proteins and activation of the insulin growth factor-related pathway in colorectal cancer[J]. Cent Eur J Immunol, 2018, 43(1): 109-113. |
| 26 | CRAWLEY D J, HOLMBERG L, MELVIN J C, et al. Serum glucose and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 985. |
| 27 | DE PERGOLA G, SILVESTRIS F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer[J]. J Obes, 2013, 2013: 291546. |
| 28 | SUH S, KIM K W. Diabetes and cancer: cancer should be screened in routine diabetes assessment[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2019, 43(6): 733-743. |
| 29 | KASPRZAK A. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signaling in glucose metabolism in colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(12): 6434. |
| 30 | BONONI G, MASONI S, DI BUSSOLO V, et al. Historical perspective of tumor glycolysis: a century with otto Warburg[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86(Pt 2): 325-333. |
| 31 | FUKUDA R, HIROTA K, FAN F, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(41): 38205-38211. |
| 32 | WERNER H. The IGF1 signaling pathway: from basic concepts to therapeutic opportunities[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14882. |
| [1] | Zhifei LIU,Yaru BI,Chenglin SUN,Suyan TIAN. Mendelian randomization analysis based on causal relationship between gut microbiota and gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1381-1389. |
| [2] | Xue WEI,Xue WEN,Xiao XIE,Yueyuan WANG,Dan HUANG,Ming YANG. Expression levels and imprinting status of lncRNA H19 and IGF2 genes in breast cancer tissue [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1109-1115. |
| [3] | Huaqing LIU,Qingkai CHEN,Yongxin CHEN,Runhao QIU,Xupeng DING,Fengjing SONG,Yan WANG,Baolin WANG,Hong CAO. Mendelian randomization study based on relationship between lifestyle and occurrence and development of hepatobiliary malignancies [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 778-785. |
| [4] | Qing YAO,Dan WANG,Xiaoshuang WANG,Yingjie WU,Liyuan RAN. Effect of ovariectomy on glucose and lipid metabolism in hyperinsulinemia MKR mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1229-1237. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lifang, CAI Lin, WANG Yunhua, ZHANG Keshi, WU Rina. Analysis on association between selenoprotein P polymorphism and risk of papillary thyriod carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 383-388. |
| [6] | DENG Ying, ZHU Yuzhen, WU Kefeng, ZHENG Xuebao, YE Hua. Effect of lncRNA H19 up-regulation mediated by IL-6/ STAT3 pathway in pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 20-25. |
| [7] | LU Mingyue, LI Jing. Relationships between expression of IGF-1 in cancer tissue of gastric cancer patients and clinicopathological parameters in China: A Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 137-142. |
| [8] | MA Licong, GAO Fang, DONG Wenjie, TIAN Xuyang, DANG Tong, JIA Yanbin. Analysis on association between polymorphism of ITGA1 gene and Helicobacter pylori infection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1275-1279. |
| [9] | XING Shaoji, ZHENG Liansheng, WANG Diandong, ZHANG Xuan, CHI Min. Analysis on association between single nucleotide polymorphism of selenoprotein S gene and risk of liver cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 558-562. |
| [10] | JIN Runhao, XU Zhongfu, LI Qing, QUAN Zhenyu, HAN Chunji. Application of blood pressure-to-height ratioin screening adolescents' hypertension in Yanjicity of Jilin province [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 639-645. |
| [11] | QIU Shuang, LIU Shicheng, PENG Bo, LEI Jie, LI Ri, BAI Ye, YU Yaqin, ZHU Xiaojuan, LIU Yawen, JIANG Huiyi. Analysis on association of PLA2G4C gene polymorphisms with autism spectrum disorder in North Han Chinese children [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(01): 80-84. |
| [12] | LEI Jie, QIU Shuang, LIU Shicheng, PENG Bo, LI Ri, BAI Ye, LIU Yawen, YU Yaqin, ZHU Xiaojuan, JIANG Huiyi. Analysis on association between PLA2G12A polymorphisms and autism spectrum disorder of Han nationality children in North China [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(06): 1132-1137. |
| [13] | TIAN Jiayi, ZHU Tong, WANG Jian, FANG Mingli, YAN Chaoying. Analysis on association between polymorphism of CD14 and IL-8 gene and susceptibilityof necrotizing enterocolitis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 958-962. |
| [14] | ZAO Hang, WANG XU, LI WEI. Influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms of CDA in prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(02): 316-320. |
| [15] | ZHANG Long, ZHU Yan, WANG Xiaochun, ZHANG Junfeng, HU Ruxin, LI Yufei, LI Chunbo. Analysis on correlation between genetic susceptibility of colorectal cancer and polymorphisms of selenoprotein P [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(05): 980-985. |
|
||