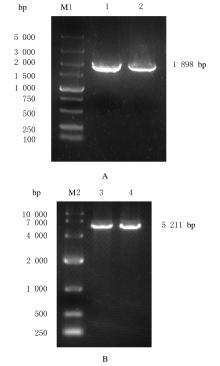
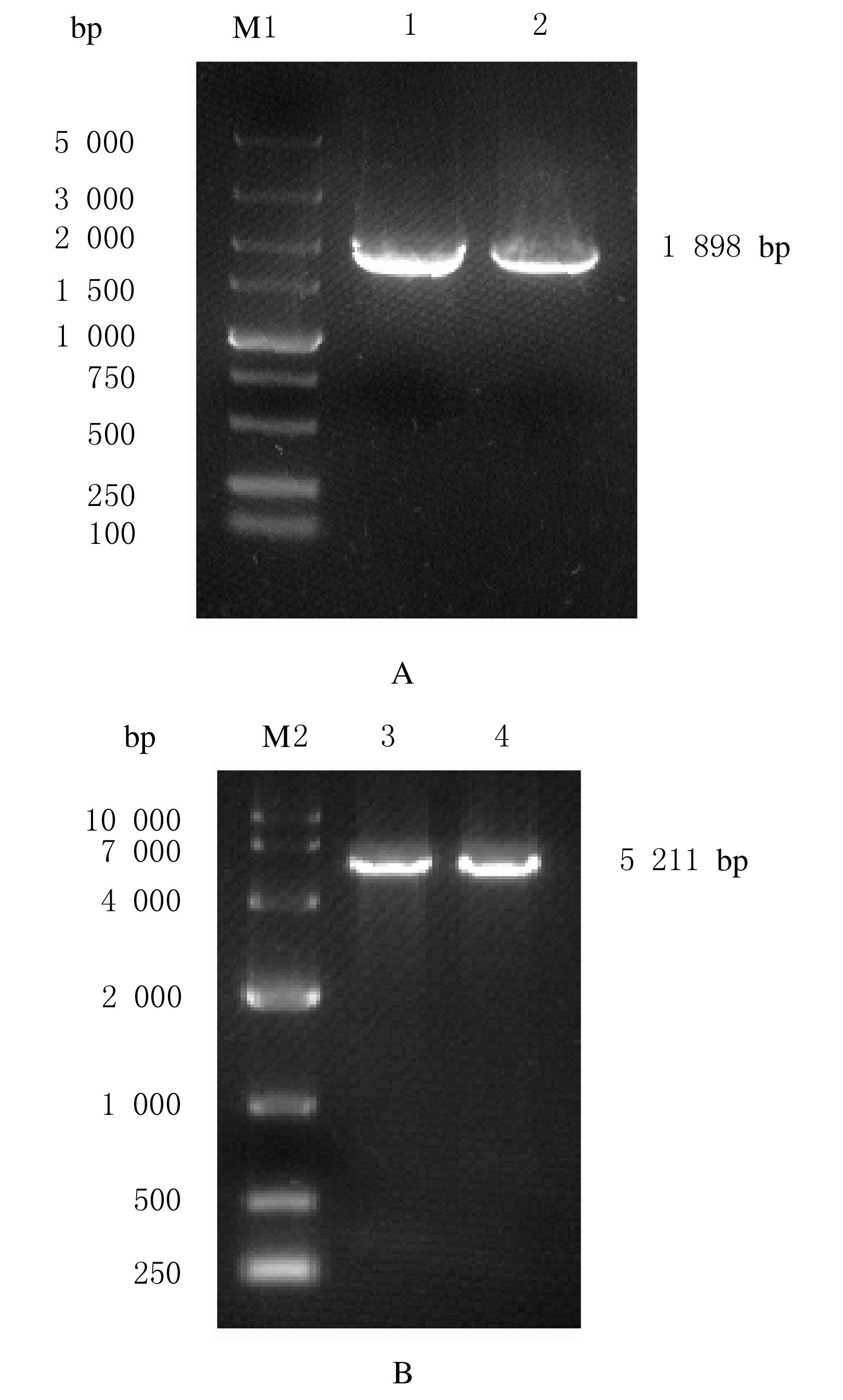
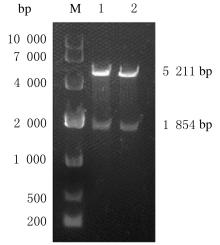
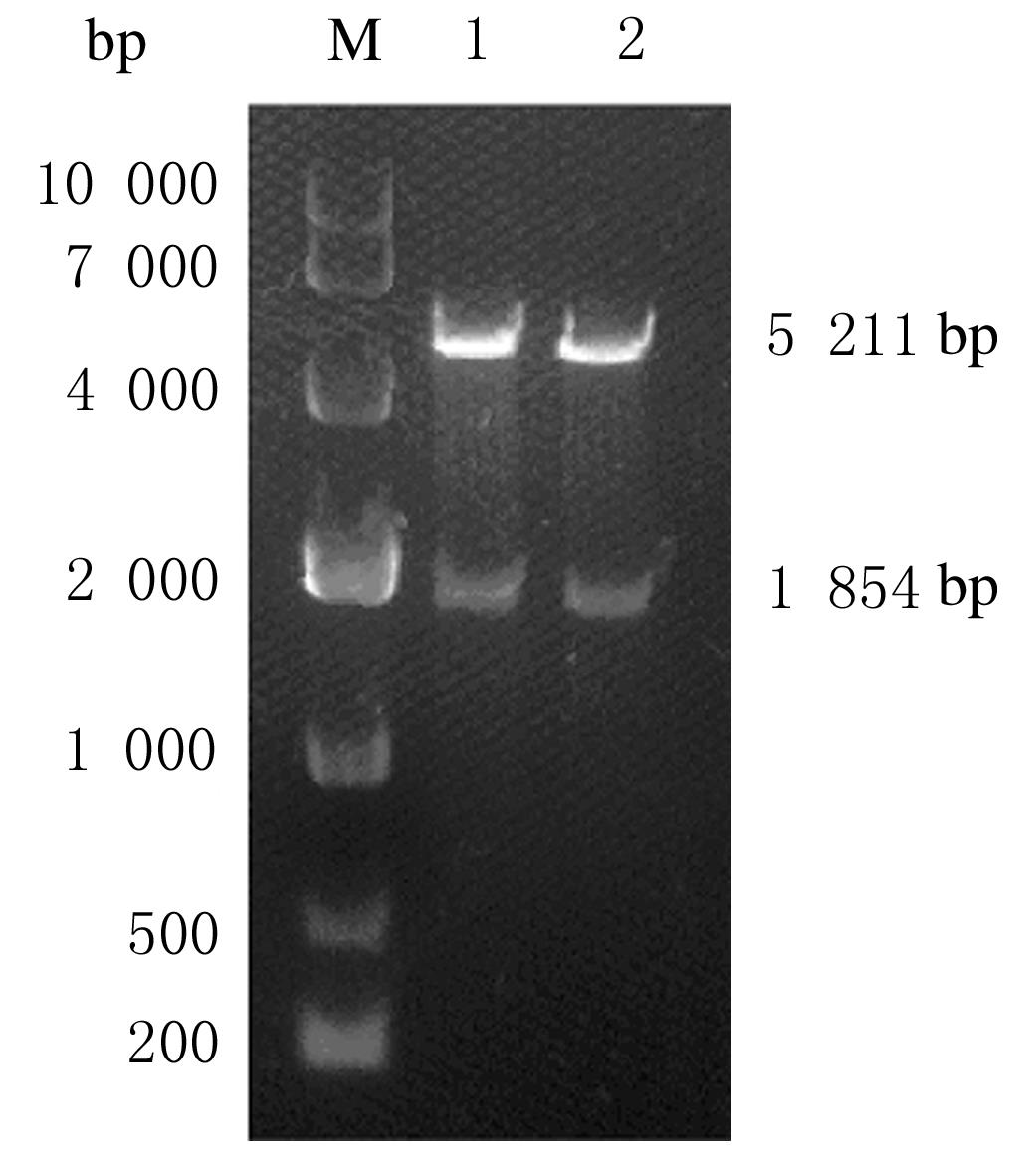
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 94-103.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220112
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
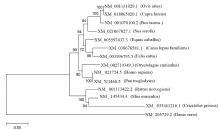
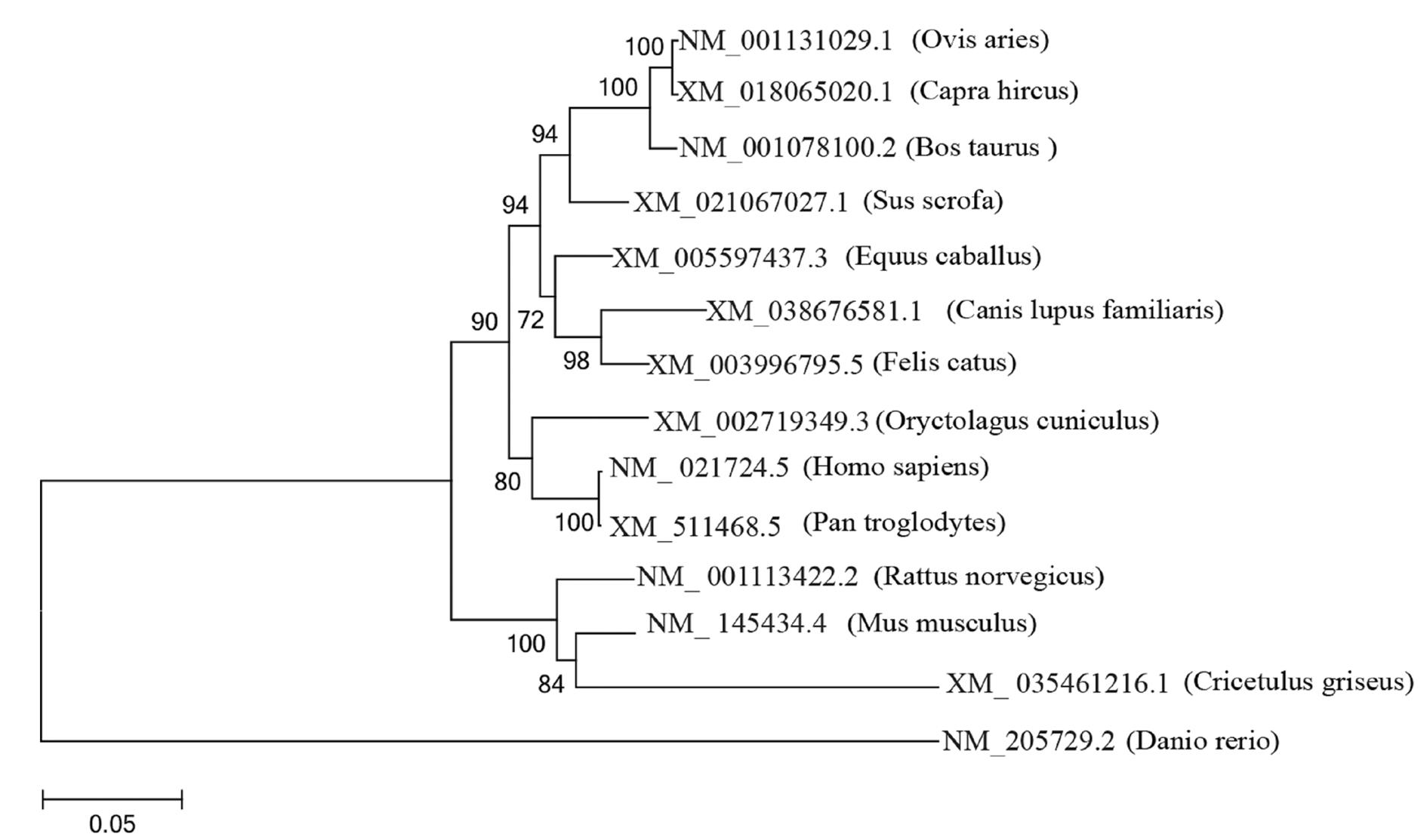
Construction of mouse NR1D1 gene overexpression vector and its bioinformatics analysis
Hao DONG1,2,Haizhen JIANG1,2,Chao LI1,2,Dengke GAO1,2,Yaping JIN1,2,Huatao CHEN1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine,College of Veterinary Medicine,Northwest A&F University,Yangling 712100,China
2.Key Laboratory of Animal Biotechnology of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Northwest A&F University,Yangling 712100,China
-
Received:2021-06-11Online:2022-01-28Published:2022-01-17 -
Contact:Huatao CHEN E-mail:htchen@nwafu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- Q78
Cite this article
Hao DONG,Haizhen JIANG,Chao LI,Dengke GAO,Yaping JIN,Huatao CHEN. Construction of mouse NR1D1 gene overexpression vector and its bioinformatics analysis[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 94-103.
share this article
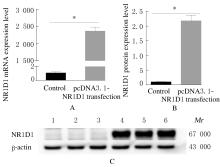
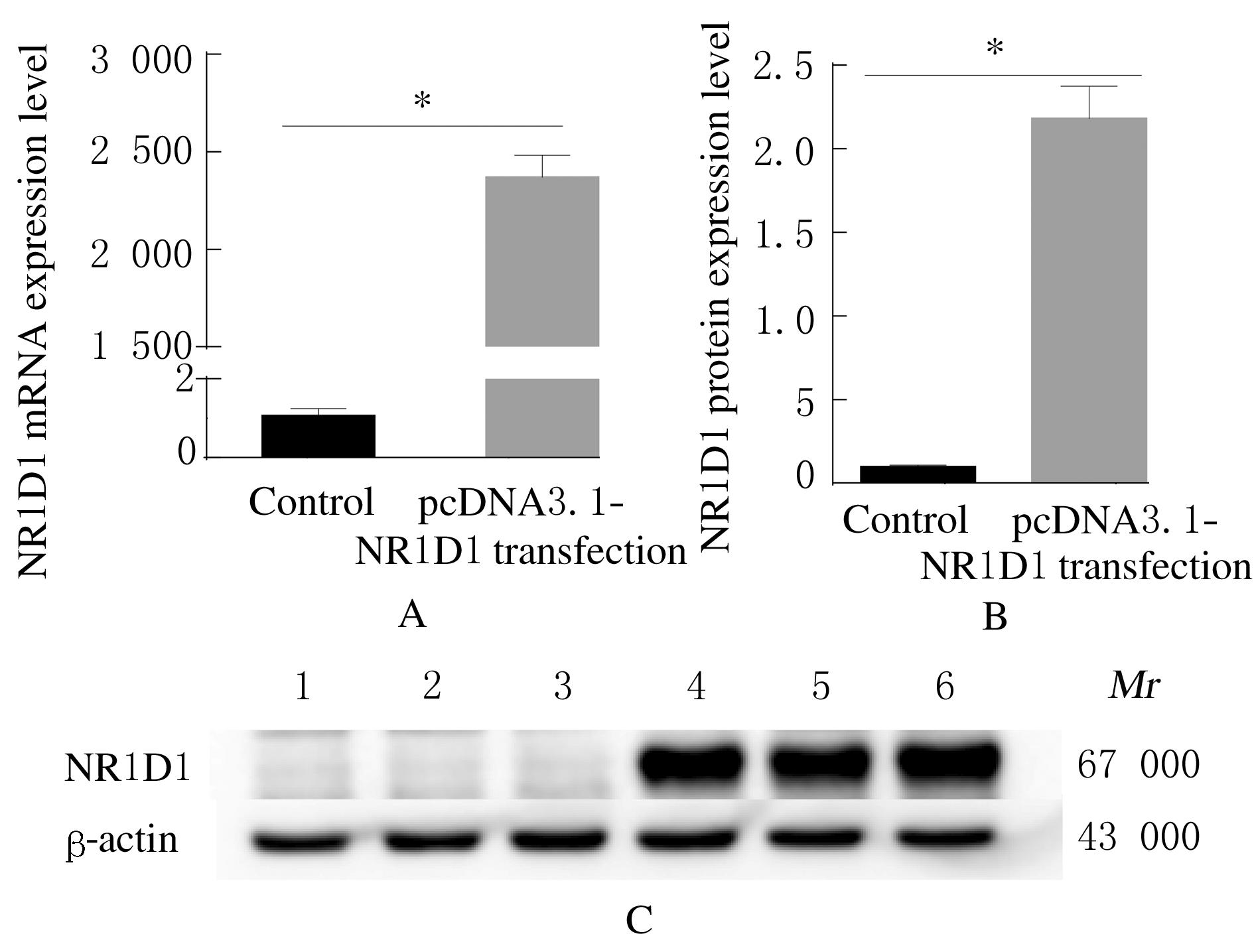
Tab.1
Primer sequences of RT-qPCR"
| Gene | Primer sequence(5'-3') | Product length(bp) | Annealing temperature(θ/℃) |
|---|---|---|---|
| hmNR1D1 | F: CGGGAGGTGGTAGAGTTTGC R: TCCTTCACGTTGAACAACGA | 134 | 60 |
| hGAPDH | F: TCAACGGATTTGGTCGTATTG R: TGGGTGGAATCATATTGGAAC | 136 | 60 |
| In hmNR1D1, h standed for human and m standed for mouse;in hGAPDH, h standed for human. | |||
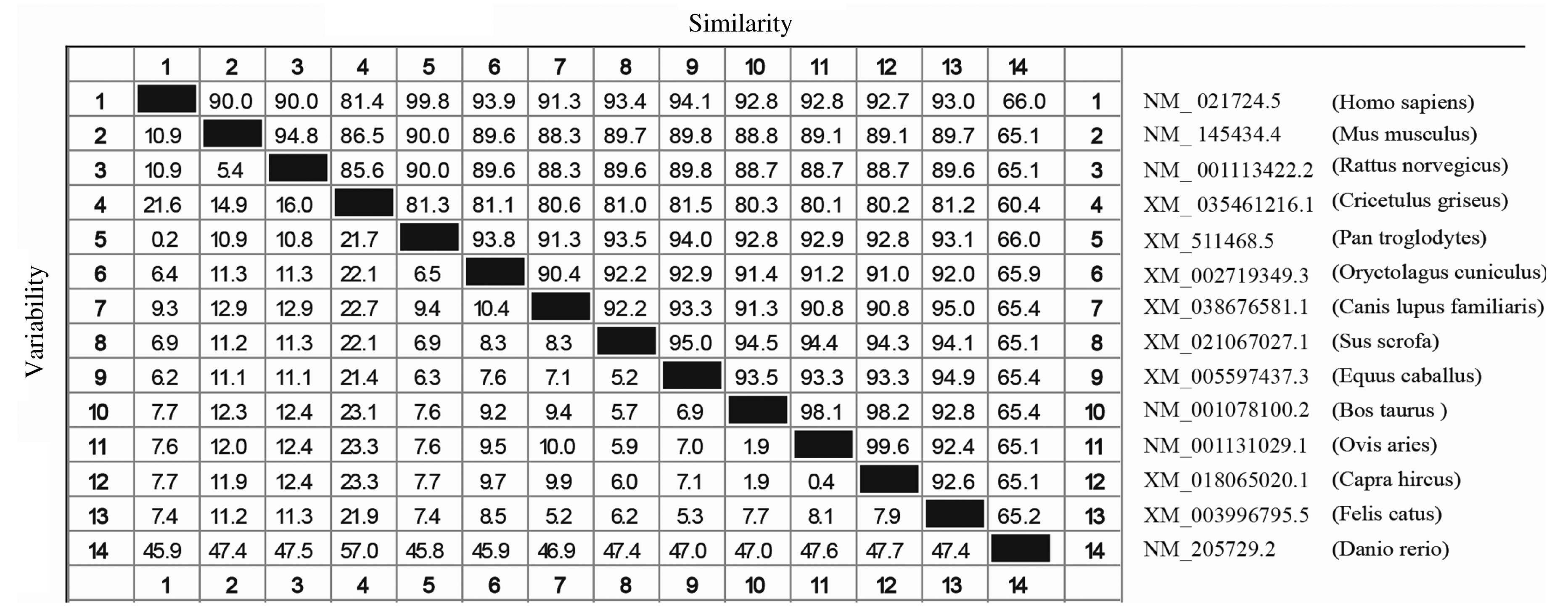
Tab. 2
Amino acid composition of mouse NR1D1 protein"
| Animo acid | n | Frequency(η/%) | Animo acid | n | Frequency(η/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala (A) | 39 | 6.3 | Lys (K) | 20 | 3.3 |
| Arg (R) | 36 | 5.9 | Met (M) | 19 | 3.1 |
| Asn (N) | 36 | 5.9 | Phe (F) | 26 | 4.2 |
| Asp (D) | 20 | 3.3 | Pro (P) | 51 | 8.3 |
| Cys (C) | 15 | 2.4 | Ser (S) | 86 | 14.0 |
| Gln (Q) | 29 | 4.7 | Thr (T) | 38 | 6.2 |
| Gly (G) | 41 | 6.7 | Trp (W) | 3 | 0.5 |
| His (H) | 17 | 2.8 | Tyr (Y) | 11 | 1.8 |
| Ile (I) | 12 | 2.0 | Val (V) | 30 | 4.9 |
| Leu (L) | 57 | 9.3 | Glu (E) | 29 | 4.7 |
| 1 | LAZAR M A, HODIN R A, DARLING D S, et al. A novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor family is encoded by the opposite strand of the rat c-erbA alpha transcriptional unit[J].Mol Cell Biol, 1989,9(3): 1128-1136. |
| 2 | MARVIN K A, REINKING J L, LEE A J, et al. Nuclear receptors homo sapiens Rev-erb beta and Drosophila melanogaster E75 are thiolate-ligated heme proteins which undergo redox-mediated ligand switching and bind CO and NO[J]. Biochemistry, 2009, 48(29): 7056-7071. |
| 3 | YIN L, WU N, LAZAR M A. Nuclear receptor Rev-erb alpha: a heme receptor that coordinates circadian rhythm and metabolism[J]. Nucl Recept Signal, 2010, 8: e001. |
| 4 | CASTAGNÉ C, TERENZI H, ZAKIN M M, et al. Solution structure of the orphan nuclear receptor rev-erb beta response element by 1H, 31P NMR and molecular simulation[J]. Biochimie, 2000, 82(8): 739-748. |
| 5 | RAMAKRISHNAN S N, LAU P, BURKE L J, et al. Rev-erbβ regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid absorption in skeletal muscle cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(10): 8651-8659. |
| 6 | RAGHURAM S, STAYROOK K R, HUANG P, et al. Identification of heme as the ligand for the orphan nuclear receptors REV-ERBalpha and REV-ERB beta[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2007,14(12):1207-1213. |
| 7 | BUGGE A, FENG D, EVERETT L J, et al. Rev-erb and Rev-erb coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic function[J]. Genes Dev, 2012,26(7): 657-667. |
| 8 | PREITNER N, DAMIOLA F, LOPEZ-MOLINA L, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERB alpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator[J]. Cell, 2002, 110(2): 251-260. |
| 9 | TRIQUENEAUX G, THENOT S, KAKIZAWA T, et al. The orphan receptor Rev-erb alpha gene is a target of the circadian clock pacemaker[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2004, 33(3): 585-608. |
| 10 | HARDING H P, LAZAR M A. The monomer-binding orphan receptor Rev-Erb represses transcription as a dimer on a novel direct repeat[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1995, 15(9): 4791-4802. |
| 11 | MAKISHIMA M. Nuclear receptors as targets for drug development: regulation of cholesterol and bile acid metabolism by nuclear receptors[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2005, 97(2): 177-183. |
| 12 | GRANT D, YIN L, COLLINS J L, et al. GSK4112, a small molecule chemical probe for the cell biology of the nuclear heme receptor Rev-erbα[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2010, 5(10): 925-932. |
| 13 | SOLT L A, WANG Y J, BANERJEE S, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists[J].Nature,2012,485(7396): 62-68. |
| 14 | LI C, ZHANG L, MA T, et al. Bisphenol A attenuates testosterone production in Leydig cells via the inhibition of NR1D1 signaling[J].Chemosphere,2021,263: 128020. |
| 15 | BONNELYE E, VANACKER J M, DESBIENS X,et al.Rev-erb beta, a new member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, is expressed in the nervous system during chicken development[J]. Cell Growth Differ, 1994, 5(12): 1357-1365. |
| 16 | CHO H, ZHAO X, HATORI M, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and REV-ERB-Β[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7396): 123-127. |
| 17 | 李翠梅. 双酚A通过生物钟基因Nr1d1影响睾酮合成的机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. |
| 18 | ERCOLANI L, FERRARI A, DE MEI C, et al. Circadian clock: Time for novel anticancer strategies?[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2015, 100: 288-295. |
| 19 | GEKAKIS N, STAKNIS D, NGUYEN H B, et al. Role of the CLOCK protein in the mammalian circadian mechanism[J]. Science, 1998, 280(5369): 1564-1569. |
| 20 | YOO S H, KO C H, LOWREY P L, et al. A noncanonical E-box enhancer drives mouse Period2 circadian oscillations in vivo [J]. PNAS, 2005, 102(7): 2608-2613. |
| 21 | OHNO T, ONISHI Y, ISHIDA N. A novel E4BP4 element drives circadian expression of mPeriod2[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2007, 35(2): 648-655. |
| 22 | CHAIX A, ZARRINPAR A, PANDA S. The circadian coordination of cell biology[J]. J Cell Biol, 2016, 215(1): 15-25. |
| 23 | EVERETT L J, LAZAR M A. Nuclear receptor Rev-erb α: up, down, and all around[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2014, 25(11): 586-592. |
| 24 | HUNTER A L, PELEKANOU C E, ADAMSON A, et al. Nuclear receptor REVERBα is a state-dependent regulator of liver energy metabolism[J]. PNAS, 2020, 117(41): 25869-25879. |
| 25 | WANG J, LIU N, LIU Z, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor Rev-erb beta recruits Tip60 and HDAC1 to regulate apolipoprotein CIII promoter[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2008, 1783(2): 224-236. |
| 26 | DELEZIE J, DUMONT S, DARDENTE H, et al. The nuclear receptor REV-ERBα is required for the daily balance of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism[J]. FASEB J, 2012, 26(8): 3321-3335. |
| 27 | LE MARTELOT G, CLAUDEL T, GATFIELD D, et al. REV-ERBalpha participates in circadian SREBP signaling and bile acid homeostasis[J]. PLoS Biol, 2009, 7(9): e1000181. |
| 28 | WOLDT E, SEBTI Y, SOLT L A, et al. Rev-erb-α modulates skeletal muscle oxidative capacity by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy[J]. Nat Med, 2013, 19(8): 1039-1046. |
| 29 | ZHANG T P, ZHAO M J, LU D Y, et al. REV-ERBα regulates CYP7A1 through repression of liver receptor homolog-1[J].Drug Metab Dispos,2018,46(3):248-258. |
| 30 | XING C, HUANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Sleep disturbance induces increased cholesterol level by NR1D1 mediated CYP7A1 inhibition[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 610496. |
| 31 | MIGITA H, MORSER J, KAWAI K. Rev-erbα upregulates NF-κB-responsive genes in vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. FEBS Lett, 2004, 561(1-3): 69-74. |
| 32 | MAZZOCCOLI G, SOTHERN R B, GRECO A,et al. Time-related dynamics of variation in core clock gene expression levels in tissues relevant to the immune system[J].Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol,2011,24(4): 869-879. |
| 33 | CHANDRA V, MAHAJAN S, SAINI A, et al. Human IL10 gene repression by Rev-erbα ameliorates Mycobacterium tuberculosis clearance[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(15): 10692-10702. |
| 34 | ZVONIC S, PTITSYN A A, CONRAD S A, et al. Characterization of peripheral circadian clocks in adipose tissues[J]. Diabetes, 2006, 55(4): 962-970. |
| [1] | Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017. |
| [2] | Qian LIU,Guoping QI,Huayi YU,Yuyang DAI,Wenbin LU,Jianhua JIN. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of colon cancer core genes and independent prognostic factors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 755-765. |
| [3] | Xiaoyan LI,Wei ZHANG,Jie HE. Promotion effect of REG1A on proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 444-453. |
| [4] | Nan LI,Lei CHEN,Tianmin XU,Kun ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of extracellular matrix related genes in patients with endometriosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 188-194. |
| [5] | Zhijuan ZHAO,Lian MENG,Chunxia LIU. Bioinformatics analysis on miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks based on fusion genes acting in rhabdomyosarcoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 154-162. |
| [6] | Ying ZHAO,Danyu ZHAO,Chao LIU. Bioinformatics analysis on prognostic evaluation value of TXNDC11 gene in pan-cancer and its immunity regulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 142-153. |
| [7] | Yang YU,Sainan LIU,Yunkai LIU,Yong LI,Yichun QIAO,Yi CHENG. Bioinformatic analysis on expression characteristics of PRPS2 and its relationship with prognosis of breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1229-1236. |
| [8] | Yuqing PAN, Yunyan SUN, Yixun LI, Liying WANG, Zhuoma SINAN, Rui CHEN, Xi ZHANG, Yan DU. Construction and analysis of competitive endogenous RNA networks in acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 669-676. |
| [9] | Lan ZHENG,Songzhe PIAO,Ran XU,Xinyue WANG,Yixuan WANG,Zhenhua LIN,Yang YANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of expression levels of m6A regulators on immune infiltration and prognosis of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 438-452. |
| [10] | Yao LIN,Chunlin LIN,Qin WANG,Bin ZHANG,Shaoyu WANG,Guangwei ZHU. Expressions of minichromosome maintenance proteins and structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue and bioinformation analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 430-437. |
| [11] | ZHANG Xi, ZHAI Li, SUN Yunyan, YANG Wei, GAO Yanzhang, LEI Ming, PAN Yuqing. Bioinformatics analysis of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1036-1042. |
| [12] | WANG Zhi, HONG Li, LI Suting, ZENG Wanling. Analysis on endometrial cancer-related genes and candidate pathways based on GEO database bioinformatics methods [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 804-809. |
| [13] | TAN Qi, REN Liqun, ZHANG Yibing, WANG Yadi, GU Zehui, HUANG Peng, CHEN Suxian. Application of bioinformatics in screening of miRNA biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1098-1105. |
| [14] | DU Yayan, LIU Yang, LU Mu, HUAI Shitao, LYU Zuoli, WEI Yutao. Expressions of adiponectin-related miR-371b-5p in epicardial adipose tissue and plasma of patients with coronary heart disease and its effect on secretion of adipocytokines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 643-650. |
| [15] | HUO Yanwei, XIE Bing, JIANG Lei, ZHANG Rui, SONG Mei, WANG Lan, WANG Xueyi, XU Shunjiang. Expressions of miRNAs related to accelerating senescence in serum of patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and analysison their biological information [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 322-327. |