Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 749-756.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250319
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Analysis on relationship between methylation of MSX1 gene and clinical pathological features and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer
Xialing HUANG,Dandan ZHANG,Xuemei ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,Affiliated Puren Hospital,Wuhan University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430080,China
-
Received:2024-06-05Accepted:2024-08-06Online:2025-05-28Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Xuemei ZHANG E-mail:529824756@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R737.33
Cite this article
Xialing HUANG,Dandan ZHANG,Xuemei ZHANG. Analysis on relationship between methylation of MSX1 gene and clinical pathological features and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 749-756.
share this article
Tab.2
Correlation between MSX1 methylation and clinicopathological features of CC patients"
| Paremeter | Number | MSX1 gene [n(η/%)] | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypo-methylation(n=50) | Hyper-methylation(n=70) | ||||
| Age | |||||
| <50 | 58 | 24(41.38) | 34(58.62) | 0.009 | 0.974 |
| ≥50 | 62 | 26(41.94) | 36(58.06) | ||
| Tumor size(cm) | |||||
| <4 | 72 | 32(44.44) | 40(55.56) | 0.632 | 0.415 |
| ≥4 | 48 | 18(37.50) | 30(63.50) | ||
| HR-HPV DNA | |||||
| Positive | 96 | 34(35.41) | 62(64.58) | 8.692 | 0.003 |
| Negative | 24 | 16(66.67) | 8(33.33) | ||
| Histological type | |||||
| Squamous carcinoma | 81 | 33(40.74) | 48(59.26) | 0.212 | 0.612 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 39 | 17(43.59) | 22(56.41) | ||
| Lymphnode metestasis | |||||
| Yes | 33 | 8(24.24) | 25(75.76) | 6.912 | 0.005 |
| No | 87 | 42(48.28) | 45(51.72) | ||
| TNM phase | |||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 89 | 42(47.19) | 47(52.81) | 6.343 | 0.005 |
| Ⅲ-Ⅳ | 31 | 8(25.81) | 23(74.19) | ||
Tab. 3
Multivariate factors Logistic regression analysis on fluencing factors of prognosis of CC patients"
| Variable | Univariate model | Multivariate model | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | Z | P | OR(95%CI) | β | SE | Z | P | OR(95%CI) | ||
| Age (<50 vs ≥50) | -1.05 | 0.48 | -1.64 | 0.167 | 0.816-1.332 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Tumor size (<4 cm vs ≥4 cm) | -0.87 | 0.82 | -0.98 | 0.213 | 0.853-1.318 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HR-HPV DNA (negative vs positive) | 0.06 | 0.01 | 4.40 | <0.01 | 1.322-5.131 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 2.71 | <0.01 | 1.265-4.278 | |
| Histological type (adenocarcinoma vssquamous carcinoma) | 1.07 | 0.82 | 0.62 | 0.458 | 0.823-1.278 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Lymphnode metestasis (no vs yes) | 0.10 | 0.02 | 4.74 | <0.01 | 1.554-4.237 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 2.91 | <0.01 | 1.634-3.928 | |
| TNM phase (Ⅰ-Ⅱ vs Ⅲ-Ⅳ) | 0.17 | 0.04 | 4.32 | <0.01 | 1.721-5.853 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 3.74 | <0.01 | 1.688-5.538 | |
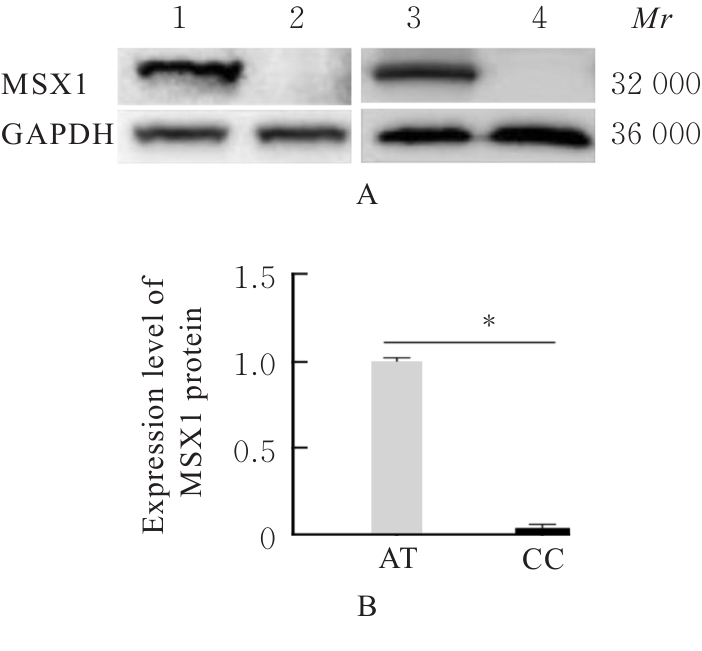
| MSX1 gene (unmethylated vs methylated) | 0.06 | 0.02 | 4.63 | <0.01 | 1.851-4.869 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 3.12 | <0.01 | 1.722-4.639 | |
| [1] | BUSKWOFIE A, DAVID-WEST G, CLARE C A. A review of cervical cancer: incidence and disparities[J]. J Natl Med Assoc, 2020, 112(2): 229-232. |
| [2] | LUVERO D, PLOTTI F, LOPEZ S, et al. Antiangiogenics and immunotherapies in cervical cancer: an update and future’s view[J]. Med Oncol, 2017, 34(6): 115. |
| [3] | PATASOVA K, LUNDBERG I E, HOLMQVIST M. Genetic influences in cancer-associated myositis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2023, 75(2): 153-163. |
| [4] | VAN DEN HELDER R, STEENBERGEN R D M, VAN SPLUNTER A P, et al. HPV and DNA methylation testing in urine for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer detection[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 28(10): 2061-2068. |
| [5] | LIANG J, VON DEN HOFF J, LANGE J, et al. MSX1 mutations and associated disease phenotypes: genotype-phenotype relations[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2016, 24(12): 1663-1670. |
| [6] | PARK K, KIM K, RHO S B, et al. Homeobox Msx1 interacts with p53 tumor suppressor and inhibits tumor growth by inducing apoptosis[J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(3): 749-757. |
| [7] | YUE Y J, ZHOU K, LI J C, et al. MSX1 induces G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis by suppressing Notch signaling and is frequently methylated in cervical cancer[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 11: 4769-4780. |
| [8] | LU Y L, TANG W C, WANG X Y, et al. Development of potential prognostic biomarkers based on DNA methylation-driven genes for patients with endometrial cancer[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2021, 14: 10541-10555. |
| [9] | LEE Y, DHO S H, LEE J, et al. Hypermethylation of PDX1, EN2, and MSX1 predicts the prognosis of colorectal cancer[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2022, 54(2): 156-168. |
| [10] | RAMALHO-CARVALHO J, HENRIQUE R, JERÓNIMO C. Methylation-specific PCR[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1708: 447-472. |
| [11] | KOH W J, ABU-RUSTUM N R, BEAN S, et al. Cervical cancer, version 3.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2019, 17(1): 64-84. |
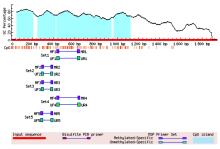
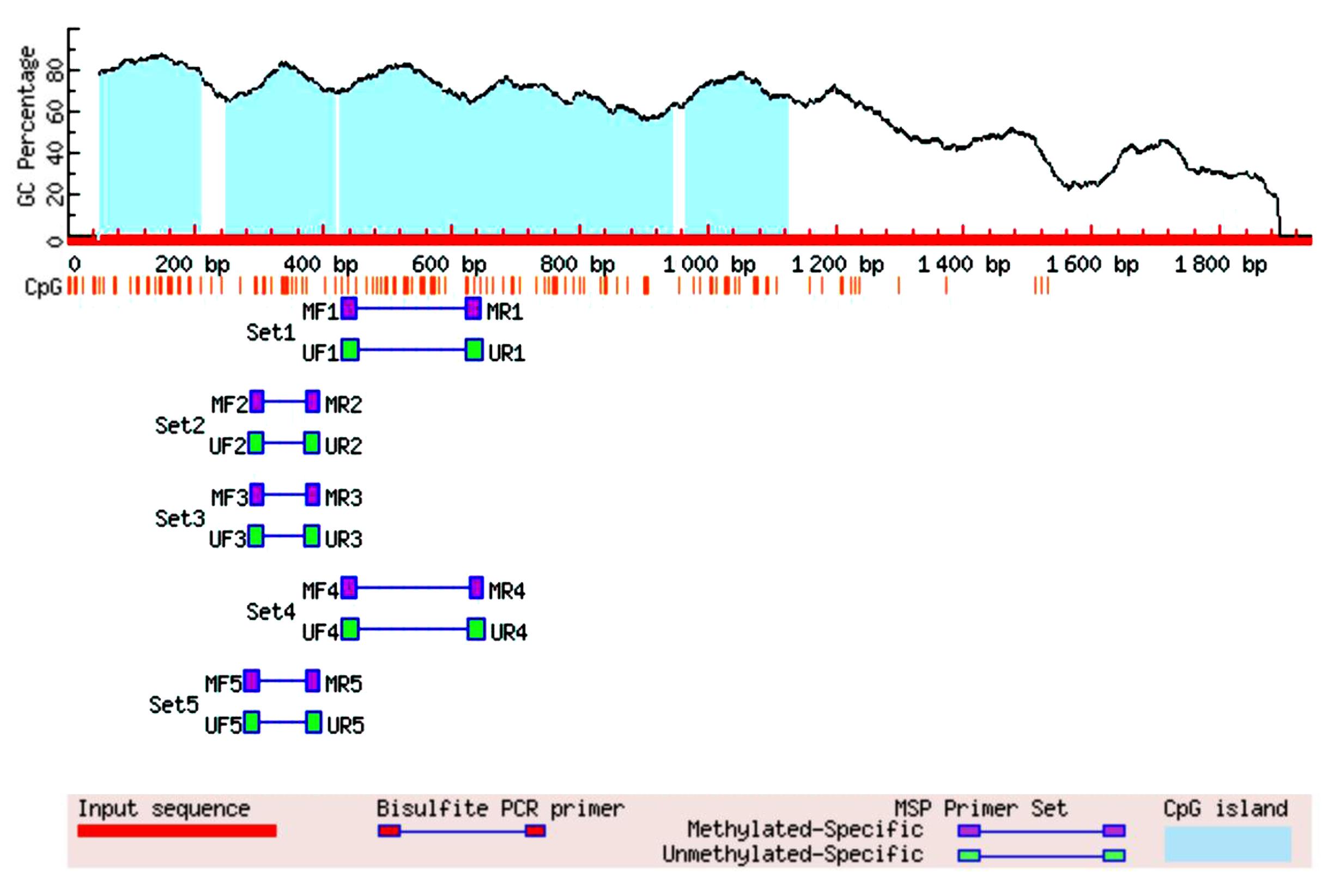
| [12] | LI L C, DAHIYA R. MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs[J]. Bioinformatics, 2002, 18(11): 1427-1431. |
| [13] | LI L M, XU C, LONG J, et al. E6 and E7 gene silencing results in decreased methylation of tumor suppressor genes and induces phenotype transformation of human cervical carcinoma cell lines[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(27): 23930-23943. |
| [14] | FAN D M, WANG Y, QI P W, et al. microRNA-183 functions as the tumor suppressor via inhibiting cellular invasion and metastasis by targeting MMP-9 in cervical cancer[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2016, 141(1): 166-174. |
| [15] | SENCHENKO V N, KISSELJOVA N P, IVANOVA T A, et al. Novel tumor suppressor candidates on chromosome 3 revealed by NotI-microarrays in cervical cancer[J]. Epigenetics, 2013, 8(4): 409-420. |
| [16] | GARCIA-FERNÀNDEZ J. The genesis and evolution of homeobox gene clusters[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2005, 6(12): 881-892. |
| [17] | NASSIF A, SENUSSI I, MEARY F, et al. Msx1 role in craniofacial bone morphogenesis[J]. Bone, 2014, 66: 96-104. |
| [18] | LALLEMAND Y, NICOLA M A, RAMOS C, et al. Analysis of Msx1; Msx2 double mutants reveals multiple roles for Msx genes in limb development[J]. Development, 2005, 132(13): 3003-3014. |
| [19] | SAADI I, DAS P, ZHAO M L, et al. Msx1 and Tbx2 antagonistically regulate Bmp4 expression during the bud-to-cap stage transition in tooth development[J]. Development, 2013, 140(13): 2697-2702. |
| [20] | DAVALOS V, ESTELLER M. Cancer epigenetics in clinical practice[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(4): 376-424. |
| [21] | GOSDEN R G, FEINBERG A P. Genetics and epigenetics: nature’s pen-and-pencil set[J]. N Engl J Med, 2007, 356(7): 731-733. |
| [22] | ZHOU B H, LIN W L, LONG Y L, et al. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 95. |
| [23] | REVET I, HUIZENGA G, CHAN A, et al. The MSX1 homeobox transcription factor is a downstream target of PHOX2B and activates the Delta-Notch pathway in neuroblastoma[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2008, 314(4): 707-719. |
| [24] | PARK J, PARK K, KIM S, et al. Msx1 gene overexpression induces G1 phase cell arrest in human ovarian cancer cell line OVCAR3[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001, 281(5): 1234-1240. |
| [25] | HU G, LEE H, PRICE S M, et al. Msx homeobox genes inhibit differentiation through upregulation of cyclin D1[J]. Development, 2001, 128(12): 2373-2384. |
| [26] | YUN J, ESPINOZA I, PANNUTI A, et al. p53 modulates Notch signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by associating with the Notch transcriptional complex via MAML1[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2015, 230(12): 3115-3127. |
| [1] | Xiaoyan WANG,Xuelian LI,Bin LIANG,Wenfei TIAN,Hailin MA,Zhijing MO. Analysis on relationship between CALU and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and its mechanism based on transcriptome and single cell sequencing data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 447-459. |
| [2] | Haiying GENG,Yan YU,Chunmei DAI,Youfeng WEN,Ning LI. Expression of TRIM24 protein in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma tissue and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 486-492. |
| [3] | Xi YANG,Qin YUAN,Lan YANG,Wenjie ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis on PDE1B expression and prognosis of gastric cancer and tumor microenvironment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1664-1676. |
| [4] | Jiaxin YI,Yangyu ZHANG,Yingli FU,Yuchen PAN,Yongjie HAN,Jing JIANG,Yanhua WU. Effect of MEIS1 expression on survival in patients after radical gastrectomy and its value in prognostic evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1358-1364. |
| [5] | Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU. Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043. |
| [6] | Yuanguo WANG,Peng ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on relationship between SSP1 and TGFB1 and occurrence, prognosis, and immune invasion of esophageal adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1076-1086. |
| [7] | Yueying SONG,Chao GAO,Wenjun CHEN,Aiyu SHAO,Yichun QIAO,Zhuolin LI. Screening of miRNAs related to prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its gene network based on TCGA Database [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 392-399. |
| [8] | Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252. |
| [9] | Haikang CUI,Xudong ZHANG,Xiaoning LI,Xi YANG,Lan YANG,Wenjie ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis on predition effect of subtypes of cell pyroptosis and APOD on prognosis of gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1268-1279. |
| [10] | Jingjing LI, REZIWANGULI·Aisikaier,Wanyi XING,Yinggang ZOU. Primary dedifferentiated liposarcoma of unilateral ovary: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1040-1045. |
| [11] | Renyi YANG,Shuwang PENG,Yongheng WANG,Yuxuan DONG,Shanshan DUAN. Construction of ferroptosis prognostic risk model of thyroid cancer and bioinformatics analysis on its potential mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 402-413. |
| [12] | Xiaoyan WANG,Yihong HU,Yucheng HAN,Xianqiong ZOU. Bioinformatics analysis on mechanism of COMMD7 in occurrence and development of brain low-grade glioma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 414-424. |
| [13] | Yang BAI,Chenxi YANG,Xiaoqiang LIU,Yu LIU,Qian XING. Changes of follicular helper T lymphocytes in peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy and its significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 166-172. |
| [14] | Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017. |
| [15] | Shan GAO,Yutong WANG,Minqiu LU,Lei SHI,Bin CHU,Yuehua DING,Mengzhen WANG,Li BAO. Analysis on causes for early death and its risk factors of patients with multiple myeloma in era of novel drugs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 783-789. |
|
||