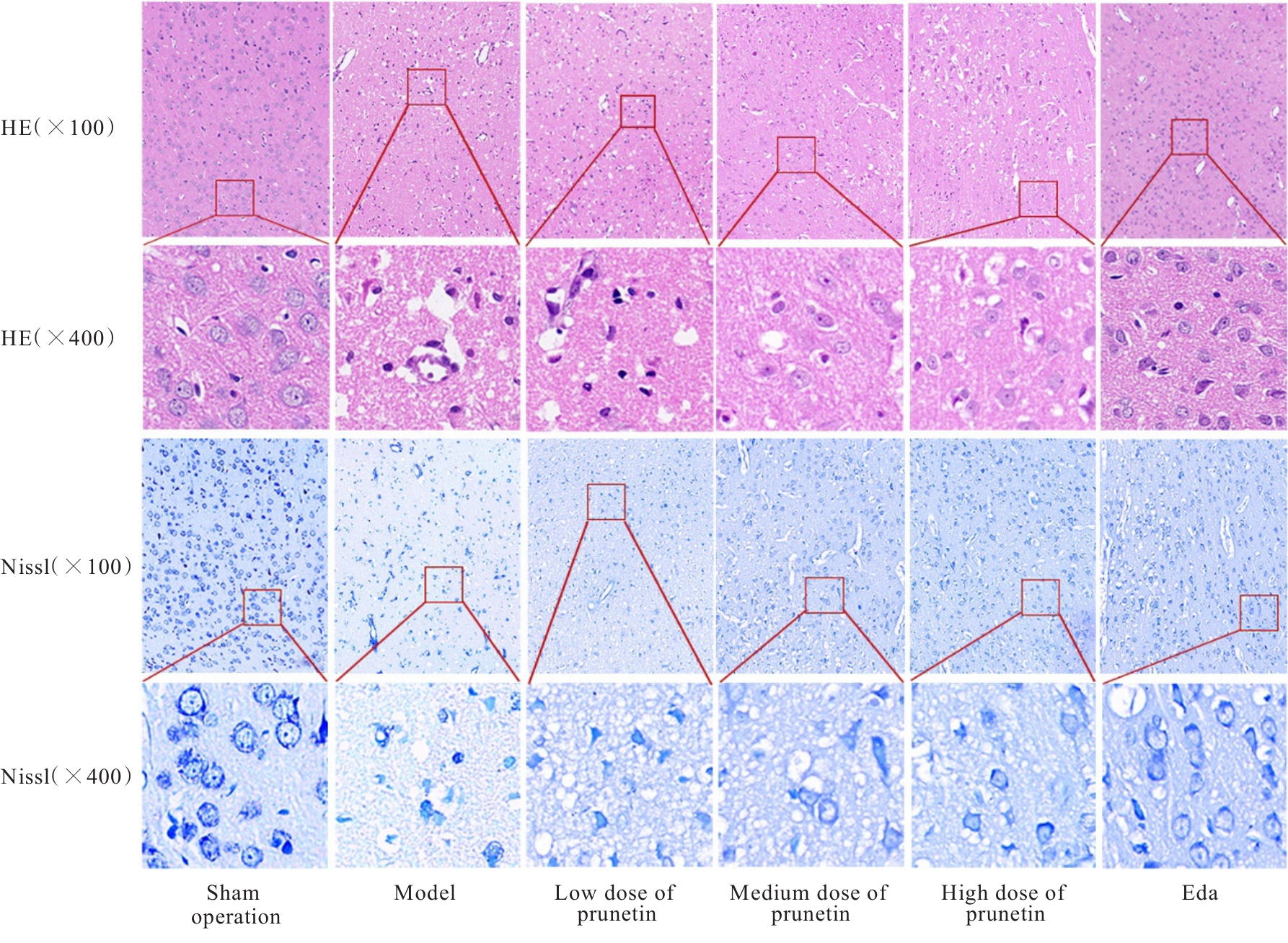
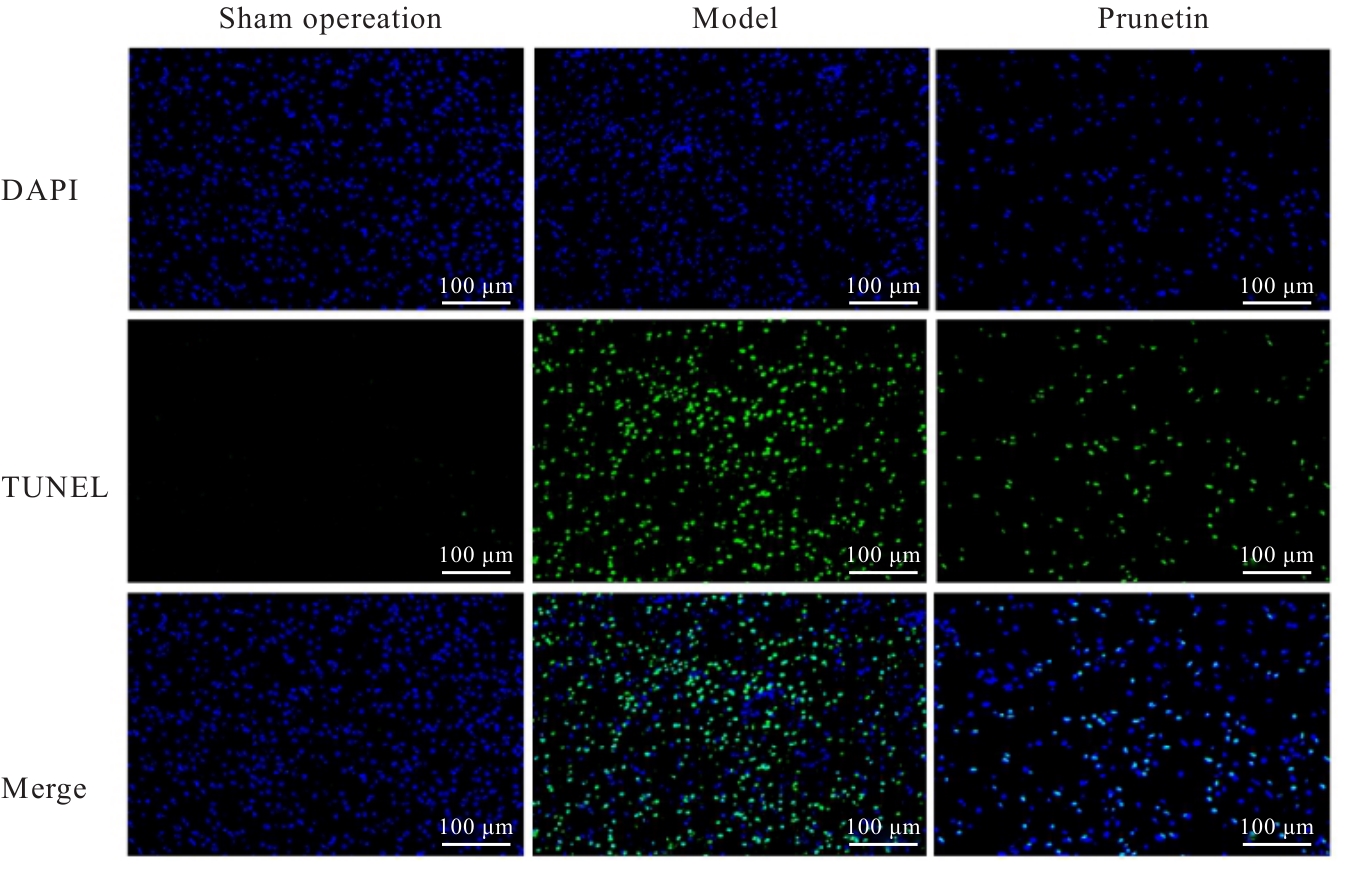
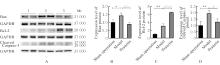
| 1 |
TUO Q Z, LIU Y, XIANG Z, et al. Thrombin induces ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 59.
|
| 2 |
王 璐, 张士滨, 华志鹏, 等. 脑缺血再灌注损伤发病机制研究进展[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2023, 40(2): 168-170.
|
| 3 |
IADECOLA C, BUCKWALTER M S, ANRATHER J. Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(6): 2777-2788.
|
| 4 |
LI C, SUN T, JIANG C. Recent advances in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11(7): 1767-1788.
|
| 5 |
SHERWOOD M W, ARIZONO M, PANATIER A, et al. Astrocytic IP3Rs: beyond IP3R2[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2021, 15: 695817.
|
| 6 |
MAUGARD M, VIGNERON P A, BOLAÑOS J P, et al. L-Serine links metabolism with neurotransmission[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2021, 197: 101896.
|
| 7 |
KUNZELMANN P, BLÜMCKE I, TRAUB O, et al. Coexpression of connexin45 and -32 in oligodendrocytes of rat brain[J]. J Neurocytol, 1997, 26(1): 17-22.
|
| 8 |
SCHOUSBOE A, WAAGEPETERSEN H S. Role of astrocytes in glutamate homeostasis: implications for excitotoxicity[J]. Neurotox Res, 2005, 8(3/4): 221-225.
|
| 9 |
HENNEBERGER C, PAPOUIN T, OLIET S H R, et al. Long-term potentiation depends on release of D-serine from astrocytes[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7278): 232-236.
|
| 10 |
TONG X P, AO Y, FAAS G C, et al. Astrocyte Kir4.1 ion channel deficits contribute to neuronal dysfunction in Huntington’s disease model mice[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2014, 17(5): 694-703.
|
| 11 |
SANCHO L, CONTRERAS M, ALLEN N J. Glia as sculptors of synaptic plasticity[J]. Neurosci Res, 2021, 167: 17-29.
|
| 12 |
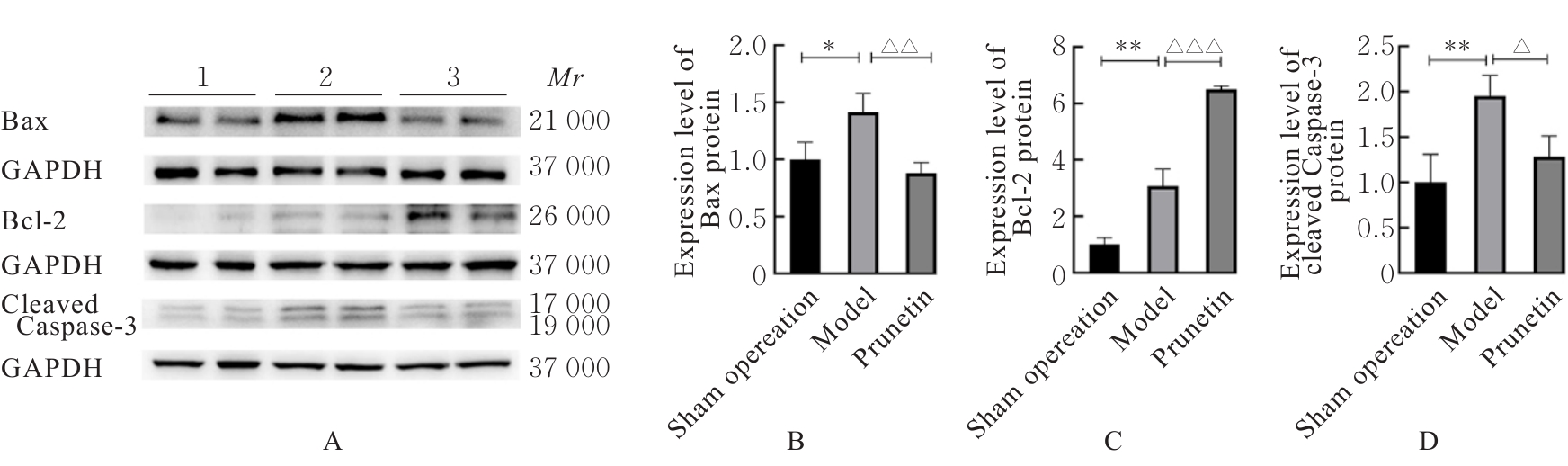
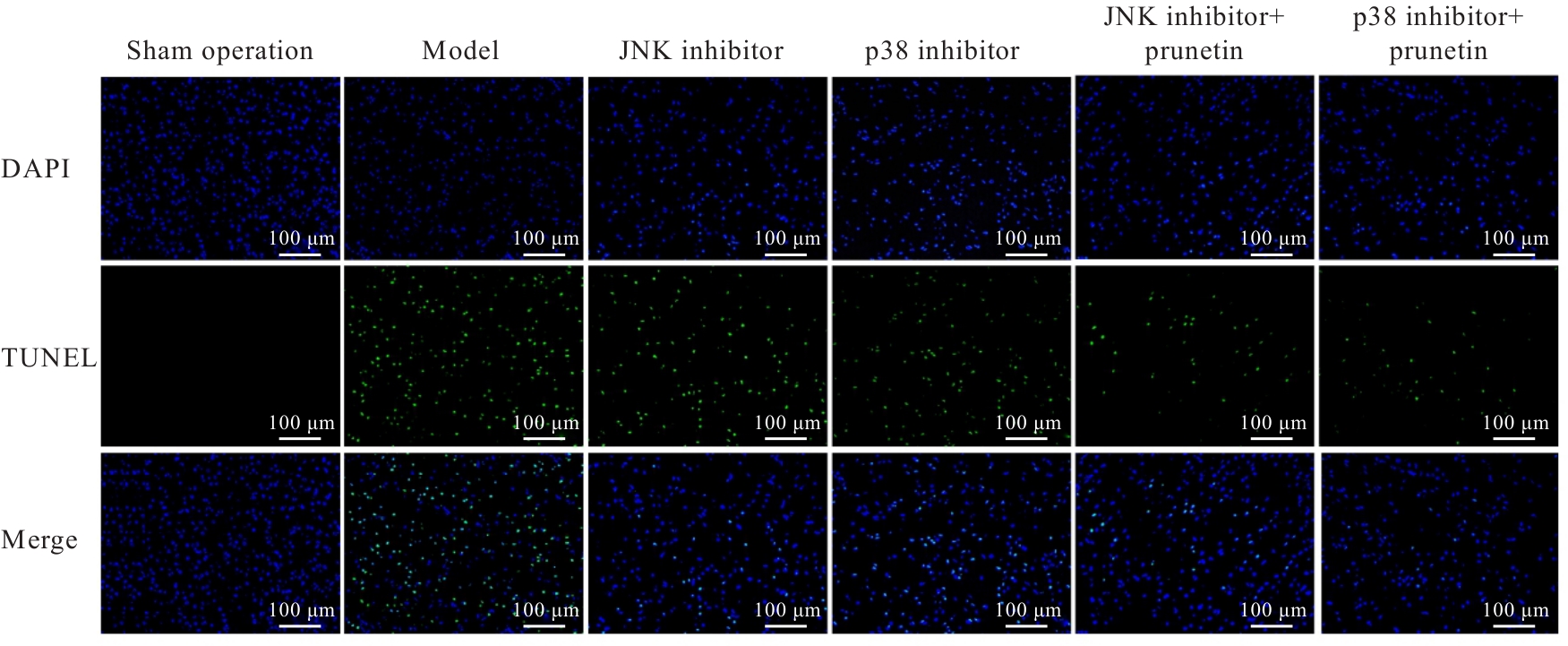
张景荣, 于秀石, 高瑞娟, 等. 玫瑰花总黄酮对脑缺血/再灌注损伤大鼠PI3K/AKT通路和内质网应激凋亡的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(5): 896-902.
|
| 13 |
KIM S D, KIM M, WU H H, et al. Prunus cerasoides extract and its component compounds upregulate neuronal neuroglobin levels, mediate antioxidant effects, and ameliorate functional losses in the mouse model of cerebral ischemia[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, 11(1): 99.
|
| 14 |
LIU Y F, LI Y F, ZANG J K, et al. CircOGDH is a penumbra biomarker and therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke[J]. Circ Res, 2022, 130(6): 907-924.
|
| 15 |
WIDIMSKY P, SNYDER K, SULZENKO J, et al. Acute ischaemic stroke: recent advances in reperfusion treatment[J]. Eur Heart J, 2023, 44(14): 1205-1215.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG L Y, HAN Y B, WU X L, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of curcumin in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: a narrative review[J]. Apoptosis, 2023, 28(9/10): 1285-1303.
|
| 17 |
BHATTI J S, BHATTI G K, REDDY P H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders - A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2017, 1863(5): 1066-1077.
|
| 18 |
FU X J, CUI J J, MENG X J, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, cell death and tumor: Association between endoplasmic reticulum stress and the apoptosis pathway in tumors (Review)[J]. Oncol Rep, 2021, 45(3): 801-808.
|
| 19 |
LAVRIK I N. Systems biology of death receptor networks: live and let die[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2014, 5(5): e1259.
|
| 20 |
BOCK F J, TAIT S W G. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(2): 85-100.
|
| 21 |
ARAYA L E, SONI I V, HARDY J A, et al. Deorphanizing caspase-3 and caspase-9 substrates in and out of apoptosis with deep substrate profiling[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2021, 16(11): 2280-2296.
|
| 22 |
RASHEVA V I, DOMINGOS P M. Cellular responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis[J]. Apoptosis, 2009, 14(8): 996-1007.
|
| 23 |
ZHOU X C, JIANG W B, LIU Z S, et al. Virus infection and death receptor-mediated apoptosis[J]. Viruses, 2017, 9(11): 316.
|
| 24 |
LI C C, MA D B, CHEN Y, et al. Selective inhibition of JNK located on mitochondria protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death caused by endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice with LPS-induced ALI/ARDS[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2022, 49(6): 85.
|
| 25 |
WANG G S, CHEN J Y, CHEN W C, et al. Surfactin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis via IRE1-ASK1-JNK signaling in human osteosarcoma[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2022, 37(3): 574-584.
|
| 26 |
TENG C C, TUNG S Y, LEE K C, et al. Novel regulator role of CIL-102 in the epigenetic modification of TNFR1/TRAIL to induce cell apoptosis in human gastric cancer[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2021, 147: 111856.
|
| 27 |
CHEN L, MENG Y, GUO X Q, et al. Gefitinib enhances human colon cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of via autophagy- and JNK-mediated death receptors upregulation[J]. Apoptosis, 2016, 21(11): 1291-1301.
|
 ),Xiushi YU(
),Xiushi YU( )
)