Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1481-1489.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220614
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of crocetin on vascular endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats and its ROCK/JNK signaling pathway mechanism
Shuhua YU1( ),Wei LIU1,Qianqian WU1,Dongwei YANG2
),Wei LIU1,Qianqian WU1,Dongwei YANG2
- 1.Department of Hypertension,Zhengzhou Central Hospital,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450000,China
2.Department of Cardiovascular Medicine,Zhengzhou Central Hospital,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450000,China
-
Received:2022-01-27Online:2022-11-28Published:2022-12-07 -
Contact:Shuhua YU E-mail:zk1jfz@163.com
CLC Number:
- R544.1
Cite this article
Shuhua YU,Wei LIU,Qianqian WU,Dongwei YANG. Effect of crocetin on vascular endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats and its ROCK/JNK signaling pathway mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1481-1489.
share this article
Tab.1
Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure of rats in various groups (n=10,x±s,P/mmHg)"
| Group | Systolic blood pressure | Diastolic blood pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 113.35±4.26 | 72.27±4.25 |
| Model | 187.68±12.03* | 116.91±5.27* |
CR Low dose | 168.76±10.03△ | 108.17±4.63△ |
| Medium dose | 137.93±8.11△# | 97.25±5.91△# |
| High dose | 124.22±6.74△#○ | 82.78±4.02△#○ |
Tab.2
Blood lipid levels and AI of rats in various groups"
| Group | TC[cB/(mmol·L-1)] | TG[cB/(mmol·L-1)] | LDL-c[cB/(mmol·L-1)] | HDL-c[cB/(mmol·L-1)] | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1.08±0.11 | 0.62±0.06 | 0.76±0.05 | 0.94±0.08 | 0.13±0.03 |
| Model | 2.25±0.16* | 1.48±0.09* | 2.33±0.15* | 0.44±0.05* | 4.08±0.57* |
CR Low dose | 2.07±0.12△ | 1.36±0.06△ | 2.18±0.08△ | 0.52±0.03△ | 2.87±0.39△ |
| Medium dose | 1.78±0.10△# | 1.14±0.06△# | 1.77±0.09△# | 0.68±0.04△# | 1.59±0.18△# |
| High dose | 1.42±0.09△#○ | 0.85±0.06△#○ | 1.32±0.10△#○ | 0.87±0.04△#○ | 0.62±0.09△#○ |
Tab.3
Serum activities of GSH-Px and levels of MDA, NO, ET-1,and TXB2 of rats in various groups"
| Group | MDA[cB/(nmol·L-1)] | GSH-Px[cB/(μmol·L-1)] | NO[cB/(μmol·L-1)] | ET-1 [ρB/(ng·L-1)] | TXB2[ρB/(ng·L-1)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8.12±0.21 | 109.52±9.68 | 22.10±2.18 | 65.85±4.31 | 32.61±3.10 |
| Model | 15.27±1.08* | 58.24±3.68* | 13.58±0.72* | 114.78±5.95* | 58.99±4.60* |
CR Low dose | 14.12±0.62△ | 65.09±4.03△ | 14.54±1.10△ | 103.70±5.64△ | 53.33±3.77△ |
| Medium dose | 11.86±0.84△# | 78.39±6.20△# | 16.66±1.14△# | 87.86±6.96△# | 46.06±3.69△# |
| High dose | 9.52±0.81△#○ | 98.67±7.51△#○ | 19.96±0.94△#○ | 72.46±4.69△#○ | 35.86±3.24△#○ |
Tab.4
Expression levels of ROCK1, ROCK2,and JNK mRNA in aorta tissue of rats in various groups"
| Group | ROCK1 | ROCK2 | JNK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1.00±0.01 | 1.01±0.01 | 1.02±0.01 |
| Model | 5.87±0.54* | 4.88±0.59* | 4.72±0.54* |
CR Low dose | 5.26±0.32# | 3.95±0.24# | 4.11±0.26# |
| Medium dose | 3.94±0.47△# | 2.89±0.21△# | 2.77±0.15△# |
| High dose | 1.96±0.18△#○ | 1.71±0.34△#○ | 1.62±0.26△#○ |
Tab.5
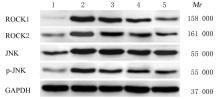
Expressions levels of ROCK1, ROCK2, JNK,and p-JNK proteins in aorta tissue of rats in various groups"
| Group | ROCK1 | ROCK2 | JNK | p-JNK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 0.09±0.02 | 0.18±0.03 | 0.38±0.03 | 0.16±0.02 |
| Model | 0.64±0.05* | 0.65±0.05* | 0.92±0.04* | 0.53±0.05* |
CR Low dose | 0.54±0.05# | 0.57±0.03# | 0.86±0.04# | 0.42±0.05# |
| Medium dose | 0.38±0.05△# | 0.41±0.02△# | 0.79±0.04△# | 0.37±0.03△# |
| High dose | 0.19±0.03△#○ | 0.24±0.04△#○ | 0.58±0.04△#○ | 0.31±0.03△#○ |
| 1 | XU S W, ILYAS I, LITTLE P J, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and beyond: from mechanism to pharmacotherapies[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2021, 73(3): 924-967. |
| 2 | MILLS K T, BUNDY J D, KELLY T N, et al. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control: a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries[J]. Circulation, 2016, 134(6): 441-450. |
| 3 | YU Q, ZHAO J, LIU B T. Bazedoxifene activates the angiotensin II-induced HUVEC hypertension model by targeting SIRT1[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2022, 23(2): 120. |
| 4 | ROSS R. Atherosclerosis: an inflammatory disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 1999, 340(2): 115-126. |
| 5 | HURTUBISE J, MCLELLAN K, DURR K, et al. The different facets of dyslipidemia and hypertension in atherosclerosis[J].Curr Atheroscler Rep,2016,18(12): 82. |
| 6 | KOCAMAN G, ALTINOZ E, ERDEMLI M E, et al. Crocin attenuates oxidative and inflammatory stress-related periodontitis in cardiac tissues in rats[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2021, 30(5): 517-524. |
| 7 | IMENSHAHIDI M, RAZAVI B M, FAAL A, et al. Effects of chronic crocin treatment on desoxycorticosterone acetate (doca)-salt hypertensive rats[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2014, 17(1): 9-13. |
| 8 | LUO Z H, DENG H J, FANG Z C, et al. Ligustilide inhibited rat vascular smooth muscle cells migration via c-myc/MMP2 and ROCK/JNK signaling pathway[J]. J Food Sci, 2019, 84(12): 3573-3583. |
| 9 | NIAZI Z R, SILVA G C, RIBEIRO T P, et al. EPA: DHA 6: 1 prevents angiotensin II-induced hypertension and endothelial dysfunction in rats: role of NADPH oxidase- and COX-derived oxidative stress[J]. Hypertens Res, 2017, 40(12): 966-975. |
| 10 | WU N, ZHENG F, LI N, et al. RND3 attenuates oxidative stress and vascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rat via inhibiting ROCK1 signaling[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 48: 102204. |
| 11 | METCHI DONFACK M F, ATSAMO A D, TEMDIÉ GUEMMOGNE R J, et al. Antihypertensive effects of the Vitex cienkowskii (Verbenaceae) stem-bark extract on L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 6668919. |
| 12 | GAO J, WANG T S, WANG C, et al. Effects of Tianshu capsule on spontaneously hypertensive rats as revealed by 1H-NMR-based metabolic profiling[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 989. |
| 13 | YARIBEYGI H, MALEKI M, MOHAMMADI M T, et al. Crocin improves diabetes-induced oxidative stress via downregulating the nox-4 in myocardium of diabetic rats[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2021, 1328: 275-285. |
| 14 | SHENG Y L, GONG X W, ZHAO J, et al. Effects of crocin on CCL2/CCR2 inflammatory pathway in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rats[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2022, 50(1): 241-259. |
| 15 | CHEN X, HUANG J Y, LV Y C, et al. Crocin exhibits an antihypertensive effect in a rat model of gestational hypertension and activates the Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J].Hypertens Res, 2021,44(6): 642-650. |
| 16 | XIAO Y, FU X W, PATTENGALE P, et al. A sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of urinary 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α (8-iso-PGF2α) including pediatric reference interval[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2016, 460: 128-134. |
| 17 | VONGPATANASIN W, PERI-OKONNY P, VELASCO A, et al. Effects of potassium magnesium citrate supplementation on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure and oxidative stress marker in prehypertensive and hypertensive subjects[J].Am J Cardiol,2016,118(6): 849-853. |
| 18 | PARK K H, PARK W J. Endothelial dysfunction: clinical implications in cardiovascular disease and therapeutic approaches[J].J Korean Med Sci, 2015, 30(9): 1213-1225. |
| 19 | LI Q, YOUN J Y, CAI H. Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction in hypertension[J].J Hypertens,2015,33(6): 1128-1136. |
| 20 | CHEN L Z, WU J, XU H S, et al. Effects of tanshinone combined with valsartan on hypertensive nephropathy and its influence on renal function and vascular endothelial function[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(5): 4788-4795. |
| 21 | RAZAVI B M, ALYASIN A, HOSSEINZADEH H, et al. Saffron induced relaxation in isolated rat aorta via endothelium dependent and independent mechanisms[J]. Iran J Pharm Res, 2018, 17(3): 1018-1025. |
| 22 | GENG P B, XU X H, GAO Z. Sinomenine suppress the vitamin D3 and high fat induced atherosclerosis in rats via suppress of oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. J Oleo Sci, 2021, 70(12): 1815-1828. |
| 23 | BADIMON L, VILAHUR G. Thrombosis formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture[J]. J Intern Med, 2014, 276(6): 618-632. |
| 24 | ZHAN B M, HUANG X, WANG J C, et al. Association between lipid profiles and arterial stiffness in Chinese patients with hypertension: insights from the CSPPT[J]. Angiology, 2019, 70(6): 515-522. |
| 25 | 闫 莹, 杨 朝, 汪 涛. 活性氧与 RhoA/ROCK 信号通路对血管平滑肌细胞钙浓度及钙敏感性的影响[J]. 国际呼吸杂志, 2015(12): 954-957. |
| 26 | TANG L, DAI F, LIU Y, et al. RhoA/ROCK signaling regulates smooth muscle phenotypic modulation and vascular remodeling via the JNK pathway and vimentin cytoskeleton[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2018, 133: 201-212. |
| 27 | CHENG C I, CHEN P H, LIN Y C, et al. High glucose activates Raw264.7 macrophages through RhoA kinase-mediated signaling pathway[J]. Cell Signal, 2015, 27(2): 283-292. |
| [1] | Junxiu LIU,Jia ZHOU,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Xuefeng ZHUANG,Jiarui ZHAO,Xiaowei HUANG,Ruili LI. Protective effect of Shenhong Buxue Granule on vascular endothelium of mice with vascular endothelial dysfunction of Qi stagnation and blood stasis type and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1437-1447. |
| [2] | Yifan ZHANG,Jie DING,Min DU,Xiaoteng FENG,Ping LIU. Effects of salvianolic acid B on atherosclerosis and efferocytosis of macrophages of mice and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 561-567. |
| [3] | WANG Tu, SUN Xiaoxu, CHEN Long, CUI Haipeng, LIU Kai, XIE Yaqin, LI Ying, ZHAO Juan. Effect of Urantide on expression of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in thoracic aorta tissue of rats with atherosclerosis and its significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 813-818. |
| [4] | ZHOU Licheng, LIU Xianfa, LI Qiang, LI Rong, HUANG Jiagan, ZHANG Qiong, LI Xiaofei. Anti-atherosclerosis effect of berberine combined with simvastatin in atherosclerosis model rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 849-854. |
| [5] | SUN Xiaoxu, WANG Tu, CUI Haipeng, LIU Kai, GAO Haicheng, ZHAO Juan. Effects of urantide on serum calcium, blood lipids and indexes of myocardial enzymes in rats with atherosclerosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 331-335. |
| [6] | BI Hongdong, XIE Yaqin, CUI Haipeng, LIU Kai, SUN Xiaoxu, WANG Tu, ZHAO Juan. Effects of urantide on expressions of type Ⅳcollagenin thoracic aorta and VSMC of atherosclerotic rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 342-346. |
| [7] | LIU Xiaojie, MEI Tao, MA Hongyan, YE Shandong. Analysis of influencing factors of carotid atherosclerosis plaque formation and stability in simple type 2 diabetic patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 350-355. |
| [8] | XU Jiguang, LI Yuning. Therapeutic effect of folic acid combined with vitamin B12 on atherosclerosis induced by hyperhomocysteinemia in rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 943-947. |
| [9] | LYU Wenxuan, FAN Sijia, LI Wenyao, YU Jingwen, CHEN Lijuan, DENG Yue. Influence of Shenhong Tongluo Granules in apoptosis in atherosclerosis plaques of ApoE-/- mice and its mechanisms of anti-atherosclerosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 882-886. |
| [10] | MAI Li, WEI Jianrui, HUA Xing. Construction of IRF5 gene lentiviral vector and its expression in macrophages RAW264.7 [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(03): 452-456. |
| [11] | LYU Wenxuan, LI Wenyao, FAN Sijia, ZHAO Shu, GUO Wuhu, CHEN Lijuan, DENG Yue. Therapeutic effect of rosuvastatin on atherosclerosis of apolipoprotein E(ApoE)-knockout mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(02): 240-244. |
| [12] | SUN Lijuan, LIU Ting, XU Xiumei, LI Jie. Evaluation on effect of rosuvastatin in treatment of lower extremity atherosclerotic disease in elderly [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(06): 1260-1263. |
| [13] | SHI Meirong, JIANG Wei, WANG Zhiyuan, SHI Weidong, SUN Ruoxue, CHEN Enqi, LIU Meihan. Ultrasonic examination of carotid artery and peripheral artery atherosclerosis and their risk factors [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(05): 1055-1059. |
| [14] | . Influence of atorvastatin in Bcl-2 methylation in cultured human umbilical endothelial cells treated with homocysteineand its mechanism of anti-arteriosclerosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(05): 1002-1006. |
| [15] | HAO Tie-zhu,SHEN Huan,TAO Zhi-kan,WANG Wei,ZHAO Dan-dan. Influence of lovastatin in expressions of MCP-1 and IL-10 of HUVECs treated with TNF-α [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(5): 928-932. |
|