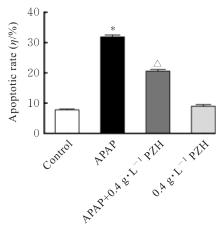
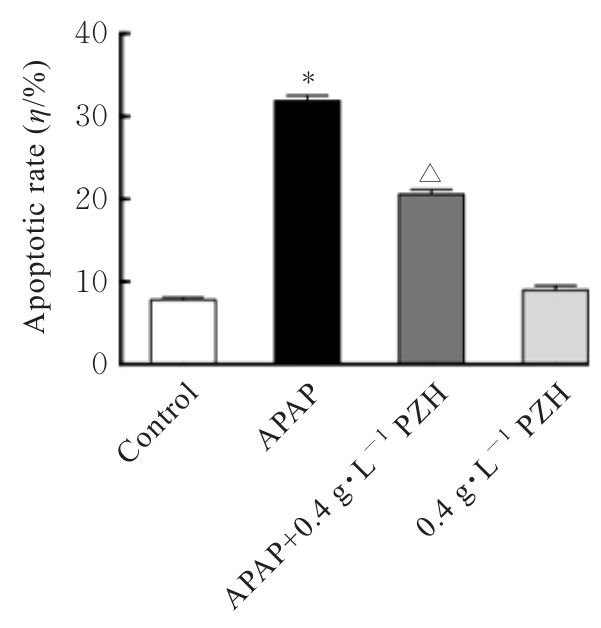
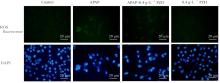
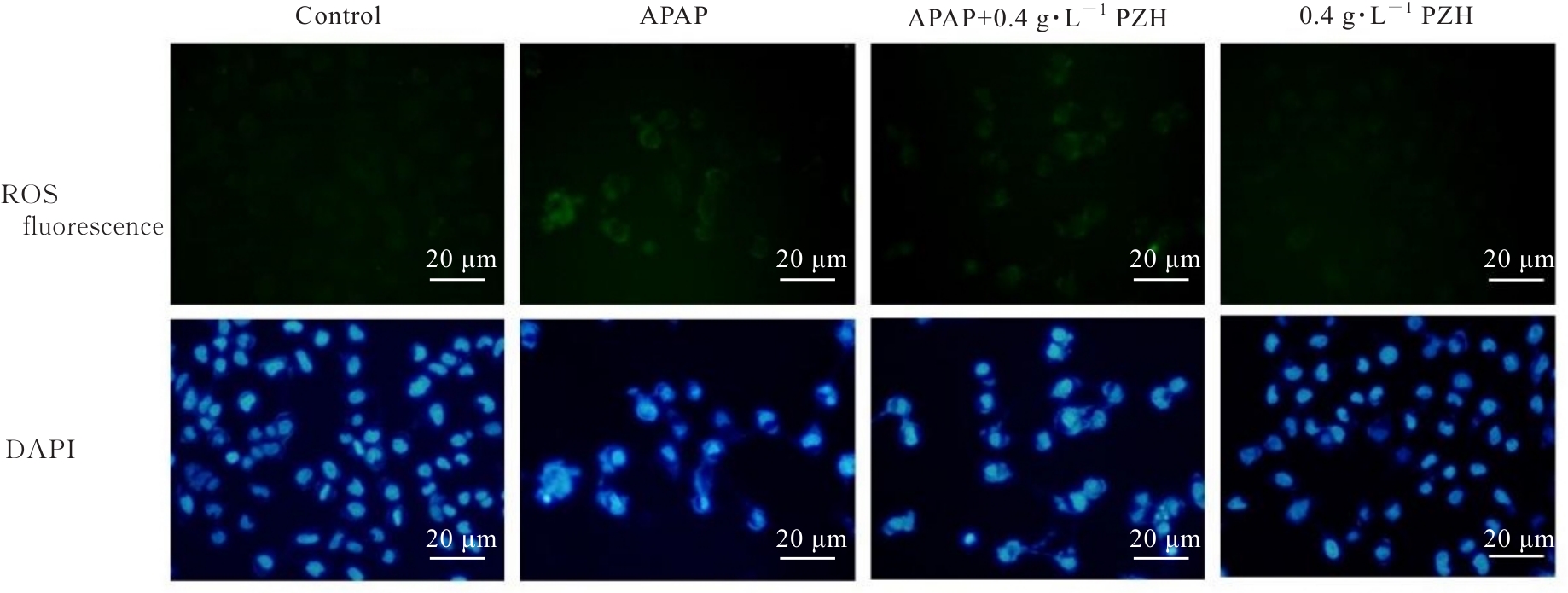
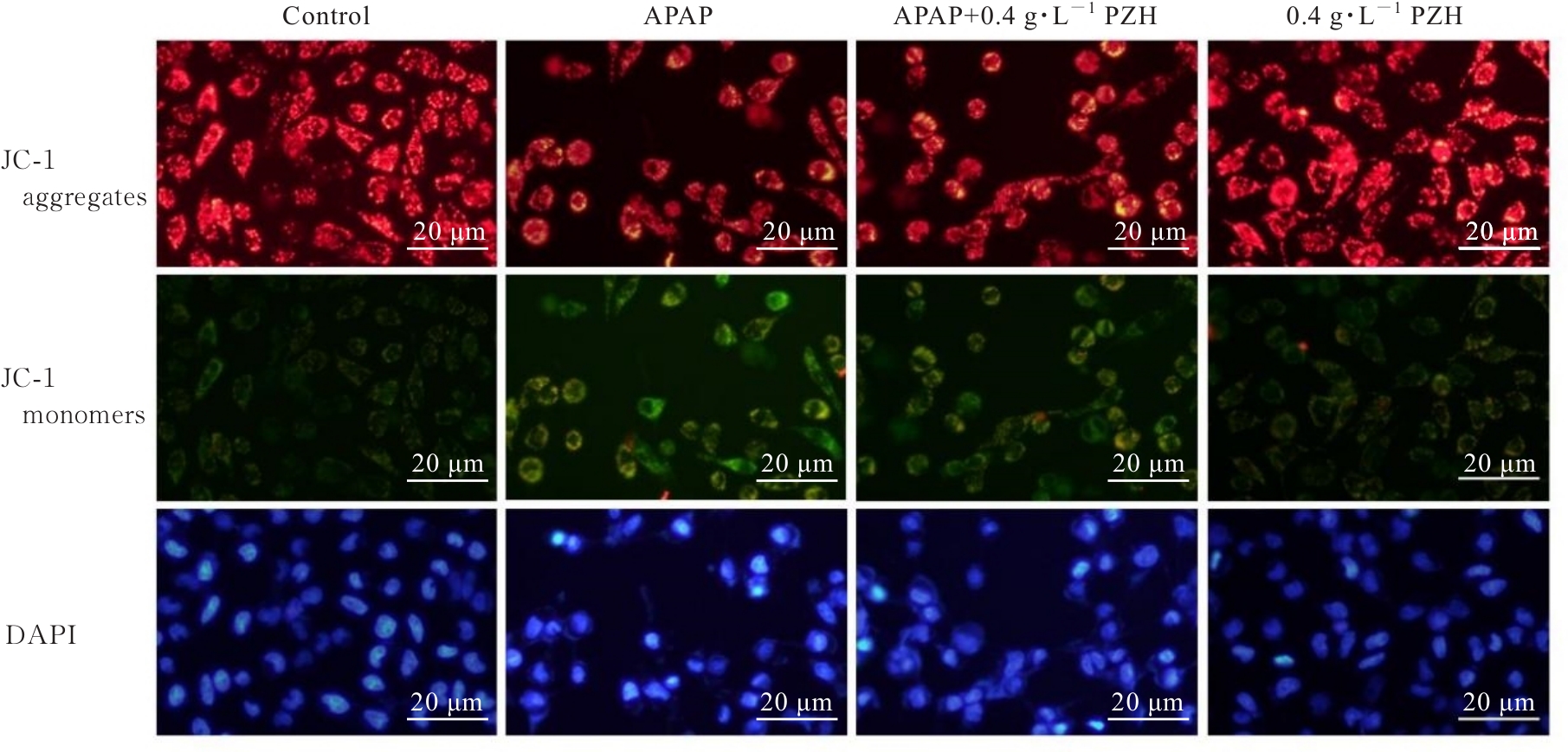
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 105-114.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250113
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism
Chaohe ZHANG1,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Hematology,Second Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130031,China
2.Department of Pharmacy,Lequn Branch,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Online:2025-01-28Published:2025-03-06 -
Contact:Xiangfeng WANG E-mail:xiangfeng1012@163.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Chaohe ZHANG,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG. Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 105-114.
share this article
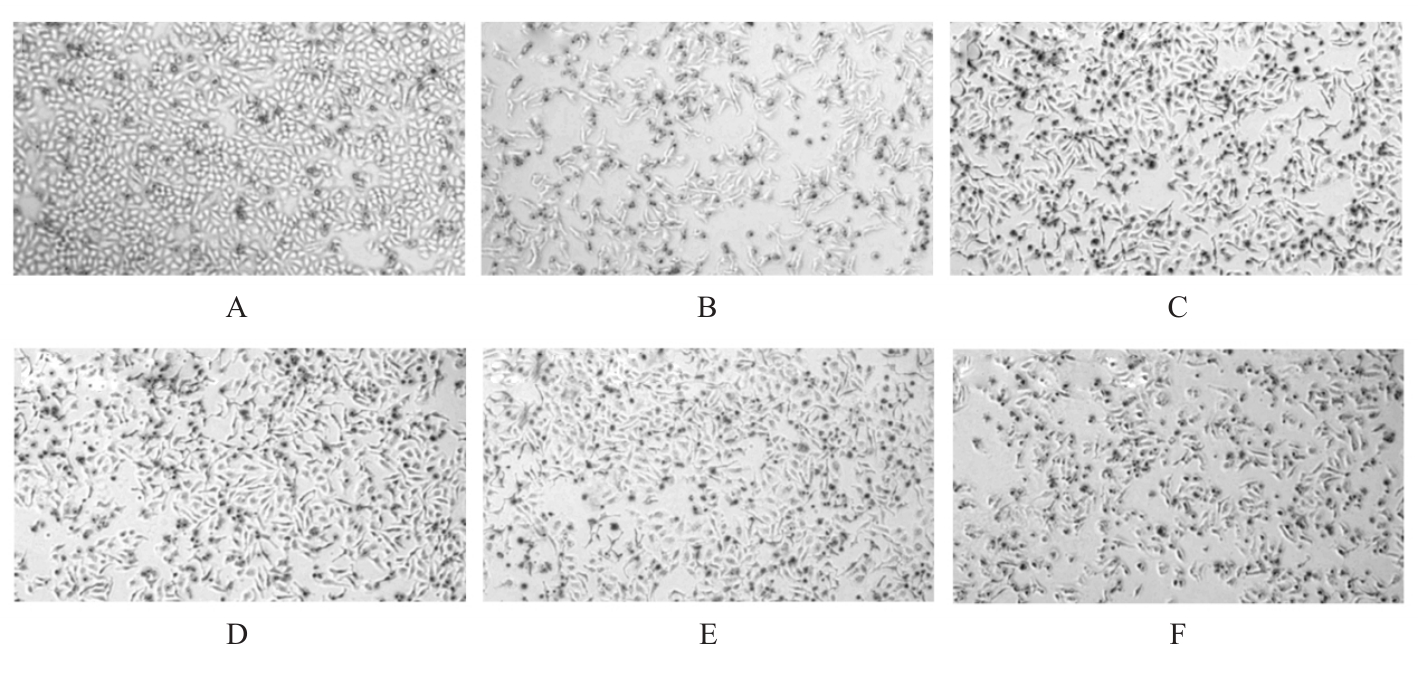
Tab.3
Survival rates of cells in various groups after treated with different doses of PZH with 10 mmol·L-1APAP"
| Group | A value(x±s) | Survival rate(η/%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.000±0.077 | 100.00 |
| APAP | 0.710±0.032* | 71.16* |
| APAP+0.1 g·L-1 PZH | 0.770±0.037 | 76.75 |
| APAP+0.2 g·L-1 PZH | 0.820±0.044△ | 81.70△ |
| APAP+0.4 g·L-1 PZH | 0.900±0.021△ | 90.30△ |
| APAP+0.8 g·L-1 PZH | 0.400±0.026△ | 40.00△ |
Tab.4
Change degrees of levels of MDA and activities of LDH and SOD in supernatants of cells in various groups"
| Group | MDA | LDH | SOD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.000±0.012 | 1.000±0.043 | 1.000±0.033 |
| APAP | 1.920±0.180* | 1.840±0.090* | 0.740±0.035* |
| APAP+0.4 g·L-1 PZH | 1.400±0.033△ | 1.290±0.071△ | 1.000±0.110△ |
| 0.4 g·L-1 PZH | 1.420±0.017 | 0.380±0.120 | 0.900±0.013 |
| 1 | 中国医药生物技术协会药物性肝损伤防治技术专业委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会药物性肝病学组. 中国药物性肝损伤诊治指南(2023年版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志,2023, 31(4): 355-384. |
| 2 | 彭小蓉, 常宇南, 秦涛, 等. 儿童药物性肝损伤临床诊治进展[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2023, 31(4): 440-444. |
| 3 | TUJIOS S R, LEE W M. Acute liver failure induced by idiosyncratic reaction to drugs: Challenges in diagnosis and therapy[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38(1): 6-14. |
| 4 | LI X, TANG J, MAO Y. Incidence and risk factors of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Liver Int, 2022, 42(9):1999-2014. |
| 5 | 沈弢, 黄昕, 王誉雅, 等. 我国药物性肝损伤流行病 学 研 究 现 状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(6):1152-1155. |
| 6 | 刘成海. 中草药相关肝损伤的研究进展与挑战[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024,40(8): 1505-1511. |
| 7 | 刘茹佳,辛小娟. 药物性肝损伤发生机制、 危险因素、 监测以及再用药的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023,39(4): 968-973. |
| 8 | 支阳, 唐洁婷, 茅益民. 药物性肝损伤的遗传易感性[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2023, 31(6): 653-658. |
| 9 | 王素媛. DDX60促进对乙酰氨基酚诱导急性肝损伤的功能和机制研究[D]. 上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学, 2021. |
| 10 | 余朋飞, 吴桥, 段钟平, 等. 对乙酰氨基酚致药物性肝损伤的机制研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(9): 2108-2112. |
| 11 | CHEN Z. Pien Tze Huang(PZH)as a multifunction medicinal agent in traditional Chinese medicine(TCM):a review on cellular,molecular and physiological mechanisms[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21(1):146. |
| 12 | LIU C, CHEN Z, WU S LY, et al. Comparative Review of effects of Pien Tze Huang and AnGong NiuHuang Pill and their potential on treatment of central nervous system diseases[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2022, 22(18):2350-2360. |
| 13 | HUANG L, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Therapeutic potential of Pien-Tze-Huang: a review on its chemical composition,pharmacology,and clinical application[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(18): 3274. |
| 14 | 熊祎, 曾鑫, 刘妙华, 等. 片仔癀治疗肝脏疾病的药理作用研究进展[J]. 江西中医药大学学报, 2023, 35(1): 116-118, 124. |
| 15 | 王帆, 朱哿瑞, 刘成海, 等. 对乙酰氨基酚致药物性肝损伤的分子机制[J]. 肝脏, 2021, 26(8): 939-942. |
| 16 | CHANG L, XU D, ZHU J, et al. Herbal therapy for the treatment of acetaminophen-associated liver injury:recent advances and future perspectives[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 313. |
| 17 | BRUNE K, RENNER B, TIEGS G. Acetaminophen/paracetamol:A history of errors, failures and false decisions[J]. Eur J Pain, 2015, 19(7): 953-965. |
| 18 | CHIDIAC A S, BUCKLEY N A, NOGHREHCHI F, et al. Paracetamol(acetaminophen) overdose and hepatotoxicity:mechanism, treatment, prevention measures, and estimates of burden of disease[J]. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2023, 19(5):297-317. |
| 19 | TANG J, GU J, CHU N, et al. Efficacy and safety of bicyclol for treating patients with idiosyncratic acute drug-induced liver injury: A multicenter, randomized,phase Ⅱ trial[J]. Liver Int,2022, 42(8): 1803-1813. |
| 20 | WANG Y, WANG Z, GAO M, et al. Efficacy and safety of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate injection in patients with acute drug-induced liver injury: A phase Ⅱ trial[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(11): 2102-2111. |
| 21 | 许赞术, 谭耀龙, 张庆, 等. 片仔癀对酒精诱导的急性肝损伤小鼠自噬和NLRP3炎症小体活化的影响[J]. 药学研究, 2023, 42(8): 537-542. |
| 22 | ZHAO R, ZHANG Q, LIU W, ET al. Pien Tze Huang attenuated acetaminophen-induced liver injury by autophagy mediated-NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 311: 116285. |
| 23 | ZHENG H, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Pien-Tze-Huang ameliorates hepatic fibrosis via suppressing NF-κB pathway and promoting HSC apoptosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2019, 244: 111856. |
| 24 | 李国平, 吴灵飞, 蒲泽锦. 氧化应激诱导HepG2肝癌细胞凋亡的研究[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2008, 24(1):105-111. |
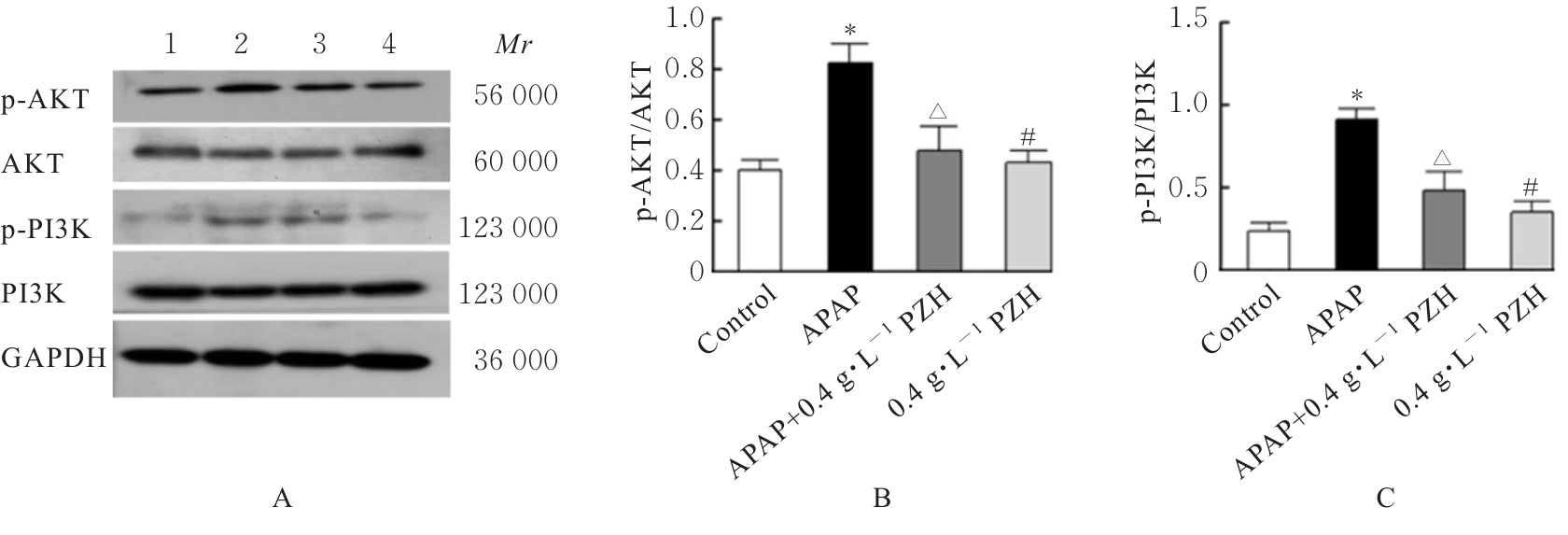
| 25 | 宋添力, 唐浪, 王一民, 等. 竹节参多糖通过PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路对急性肝损伤大鼠的影响[J]. 精细化工, 2023,40(11): 2472-2479, 2534. |
| [1] | Xinyue MA,Hui XU,Jiawen DIAO,Aihua JIN,Jishu QUAN. Inhibitory effect of Boschnikia rossica polysaccharides on THP-1 macrophage inflammation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1499-1511. |
| [2] | Siqi LI,Guangdao CHEN,Qiyi ZENG. Improvement effect of chrysophanol on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of EA. hy926 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1512-1518. |
| [3] | Gao SUN,Jing HE,Qi ZHAO,Jianhong SHI,Zhiling LIAO,Yuanye TIAN,Guomin WU. Therapeutic effect of resveratrol on osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1547-1556. |
| [4] | Meng QU,Rui HUANG,Xinda JU,Yuxin LIU,Jichen XIA,Jiaxin HUANG,Chunyan YU,Zhiheng DONG. Ameliorative effect of ginsenoside Rh1 on kidney injury in diabetic mice through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1565-1571. |
| [5] | Lianzhi CUI,Xiaowei ZHANG,Hua ZHU,Yue PAN,Xiuyan YU. Promotion effect of chemokine CCL19-induced macrophage M1 polarization on chronic pancreatitis in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1587-1596. |
| [6] | Yi LONG,Ziyi YOU,Xiuying TAN,Rou ZHANG,Yuhan ZHANG,Lina YANG. Protective effect of sodium butyrate on acute liver injury in mice induced by lipopolysaccharide combined with D-galactosamine and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1614-1620. |
| [7] | Jing LOU,Lei ZHAO,Yanjie ZHU,Shuaiqiang YUAN,Fei WANG,Hangzhou ZHANG,Jiaojiao XU,Xiaoke YU,Liufa HOU. Effect of Fuzheng Ruanjian Anticancer Formula on malignant biological behaviors of hepatocellulars carcinoma HepG2 cells by regulating Akt/MDM2/P53 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1654-1663. |
| [8] | Haoyu WANG,Yuqi WANG,Bingqian WANG,Jinhan NIE,Jiaqing YAN,Min HU. Inhibitory effect of mesalazine on pro-inflammatory factors and peroxides in RAW264.7 cells and its therapeutic effect on periodontitis model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1250-1258. |
| [9] | Fengmei XIONG,Yuxiang CAI,Zhuo LIU,Na SUN,Yang LI. Alleviatory effect of curcumin on cardiomyocyte toxicity induced by doxorubicin by regulating SIRT3/SOD2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1339-1347. |
| [10] | Xueting CHI,Fangyuan CHEN,Zifeng PI,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Yinqing LI,Xiaowei HUANG,Zhe LIN. Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 963-969. |
| [11] | Tengfei WANG, Feng CHEN, Ling QI, Ting LEI, Meihui SONG. Inhibitory effect of D-limonene on proliferation of glioblastoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 647-657. |
| [12] | Xuejun JIN,Chuyuan LU. Inhibitory effect of leucovorin on growth and angiogenesis of subcutaneous transplanted tumors in mouse lung cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 612-619. |
| [13] | Jianan HAN,Zhuorui LIU,Peiyong ZENG,Shuang JIANG,Hongyu LI. Anti-fatigue effect of Wujia Shengmai Yin in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 689-696. |
| [14] | Jing TANG,Huan LI,Shuo ZHANG,Ligang JING. Analysis on association between serum homocysteine and inflammatory response and oxidative stress in patients with acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 786-790. |
| [15] | Yingxin RUAN,Junya JIA,Zhanfei WU,Wenya SHANG,Pengyu ZHANG. Effect of NLRP3 inflammatome in renal interstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 587-595. |
|
||