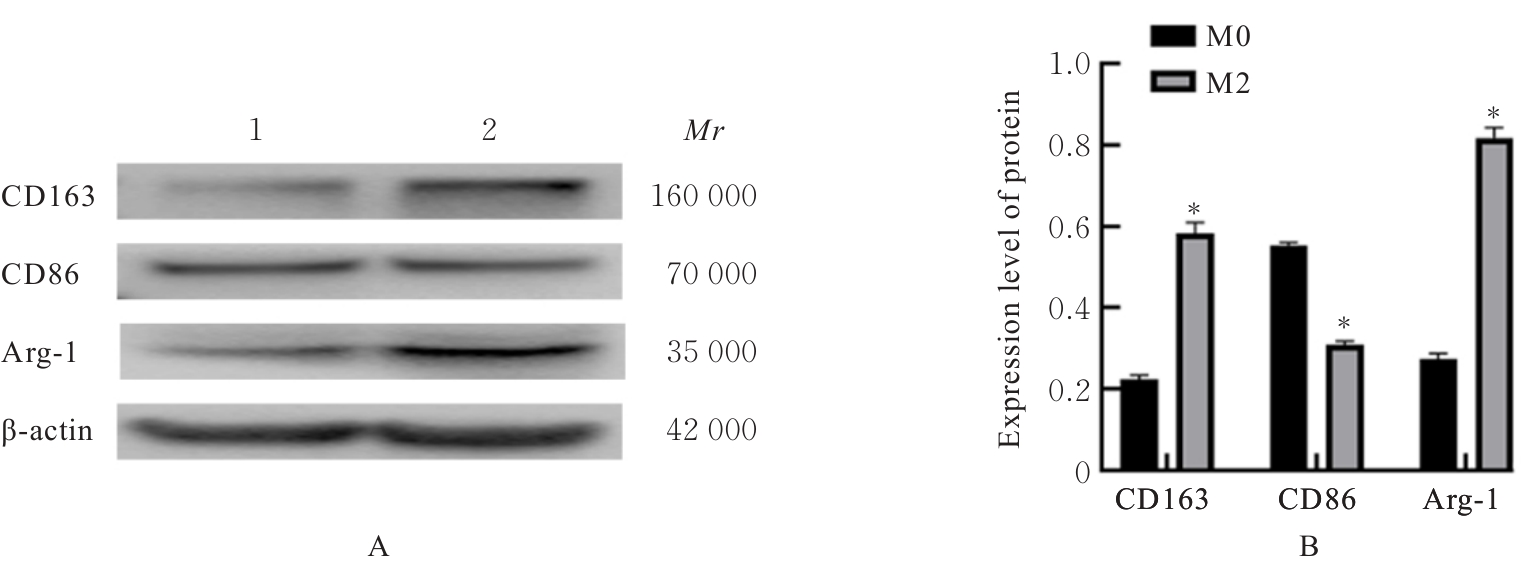
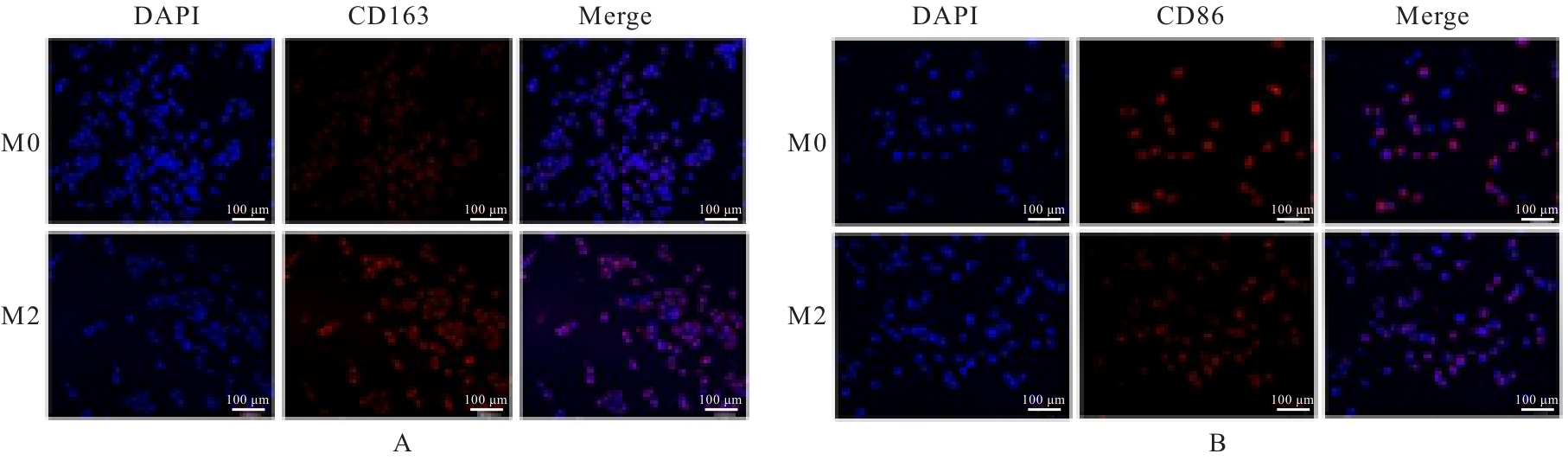
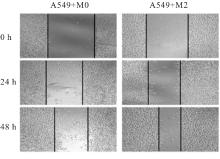
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 642-652.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250309
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
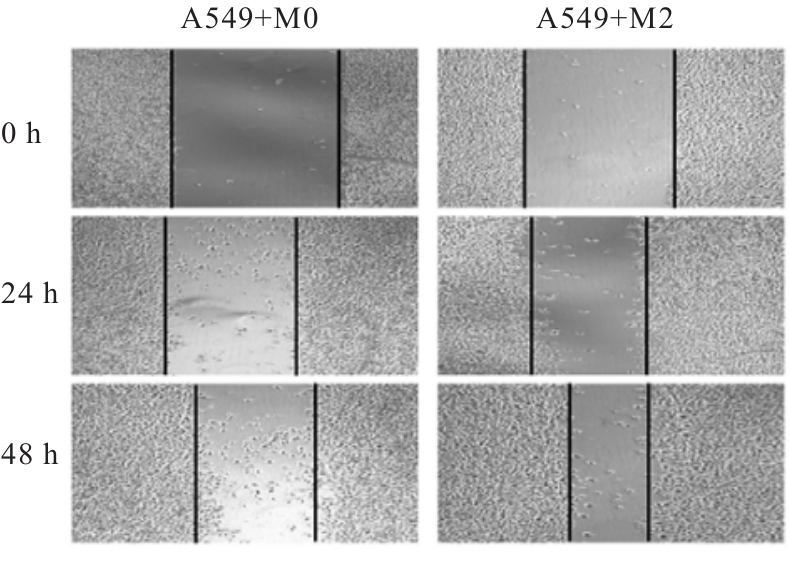
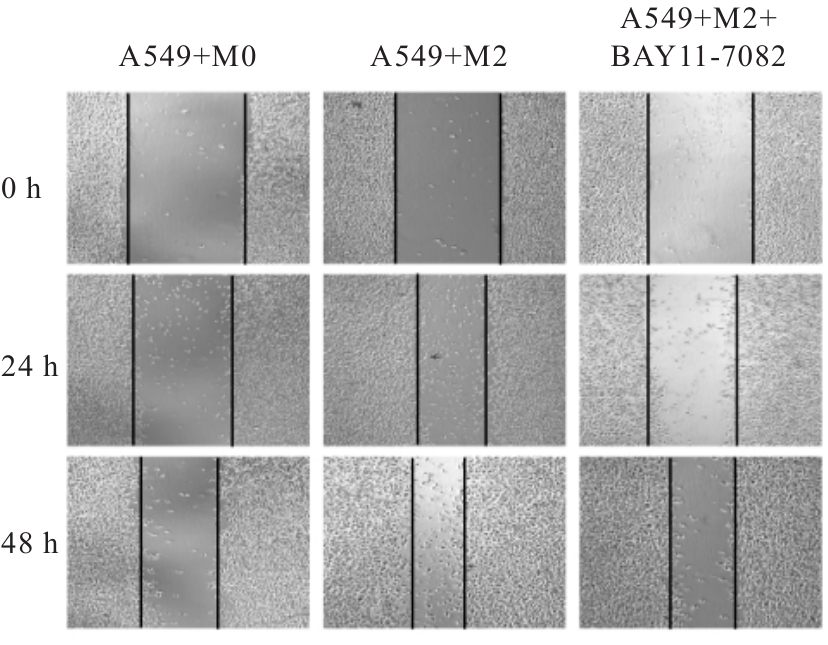
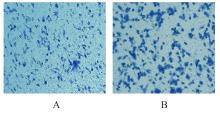
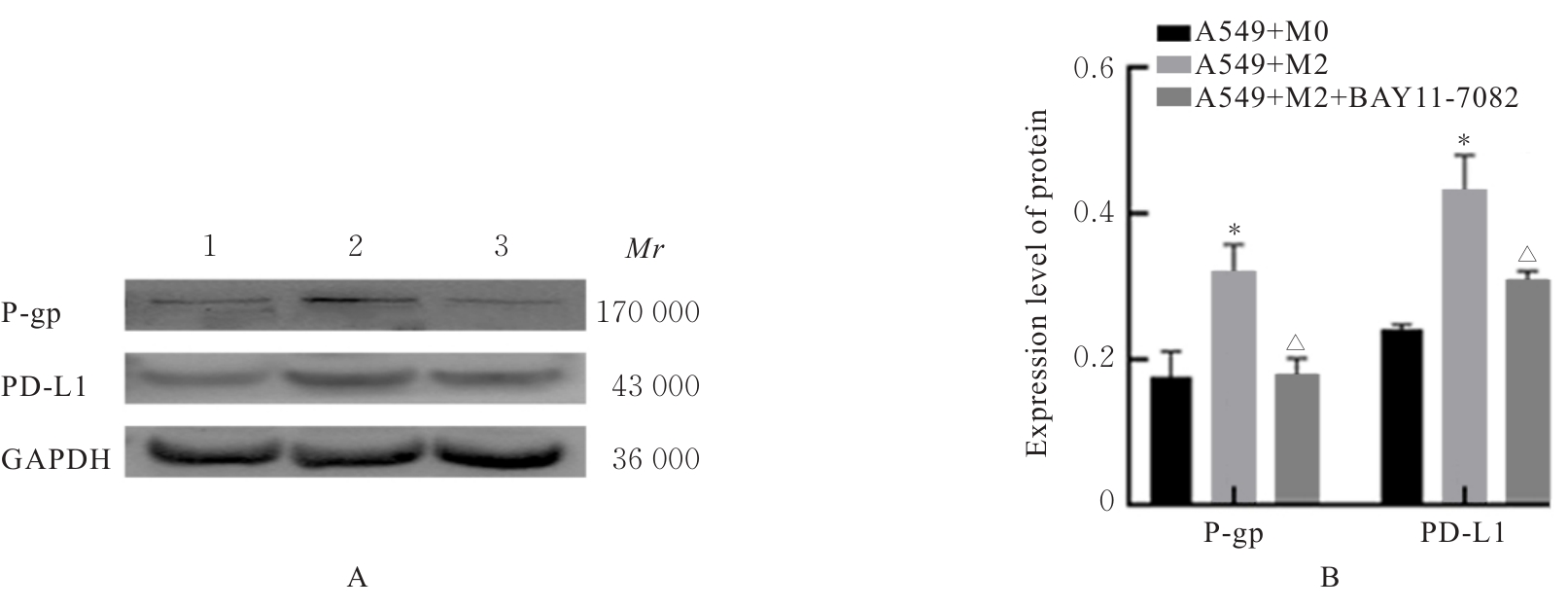
Promotive effect of M2 macrophages on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway
Xingxiang WANG1,Ying ZHAO1,Qiaotong REN1,Hefei WANG2,Gang PU1,Chun LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Immunology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
2.Department of Oncological Gynecology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2024-06-18Accepted:2024-08-24Online:2025-05-28Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Chun LI E-mail:lichunjl@126.com
CLC Number:
- R734.2
Cite this article
Xingxiang WANG,Ying ZHAO,Qiaotong REN,Hefei WANG,Gang PU,Chun LI. Promotive effect of M2 macrophages on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 642-652.
share this article
Tab.3
Inhibitory rates of proliferation and IC50 values in A549 cells in two groups after treated with different concentrations of DDP"
| Group | Inhibitory rate of proliferation (η/%) | IC50 value[ρB/(mg·L-1)] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.25 mg·L-1 DDP | 2.50 mg·L-1 DDP | 5.00 mg·L-1 DDP | 10.00 mg·L-1 DDP | 20.00 mg·L-1 DDP | 40.00 mg·L-1 DDP | ||
| A549+M0 | 2.29±0.60 | 7.37±0.46 | 12.94±1.19 | 48.34±2.18 | 54.88±1.29 | 65.77±0.46 | 17.54±0.28 |
| A549+M2 | 2.18±0.15 | 5.41±0.44* | 9.40±1.47** | 36.43±3.36** | 45.31±3.11** | 54.46±3.36** | 26.55±2.94** |
Tab.4
Inhibitory rates of proliferation and IC50 values of A549 cells in co-culture system in three groups after treated with different concentrations of DDP"
| Group | Inhibitory rate of proliferation (η/%) | IC50 value[ρB/(mg·L-1)] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.25 mg·L-1 DDP | 2.50 mg·L-1 DDP | 5.00 mg·L-1 DDP | 10.00 mg·L-1 DDP | 20.00 mg·L-1 DDP | 40.00 mg·L-1 DDP | ||
| A549+M0 | 2.25±0.23 | 7.35±0.41 | 15.20±0.75 | 44.68±1.85 | 56.50±1.33 | 62.95±2.98 | 18.21±0.79 |
| A549+M2 | 2.07±0.16 | 4.17±1.89* | 9.21±1.14** | 33.76±2.09** | 46.93±2.34** | 53.07±1.55** | 27.03±1.39** |
| A549+M2+BAY11-7082 | 2.19±0.19 | 6.43±0.78△ | 13.82±2.20△ | 40.50±1.64△ | 53.07±1.52△ | 56.85±1.39△ | 21.80±0.71△ |
| [1] | HAN B F, ZHENG R S, ZENG H M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4(1): 47-53. |
| [2] | 盖晓东, 赵颖, 王鹤霏, 等. FOXP3调控非小细胞肺癌A549细胞对阿霉素敏感性的作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49(5): 1161-1167. |
| [3] | 石安辉, 朱广迎. 局部晚期非小细胞肺癌放化疗的现状与进展[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2016, 24(7): 505-508. |
| [4] | 何程远, 杨红宇, 谭钰晶, 等. IL-17A在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及其通过NF-κB信号通路对VEGF表达的调控作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(4): 1003-1009. |
| [5] | MAHMOUD S A, LEE A S, PAISH E C, et al. Tumour-infiltrating macrophages and clinical outcome in breast cancer[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2012, 65(2): 159-163. |
| [6] | TARIQ M, ZHANG J Q, LIANG G K, et al. Macrophage polarization: anti-cancer strategies to target tumor-associated macrophage in breast cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2017, 118(9): 2484-2501. |
| [7] | CAO L L, CHE X F, QIU X S, et al. M2 macrophage infiltration into tumor islets leads to poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 6125-6138. |
| [8] | CHEN S H, MORINE Y, TOKUDA K, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-induced M2-polarized macrophages promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2021, 59(2): 59. |
| [9] | LIN S C, LIAO Y C, CHEN P M, et al. Periostin promotes ovarian cancer metastasis by enhancing M2 macrophages and cancer-associated fibroblasts via integrin-mediated NF-κB and TGF-β2 signaling[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2022, 29(1): 109. |
| [10] | 姜一弘, 张 丹, 张天择, 等. 核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路在炎症与肿瘤中作用的研究进展[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2018, 34(12): 1130-1135. |
| [11] | 朱帅旗, 段海潇, 汪 洋, 等. NF-κB在非小细胞肺癌中的作用及治疗研究[J]. 生命科学, 2022, 34(4): 409-419. |
| [12] | YAO M, MAO X H, ZHANG Z R, et al. Tumor-derived CircRNA_102191 promotes gastric cancer and facilitates M2 macrophage polarization[J]. Cell Cycle, 2023, 22(18): 2003-2017. |
| [13] | MANTOVANI A, ALLAVENA P, MARCHESI F, et al. Macrophages as tools and targets in cancer therapy[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2022, 21(11): 799-820. |
| [14] | 万小英, 周崧雯. M2型肿瘤相关巨噬细胞在肺癌中的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(7): 733-737. |
| [15] | SUMITOMO R, HIRAI T, FUJITA M, et al. M2 tumor-associated macrophages promote tumor progression in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 18(6): 4490-4498. |
| [16] | BAO Z, ZENG W, ZHANG D, et al. Snail induces emt and lung metastasis of tumours secreting cxcl2 to promote the invasion of m2-type immunosuppressed macrophages in colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(7): 2867-2881. |
| [17] | 张 帆, 郭咸希. 肿瘤微环境中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞与上皮间质化“对话”的研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2020, 28(20): 3640-3646. |
| [18] | LI X, CHEN L, PENG X, et al. Progress of tumor-associated macrophages in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tumor[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 911410. |
| [19] | 施鹏冲, 祝先进, 曹颖平. 化疗药物诱导肿瘤细胞耐药研究进展[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2021, 37(11): 1400-1403. |
| [20] | CHEN Y B, SONG Y C, DU W, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages: an accomplice in solid tumor progression[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2019, 26(1): 78. |
| [21] | SUN C, MEZZADRA R, SCHUMACHER T N. Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint[J]. Immunity, 2018, 48(3): 434-452. |
| [22] | 张润兵, 史婷婷, 伍杨, 等. 自噬介导肝细胞癌耐药的相关机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(11): 2315-2319. |
| [23] | TANG D F, ZHAO D D, WU Y, et al. The miR-3127-5p/p-STAT3 axis up-regulates PD-L1 inducing chemoresistance in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(8): 3847-3856. |
| [24] | MIRZAEI S, SAGHARI S, BASSIRI F, et al. NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: a focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(7): 2770-2795. |
| [25] | 王方园, 孔宪斌, 杨玉莹, 等. M2型TAMs激活NF-κB通路促进结肠癌细胞侵袭转移的实验研究[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2020, 28(21): 3651-3656. |
| [26] | WEI R, ZHU W W, YU G Y, et al. S100 calcium-binding protein A9 from tumor-associated macrophage enhances cancer stem cell-like properties of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 2021, 148(5): 1233-1244. |
| [1] | Cheng CHEN,Jingyao LI,Wanxiang HU,Donghui LIU,Zhihong CHEN. Protective effect of sericin on streptozotocin-induced INS-1 cell damage by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway through Akt1 and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 590-598. |
| [2] | Yan WANG,Zouyu ZHAO,Panpan YU,Ping YANG. Expression of I kappa B kinase-interacting protein in cervical cancer tissue and its effect on proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 341-351. |
| [3] | Kaiqi NIU,He CHANG,Guangfu LYU,Pengyu ZHENG,Xueting CHI,Jia ZHOU,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG. Inhibitory effect of astragaloside Ⅳ on cisplatin-induced liver injury in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 370-377. |
| [4] | Chaohe ZHANG,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG. Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 105-114. |
| [5] | Xinyue MA,Hui XU,Jiawen DIAO,Aihua JIN,Jishu QUAN. Inhibitory effect of Boschnikia rossica polysaccharides on THP-1 macrophage inflammation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1499-1511. |
| [6] | Lianzhi CUI,Xiaowei ZHANG,Hua ZHU,Yue PAN,Xiuyan YU. Promotion effect of chemokine CCL19-induced macrophage M1 polarization on chronic pancreatitis in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1587-1596. |
| [7] | Fangyang JIANG,Jing XIAO,He CHANG,Mingyang SUN,Wenjing ZHANG,Guangfu LYU,He LIN,Zhe LIN,Xiaowei HUANG,Yuchen WANG. Effect of polygonatum odoratum polysaccharide on acute kidney injury in mice induced by cisplatin and its ferroptosis mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1235-1242. |
| [8] | Feina WANG,Xuguang MI,Xiuying LIN,Jianhua FU,Lei LIU,Xinyue YU,Huanhuan ZANG,Linjun LIU,Shiling CHEN,Yanqiu FANG. Effect of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway inhibitor MSAB on fibrogenic responses of human endometrial stromal cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1266-1274. |
| [9] | Tan CHEN,Yan CHEN. Research progress in mechanism of fibrosis regulated by macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1465-1473. |
| [10] | Shilei GAO,Jiaqiang WANG,Weitao YAO,Zhichao TIAN,Chao LI,Xiaoxiao LIANG,Xin WANG. Effect of miR-761 on epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma MG63 cells by regulating tumor-associated macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 978-988. |
| [11] | Xuejun JIN,Chuyuan LU. Inhibitory effect of leucovorin on growth and angiogenesis of subcutaneous transplanted tumors in mouse lung cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 612-619. |
| [12] | Haifeng WEI,Zhiqiang NI,Yanhong WEI,Qilai WANG,Shouqing LI,Yinfu MA,Yan TAN,Yanqiu FANG. Effects of miR-126 over-expression and ADAM9 gene silencing on biological behavior of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 310-319. |
| [13] | Ying ZHANG,Xianxun JIANG,Zhaohui WAN. Enhancement effect of TPX2 gene silencing on chemosensitivity of bladder cancer cell line T24/DDP to cisplatin and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 346-354. |
| [14] | Shuang CHEN,Hong LI. Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378. |
| [15] | Buqi NA,Chunji QUAN,Fang ZHAO,Fan YANG,Ru XIAO,Xuemei JIN,Zhenling LI. Effect of histone deacetylase inhibitor CUDC-101 on DNA damage, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer DU145 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 400-410. |
|
||