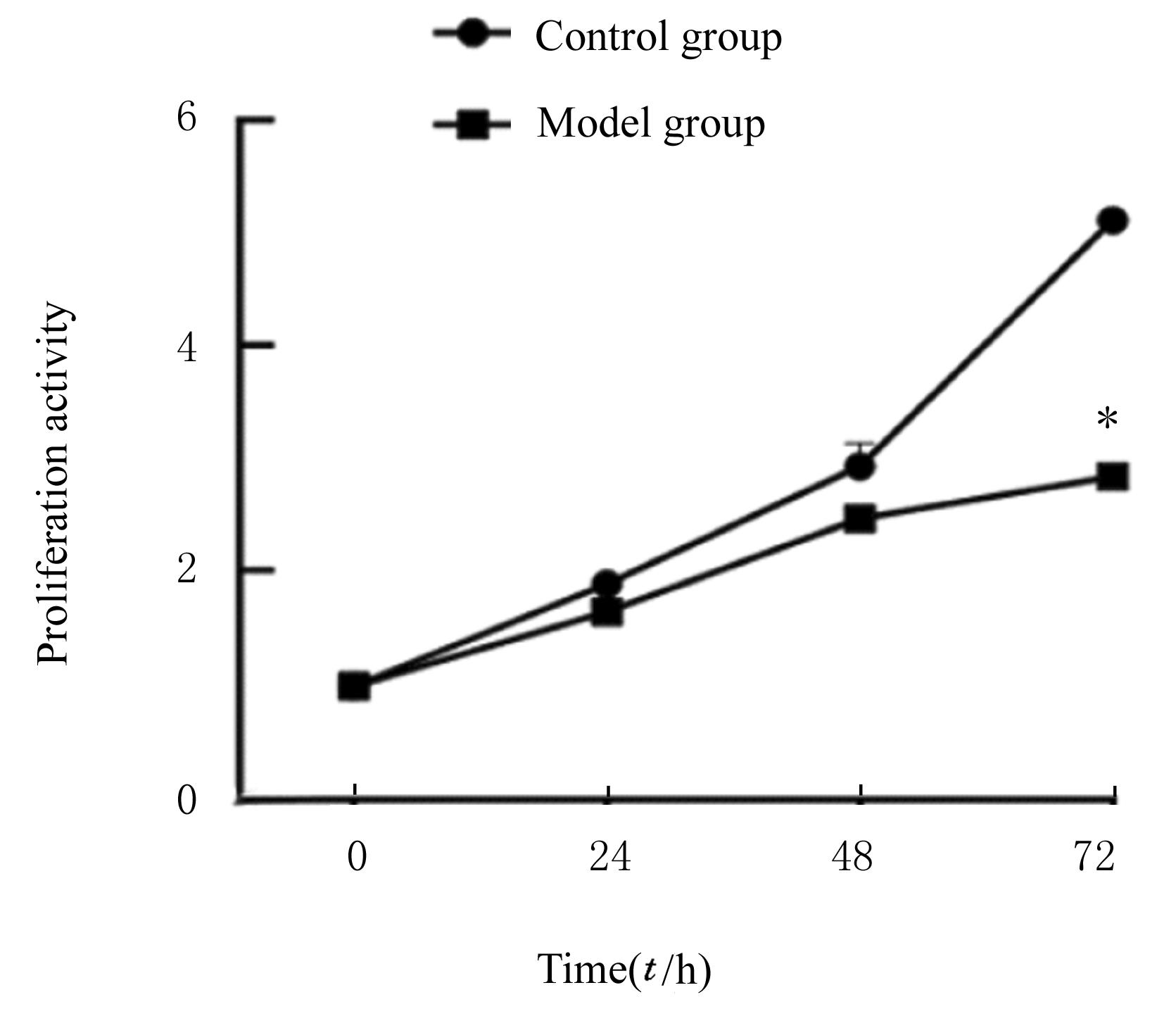
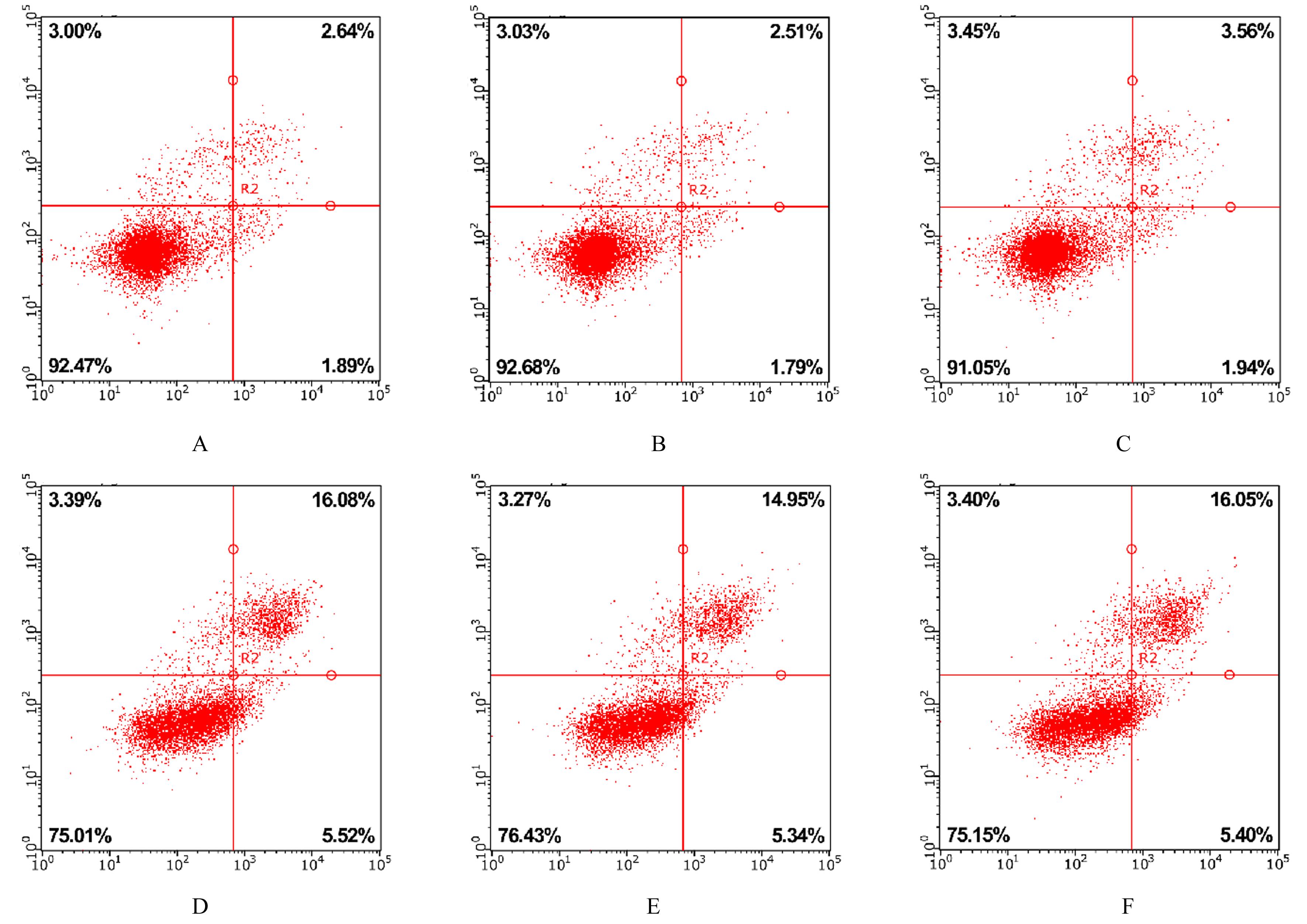
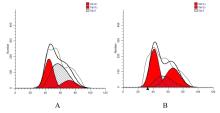
| [1] |
Hongyuan TIAN,Caiyun YIN,Li WANG,Peiyun HU,Chenyang ZHANG,Qiuyue LI,Qingzhao ZHENG,Yali QI,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG.
Effects of hydroxyurea combined with radiation on cell cycle and apoptosis of cells after silencing ATRX
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 590-598.
|
| [2] |
Xingye WANG,Xiangri KONG,Mengli JIN,Bingmei WANG,Mingquan LI.
Improvement effect of β-sitosterol on cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease model mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 599-607.
|
| [3] |
Shengyu YAN,Changhua LIU,Zhijie XU,Yating DING,Yafeng XIE,Qiao ZHANG,Wanying LIU.
Effect of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 on proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 656-664.
|
| [4] |
Jiaojiao XUE,Lei HAO,Yuxiu ZHANG,Heyang DAI,Lixia ZHANG,Shaowei GUO,Jingjing ZHANG,Yang LI,Qingxia LI.
Effect of Huaier aqueous extract on breast cancer tamoxifen-resistant LCC2 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 714-721.
|
| [5] |
Kai WANG,Han HUANG.
Effects of atorvastatin on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL-27 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 324-331.
|
| [6] |
Yifei SUN,Dinuo LI,Yubin WANG.
Inhibitory effect of curcumin on proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells by down-regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway protein expression
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 332-340.
|
| [7] |
Lijun SUN,Jie FENG,Xiaoming LIU,Guangwei REN,Lin RUAN.
Expression of ADAM10 in vascular tissue at stenosis of human arteriovenous fistula and its effect on proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 482-491.
|
| [8] |
Junyi JIN,Mu LI,Yaoyuan HU,Yihui WANG.
Targeting relationship between miR-150-5p and NCAPG and its inhibitory effect on hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 122-130.
|
| [9] |
Yanya CHEN,Jinlan ZHAO,Chan LI,Lishan HUANG.
Expression of miR-223 in ovarian cancer tissue and its promoting effect on proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer OVCAR3 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 150-157.
|
| [10] |
Pei LI,Yanru HUANG,Guilan PENG,Shuxiang HU,Yangdan WANG.
Sotos syndrome with epilepsy and necrotic enterocolitis as performance:A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 180-186.
|
| [11] |
Jie ZHAO,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Juanjuan DAI,Dandan WANG,Yan WU.
Effects of up-regulation of protein phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent 1F on proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 39-45.
|
| [12] |
Junxiong ZHAO,Qian WU,Liangui NIE,Shengquan LIU,Zhentao JIANG,Jian CHEN,Ting XIAO,Jun YANG.
Ameliorative effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 8-14.
|
| [13] |
Donghui LIU,Mingxi ZHANG,Wenliang FU,Xiumei FU,Chengjun SONG,Zhihong CHEN.
Effects of sericin on injury of podocytes induced by high glucose and JNK signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1403-1410.
|
| [14] |
Xingzhu CHEN,Mingyue YU,Shuang LIU,Jianing LI,Zunxuan XIE,Jinyao LIU,Yuyan LIU.
Remineralization property of fluoride loaded poly (propylene carbonate) dental patch and its cytotoxicity on fibroblast L929 cells of mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1429-1436.
|
| [15] |
Qingyu ZHANG,Tingrui XU,Junjun JIAO,Degeng XIA,Tianyi ZHANG,Li ZHANG,Ning MA.
Preparation method of platelet-rich fibrin and hydroxyapatite complex and property evaluation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1448-1454.
|
 ),Jian MAO1,Chengxi MENG1,Gelong BA3
),Jian MAO1,Chengxi MENG1,Gelong BA3