Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1044-1054.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240419
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
CatBoost algorithm and Bayesian network model analysis based on risk prediction of cardiovascular and cerebro vascular diseases
Aimin WANG1,Fenglin WANG1,Yiming HUANG1,Yaqi XU1,Wenjing ZHANG1,Xianzhu CONG1,Weiqiang SU1,Suzhen WANG1,Mengyao GAO1,Shuang LI1,Yujia KONG1,Fuyan SHI1( ),Enxue TAO2(
),Enxue TAO2( )
)
- 1.Department of Health Statistics,School of Public Health,Shandong Second Medical University,Weifang 261053,China
2.School of Basic Medical Sciences,Shandong Second Medical University,Weifang 261053,China
-
Received:2023-09-02Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Fuyan SHI,Enxue TAO E-mail:shifuyan@126.com;sdwftex@163.com
CLC Number:
- R54
Cite this article
Aimin WANG,Fenglin WANG,Yiming HUANG,Yaqi XU,Wenjing ZHANG,Xianzhu CONG,Weiqiang SU,Suzhen WANG,Mengyao GAO,Shuang LI,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Enxue TAO. CatBoost algorithm and Bayesian network model analysis based on risk prediction of cardiovascular and cerebro vascular diseases[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1044-1054.
share this article
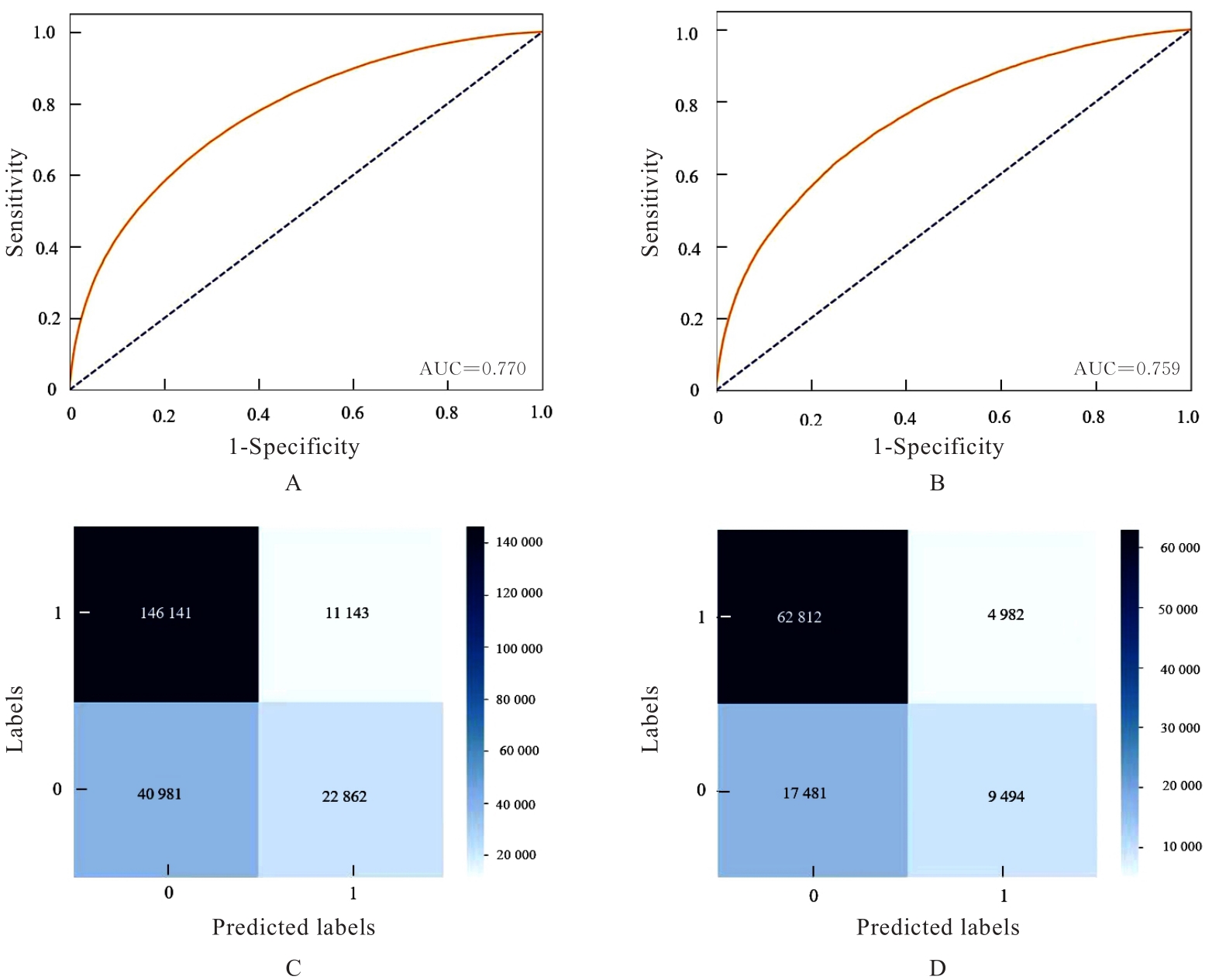
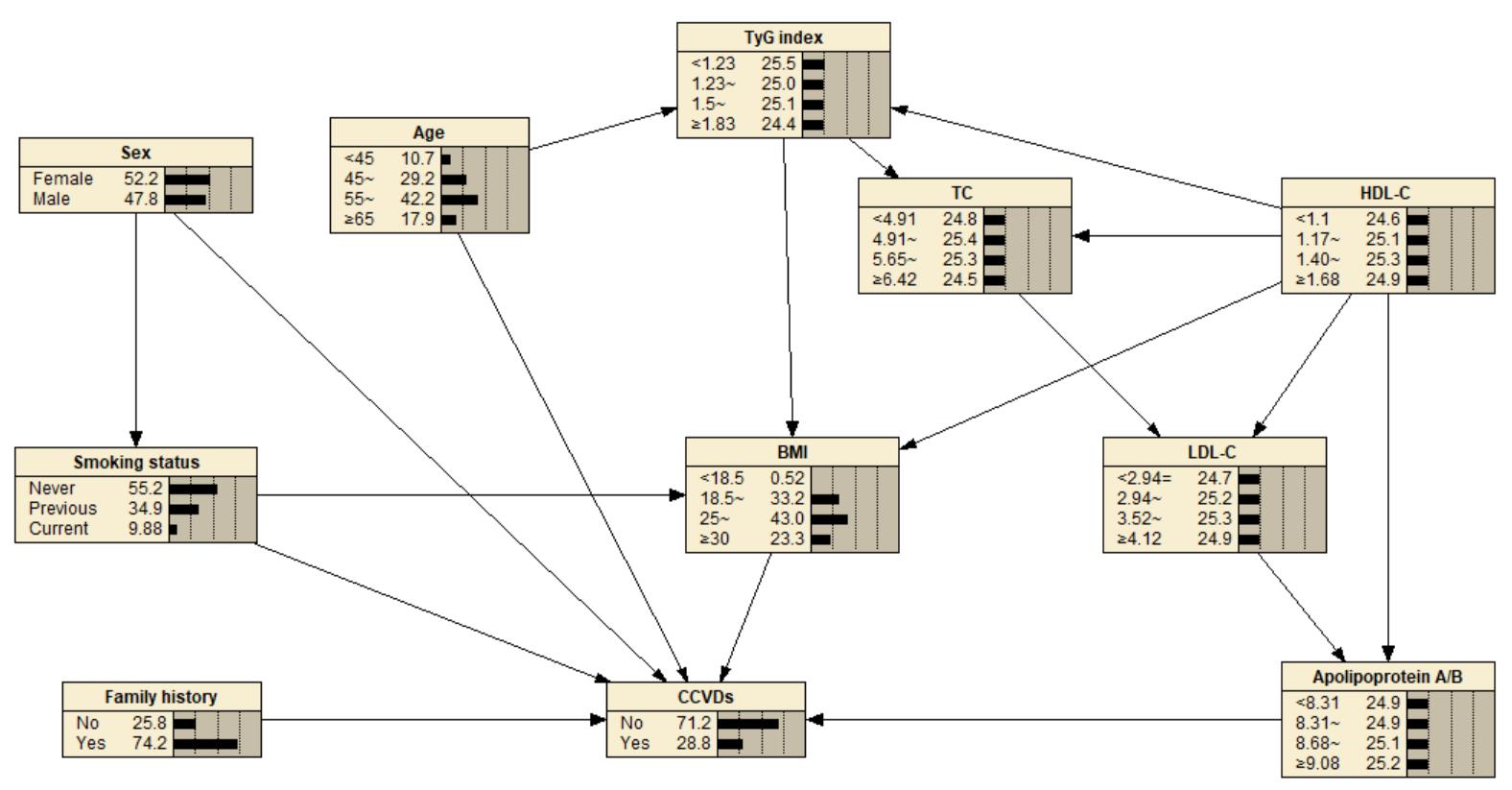
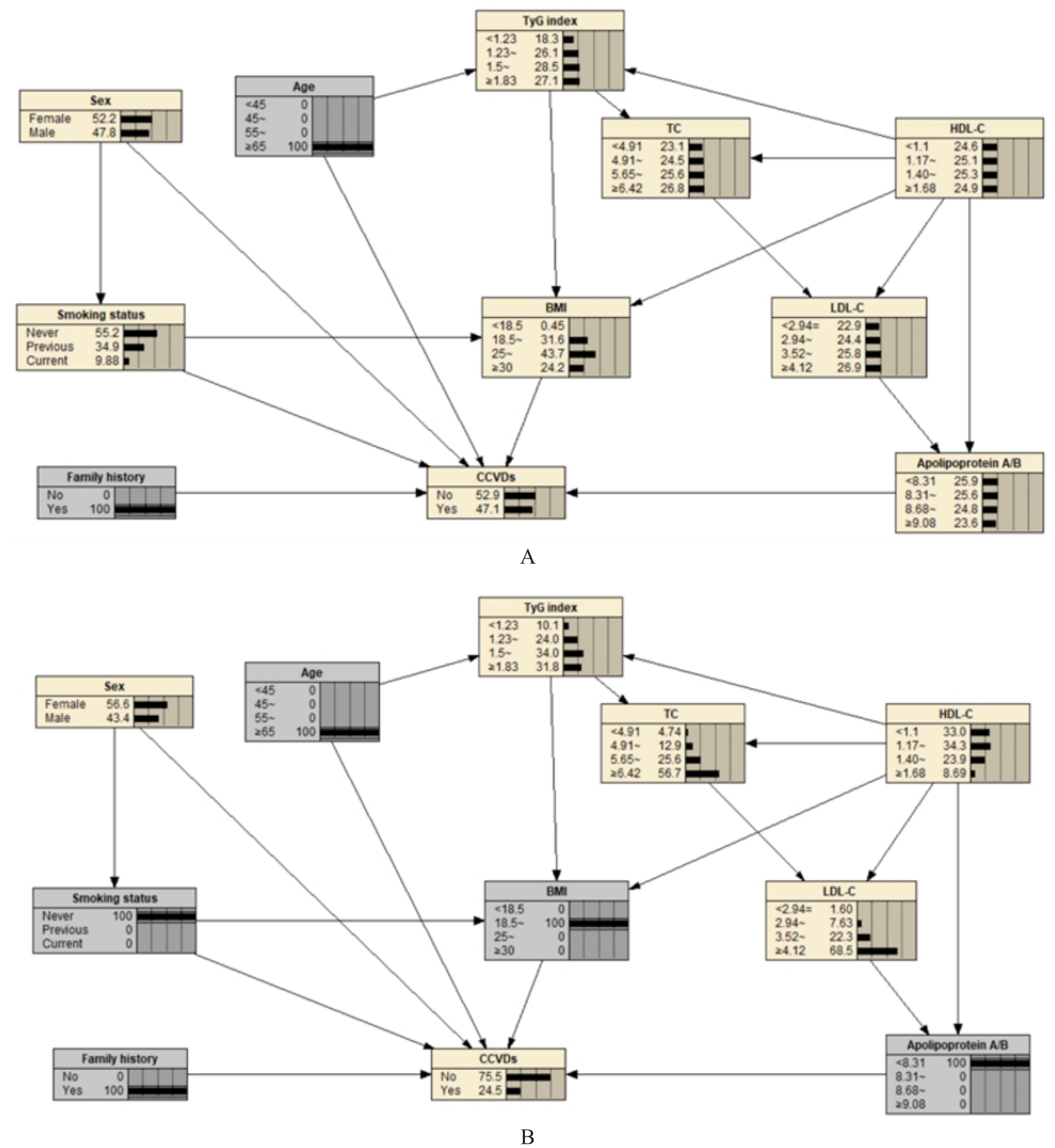
Tab.1
Main variables related to occurrence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and their assignments"
| Variable | Assign | Variable | Assign |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (x1, year) | <45=0 | TC (x11, mmol·L-1) | <4.91=0 |
| 45-54=1 | 4.91-5.64=1 | ||
| 55-64=2 | 5.65-6.41=2 | ||
| ≥65=3 | ≥6.42=3 | ||
| Gender (x2) | Female=0 | LDL-C (x12, mmol·L-1) | <2.94=0 |
| Male=1 | 2.94-3.51=1 | ||
| Smoking status (x3) | Never=0 | 3.52-4.11=2 | |
| Previous=1 | ≥4.12=3 | ||
| Current=2 | HDL-C (x13, mmol·L-1) | <1.17=0 | |
| Drinking status (x4) | Never=0 | 1.17-1.39=1 | |
| Previous=1 | 1.40-1.67=1 | ||
| Current =2 | ≥1.68=3 | ||
| Family history (x5) | No=0 | BMI (x14, kg·m-2) | <18.5 = 0 |
| Yes=1 | 18.5-24.9=1 | ||
| Mental illness (x6) | No=0 | 25.0-29.9=2 | |
| Yes=1 | ≥30.0=3 | ||
| Physical activity (x7) | Low=0 | Apolipoprotein A/B ratio (x15) | <8.31=0 |
| Moderate=1 | 8.31-8.67=1 | ||
| High=2 | 8.68-9.07=2 | ||
| Vegetables/Fruits (x8,≥5 d-1) | No=0 | ≥9.08=3 | |
| Yes=1 | TyG index(x16) | <1.23=0 | |
| Red meat (x9, ≥2/week) | No=0 | 1.23-1.49=1 | |
| Yes=1 | 1.50-1.82=2 | ||
| Oily fish (x10, ≥1/week) | No=0 | ≥1.83=3 | |
| Yes=1 | CCVDs | No=0 | |
| Yes=1 |
Tab. 2
Clinical data of subjects in non-cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases group and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases group [N=315 896,n(η/%)]"
| Variable | Non-cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases | Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(year) | 17 796.741 | <0.01 | ||
| <45 | 29 941(9.48) | 3 762(1.19) | ||
| 45-54 | 74 686(23.64) | 17 591(5.57) | ||
| 55-64 | 89 276(28.26) | 43 955(13.91) | ||
| ≥65 | 31 175(9.87) | 25 510(8.08) | ||
| Gender | 3 301.340 | <0.01 | ||
| Female | 124 833(39.52) | 40 123(12.70) | ||
| Male | 100 245(31.73) | 50 695(16.05) | ||
| Smoking status | 2 065.759 | <0.01 | ||
| Never | 129 253(40.92) | 45 183(14.30) | ||
| Previous | 73 069(23.13) | 37 184(11.77) | ||
| Drinking status | 393.526 | <0.01 | ||
| Never | 8 159(2.58) | 3 949(1.25) | ||
| Previous | 6 746(2.14) | 3 813(1.21) | ||
| Current | 210 173(66.53) | 83 056(26.29) | ||
| Family history | 4 275.264 | <0.01 | ||
| Yes | 159 655(50.54) | 74 638(23.63) | ||
| No | 65 423(20.71) | 16 180(5.12) | ||
| Mental illness | 532.280 | <0.01 | ||
| Yes | 72 230(22.87) | 33 027(10.46) | ||
| No | 152 848(48.39) | 57 791(18.29) | ||
| Physical activity | 668.927 | <0.01 | ||
| Low | 39 911(12.63) | 19 262(6.10) | ||
| Moderate | 91 891(29.09) | 37 489(11.87) | ||
| High | 93 276(29.53) | 34 067(10.78) | ||
| Vegetables/Fruits(≥5 d-1) | 1.471 | 0.225 | ||
| Yes | 182 024(57.62) | 73 616(23.30) | ||
| No | 43 054(13.63) | 17 202(5.45) | ||
| Red meat (≥2/week) | 593.884 | <0.01 | ||
| Yes | 72 763(23.03) | 33 470(10.60) | ||
| No | 152 315(48.22) | 57 348(18.15) | ||
| Oily fish (≥1/week) | 558.101 | <0.01 | ||
| Yes | 124 776(39.50) | 54 525(17.26) | ||
| No | 100 302(31.75) | 36 293(11.49) | ||
| TC (mmol·L-1) | 11 031.944 | <0.01 | ||
| <4.91 | 44 548(14.10) | 33 847(10.71) | ||
| 4.91-5.64 | 58 769(18.60) | 21 358(6.76) | ||
| 5.65-6.41 | 61 435(19.45) | 18 473(5.85) | ||
| ≥6.42 | 60 326(19.10) | 17 140(5.43) | ||
| LDL-C (mmol·L-1) | 9 949.487 | <0.01 | ||
| <2.94 | 44 785(14.18) | 33 120(10.48) | ||
| 2.94-3.51 | 58 282(18.45) | 21 295(6.74) | ||
| 3.52-4.11 | 61 140(19.35) | 18 714(5.92) | ||
| ≥4.12 | 60 871(19.27) | 17 689(5.60) | ||
| HDL-C (mmol·L-1) | 7 270.807 | <0.01 | ||
| <1.17 | 47 390(15.00) | 30 458(9.64) | ||
| 1.17-1.39 | 55 303(17.51) | 24 100(7.63) | ||
| 1.40-1.67 | 59 873(18.95) | 20 047(6.35) | ||
| ≥1.68 | 62 512(19.79) | 16 213(5.13) | ||
| BMI (kg·m-2) | 17 839.780 | <0.01 | ||
| <18.5 | 1 350(0.43) | 203(0.06) | ||
| 18.5-24.9 | 87 643(27.74) | 17 399(5.51) | ||
| 25.0-29.9 | 95 984(30.38) | 39 796(12.60) | ||
| ≥30.0 | 40 101(12.69) | 33 420(10.58) | ||
| Apolipoprotein A/B ratio | 512.794 | <0.01 | ||
| <8.31 | 57 986(18.36) | 20 441(6.47) | ||
| 8.31-8.67 | 56 199(17.79) | 22 458(7.11) | ||
| 8.68-9.07 | 56 193(17.79) | 23 142(7.33) | ||
| ≥9.08 | 54 700(17.32) | 24 777(7.84) | ||
| TyG index | 8 133.568 | <0.01 | ||
| <1.23 | 65 110(20.61) | 15 186(4.81) | ||
| 1.23-1.49 | 58 735(18.59) | 20 715(6.56) | ||
| 1.50-1.82 | 54 162(17.15) | 25 197(7.98) | ||
| ≥1.83 | 47 071(14.90) | 29 720(9.41) |
Tab.3
Conditional probability table of independent parent node of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases"
| Variable | Risk | Variable | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age(year) | Gender | ||
| <45 | 12.5 | Female | 25.0 |
| 45-54 | 19.9 | Male | 33.1 |
| 55-64 | 33.0 | BMI (kg·m-2) | |
| ≥65 | 43.4 | <18.5 | 22.6 |
| Family history | 18.5-24.9 | 18.0 | |
| Yes | 31.9 | 25.0-29.9 | 28.7 |
| No | 20.2 | ≥30.0 | 44.7 |
| Smoking status | Apolipoprotein A/B | ||
| Never | 27.1 | <8.31 | 26.7 |
| Previous | 31.3 | 8.31-8.67 | 28.3 |
| Current | 29.9 | 8.68-9.07 | 28.6 |
| ≥9.08 | 31.6 |
| 1 | REN Q Q, LI S Y, XIAO C L, et al. The impact of air pollution on hospitalization for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in Shenyang, China[J]. Iran J Public Health, 2020, 49(8): 1476-1484. |
| 2 | YOU Q, SHAO X Y, WANG J P, et al. Progress on physical field-regulated micro/nanomotors for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease treatment[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(10): e2300426. |
| 3 | BENJAMIN E J, MUNTNER P, ALONSO A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(10): e56-e528. |
| 4 | MENSAH G A, ROTH G A, FUSTER V. The global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors: 2020 and beyond[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 74(20): 2529-2532. |
| 5 | DISEASES AND INJURIES COLLABORATORSGBD. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10258): 1204-1222. |
| 6 | MELA A, RDZANEK E, PONIATOWSKI Ł A, et al. Economic costs of cardiovascular diseases in Poland estimates for 2015-2017 years[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 1231. |
| 7 | QIAO W J, ZHANG X Y, KAN B, et al. Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases[J]. Open Med, 2021, 16(1): 149-155. |
| 8 | STROKE COLLABORATORSGBD. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2021, 20(10): 795-820. |
| 9 | BOYD C, BROWN G, KLEINIG T, et al. Machine learning quantitation of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease: a systematic review of clinical applications[J]. Diagnostics, 2021, 11(3): 551. |
| 10 | CHEUNG C Y, XU D J, CHENG C Y, et al. A deep-learning system for the assessment of cardiovascular disease risk via the measurement of retinal-vessel calibre[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2021, 5(6): 498-508. |
| 11 | AZMI J, ARIF M, NAFIS M T, et al. A systematic review on machine learning approaches for cardiovascular disease prediction using medical big data[J]. Med Eng Phys, 2022, 105: 103825. |
| 12 | KELSHIKER M A, SELIGMAN H, HOWARD J P, et al. Coronary flow reserve and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Heart J, 2022, 43(16): 1582-1593. |
| 13 | ZHENG P F, CHEN L Z, LIU P, et al. Identification of immune-related key genes in the peripheral blood of ischaemic stroke patients using a weighted gene coexpression network analysis and machine learning[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 361. |
| 14 | BIEDERMANN A, TARONI F. Bayesian networks and probabilistic reasoning about scientific evidence when there is a lack of data[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2006, 157(2/3): 163-167. |
| 15 | BYCROFT C, FREEMAN C, PETKOVA D, et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data[J]. Nature, 2018, 562(7726): 203-209. |
| 16 | 黄夏璇, 黄 韬, 杨 瑞, 等. UK Biobank数据的应用介绍[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2022, 22(9): 1099-1107. |
| 17 | UCHAI S, ANDERSEN L F, THORESEN M, et al. Does the association between adiposity measures and prefrailty among older adults vary by social position?Findings from the Tromsø study 2015/2016[J]. BMC Public Health, 2024, 24(1): 1457. |
| 18 | MACH F, BAIGENT C, CATAPANO A L, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk[J]. Eur Heart J, 2020, 41(1): 111-188. |
| 19 | PIZZI N J. Fuzzy quartile encoding as a preprocessing method for biomedical pattern classification[J]. Theor Comput Sci, 2011, 412(42): 5909-5925. |
| 20 | JAYAWARDENA R, SOORIYAARACHCHI P. The inside story of fruits; exploring the truth behind conventional theories[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2021, 15(6): 102085. |
| 21 | CHUDASAMA Y V, KHUNTI K K, ZACCARDI F, et al. Physical activity, multimorbidity, and life expectancy: a UK Biobank longitudinal study[J]. BMC Med, 2019, 17(1): 108. |
| 22 | 苗丰顺, 李 岩, 高 岑, 等. 基于CatBoost算法的糖尿病预测方法[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2019, 28(9): 215-218. |
| 23 | HANCOCK J T, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M. CatBoost for big data: an interdisciplinary review[J]. J Big Data, 2020, 7(1): 94. |
| 24 | 胡建锦, 熊 伟, 方陆明, 等. 基于距离相关系数和Catboost方法的森林蓄积量估测[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 27-35. |
| 25 | PRABU S, THIYANESWARAN B, SUJATHA M, et al. Grid search for predicting coronary heart disease by tuning hyper-parameters[J]. Comput Syst Sci Eng, 2022, 43(2): 737-749. |
| 26 | ROUSSON V, ZUMBRUNN T. Decision curve analysis revisited: overall net benefit, relationships to ROC curve analysis, and application to case-control studies[J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2011, 11: 45. |
| 27 | 唐 末. 基于循证医学及机器学习的中医药影响早中期结直肠癌预后模型研究[D]. 北京: 中国中医科学院, 2022. |
| 28 | 钟 璐, 薛付忠. 基于贝叶斯网络不确定性推理的肺癌风险预测模型[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2023, 61(4): 86-94. |
| 29 | 王旭春, 宋伟梅, 潘金花, 等. MMPC-Tabu 混合算法的贝叶斯网络模型在高脂血症相关因素研究中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2022, 39(3): 345-350, 355. |
| [1] | Xiaoyu WANG,Bing LI,Guohui LIU. Research progress in application of inflammatory markers in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1173-1181. |
| [2] | Li ZHANG,Binfeng XIA,Huihui HUANG,Ru WANG,Min KONG,Xia YIN. Research progress in pathophysiological mechanism and clinical diagnosis and treatment of hypertension associated with vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor inhibitors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 854-863. |
| [3] | Xing LIU,Jiali LIU,Liangui NIE,Maojun LIU,Junxiong ZHAO,Liuyang WANG,Jun YANG. Improvement effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial ischemic injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1125-1133. |
| [4] | . Research progress in gastrointestinal bleeding casued by hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1394-1399. |
| [5] | Mingfei JU,Chao LIU,Zhigang MA,Juan ZHAO,Tu WANG,Zhihao WANG. Predictive value of residual cholesterol in occurrence of patients with acute coronary syndrome [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 765-769. |
| [6] | Chang LI,Zishan MA,Shanmei HUANG,Bangqiao YIN,Zhifan CHEN,Sha NIE,Ziqian ZHANG,Li LI,Ying LIU,Yaoping TANG. Protective effect of Yiyi Fuzisan on myocardium ischemia and vascular endothelial function injury in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 580-589. |
| [7] | . Research progress in mechanism and treatment strategy of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy patients complicated with mitral insufficiency [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 802-810. |
| [8] | Haitao LI, Qin LI, Fei CAI, Guofu HU, Yunfei TENG. Effect of apigenin on polarization and inflammation of mouse RAW264.7 macrophages and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 549-556. |
| [9] | Yintao ZHAO, Yingying YANG, Xiangqin ZHANG, Lu ZHENG, Yawei XU, Haibo YANG, Yuan LIU. Improvement effect of follistatin-like 1 on doxorubicin-induced acute myocardial injury in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 565-572. |
| [10] | Zhouxin REN,Haibin YU,Xiaofeng MEI,Haoran DONG,Junling SHEN,Jiansheng LI. Improvement effect of Bufei Yishen prescription Ⅲ on experimental pulmonary hepertension of rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 280-288. |
| [11] | Shuhua YU,Wei LIU,Qianqian WU,Dongwei YANG. Effect of crocetin on vascular endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats and its ROCK/JNK signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1481-1489. |
| [12] | Jilin FAN,Tingting ZHU,Xiaoling TIAN,Sijia LIU,Jing SU,Shiliang ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network construction and immune cell infiltration in atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1535-1545. |
| [13] | Yue WANG,Meili LU,Hongxin WANG. Protective effect of astragaloside Ⅳ on hypoxia-induced vascular injury and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1101-1108. |
| [14] | Yifan ZHANG,Jie DING,Min DU,Xiaoteng FENG,Ping LIU. Effects of salvianolic acid B on atherosclerosis and efferocytosis of macrophages of mice and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 561-567. |
| [15] | Yinong LIU,Qiang ZHANG,Li XU. Improvement effect of atorvastatin on vascular endothelial dysfunction induced by Ox-LDL/β2GPⅠ/anti-β2GPⅠ complex and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 317-323. |
|